Module 1- The Energy Molecules Objectives: Students will be able
advertisement

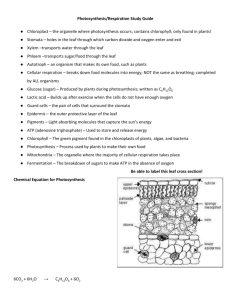
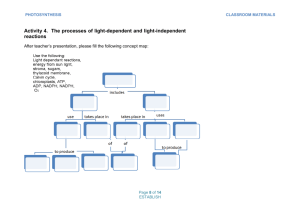
Module 1- The Energy Molecules Objectives: 1. Students will be able to identify the chemical formula for glucose and describe where glucose comes from 2. Students will be able to explain how ATP is the energy currency of the cell 3. Students will be able to describe the structure of ATP Notes- Read the passage and watch the video. Write your notes in the box below. Anaysis Questions 1. What is the chemical formula of glucose? Describe the structure of glucose molecules. _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ 2. Where does our glucose come from? What happens to this glucose? _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ 3. The fact that all organisms use similar energy-carrying molecules shows one aspect of the grand "Unity of Life." Name two universal energy-carrying molecules, and explain why most organisms need both carriers rather than just one. _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ 4. 2. A single cell uses about 10 million ATP molecules per second. Explain how cells use the energy and recycle the materials in ATP. _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ 5. 3. ATP and glucose are both molecules that organisms use for energy. They are like the tank of a tanker truck that delivers gas to a gas station and the gas tank that holds the fuel for a car. Which molecule is like the tank of the delivery truck, and which is like the gas tank of the car? Explain your answer. _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ Activity- ATP Model Building Collect the packet “Cell Energy” from the file bin Complete the questions and model build Art supplies and blank computer paper are available for use Module 1 Assessment Complete quiz for Module 1 Up to 3 attempts allowed for this module Module 2: What’s in a Pigment? Objectives: 1. Students will be able to identify the different pigments found in plants and describe how they are used to gather energy from sunlight 2. Students will be able to identify the parts of the a leaf in a diagram and describe their function 3. Students will be able to describe the role of chloroplasts in photosynthesis Notes: Watch the video and take notes in the box below. Notes: Read the information on leaf pigments, and leaf structure and function, and take notes Activity: Pigment Chromatography Lab Collect the packet “Plant Pigments” from the file bin Complete the lab and analysis questions Lab set ups are on the supply table o Make sure to clean and dry materials after use and return to supply table Activity: Leaf Anatomy The leaf is the primary photosynthetic organ of the plant. It consists of a flattened portion, called the blade, that is attached to the plant by a structure called the petiole. Sometimes leaves are divided into two or more sections called leaflets. Leaves with a single undivided blade are called simple, those with two or more leaflets are called compound. The outer surface of the leaf has a thin waxy covering called the cuticle (A), this layer's primary function is to prevent water loss within the leaf. (Plants that leave entirely within water do not have a cuticle). Directly underneath the cuticle is a layer of cells called the epidermis (B). The vascular tissue, xylem and phloem are found within the veins of the leaf. Veins are actually extensions that run from to tips of the roots all the way up to the edges of the leaves. The outer layer of the vein is made of cells called bundle sheath cells (E), and they create a circle around the xylem and the phloem. On the picture, xylem is the upper layer of cells (G) and is shaded a little lighter than the lower layer of cells - phloem (H). Recall that xylem transports water and phloem transports sugar (food). Within the leaf, there is a layer of cells called the mesophyll. The word mesophyll is greek and means "middle" (meso) "leaf" (phyllon). Mesophyll can then be divided into two layers, the palisade layer (D) and the spongy layer (F). Palisade cells are more column-like, and lie just under the epidermis, the spongy cells are more loosely packed and lie between the palisade layer and the lower epidermis. The air spaces between the spongy cells allow for gas exchange. Mesophyll cells (both palisade and spongy) are packed with chloroplasts, and this is where photosynthesis actually occurs. Epidermis also lines the lower area of the leaf (as does the cuticle). The leaf also has tiny holes within the epidermis called stomata. Specialized cells, called guard cells (C) surround the stomata and are shaped like two cupped hands. Changes within water pressure cause the stoma (singular of stomata) to open or close. If the guard cells are full of water, they swell up and bend away from each other which opens the stoma. During dry times, the guard cells close. Questions 1. What two tissues are found within a vein? ____________________________________ 2. What does the word "mesophyll" mean? _____________________________ 3. What two layers of the plant contain chloroplasts? _______________________________________ 4. The outermost layer of cells: ________________________________ 5. The waxy covering of the leaf: _______________________________ 6. These cells function to open and close stomata. _________________________ 7. Outer layer of the vein: ______________________________ 8. Column like cells that lie just under the epidermis. __________________________ 9. Openings that allow for gas exchange. _______________________________ 10. The stalk that connects the leaf to the stem. ______________________ Leaf Structure Diagram Coloring Color the structures bolded above in the picture on the next page. Make sure that the entire picture is colored and that the color matches the words. For simplicity only part of the picture is labeled. Cuticle (light blue) Epidermis (yellow) Guard cells (pink) Palisade Mesophyll .........