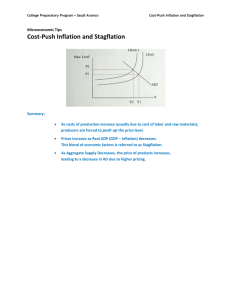
INFLATION with Practice and LInks
advertisement

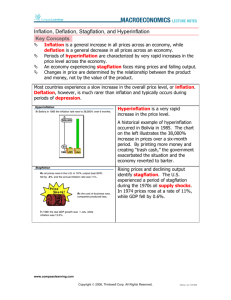
GROUP WORK , but everybody records answers on individual sheets! INFLATION ON COCO ISLE Terms: INFLATION: A rise in price level (TOOOOOO MUCH MONEY chasing TOOOOOO FEW GOODS!) DEFLATION: A drop below the initial price level DISINFLATION: A lowering in price level which does not drop below the original price FOCUS: INFLATION OBJ: 1. Define. 2. ID and explain appropriate contractionary policy: A. fiscal policy B. monetary policy 3. Define & differentiate A. demand-pull inflation B. cost-push inflation 4. Define and differentiate: A. disinflation B. hyperinflation C. deflation What is INFLATION? A rise in price level that DECREASES the purchasing power of money Who does it help or hurt? Helps DEBTORS Borrow GOOD money and buy GOOD STUFF Pay back BAD money Hurts CREDITORS Loan out GOOD money and get paid back in BAD INFLATION eats up INTEREST and EARNINGS PEOPLE on FIXED INCOMES Retirees on Social Security 2 KINDS OF INFLATION: COST-PUSH INFLATION: prices rise because there is an increase in the cost of inputs (factors of production); supply shrinks in relation to demand, pushing EQUILIBRIUM PRICE UP! DEMAND-PULL INFLATION: prices rise because there is an increase in demand (“gimmie-gimmie”); demand increases in relation to supply PUSHING EQUILIBRIUM PRICE UP! Due to SUPPLY SHOCKS! MEASURING INFLATION: CPI - CONSUMER PRICE INDEX: a tool the government uses to measure INFLATION (the CHANGE IN PRICE of a market basket of goods and services used by average households OVER TIME!) compiled monthly by the BLS – Bureau of Labor Statistics; they pick a BASE YEAR as 100 and compare current prices to base year prices; > 100 = INFLATION; <100=DEFLATION; most COMMON measure (See p. 339-40) PPI- PRODUCER PRICE INDEX: tool that measures inflation on the SUPPLY SIDE GDP DEFLATOR: a tool the government uses to measure INFLATION; more accurate, but less common Compiled by Bureau of Labor Statistics PROBLEMS & SOLUTIONS: PROBLEM=INFLATION; solution = SUCK money out of the economy to slow things down (TIGHT MONEY POLICY – CONTRACTION!) PROBLEM=UNEMPLOYMENT; solution = BLOW money into the economy to stimulate growth (LOOSE MONEY POLICY – EXPANSION!) CONTROLLING THE MONEY SUPPLY FISCAL POLICY: What the government can do (congress and the president) – DUSTBUSTER! MONETARY POLICY: What the Federal Reserve can do – BIG VAC! (Ben Bernanke – CHAIRMAN OF THE FED – and his gang – THE FEDERAL RESERVE BD.) Keynesian Economics: Fiscal Policy and Demand Side Economics The Employment Act of 1946 Video Tutorial EPISODE 26: Fiscal Policy (4:34) EPISODE #26: FISCAL POLICY PAUL SOLMAN VIDEO FISCAL POLICY TAX : raise or lower taxes --EXPANSIONARY POLICY (BLOW! to stimulate growth) cut taxes! LOOSE MONEY! --CONTRACTIONARY POLICY (SUCK! to fight inflation) raise taxes! TIGHT MONEY! SPEND: increase or decrease spending --EXPANSIONARY POLICY (BLOW! to stimulate growth) increase spending! --CONTRACTIONARY POLICY (SUCK! to fight inflation) decrease spending AUTOMATIC STABILIZERS & DISCRETIONARY POLICY AUTOMATIC STABILIZERS: Changes in spending which DO NOT require deliberate action from policy makers Kick in when needed during an economic downturn Example: UNEMPLOYMENT BENEFITS in a recession DISCRETIONARY Changes in spending that require the government to act Corporate BAILOUT New legislation on infrastructure projects like high speed rail, to create jobs FISCAL STIMULUS HIGH MPC LOW MPS Secretary of the Treasury Jacob “Jack” Lew Federal Budget: (See Solman video) DEFICIT: Total amount by which EXPENDITURES exceed REVENUES in a single year SURPLUS: Total amount by which REVENUES exceed EXPENDITURES in a single year DEBT: Total amount of money owed by the federal government, accumulated over the years THE CROWDING OUT EFFECT EPISODE 27: Crowding Out - Lags (5:51) EPISODE #27: CROWDING OUT - LAGS Video Tutorial EPISODE 31: The Fed (2:30) EPISODE #31: THE FED EPISODE 32: Monetary Policy (7:18) EPISODE #32: MONETARY POLICY PAUL SOLMAN VIDEO MONETARY POLICY: The process by which the Fed controls the money supply What is the Federal Reserve? The central banking system for the United States Responsible