Project Charter - New Mexico Department of Information Technology
advertisement

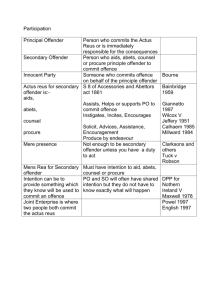
OFFENDER MANAGEMENT SYSTEM (OMS) REPLACEMENT PROJECT PR OJ EC T CHA R TER FOR CER TIFIC A TION EXECUTIVE SPONSOR – GREGG MARCANTEL, SECRETARY OF CORRECTIONS BUSINESS OWNER – JOE BOOKER, DEPUTY SECRETARY OF OPERATIONS AGENCY CIO – IT LEAD – TIMOTHY OAKELEY, CHIEF INFORMATION OFFICER PROJECT MANAGER – JERRY BRINEGAR, DEPUTY CHIEF INFORMATION OFFICER ORIGINAL PLAN DATE: MARCH 31, 2015 REVISION DATE: APRIL 15, 2015 REVISION: 1.1 ABOUT THIS PROJECT CHARTER DOCUMENT PERMISSION TO PLAN THE PROJEC T AND SETTING THE GOVERNANCE STRUCTURE The Project Charter provides the project manager and project team with permission to proceed with the work of the project, within the scope delineated in this document. The Project Charter should be the outcome of a number of documents that went into the pre-planning for the project, and in many cases the agency IT Plan, Business Case for appropriations, Federal funding requests and the like. Project sponsors sign the Project Charter signifying that they have agreed to the governance structure for guiding the direction for the further planning of the project, discovery and defining the requirements, acquiring necessary resources, and within that context the statement of work for any related contracts including a contract for the Independent Validation and Verification. The Project Charter is also the foundation for the creation of the project management plan, and much of the thinking and writing for this charter will be immediately usable for that project management plan. PROJECT CERTIFICATION INITIAL PHASE DOCUMENTATION The Project Charter is also used within the State of New Mexico IT Project Certification process as evidence of the project’s worthiness for the Initial Phase certification. The Initial Phase certification is especially critical to many state and agency projects because of its related release of the initial funds required for the project. Initiation Phase funding is requested by an agency for use in developing project phases, developing Independent Verification and Validation (“IV&V”) plan and contract; address project review issues and/or to develop an overall project management plan. Note: Waiver of the IV&V requirement requires specific written approval by the Secretary of the DoIT. DoIT “Project Certification” Memorandum July 2, 2007 The Project Charter and the Request for Certification Form are meant to provide a comprehensive picture of the project’s intention and initial planning, that includes the project’s place in the context of the State of New Mexico’s IT Strategic Plan, Enterprise Architecture, and DoIT project oversight process. See “IT Project Oversight Process” Memorandum July 5th 2007 on the OCIO-DoIT web site. i TABLE OF CONTENTS ABOUT THIS PROJECT CHARTER DOCUMENT .......................................................................................................... I TABLE OF CONTENTS .............................................................................................................................................. II 1. PROJECT BACKGROUND ..................................................................................................................................... 1 1.1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY -RATIONALE FOR THE PROJECT ..................................................................................................1 1.2 SUMMARY OF THE FOUNDATION PLANNING AND DOCUMENTATION FOR THE PROJECT........................................................1 1.3 PROJECT CERTIFICATION REQUIREMENTS ......................................................................................................................2 2.0 JUSTIFICATION, OBJECTIVES AND IMPACTS ...................................................................................................... 3 2.1 AGENCY JUSTIFICATION .............................................................................................................................................3 2.2 BUSINESS OBJECTIVES ...............................................................................................................................................3 2.3 TECHNICAL OBJECTIVES .............................................................................................................................................4 2.4 IMPACT ON ORGANIZATION .......................................................................................................................................5 2.5 TRANSITION TO OPERATIONS ......................................................................................................................................6 3.0 PROJECT/PRODUCT SCOPE OF WORK ............................................................................................................... 9 3.1 DELIVERABLES .........................................................................................................................................................9 3.1.1 Project Deliverables .....................................................................................................................................9 3.1.2 Product Deliverables..................................................................................................................................11 3.2 SUCCESS AND QUALITY METRICS ..........................................................................................................................13 4.0 SCHEDULE ESTIMATE ...................................................................................................................................... 14 5.0 BUDGET ESTIMATE ......................................................................................................................................... 