(dark green) Phloem (purple) Xylem (orange) Spongy Mesophyll ....(light green) Bundle Sheath .......(dark blue) Activity: Leaf Structure Virtual Lab You are going to analyze the cells in an elodea plant leaf Questions 1. What type of objective lens is used for the first leaf examination? _________________________________________________________ 2. What is the midrib? Draw what you see in the box below _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ 3. After turning to the higher magnification, draw what you see in both pictures in the boxes below and label the chloroplasts and cell wall. 4. Where are the chloroplasts and other organelles located inside the cell? What holds them in that location? _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ 5. What observations do you make concerning how does the cytoplasm affects the chloroplasts? _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ Module 2 Assessment Complete quiz for Module 2 Up to 3 attempts allowed for this module Module 3: Photosynthesis Objectives: 1. Students will be able to describe the process of photosynthesis 2. Students will be able to identify the different stages of photosynthesis and where each stage takes place 3. Students will be able to summarize how carbon dioxide and water are used in photosynthesis to make glucose and oxygen 4. Students will be able to describe the role of electron transport molecules, like NADPH Notes- Read the passage and watch the video. Write your notes in the box below. Analysis Questions 1. Where does the energy for photosynthesis come from? ___________________________________ 2. How is the process of photosynthesis central to sustaining life on Earth? _________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ 3. What are the products produced by photosynthesis? _________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ 4. What two raw materials are needed by plants in order to perform photosynthesis? _________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ 5. What two electron transport molecules are produced in the light-dependent reactions that are needed to begin the light-independent reactions? ________________________________________ 6. What gas is needed to convert the energy in the carrier molecules into the 6-carbon compound glucose?________________________________________________________________________ 7. Hypothesize: What do you predict would happen to the rate of photosynthesis if the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere were to increase? Explain. _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ Activity: Analyzing Data- study the graph and answer the questions in the space provided 1. __________________________________________________________________________________________________ 2. __________________________________________________________________________________________________ 3. __________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________ Activity- Light- Dependent vs. Light-Independent Reactions Fill in words from the bank onto the appropriate line Questions 1. What is the function of NADPH? _________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ 2. How is light energy converted into chemical energy during photosynthesis? _________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ 3. How would photosynthesis be affected if there were a shortage of NADP+ in the cells of plants? _________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ 4. Into which set of reactions—light-dependent or light-independent – does each reactant of photosynthesis enter? From which set of reactions is each product of photosynthesis generated? _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ Activity: Virtual Lab Collect the “Photosynthesis Virtual Lab” packet from the file bin Complete the labs and analysis questions Lab must be completed using Puffin- flash is required Module 3 Assessment Complete quiz for Module 3 Up to 3 attempts allowed for this module Module 4: Cellular Respiration Objectives: 1. Students will be able to summarize how photosynthesis and cellular respiration are cylical processes 2. Students will be able to differentiate between aerobic and anaerobic respiration 3. Students will be able to explain the evolutionary importance of aerobic respiration 4. Students will be able to state how many ATP can potentially be made from aerobic respiration Notes- Read the passage and watch the video. Write your notes in the box below. Analysis Questions 1. Why do all organisms need food?______________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ 2. Write the overall reaction for cellular respiration. ________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ 3. How does the process of cellular respiration maintain homeostasis at the cellular level? _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ 4. In what ways are cellular respiration and photosynthesis considered opposite processes? _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ 5. How is the function of NADH and FADH2 similar to that of NADPH? __________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ 6. How many molecules of ATP are produced in the entire breakdown of glucose? ________________________ 7. Compare and contrast aerobic versus anaerobic respiration. _______________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ 8. Can ATP be made without the presence of oxygen? Explain. ________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ 9. Why do the majority of organisms that presently live perform aerobic respiration more often than anaerobic? [Hint: think in terms of the evolution of these biochemical pathways] ________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ Activity: The Effects of Exercise on Cellular Respiration Lab Collect the packet “The Effects of Exercise on Cellular Respiration” from the file bin Complete the lab and analysis questions Lab set ups are on the supply table o Make sure to clean and dry materials after use and return to supply table Activity: Do Plants Consume or Release CO2? Lab Collect the packet “Do Plants Consume or Release CO2?” packet form the file bin Complete the lab and analysis questions o Set up lab on day 1, come back next day to analyze results Lab set ups are on the supply table o Make sure to clean and dry materials after use and return to supply table Module 4 Assessment Complete quiz for Module 4 Up to 3 attempts allowed for this module Module 5: Carbon Cycle & the Environment Objectives 1. Students will be able to summarize how carbon moves through the environment in a cylical pattern 2. Students will be able to describe the role that carbon plays in photosynthesis and respiration 3. Students will be able to explain how trees are “carbon sinks” and the role carbon plays in their growth and function. 