CIA4U: Chapters 13 and 14 - Review FISCAL AND MONETARY
advertisement

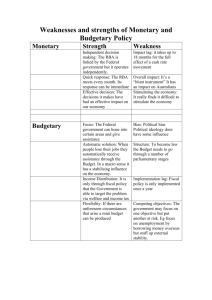
1 CIA4U: Chapters 13 and 14 - Review FISCAL AND MONETARY POLICY REVIEW 1. What is the difference between monetary and fiscal policy? 2. What is the purpose of monetary and fiscal policy? 3. Name the three ways Monetary Policy is conducted and briefly describe how each method is used. 4. Which is more effective at maintaining economic goals – monetary policy or fiscal policy? Explain. 5. How do banks make money? 6. Describe the Canadian fractional reserve system? 7. Describe the 4 functions of the BOC. 8. What is the difference between the overnight rate and the prime rate of interest? 9. What are the drawbacks and benefits of monetary policy? 10. What is the difference between demand pull inflation and cost-push inflation? 11. Contrast progressive, regressive and excise taxes. Provide an example of each. TRUE AND FALSE: (IF FALSE, EXPLAIN WHY) 1. Fiscal Policy is used when the government changes either the level of taxes and or the level of government spending. 2. The government’s goal is to ensure every single person is working – so zero unemployment. 3. When expansionary fiscal policy is used, it decreases the government deficit. 2 CIA4U: Chapters 13 and 14 - Review 4. When the government stimulates the economy through fiscal policy, the aggregate demand curve shifts left. 5. When there is a recessionary GAP, actual output (GDP) is lower than potential output. 6. “Crowding Out” is a drawback of monetary policy. 7. Contractionary fiscal policy means the same thing as fiscal restraint. 8. When the government increases taxes, this is an example of expansionary fiscal policy. 9. When the government raises the required reserve ratio, they are trying to increase the money supply – this is known as expansionary monetary policy. 10. If we are in a recession, the government would chose to initiate either expansionary fiscal and or monetary policy to improve liquidity. 11. The main source of provincial government spending is education and health care. 12. The main sources of government revenue are personal and corporate taxes. 13. An example of an automatic stabilizer is monetary policy. 14. An example of an automatic stabilizer includes unemployment insurance, welfare and progressive taxation. 15. Our Canadian federal budget deficit has improved over the years due to economic growth, increased tax revenues, and decrease in government spending. 16. When the aggregate demand curve shifts right, this is known as demand pull inflation. 17. Demand pull inflation is caused by contractionary fiscal policy. 18. Contractionary fiscal policy is used to fight demand-pull inflation. 19. In times of deflation or declining unemployment (below the natural rate) the government could slow down growth by pursuing contractionary monetary or fiscal policy. 3 CIA4U: Chapters 13 and 14 - Review 20. The money supply is known as M2 and includes all money held inside and outside chartered banks. 21. New money creates wealth in the economy. 22. A bank run is caused by inflation. 23. The prime rate is always lower than the target overnight rate. 24. Expansionary fiscal policy alleviates a recessionary gap. 25. When the BOC buys bonds, it is exercising contractionary fiscal policy.