14 5.1 FUNDING SOURCE(S) ..............................................................................................................................................14 5.2. BUDGET BY MAJOR DELIVERABLE OR TYPE OF EXPENSE - ..............................................................................................15 5.3 BUDGET BY PROJECT PHASE OR CERTIFICATION PHASE..................................................................................................15 6.0 PROJECT AUTHORITY AND ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE ............................................................................. 16 6.1 STAKEHOLDERS .................................................................................................................................................16 6.2 PROJECT GOVERNANCE PLAN............................................................................................................................17 6.3 PROJECT MANAGER ...........................................................................................................................................18 6.3.1 PROJECT MANAGER CONTACT INFORMATION ..........................................................................................18 6.3.2 PROJECT MANAGER BACKGROUND ..........................................................................................................19 6.4 PROJECT TEAM ROLES AND RESPONSIBILITIES ..................................................................................................19 6.5 PROJECT MANAGEMENT METHODOLOGY ....................................................................................................................20 7.0 CONSTRAINTS ................................................................................................................................................ 21 8.0 DEPENDENCIES ............................................................................................................................................... 22 9.0 ASSUMPTIONS ............................................................................................................................................... 23 10.0 SIGNIFICANT RISKS AND MITIGATION STRATEGY ......................................................................................... 23 INABILITY TO CONTINUE FUTURE MODIFICATION OF THE POWERBUILDER SOURCE CODE .............................................................23 INABILITY TO PROVIDE ADEQUATE PUBLIC SAFETY ...............................................................................................................24 NO OR INADEQUATE MANAGEMENT COMMITMENT AND SUPPORT ........................................................................................24 ii IMPROPER MANAGEMENT OF OFFENDER FROM INCARCERATION THROUGH COMMUNITY SUPERVISION .........................................24 PROJECT FUNDING UNCERTAINTIES..................................................................................................................................25 ORGANIZATIONAL READINESS ........................................................................................................................................25 CHANGES IN STATE OR FEDERAL LAWS ..............................................................................................................................25 11.0 COMMUNICATION PLAN FOR EXECUTIVE REPORTING.................................................................................. 26 12.0 INDEPENDENT VERIFICATION AND VALIDATION - IV&V ................................................................................ 26 13.0 PROJECT CHARTER AGENCY APPROVAL SIGNATURES ................................................................................... 27 14.0 PROJECT CHARTER CERTIFICATION APPROVAL SIGNATURE .......................................................................... 28 iii Revision History REVISION NUMBER DATE COMMENT 1.0 March 31, 2015 Initial Draft 1.1 April 15, 2016 Input from DoIT EPMO iv PROJECT CHARTER - NMCD OFFENDER MANAGEMENT SYSTEM (OMS) REPLACEMENT 1. PROJECT BACKGROUND The project background section is meant to provide the reviewer with a picture of the development of the project from inception to its being submitted for certification. 1.1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY -RATIONALE FOR THE PROJECT The New Mexico Corrections Department (NMCD) has made the reduction of recidivism by 10% over the next 3 years its’ top priority. The current 15-year old client-server offender management system is end-of-life, end-of-support, and needs to be replaced in order to support the changing business processes to accomplish this and other agency goals. The offender management system must use new technology and design standards to streamline and improve business processes for end-users who manage and supervise offenders. The Agency’s direction to accomplish this is to purchase a Commercial-off-the-shelf (COTS) web system using current technologies. The complete offender management system (OMS) will have seventeen (17) unique modules as necessary components to manage inmates and offenders through the correctional system and will provide much-needed new functionality to support and improve the business process. Providing one seamless web-based system for the management of inmates and offenders supports the state government initiatives relating to reducing the cost of government operations, improving customer service and increasing public safety. The ability to manage the application online, instead of pushing out updates to over a thousand computers will greatly reduce support and maintenance costs. Based on previous project cycles of development and the inability to quickly provide the right business functionality to accomplish this goal, the Department has dedicated its’ efforts to implement a new Offender Management System (OMS) Replacement and will fully implement all application modules of the offender management system and transition them to a production environment as one cohesive system in a phased approach. 