for carrying on MONETARY POLICY Created in 1913 by the Federal Reserve Act 12 District Banks – 25 Branches Chairman of the Fed WAS: Ben Bernanke IS: Janet Yellen MONETARY POLICY RESERVE REQUIREMENT (raise or lower – just NOT done!) OPEN MARKET OPERATIONS (buy or sell federal government bonds) INTEREST RATE (raise or lower the DISCOUNT RATE or FEDERAL FUNDS RATE) --DISCOUNT RATE: interest rate at which member banks borrow from the federal reserve --FEDERAL FUNDS RATE: interest rate at which banks borrow from each other TWO TYPES OF POLICIES: EXPANSIONARY POLICY (loose money policy) geared to stimulate growth and create jobs …………………...BLOW MONEY INTO THE ECONOMY! CONTRACTIONARY POLICY (tight money policy) geared to slow growth and tame inflation) ……………………SUCK MONEY OUT OF THE ECONOMY! The U.S. Economy Stagnated in the 1970s President Lyndon B. Johnson’s spending on the Vietnam War and on his Great Society program also depleted the U.S. treasury Also, since the U.S. did not continue advancing, they were caught by the Japanese and the Germans in industries that the U.S. once dominated: steel, automobiles, consumer electronics. 1973 OIL SHOCK Yom Kippur War STAGFLATION POLITICAL POISON! Video Tutorial STAGFLATION: (30:00) CARDS UP on INFLATION 1. A rise in the price level which decreases the purchasing power of money is called a. inflation b. deflation c. disinflation d. hyperinflation e. stagflation 2. A decline in the price level is called a. hyperinflation b. inflation c. stagflation d. disinflation e. deflation 3. A decline in the rate of inflation is called a. hyperinflation b. disinflation c. inflation d. deflation e. stagflation 4. Modern fiscal policy results from the work of a. Jean Baptiste Say b. Arthur Laffer c. John Maynard Keynes d. Arthur Okun e. Thomas Malthus 5. Which policy measure would a Keynesian economist support to combat recession? a. doing nothing b. balanced budget c. decreasing wages d. deficit spending e. printing money 6. What is an appropriate fiscal policy measure to combat recession? a. decreasing the federal funds rate b. increasing government spending c. purchasing government securities d. increasing the reserve ratio e. There is no appropriate fiscal policy measure to combat recession. 7. What is an appropriate fiscal policy measure to combat inflation? a. increasing government spending b. increasing the discount rate c. increasing the tax rate d. increasing the federal funds rate e. There is no appropriate fiscal policy measure to combat inflation. 8. What is an appropriate fiscal policy measure to combat stagflation? a. increasing the discount rate b. decreasing the tax rate c. decreasing government spending d. purchasing government securities e. There is no appropriate fiscal policy measure to combat stagflation 9. An example of discretionary fiscal policy is a. corporate bailouts b. monetarism c. Social security payments d. open market operations e. unemployment insurance payments 10. An example of automatic stabilizer in fiscal policy is a. open market operations b. corporate bailouts c. monetarism d. unemployment insurance payments e. Social Security payments 11. How many district banks make up the Federal Reserve? a. 5 b. 7 c. 10 d. 12 e. 14 12. How many people serve on the Federal Reserve Board of Governors? a. 5 b. 12 c. 7 d. 10 e. 14 13. Each member of the Federal Reserve Board of Governors is appointed a. to a 4-year term b. for life c. to a 14-year term d. to a 10-year term e. to a 6-year term 14. The primary tool of monetary policy is a. open market operations b. the discount rate c. the reserve ratio d. government expenditures e. taxation 15. The interest rate the Federal Reserve charges for loans to banks is called the a. consumer rate b. discount rate c. reserve rate d. federal funds rate e. prime rate 16. The interest rate on overnight loans between banks is called the a. consumer rate b. discount rate c. federal funds rate d. reserve rate e. prime rate 17. The main function of the Federal Reserve is to a. regulate the money supply b. levy taxes c. conduct fiscal policy d. regulate wages e. regulate international trade 18. A monetary policy measure to combat inflation is a. decreasing the tax rate b. increasing government expenditures