4. Students will be able to identify the different reservoirs for carbon in the environment and their role in the carbon cycle 5. Students will be able to explain the process of deforestation and identify the consequences to the carbon cycle because of this activity Lab 1: Living in a Carbon World 1. Before you begin “Keeping up with Carbon”, make a list of what you think you already know about carbon and the carbon cycle 2. As you watch the video, make a list of where on Earth carbon can be found, its relationship to life, climate change and any other carbon fact that interests you. 3. Why can carbon atoms form the basis of millions of different types of carbon compound molecules? _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ 4. How do the carbon atoms in CO2 absorb via plant photosynthesis provide the carbon atoms for all of the new carbon compounds a plant produces and uses to build its cells and tissues and to burn for energy? _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ 5. How are carbon compounds transformed between photosynthesis and cell respiration? _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ 6. Can trees and other plants absorb ever increasing amounts of carbon dioxide from the air or is the process limited by environmental factors? _____________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ Lab 1A- Trees: The Carbon Storage Experts 1. After reading the Giant Sequoia article, write down a hypothesis as to how a Giant Sequoia tree can add over four million pounds of mass as it grows from a small seed to a fully grown tree. ________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ 2. As you watch “Where Do Trees Come From?” write down the hypotheses mentioned as to where tree growth comes from. 3. In the video, were there any major misconceptions that people had about where the mass of a tree comes from as it grows? If so, do they match any of the hypotheses on the class list? 4. Checking In: Think about a large tree that is close to where you live and imagine that this tree weighs 100,000 pounds. The tree gained most of its 100,000 pounds of mass from…? ________________________________ 5. Checking In: where does carbon go once it enters a tree? Record your answers from the three question in the space provided. a. ____________________________________________________ b. ____________________________________________________ c. ____________________________________________________ 6. Stop & Think: Draw a simple diagram to illustrate how trees (and all plants) represent a small but complete carbon cycle. 7. Checking In: Check your understanding of how carbon moves through food webs by answering the questions and recording your answers below a. ______________________________________________________________ b. ______________________________________________________________ c. ______________________________________________________________ d. ______________________________________________________________ 8. Stop and Think: Examine the Terrestrial Carbon Cycle food web diagram again. Describe how the carbon from carbon dioxide molecules in the atmosphere can end up in a coyote. Use a diagram to help you explain your answer if you need to. 9. Carbon storage in trees and forests. Why care? a. Why are trees considered to be “carbon sinks”? ___________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ b. What role do trees play concerning carbon dioxide that is released due to fossil fuel use? __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ c. How much CO2 do forests absorb? _____________________________________________________ 10. Forest Carbon 101 a. Why should we care about trees and forests storing carbon? _________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ b. What solutions can you think of to increase carbon storage in your community? __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ c. Can trees and forests keep absorbing and storing ever-increasing amounts of CO2in the air? If not, what might limit carbon uptake and storage in trees? ______________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 11. What limits carbon storage and growth in trees? _________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ *Stop reading at “Experimental Title” Lab 2- The Carbon Cycle: What Goes Around, comes around 1. What is the goal of the Lab 2 activities? ________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ Lab 2A- A Forest Carbon Cycle 1. Look at the picture “A Forest Carbon Cycle”. What neighborhoods are shown in this image? _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ 2. Checking In: Which of the four Earth System's spheres are represented in the forest carbon cycle image? _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ 3. What is a reservoir? ________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ *Skip the carbon cycle game 4. Carbon Dioxide and the Carbon Cycle (animation) a. Checking In: In a forest carbon cycle, which process(s) moves carbon out of the atmosphere to another reservoir? ___________________________________________________________________ b. Checking In: Which process(s) moves carbon into the atmosphere? ___________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 5. How much carbon moves between reservoirs per year? ___________________________________________ 6. The Global Carbon Cycle Diagram a. Which areas depicted are considered carbon sinks? Why? ___________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ b. What is a carbon source? _____________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 7. Checking In- write your answer choice in the space provided a. Is the ocean behaving as a carbon sink or a carbon source?