1.2 SUMMARY OF THE FOUNDATION PLANNING AND DOCUMENTATION FOR THE PROJECT As stated, the agency will accomplish this project utilizing a phased approach. In April, 2015 the agency will meet with the PCC to request certification of the initiation of the project and the release of funding for Phase I activities, which include Project Initiation and the start of Project Planning. During this phase, a Request for Information (RFI) will be conducted to outline various system options available to NMCD. Once completed, an RFP will be conducted and awarded. During this time period, project planning will begin, with the initial draft project management plan, the IV&V plan, the high-level project schedule and project budget estimates being completed. Data and infrastructure planning will also begin during this timeframe. PAGE 1 1 PROJECT CHARTER - NMCD OFFENDER MANAGEMENT SYSTEM (OMS) REPLACEMENT 2 Other activities in this phase includes the documentation of the remaining module requirements that have not been updated or revisited (Classification, Discipline/Grievance, Caseload Management, Security, Housing/Bed Management, Visitation, Inmate Trust Accounting, and Investigation Gang Management). At the point that the RFP is awarded, the agency will again meet with the PCC to request certification of the planning of the project and the release of the remainder of the funding for Phase I activities – Project Planning. Data and infrastructure planning and preparation will continue during this timeframe. As part of the FY17 IT Plan, a new business case will be written based on the status of the project and the knowledge known at that time, being prior to an RFP award. An update to the business case to include Offender Management System (OMS) Replacement system selected, vendor, and cost will occur by the end of December, 2015/early January, 2016. Depending upon funding awarded in the legislative session, the agency will request PCC certification and release of funding for Phase I activities – Project Execution and Implementation. Depending on the cost of the system and the amount of future funding, Project Execution and Implementation may be separated out in additional phases. 1.3 PROJECT CERTIFICATION REQUIREMENTS CRITERIA YES/NO EXPLANATION Project is mission critical to the agency Yes The agency’s offender management system is the system for NMCD and holds data for 26,000 offenders that are under the jurisdiction of the state. Project cost is equal to or in excess of $100,000.00 Yes Laws of 2015, Chapter 101, Section 7 (22) Project impacts customer on-line access Yes Rather than connect to the application with a thick client connection that users will connect to the application via an Internet browser. Project is one deemed appropriate by the Secretary of the DoIT Yes The agency appreciates the support shown thus far for this effort and the advice given by the EPMO for improvement as the project moves forward. PAGE 2 PROJECT CHARTER - NMCD OFFENDER MANAGEMENT SYSTEM (OMS) REPLACEMENT Will an IT Architecture Review be required? Yes 3 At the point that an RFP is awarded and a system selected, an architectural review will be needed. 2.0 JUSTIFICATION, OBJECTIVES AND IMPACTS 2.1 AGENCY JUSTIFICATION The purpose of this project is to replace the 15 year old client server offender management system with a new Commercial off the Shelf (COTS) offender management system (OMS) based on new technology and in a web environment. All 17 modules necessary to manage an offender population from intake to community supervision, as specified by the Corrections Technology Association (CTA) will be replaced in the new Offender Management System (OMS) Replacement. NAME DESCRIPTION NMCD The mission of the NMCD is to do the right thing, always. The agency has made a top-level management decision to replace the 15year old client-server application with a new web-based, commercial, off-the-shelf (COTS) application to support the improvement and streamlining of business processes for end-users who manage and supervise inmates and offenders. The agency has set an internal goal to reduce inmate recidivism by 10% over the next three years. 2.2 BUSINESS OBJECTIVES Below are the high level business objectives of the Offender Management System (OMS) Replacement project. NUMBER B-OBJ-1 B-OBJ-2 B-OBJ-3 DESCRIPTION Release inmates timely and accurately. Automate the calculation of inmate good time and institute method of modifying rules surrounding good time based on changing laws. Provide ability for Probation and Parole to link directly with courts to provide pre-sentence, diagnostic, executive clemency and other PAGE 3 PROJECT CHARTER - NMCD OFFENDER MANAGEMENT SYSTEM (OMS) REPLACEMENT NUMBER B-OBJ-4 B-OBJ-5 B-OBJ-6 B-OBJ-7 B-OBJ-8 B-OBJ-9 B-OBJ-10 DESCRIPTION reporting services to the court. Send and receive court sentencing data electronically. Provide system mobility to allow Probation and Parole officers more time in the field supervising offenders. Notify office of the DA and victims of inmate releases via real-time processing rather than batch updates. Track offender program costs and report on program efficacy accurately to enable administrators to make better program choice decisions. Implement industry best practices for segregation and other alternative placement scenarios. Improve cross-jurisdictional data sharing and collaboration with other public safety/justice entities. Improve public safety through enhanced ability to classify, re-classify and provide housing, movement and transportation of inmates. 