Interactive questions. Test 6: Human physiology

INTERACTIVE
MULTIPLE-CHOICE
QUESTIONS
Human Physiology
The answers are provided.
Explanations of why the alternatives are unsatisfactory are also offered
© D.G. Mackean
These multiple choice questions are similar to the ones set by the GCSE and IGCSE Examination Boards except that, in some cases, there may be more than one acceptable answer.
For this reason, even if you select a correct answer at your first attempt, it is worth looking at all the alternatives
(a) to see if there is a better answer and
(b) to see why some of the alternatives are unacceptable
Question 1
Question 1
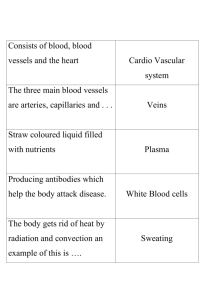
Iron is an important component of a balanced diet because it is needed mainly by …
(a) the blood
(b) the bones
(c) the brain
(d) the nerves
Question 2
Yes
Iron is an important component of haemoglobin , the red pigment which combines with oxygen in the red blood cells
No
Iron is not specifically needed by the bones
No
Iron is not specifically needed by the nerves
No
Iron is not specifically needed by the brain
Question 2
Shortage of vitamin D in the diet of children can lead to …
(a) poor night vision
(b) anaemia
(c) deformed bones
(d) bleeding gums
Question 3
No
It is shortage of vitamin A (retinol) which is a cause of poor night vision, as well as reduced resistance to disease
No
A shortage of iron can be one cause of anaemia
Yes
A shortage of vitamin D (calciferol) causes defective incorporation of calcium into the bones, which therefore remain soft and are easily deformed. This condition is known as ‘rickets’
No
A shortage of vitamin C (calciferol) can be one cause of bleeding gums
Question 3
The final digestion products of proteins are …
(a) sugars
(b) glycerols
(c) fatty acids
(d) amino acids
Question 4
No
Sugars (e.g. glucose and fructose) are the final digestion products of carbohydrates , such as starch
No
Glycerol is one of the products of fa t digestion
No
Fatty acids are one of the products of digestion of fats
Yes
The final digestion products of proteins are amino acids
Question 4
In the small intestine, the villi …
(a) speed up digestion
(b) propel food through the intestine
(c) increase the absorptive surface
(d) secrete digestive enzymes
Question 5
No
The villi speed up absorption
No
Food is propelled through the alimentary canal by a muscular process called peristalsis
Yes
The numerous, finger-like processes called villi , greatly increase the absorptive surface of the small intestine
Section of small intestine opened to show villi
No
The villi contain enzymes but they do not secrete them into the intestine
Question 5
When the ventricles contract, blood is forced into …
(a) the aorta
(b) the vena cava
(c) the pulmonary artery and the aorta
(d) the pulmonary artery
Question 6
Yes but …
Contraction of the left ventricle forces blood into the aorta, but the right ventricle is contracting at the same time
No
The vena cava brings blood to the right ventricle
Yes
Contraction of the left ventricle forces blood into the aorta. Contraction of the right ventricle forces blood into the pulmonary artery
Yes but …
Contraction of the right ventricle forces blood into the pulmonary artery but remember that the left ventricle is also contracting.
Question 6
In the lungs, gaseous exchange takes place in …
(a) the alveoli
(b) the bronchioles
(c) the bronchi
(d) the trachea
Question 7
Yes The alveoli are tiny air pockets at the ends of the bronchioles. Oxygen from the air diffuses into the blood capillaries in their walls and carbon dioxide diffuses out trachea alveoli bronchiole bronchi lung
No
The bronchioles are the fine tubes which carry air to the alveoli but significant gaseous exchange does not take place here
No
The bronchi are the wide tubes which branch repeatedly to form the bronchioles. No significant gaseous exchange takes place here.
No
The trachea is the wide tube leading from the back of the mouth and dividing into bronchi. No significant gaseous exchange takes place here
Question 7
Which of the following are excretory organs?
(a) The lungs
(b) The skin
(c) The kidneys
(d) The large intestine
Question 8
Yes
The lungs excrete carbon dioxide which is a waste product of cellular respiration.
They also expel water vapour some of which could be a waste product of respiration, but this is incidental to their main function and an inevitable consequence of the moist lining of the alveoli
No
Sweat, from the sweat glands in the skin, contains salt
(sodium chloride) but this is incidental to the main function of sweat production (cooling the body). The sweat glands do not produce sweat in response to an increase in sodium chloride in the blood and are not, therefore, organs of excretion.
In fact, loss of salt which results from prolonged sweating can be harmful.
Yes
The kidneys excrete, urea, uric acid, excess salts and the breakdown products of hormones or drugs. These substances are all waste products of the body’s metabolism.
The kidneys also excrete excess water, some of which has been produced in the process of respiration.