___________________________________ b. Are Fossil fuels and land use (burning forests for agriculture) currently behaving as a carbon sink or a carbon source? _____________________________________________________________________ c. Which biosphere process(s) are responsible for moving 450 GT of carbon from the atmosphere into the vegetation and land? _____________________________________________________________ d. Which biosphere process is responsible for moving 439 GT of carbon from the vegetation and land into the atmosphere? ________________________________________________________________ e. Which chemical process is responsible for moving gigatons of carbon from the fossil fuels into the atmosphere? _______________________________________________________________________ 8. Stop and Think: a. Does the carbon cycle in this diagram appear to be in balance or out of balance? Use specific evidence from the diagram to support your answer. b. Imagine that we could go back to pre-industrial times before fossil fuels were being burned for energy. Would a pre-industrial carbon cycle be in balance or out of balance? What makes you think so? Lab 2B: Carbon- Going Global! 1. Checking In: Identify the four largest reservoirs of carbon. Explain *Skip making the poster and just answer the discussion questions 2. Does carbon move fastest through the biosphere or the geosphere? How do you know? _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ 3. Many countries are cutting down forests to make way for agriculture and roads. How might this practice disrupt the carbon cycle? _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ 4. The world's population has passed the 7 billion mark. As the population increases, the need for energy will increase. More coal, gas and oil will be burned to provide that energy. How might this disrupt the global carbon cycle? Why? _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ Lab 2C: Systems Thinking and The Carbon Cycle *Skip to Part 2: Using Connection Circles in a Case Study 1. What is going on as described in the passage? What could pine bark beetle infestations have to do with the carbon cycle? 2. Video: Attacks on a Protective Canopy and reading: “Climate Change Sends Beetles into Overdrive a. What does the infestation do to forests? _________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ b. What causes the infestation and why is it getting worse? ____________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ c. What changes have been observed in the Pine Bark Beetle infestation? ________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ d. What are scientists observing and thinking about? _________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ e. What is the relationship between temperature and the beetle infestation? _____________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ *Skip Pine Beetle Connections Circle, Jump to Positive & Negative Feedback Loops 3. Positive & Negative Feedback Loops a. What is a positive feedback loop? ______________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ b. What is a negative feedback loop? ______________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ c. Is the situation with the Pine Bark Beetle a positive or a negative feedback loop? How do you know? Lab 3: Carbon and the Atmosphere: My Life as a Greenhouse Gas 1. What is the greenhouse effect? _______________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ 2. How does carbon dioxide contribute to the greenhouse effect? _____________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ Lab 3C: What’s My Carbon Footprint? * Skip to the bottom to complete the “What’s my Carbon Footprint” Activity 1. What is the difference between a primary carbon footprint and a secondary carbon footprint? 2. Fill in the information for the Carbon Footprint Calculator. Calculate for yourself, then complete it for your whole house. 3. Checking In: a. How do your GHG emissions (Tons of CO2 eq/year) compare with the United States average and the World average? b. Which behavior is responsible for contributing the most GHG emissions? .... the least? 4. Discuss a. Compare your carbon footprint with others. How do they compare? Were you surprised by your results? Why or why not? b. Share two ways you can reduce your carbon footprint with your classmates. Do some types of changes seem easier than others? Why? Lab 4: Forests- Changes in the Land 1. What is the goal of this lab section? ___________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ Lab 4A: Changes in Forest Cover 1. Video Clip: Disappearing Trees in a Swedish City a. What do you observe is happening to the city landscape? ___________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 2. Picture: Changes in Forest Cover over Time a. What do you observe is happening to the amount of forest cover on the globe? _________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 3. Discussion a. What has happened to global forest cover over the past few thousands of years? What countries or regions around the world have experienced the greatest change in forest cover? What do you think the causes of these changes might be? List as many as you can. b. Next, look at changes in forest cover from 2000 to 2012. What countries or regions show higher losses in forest/tree cover compared to other countries and regions? Why do you think these