2.3 TECHNICAL OBJECTIVES Below are the high-level technical objectives of the Offender Management System (OMS) Replacement Project. NUMBER DESCRIPTION T-OBJ-1 Replace / discontinue use of legacy OMS application. T-OBJ-2 Collapse development and maintenance overhead due to multiple, disparate systems. T-OBJ-3 Provide the technical components and platform to allow application mobility. T-OBJ-4 Migrate existing data and data structures from Informix to NIEM and GRA-compliant data format, to ease migration to new Offender Management System (OMS) Replacement. T-OBJ-5 Provide ability for Offender Management System (OMS) Replacement application to be database independent. T-OBJ-6 Ensure that the technical aspects and capabilities of the new OMS application is service-oriented to the business need. T-OBJ-7 Replicate production data to separate environment for the purpose of disaster recovery, reporting, statistical analysis and business PAGE 4 4 PROJECT CHARTER - NMCD OFFENDER MANAGEMENT SYSTEM (OMS) REPLACEMENT NUMBER DESCRIPTION intelligence efforts. T-OBJ-8 Ensure that NMCD IT staff gains sufficient experience and knowledge to implement the Offender Management System (OMS) Replacement application and to maintain after implementation independently. T-OBJ-9 Document the Offender Management System (OMS) Replacement application thoroughly, both from a functional and technical perspective prior to implementation and ensure process for future updates and maintenance of the documentation. T-OBJ-10 Create a virtual server environment for high-availability, increased reliability, redundancy and streamlined administration of the Offender Management System (OMS) Replacement system. 2.4 IMPACT ON ORGANIZATION The high-level organizational impacts appear below. AREA DESCRIPTION END USER The overarching impact for the end user will be improved system functionality, mobility and portability. A strategy will be planned as to ensure seamless access to the system and to offender data at all levels, whether it is a Probation/Parole officer in the home of an offender completing a supervision contact, an Educator providing programming to an inmate, another system needing access to offender data for a multitude of reasons, etc. System and Business Process Training, User Acceptance testing, requirements gathering will all be processes that will affect the end user both during the course of the project as SME project team members and the overall user community at the point the system is fully implemented. BUSINESS PROCESSES All business processes will need to be reviewed as the current system is more than 15 years’ old. Of the seventeen modules in the OMS application, ten of these have recently been reviewed, and in some cases, new applications coded that can be used as a baseline for the new Offender Management System (OMS) Replacement application. During the initiation and planning phases, the remaining modules PAGE 5 5 PROJECT CHARTER - NMCD OFFENDER MANAGEMENT SYSTEM (OMS) REPLACEMENT AREA DESCRIPTION will be updated with requirements based on current business processes. Gap analysis will occur when the Offender Management System (OMS) Replacement solution is selected to ensure that the client configuration layer of the application meets the business need. Potential re-engineering of business processes will be addressed throughout project activities. Business process-reengineering has to be watched closely as it can lead to scope creep. PM will need to monitor this closely, determining what must be done now and what could be enhanced later. IT OPERATIONS AND STAFFING A major goal of the Information Technology Division is to ensure that the staff is intricately involved in the entire process of system configuration and implementation so that the agency can support the system independently post-implementation. The agency’s plan is to backfill production support through contract staffing augmentation. OTHER As a new Offender Management System (OMS) Replacement solution is implemented, the agency has additional opportunities to revisit agency policies and procedures, to ensure the new application supports these policies and procedures, or, where necessary, the policies and procedures are updated due to technological and business process improvements the application provides. This process of revisiting policy and procedure can be an arduous one. The strategy is to begin implementation planning early to ensure that the appropriate amount of time is dedicated to this important process. 2.5 TRANSITION TO OPERATIONS The transition to operations areas include items that are asked in the certification form to assure that the project has accounted or will account for these matters in its planning and requirements specifications. AREA DESCRIPTION PRELIMINARY OPERATIONS LOCATION AND STAFFING PLANS Production applications will be hosted in Santa Fe on existing Fault Tolerant infrastructure. Agency ITD staff will provide ongoing support and will be addressed as the system is implemented. ITD internal staff will work in conjunction with the selected vendor and application to complete the client configuration and installation for the Offender Management System (OMS) Replacement system, and all support and maintenance activities for the legacy Powerbuilder application will utilize contract resources utilizing a staff PAGE 6 6 PROJECT CHARTER - NMCD OFFENDER MANAGEMENT SYSTEM (OMS) REPLACEMENT AREA DESCRIPTION augmentation strategy. The goal of the agency is to need minimal to no contract employee support of the Offender Management System (OMS) Replacement application once deployed to production, other than a standard maintenance and support agreement. DATA SECURITY, BUSINESS CONTINUITY Security The agency security architecture is comprised of a multi-layer security model. The Data Center is located in Santa Fe at DoIT and is physically secure from the public and the agency end users. Santa Fe Central Office is protected from the Internet by redundant Juniper enterprise firewalls. The public prisons are each protected by a single Juniper