RS01 A3 Unit 4 – Religion and Community Cohesion
advertisement
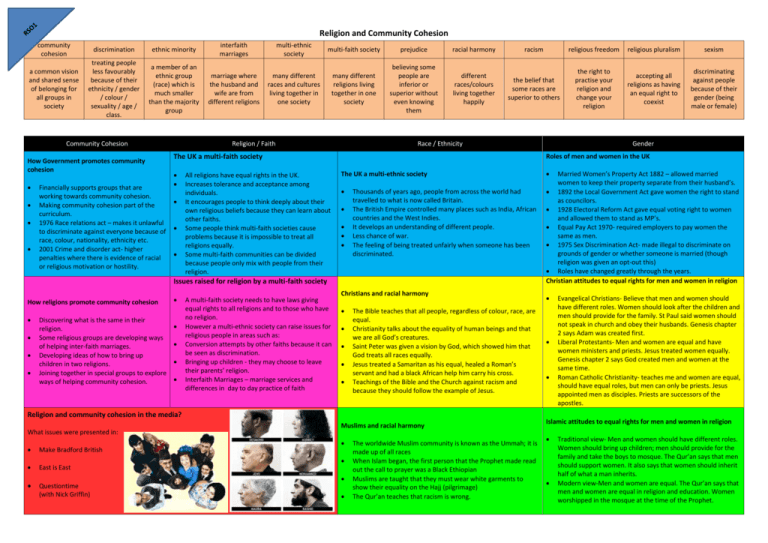
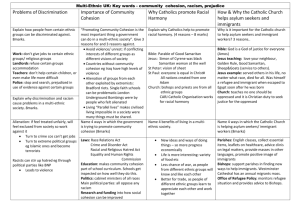
Religion and Community Cohesion community cohesion discrimination ethnic minority a common vision and shared sense of belonging for all groups in society treating people less favourably because of their ethnicity / gender / colour / sexuality / age / class. a member of an ethnic group (race) which is much smaller than the majority group Community Cohesion How Government promotes community cohesion Financially supports groups that are working towards community cohesion. Making community cohesion part of the curriculum. 1976 Race relations act – makes it unlawful to discriminate against everyone because of race, colour, nationality, ethnicity etc. 2001 Crime and disorder act- higher penalties where there is evidence of racial or religious motivation or hostility. interfaith marriages marriage where the husband and wife are from different religions multi-ethnic society multi-faith society prejudice racial harmony racism religious freedom religious pluralism sexism many different religions living together in one society believing some people are inferior or superior without even knowing them different races/colours living together happily the belief that some races are superior to others the right to practise your religion and change your religion accepting all religions as having an equal right to coexist discriminating against people because of their gender (being male or female) many different races and cultures living together in one society Religion / Faith Race / Ethnicity The UK a multi-faith society All religions have equal rights in the UK. Increases tolerance and acceptance among individuals. It encourages people to think deeply about their own religious beliefs because they can learn about other faiths. Some people think multi-faith societies cause problems because it is impossible to treat all religions equally. Some multi-faith communities can be divided because people only mix with people from their religion. Roles of men and women in the UK The UK a multi-ethnic society Thousands of years ago, people from across the world had travelled to what is now called Britain. The British Empire controlled many places such as India, African countries and the West Indies. It develops an understanding of different people. Less chance of war. The feeling of being treated unfairly when someone has been discriminated. Issues raised for religion by a multi-faith society How religions promote community cohesion Discovering what is the same in their religion. Some religious groups are developing ways of helping inter-faith marriages. Developing ideas of how to bring up children in two religions. Joining together in special groups to explore ways of helping community cohesion. A multi-faith society needs to have laws giving equal rights to all religions and to those who have no religion. However a multi-ethnic society can raise issues for religious people in areas such as: Conversion attempts by other faiths because it can be seen as discrimination. Bringing up children - they may choose to leave their parents’ religion. Interfaith Marriages – marriage services and differences in day to day practice of faith Christians and racial harmony The Bible teaches that all people, regardless of colour, race, are equal. Christianity talks about the equality of human beings and that we are all God’s creatures. Saint Peter was given a vision by God, which showed him that God treats all races equally. Jesus treated a Samaritan as his equal, healed a Roman’s servant and had a black African help him carry his cross. Teachings of the Bible and the Church against racism and because they should follow the example of Jesus. Religion and community cohesion in the media? What issues were presented in: Make Bradford British East is East Questiontime (with Nick Griffin) Gender Muslims and racial harmony The worldwide Muslim community is known as the Ummah; it is made up of all races When Islam began, the first person that the Prophet made read out the call to prayer was a Black Ethiopian Muslims are taught that they must wear white garments to show their equality on the Hajj (pilgrimage) The Qur’an teaches that racism is wrong. Married Women’s Property Act 1882 – allowed married women to keep their property separate from their husband’s. 1892 the Local Government Act gave women the right to stand as councilors. 1928 Electoral Reform Act gave equal voting right to women and allowed them to stand as MP’s. Equal Pay Act 1970- required employers to pay women the same as men. 1975 Sex Discrimination Act- made illegal to discriminate on grounds of gender or whether someone is married (though religion was given an opt-out this) Roles have changed greatly through the years. Christian attitudes to equal rights for men and women in religion Evangelical Christians- Believe that men and women should have different roles. Women should look after the children and men should provide for the family. St Paul said women should not speak in church and obey their husbands. Genesis chapter 2 says Adam was created first. Liberal Protestants- Men and women are equal and have women ministers and priests. Jesus treated women equally. Genesis chapter 2 says God created men and women at the same time. Roman Catholic Christianity- teaches me and women are equal, should have equal roles, but men can only be priests. Jesus appointed men as disciples. Priests are successors of the apostles. Islamic attitudes to equal rights for men and women in religion Traditional view- Men and women should have different roles. Women should bring up children; men should provide for the family and take the boys to mosque. The Qur’an says that men should support women. It also says that women should inherit half of what a man inherits. Modern view-Men and women are equal. The Qur’an says that men and women are equal in religion and education. Women worshipped in the mosque at the time of the Prophet.