countries or regions have higher losses? c. Compare the changes in forest cover in the two images. What patterns or trends in forest cover change do you see when comparing changes over a thousand years to changes over a recent decade? d. Think about how the loss of forest cover over time might affect the global carbon cycle. List as many as you can. e. How can preserving forests help to mitigate the effects of rising atmospherics CO2 and climate change? f. At the end of Lab 4A, you will have the opportunity to use the Global Forest Watch tool to develop and investigate your own research question. But, why should we care about changes in forest cover, especially if these changes are happening far away from where we live? 4. What causes losses in forest cover over time? a. Identify both natural and man-made causes ______________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 5. Drought & Wildfires a. Which image - false color or natural color- is the most useful to you for determining the extent of damage from this fire? Why? __________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ b. What happens to the carbon stored in the 3 million trees that died due to the 2011 Texas drought? Where will that carbon go? ____________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ c. Should Texas implement a reforestation project to replace these trees? Why or why not? __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 6. Wildfires Video a. What did you hear/see in the video clip about wildfires? ____________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 7. Yellowstone Fires: Ecological Blessings a. Summarize what you read concerning wildfires at Yellowstone. 8. Video: A Global Tour of Fire a. What did you see/hear in the video clip “A Global Tour of Fire”? ______________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 9. How Does the Carbon Cycle Respond to Wildfires- Discussion a. Draw two conceptual model diagrams illustrating how the carbon cycle responds to wildfires at different time scales. i. Drawing 1 assumes regeneration of the forest will occur after the fire through natural regeneration and/or purposeful planting of trees. ii. Drawing 2 assumes that no regeneration of the forest will occur after the fire. 10. Deforestation: Permanent loss of forest cover- Discussion Let's examine a well-known example of deforestation - Haiti and the Dominican Republic. Both these countries share the same island. The NASA satellite image above shows the border between Haiti on the left and the Dominican Republic on the right. Click on the image to make it larger. Then, take a few minutes to carefully look at and think about the image you are viewing. a. What difference(s) in forest cover can you observe in this satellite image? What is the evidence for the difference(s) you observe? _________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ b. What do you think might be some contributing causes to the differences in forest cover between these two countries? List all that you can think of. _________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 11. Stages of Deforestation Image a. What observations do you make about the stages of deforestation? 12. Video- Planet in Peril: Checking In a. What stage(s) of deforestation releases higher than normal amounts of carbon dioxide to the atmosphere? _______________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ b. Which stage(s) represents a carbon sink? ________________________________________________ c. When deforestation occurs, which carbon cycle process(s) increase the emission of carbon dioxide to the atmosphere? ____________________________________________________________________ d. Which of these stages could contribute to soil erosion? _____________________________________ 13. What is biomass as described in the section titled “How much carbon is in tropical rainforests? _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ 14. Trouble in the Amazon a. What observations do you make concerning the level of forest coverage in the interactive “Forest changes in Rondonia, Brazil? ___________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ b. What do you see/hear in the video clip “Amazon Deforestation”? ____________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ c. Checking In i. By 2003, how many square kilometers had been cleared from the Amazonian Forest in Rondônia? How many acres would that be? ____________________________________________________________________________ ii. One acre of forests can absorb approximately one ton of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere each year. If deforestation has cleared 16,744,609 acres in just Rondônia, how many less tons of atmospheric carbon dioxide will be stored in the trees every year? ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ d. Stop and Think i. Describe how deforestation can impact the the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. 15. Up in Smoke: Deforestation, Fire, Farmers and the Carbon Cycle - a mini case study. a. What is the situation that is being described in the reading? b. Watch the short video clips through The Guardian website. You’ll see the links for part 2-5 if you scroll down on the page. Take notes while viewing. c. Model & Discussion- How does the carbon cycle differ when "slash and burn" methods are used versus sustainable "crop alley" methods. Describe as many changes to the carbon cycle and the community that are part of this carbon cycle story. d. Unit Assessment You are going to be writing a short essay using the information you learned through this virtual classroom experience. In you essay you must address the following concepts. o Insert list of concepts here Use the provided rubric [must be attached] to guide your writing. When you have completed the virtual classroom materials, and practiced your essay, you are to write a final draft o You will be provided with a clean rubric to reference while you write.