Plants Long Part A - Phillips Scientific Methods
advertisement

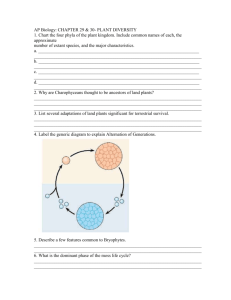
Plants Ch 21-23 Adapted from Prentice Hall What are Plants? •Plants are multicellular , autotrophic eukaryotes that have cell walls made of cellulose. •Plants develop from multicellular embryos and carry out photosynthesis using the green pigments chlorophyll a and b Plant Life Cycle Plants go through Alternation of Generations The Plant Life Cycle •During the two phases of the life cycle, mitosis and meiosis alternate to produce the two types of reproductive cells — gametes and spores. •The diploid (2N) phase is called the sporophyte, or spore-producing plant. •The haploid (N) phase is called the gametophyte, or gamete-producing plant. What Plants Need to Survive –In order to survive, plants need: • sunlight • water and minerals • gas exchange (need CO2 & give off O2) • transport of water and nutrients throughout the plant body Early Plants • The first plants evolved from an organism similar to the multicellular green algae living today. Early Plants •The oldest known plant fossils, about 450 million years old, are similar to today’s mosses. •They had a simple structure and grew close to the ground. Overview of the Plant Kingdom – Plants are divided into groups based on these features: – water-conducting tissues – seeds – flowers Evolution of the Plant Kingdom Flowering plants Cone-bearing plants Ferns and their Mosses and relatives their relatives Flowers; Seeds enclosed in fruit Seeds Water-conducting (vascular) tissue Green algae ancestor Bryophytes Moss Groups of Bryophytes •Mosses and their relatives are called bryophytes, or nonvascular plants. •They do not have vascular tissues, or specialized tissues that conduct water and nutrients. Groups of Bryophytes –Bryophytes have life cycles that depend on water for reproduction. Gametophyte is the dominant generation in non vascular plants –Bryophytes draw up water by osmosis only a few centimeters above the ground. –Holdfast structures called rhizoids Phyla (Divisions) of non vascular plants – The three groups are: • Mosses (Bryophytes) • Liverworts (Hepatophyta) • Hornworts (Antherophyta) • In non vascular plants, the GAMETOPHYTE is the dominant generation Groups of Bryophytes – Mosses • The most common bryophytes are mosses. • Mosses: – are adapted to life in wet habitats (flagellated sperm swims to egg) and nutrient-poor soils. – can tolerate low temperatures. – are clumps of gametophytes growing together. Capsule Structure of a Moss Plant Stalk Sporophyte Stem like structure Leaf like structure Rhizoid Gametophyte Human Use of Mosses – Sphagnum mosses thrive in the acidic water of bogs. – Dried sphagnum can accumulate to form peat deposits. – Peat can be used as fuel. – Peat can be used to improve the soil’s ability to retain water and to increase soil acidity.