S4 Religion & community cohesion revision
advertisement

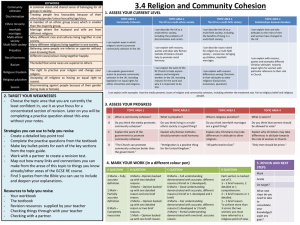
Religion and community cohesion Spec How and why attitudes to the roles of men and women have changed in the UK. Different Muslim attitudes to equal rights for women in religion and the reasons for them. The nature of the UK as a multi-ethnic society, including the problems of discrimination and racism. Government action to promote community cohesion in the UK, including legislation on equal rights for ethnic minorities and religions. The work of a Muslim organisation to help asylum seekers and/or immigrant workers in the UK, including the reasons for the work and its importance and significance. Why Muslims should help to promote racial harmony. Differences among Muslims in their attitudes to other religions(exclusivism, inclusivism, pluralism). The UK as a multi-faith society, including the benefits of living in a multi-faith society. Issues raised for religion by a multi-faith society — conversion, bringing up children, interfaith marriages. Ways in which religions work to promote community cohesion in the UK. How an issue arising from religion and community cohesion has been presented in one form of the media, for example television or radio programme, or in a film, or in the national press; including whether the treatment was fair to religious beliefs and religious people. Unit 4: S4 Religion & Community Cohesion 1 Religion and community cohesion Keywords community cohesion a common vision and shared sense of belonging for all groups in society discrimination treating people less favourably because of their ethnicity/gender/colour/ sexuality/age/class ethnic minority a member of an ethnic group (race) which is much smaller than the majority group interfaith marriages marriage where the husband and wife are from different religions multi-ethnic society many different races and cultures living together in one society multi-faith society many different religions living together in one society prejudice believing some people are inferior or superior without even knowing them racial harmony different races/colours living together happily racism the belief that some races are superior to others religious freedom the right to practise your religion and change your religion religious pluralism accepting all religions as having an equal right to coexist sexism discriminating against people because of their gender (being male or female) Unit 4: S4 Religion & Community Cohesion 2 How and why attitudes to the roles of men and women have changed Traditionally certain roles have seemed more suited to certain genders. Advances in Equal Rights for Women ‘The Qualification of Women Act 1918’ gave women over 31 the right to vote in elections. In 1928 the age was lowered to 21 to be the same as men. Today all people over the age of 18 can vote. ‘The Equal Pay Act 1970’ ensures men and women are paid equally for doing the same jobs. ‘The Sex Discrimination Act 1975’ made it illegal to discriminate against any person because of their gender (sex). Why Attitudes Have Changed Towards Women During the First and Second World Wars women had to take on the jobs previously done by men and proved they could do them just as well. Successful women in business and politics around the world show that women are every bit equal to men UN Declaration of Human Rights includes equality for all people no matter of race or gender. Unit 4: S4 Religion & Community Cohesion 3 Women in Islam The Qur’an puts equal religious duties on men and women. Men and women are equal in the eyes of Allah and they will be judged equally on judgement day Role as a Mother Other roles of women The most important role a women has is to be a mother. Muhammad said ‘Paradise lies at the feet of your mother’ • Women are the heart of the family. A Muslim woman is responsible for the care of the home and the welfare of the family, but is allowed to go to work and earn her own money. The education of women is considered to be very important in Islam. Muhammad* said: “The search for knowledge is a duty for every Muslim.” Unit 4: S4 Religion & Community Cohesion 4 The Effects of Discrimination & Racism • Racism and discrimination in society can lead to the rise in groups such as the BNP who encourage division between different ethnic groups in society. • If certain groups feel that they are being treated unfairly by society, they may become insular, cut themselves off from society, and even work against that society. • In 2001, white and Asian youths from communities isolated themselves off from each other, rioted and attacked and killed each other on the streets of Oldham, Burnley and Bradford. Unit 4: S4 Religion & Community Cohesion 5 • Police believe that when people feel discriminated against they are more likely to join extremist groups and take part in acts of terrorism. • The July 7th (2005) bombers were British citizens who had lost their sense of allegiance to Britain and were prepared to kill because they felt society worked against them. • It is thought that some young people from minority backgrounds turn to crime because they cannot see a future for themselves in a discriminating society. Unit 4: S4 Religion & Community Cohesion 6 The Law & Racism The Race Relations Act 1976 • It is unlawful to discriminate against anyone because of race, colour, nationality or ethnic origin in regard to jobs, training, housing, education, and services. • It is unlawful to use threatening, abusive or insulting words in public that could stir up in racial hatred. • It is unlawful to publish anything that is likely to cause racial hatred. Leading to... The Commission for Racial Equality • An organisation set up by the Government in 1976 to enforce the Race Relations Act. • To advice the Government on how the law was working and any necessary alterations. • To promote the concept of equal opportunities. Unit 4: S4 Religion & Community Cohesion 7 Government Action to Promote Community Cohesion Community Cohesion: when a common vision and shared sense of belonging exists for all groups in society. Education Funding Community Cohesion was made part of the national curriculum in 2006. Ofsted judge all schools on how they include community cohesion into their lessons and overall school life. Laws Giving financial support to groups and community projects which promote equality and unity or provide research in to the best ways of achieving Community Cohesion. What can be done to promote community cohesion? Passing laws such as