No
The contents of the large intestine are largely made up of undigested vegetable matter (fibre), bacteria and water.
These have not been incorporated into the body or taken part in chemical changes in the body so they are not excretory products.
The process of expelling faeces is egestion , not excretion
The break down products of bile pigments, which colour the faeces, are excretory products but are excreted by the liver
Question 8
oestrogen follicle-stimulating hormone progesterone
Days
The graphs represent the relative concentrations of 3 female hormones in the blood over a 28 day period. In which period is fertilisation (conception) most likely to occur?
(a) Days 1 - 5
(b) Days 10 -12
(c) Days 13-16
(d) Days 20 - 24
Question 9
No
This is the period when menstruation is taking place
No
Although the concentration of oestrogen is high, there is unlikely to be an ovum present in the oviduct at this stage
Yes
Follicle-stimulating hormone is one of the hormones that triggers the release of an ovum from the ovary (ovulation).
Assuming the ovum can survive for a day, and sperms can survive for 2 days this is the fertile period when conception is most likely
No
The ovum is unlikely to survive into this period. The increase in progesterone causes the lining of the uterus to thicken in preparation for the ovum, if it has been fertilised
Question 9
Which of the following are the likely effects of release of adrenaline from the adrenal gland into the bloodstream?
(a) The rate and depth of breathing increases
(b) The liver converts glucose in the blood to glycogen
(c) The skeletal muscles relax
(d) The heart rate increases
Question 10
Yes
Adrenaline is the ‘fight or flight’ hormone and prepares the body for action. An increase in the rate and depth of breathing gets more oxygen into the blood. This means that more prolonged activity can occur.
No
Adrenaline causes the liver to convert its glycogen store to glucose which is released into the bloodstream where it becomes available for rapid muscular contraction.
No
Adrenaline causes the muscles to tense up in preparation for ‘flight or fight’
Yes
An increased heart rate helps to supply extra oxygen and glucose to the muscles for their heightened activity during ‘flight or fight’
Question 10
Which of the following are reflex actions?
(a) You ‘jump’ in response to a sudden and unexpected loud noise
(b) You automatically move the handlebars of your
bicycle to steer or to keep your balance
(c) You walk without thinking about it
(d) You blink when a particle of sand blows into your eye
Question 11
Yes
You have no control over whether you ‘jump’ or not.
This is a reflex action
No
Although this happens without your having to think about it, it is a ‘learned’ reaction and not a reflex. An acquired skill is not a reflex
No
Although this happens without your having to think about it, it is a ‘learned’ reaction and not a reflex. An acquired skill is not a reflex
Yes
You have no control over whether you blink or not
Question 11
The drawing represents the skeleton and muscles of the leg.
When the leg straightens to thrust the body forwards, which of the following is the correct sequence?
(a) A contracts, B relaxes,
C relaxes, D contracts
(b) B contracts, A relaxes,
D contracts, C relaxes
(c) A contracts, B relaxes,
C contracts, D relaxes
(d) A contracts, B contracts,
C relaxes, D relaxes
B
D
Question 12
A
C
No
If D contracts, it flexes the foot at the ankle. The foot must be extended if it is to push the body forwards
No
If B contracts, it will flex (bend) the leg at the knee. This will not help to push the body forward
If D contracts, it flexes the foot at the ankle. The foot must be extended if it is to push the body forwards
Yes
A contracts and extends
(straightens) the leg at the knee
C contracts and extends (straightens) the foot at the ankle
B relaxes
C contracts
These two movements make the leg push against the ground and thrust the body upwards and forwards
B
D relaxes and D
A contracts their antagonistic muscles to contract must be relaxed to allow
No
A and B are antagonistic muscles. If they both try to contract there will be no movement. However, the tension in both must be retained in order to hold the body upright in a standing position
If C and D both relax, there will be nothing to support the ankle and you will fall flat on your face
Question 12
Which of the following is the best definition of
‘homeostasis’ in mammals?
(a) Keeping the body temperature constant
(b) Maintaining a constant internal environment
(c) Getting rid of the waste products of metabolism as fast as they accumulate
(d) Maintaining a constant body mass
No
Keeping the body temperature within limits is only one aspect of homeostasis
Yes
This is the best definition (provided you know what it means)
The ‘internal environment’ refers mainly to the blood, lymph and tissue fluid. Homeostasis involves all the processes which keep the temperature and composition of these fluids within narrow limits
The lungs control the levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide. The kidneys eliminate excretory products and maintain the concentration.
The skin helps to regulate the temperature
The liver controls the concentration of glucose
And the brain, nervous system and endocrine system control them all
No
This is just one aspect of homeostasis. The kidneys get rid of the waste products of metabolism as fast as they accumulate and control the amount of water retained in the body
No
Even in a mature animal, the body mass will fluctuate with the seasons, the activity and the availability of food.
With an immature animal the body mass will increase
End of questions
Back to start
End show