c. increasing the discount rate d. decreasing the reserve ratio e. decreasing the prime rate 19. A monetary policy measure to combat recession is a. increasing government expenditures b. increasing the reserve ratio c. purchasing government securities d. decreasing the tax rate e. increasing the federal funds rate 20. The current head of the Federal Reserve is a. Janet Yellen b. Robert Zoellick c. Paul Wolfowitz d. Alan Greenspan e. Ben Bernanke 21. A shortfall in the annual federal budget: a. inflation b. recession c. deficit d. debt e. depression 22. The total amount of money owed by the federal government, accumulated over the years: a. debt b. deficit c. surplus d. recession e. trough 23. Government borrowing for expansionary fiscal policy increases demand for money and interest rates, so part of the increase in government spending is counteracted by a decrease in private investment. a. the wealth effect b. the price effect c. the income effect d. the crowding out effect e. the recession effect 24. The central banking system of the United States: a. the Treasury Department b. the Commerce Department c. FDIC d. SEC e. Federal Reserve 25. The current Secretary of the Treasury is a. Timothy Geithner b. Ben Bernanke c. Alan Greenspan d. Henry Paulson e. Larry Summers 26. A supply shock (an increase in the cost of an input) causes: a. demand-pull inflation b. cost-push inflation 27. If you want to stimulate the economy, a tax cut should target people with a. a high marginal propensity to save and a low marginal propensity to consume. b. a high marginal propensity to consume and a low marginal propensity to save. 28. High inflation and high unemployment: a. deflation b. disinflation c. hyperinflation d. stagflation e. none of these 29. If the CPI is 138, prices a. have decreased 38%. b. have increased by 38%. c. have stayed the same. 29. If we’re in a recession, we need a a. tight money policy b. loose money policy 29. A contractionary policy is a a. tight money policy b. loose money policy END OF QUIZ WHAT IS A TAX? A compulsory charge or levy enacted by the government to raise revenue to fund government spending May also be used to Encourage behavior (TAX CREDIT/DECUDTION) Discourage behavior (SIN TAX) TAX SYSTEMS: TAX REVENUE: Arthur Laffer: Reagan’s Econ. Advisor High taxes harm the economy by Stifle INVESTMENT (drawing CAPITAL away), thus… Stifle GROWTH, so… TAX CUTS for the RICH Stimulate investment, thus Spur GROWTH! Growth reduces DEFICIT increases TAX REVENUES Allowing gov’t to CUT SPENDING Laffer and Wanisky Laffer Curve Laffer Curve Assume 15% The Laffer Curve in… THEORY PRACTICE 1. The largest source of federal revenue is the a. property tax b. personal income tax c. social security tax d. sales tax e. corporate income tax 2. The two largest sources of tax revenue for state and local governments are a. sales and property taxes b. personal income and corporate income taxes c. sales and personal income taxes d. sales and corporate income taxes e. property and personal incomes taxes 3. Personal income tax in the United States and in the states which have it is a a. flat tax b. fair tax c. regressive tax d. liberal tax e. progressive tax 4. Sales taxes are _____ because they fall more heavily on those least able to pay. a. regressive tax b. progressive tax c. fair tax d. flat tax e. liberal tax 5. Another name for proportional tax: a. liberal tax b. regressive tax c. fair tax d. flat tax e. progressive tax A tax on a specific good or service like gas: a. sales tax b. excise tax c. income tax d. property tax e. capital gains tax An excise tax which attempts to influence behavior harmful to society as well as to raise revenue: a. capital gains tax b. value added tax c. regressive tax d. sin tax e. ad valorem tax To create the biggest stimulus, a tax cut should be designed to benefit those with a a. high MPC and a low MPS b. low MPC and a high MPS c. high MPC and a high MPS d. low MPC and a low MPS A tax benefit which can be subtracted from one’s income before figuring taxes, thus reducing the amount of taxable income counted: a. a tax deduction b. a tax credit A tax benefit which is subtracted directly from your total tax bill: A. a tax dedcuction B. a tax credit END OF QUIZ