the Race Relations Act and the Crime and Disorder Act and the Race and Religious Hatred Act which make it illegal to discriminate against people or encourage hatred due to race or religion. People Establishing groups such as the Equality and Human Rights Commission to ensure government laws are acted upon. Making sure all groups in society are represented fairly in education, social services, police and government. Unit 4: S4 Religion & Community Cohesion 8 Over the years Muslim Aid has provided financial support for students, patients, asylum seekers, and families in distress in the UK. Muslim Aid aims to provide support for those in need to improve their quality of life. Eligibility Criteria for the grants are: Patients suffering from life threatening diseases; Families in distress due to death of the breadwinner; Victims of disasters who need funds to rebuild their lives; Students in the last stage of their course (mainly higher education) facing financial problems due to unexpected calamity in their families; Women victims of abuse; Unit 4: S4 Religion & Community Cohesion 9 How racial harmony is shown All wear white Ihram Stand shoulder to shoulder in prayer All pray together on Friday Jummah Hajj (pilgrimage) All pray in Arabic All face Mecca when praying Teaches respect to al races, ages, faiths Accepts different cultures Unit 4: S4 Religion & Community Cohesion How racial harmony is shown All judged equally on Judgement day All fast in Ramadan The Quran teaches that racism is wrong, because regardless of differences, all people have the same common origin; 'Allah created you from a single being... out of him spread many men and women'. 10 (Quran 4:1) Muslims in their attitudes to other religions Exclusivism Inclusivism Most Muslims believe that only Islam has God’s true message and so everyone should be reverted to Islam otherwise they will not get to Paradise Some Muslims believe you should only go to Paradise by accepting Allah and his teachings, but, some members of other religions and some may also be able to go to Paradise. If you don’t believe in Allah you cannot get to paradise. There is only one saving truth, namely the Words of Allah and the example of Muhammad. The Qur’an says Muslims who give up the faith deserve to die. There is only one-way Paradise you must be Muslim Some people don’t know about Islam. People respond to what they know about God counts. Your actions and how you live is most important So some people may be able to get to Paradise even if they are not Muslim Unit 4: S4 Religion & Community Cohesion Pluralism Accepting all religions as equally valid and correct and can all coexist Muslim men are able to marry women of the book with out them reverting to Islam. the Qur’an implies that Jews and Christians have some of the truth about God; the Qur’an says there should be no compulsion in religion. You do not have to be Muslim to get to Paradise all religions are equal and important 11 Multi-Faith Britain Most people believe that individuals have the right to believe in the god of their choice and follow the religion they choose. Religious Freedom: ‘The right to practice your religion and change your religion if you want to.’ Every 10 years the British Government holds a census (national questionnaire) of the population. The purpose is to build an accurate picture of Britain today. One question is about people’s religious belief. Outline of Religious belief in Britain - 2001 42,558,000 Christian 8,197,221 No Religion 4,823,000 No Answer 1,591,207 Muslim 558,746 Hindu 336,040 Sikh 267,711 Jewish 149,237 Buddhist 157,000 Other Religion HM Office of National Statistics 2001 Census Unit 4: S4 Religion & Community Cohesion 12 Interfaith Marriages As a multi-faith society expands there will be people from different religions who fall in love and want to marry. But, does it matter? • Religious wedding services are difficult as each religion has its own unique style. • The religion of any children may cause conflict. • Funeral services will be a problem for family members from other religious traditions. • Some family members may feel a person has betrayed their faith by marrying a person with an opposing view. • Most religions encourage equality - why not in interfaith marriages also? • Interfaith marriages might encourage religious tolerance between families. • Children will have a wider understanding from which to choose their own faith. • Islam allows men to marry Christian or Jewish women without them reverting to Islam. Unit 4: S4 Religion & Community Cohesion 13 Film/ White Girl Issue Community cohesion – A white family move into a predominately Asian Muslim area and have to adjust to the more diverse surroundings. Why is the issue important? Community cohesion and how different religions and races get along with each other Was the presentation fair to religious people and beliefs? Fair: The Muslim family are portrayed well as caring, loving strongly religious family There are strong Muslim role models throughout the film They should the importance of prayer in the film The mother of the man character is a loving mother who struggles to do the best for her kids. Does present problems and prejudices that communities may have of other another. Unfair While the Muslim family is positively portrayed in the film the extended family of the main character is unfairly portrayed as racist, drug dealing drunks. Generally the white characters in the family are portrayed badly and so this would not be a fair representation of the white community. Unit 4: S4 Religion & Community Cohesion 14 Film/ Programme watched East is East Bend it like Beckham Issue Community cohesion – how modern life conflicts with traditional values of parents Why is the issue important? This reflects the difficulty people can have growing up part of a different faith and culture from mainstream society Was the presentation fair to religious people and beliefs? Fair: Families were loving and generally happy Parents wanted what was best for their children and thought the traditional way was best Religion was not really the source of conflict but culture. Dad’s were worried what other people and families thought of their kids rather than the right thing to do in their faith Unfair Dad in East is East seemed out of touch and a hypocrite. Kids in East is East were disrespectful to Islam did not show the value of Islam in community cohesion Forced marriage is against the teaching of Islam this was not clear in the film Unit 4: S4 Religion & Community Cohesion 15