enterprise firewall. This provides a physical separation from the agency network and the Inmate Education Network. Each Probation and Parole office is securely connected within the Qwest cloud via MPLS and QMOE. This connection allows all offices to securely communicate between each other, Central Office, CNMCF and DoIT datacenters Business Continuity Disaster recovery – In FY07 the NMCD completed the project “Build a Fault Tolerant Environment”. To do this, ITD built a high availability Web farm. The Web farm is load balanced architecture with two Web servers answering requests from clients. These requests are balanced across the Web servers so the load is shared. The redundancy of this fault tolerant design provides Disaster Recovery (DR) at the equipment fail level. In the event NMCD experiences a disaster at the IT Data Center located in the NMCD Central Office, ITD has identified a location that is equipped as a Warm Site. The NMCD network is designed with a remote Active Directory domain controller and a second remote DR domain controller has been configured for the DR site. Therefore additional equipment is not required for a Warm Site to be activated. The agency has identified and tested disaster recovery at various levels. However, when the time comes NMCD would like to join the state efforts and step from a Warm Site Model to a Fail-Over Site PAGE 7 7 PROJECT CHARTER - NMCD OFFENDER MANAGEMENT SYSTEM (OMS) REPLACEMENT AREA DESCRIPTION Model and comply with all the state standards. MAINTENANCE STRATEGY Maintenance is currently part of day to day operations for the existing Powerbuilder. Depending on future funding and project time line for future phases, the agency will have to expand maintenance and support activities to include both the existing environment and the new web environment. During the course of the project, while both Powerbuilder and the Offender Management System (OMS) Replacement are on-line, support costs will increase. As previously stated, from a person resource point of view, the agency will backfill the production support utilizing contract resources. INTEROPERABILITY Requirements exist to maintain the current client server PowerBuilder application throughout the project lifecycle until such time all the new Offender Management System (OMS) Replacement application and all business functionality and modules have been implemented in a production environment. RECORD RETENTION ITD has taken direction from the Title 1 – General Government Administration Retention and disposition schedules in addressing record retention as listed below: Disaster Recovery File Retention: until superseded by new plan or information. A copy of this file will be stored off-site. In the event of a disaster, all copies of this file shall be retained until any or all investigations are concluded. Project Control File Retention: one year after close of fiscal year in which project completed or cancelled. Documentation Tape File Retention: one year after discontinuance of system provided all magnetic data files are authorized for disposal or transferred to new or alternate system. System test documentation for approved systems may be destroyed one year after completion of testing. Test Files Retention: two years after system goes into production. Website PAGE 8 8 PROJECT CHARTER - NMCD OFFENDER MANAGEMENT SYSTEM (OMS) REPLACEMENT AREA DESCRIPTION Retention: • Platform (software): one year after discontinuance of the system. • web content: • unique records or information: see the general or agency program schedule for retention. • replicated information: until superseded or no longer relevant. • web site structure: • informational web site: one year after site is updated or changed. • transactional web site: three years after site is updated or changed. CONSOLIDATION STRATEGY The NMCD has actively participated with DoIT on server and storage consolidation efforts and will continue to work to provide the same level of security and availability for the new Offender Management System (OMS) Replacement application. Continued consolidation effort must consider the mission-critical nature of the agency’s offender management system. It is the agency’s core business application and is unique to Corrections and only used by NMCD in New Mexico. 3.0 PROJECT/PRODUCT SCOPE OF WORK In its efforts to move from the high level business objectives to the desired end product/service the project team will need to deliver specific documents or work products. The State of New Mexico Project Management Methodology distinguishes between the project and the product. Project Deliverables relate to how we conduct the business of the project. Product Deliverables relate to how we define what the end result or product will be, and trace our stakeholder requirements through to product acceptance, and trace our end product features and attributes back to our initial requirements 3.1 DELIVERABLES 3.1.1 PROJECT DELIVERABLES This initial list of project deliverables are those called for by the IT Certification Process and Project Oversight memorandum, but does not exhaust the project deliverable documents PAGE 9 9 PROJECT CHARTER - NMCD OFFENDER MANAGEMENT SYSTEM (OMS) REPLACEMENT 10 Project Charter The Project Charter for Certification sets the overall scope for the project, the governance structure, and when signed is considered permission to proceed with the project. The Project Charter for Certification is used to provide the Project Certification Committee with adequate knowledge of the project and its planning to certify the initiation phase of the project Certification Form The Request for Certification and Release of Funds form is submitted when a project goes for any of the certification phases. It deals with the financial aspects of the project, as well as other topics that indicate the level of planning that has gone into the project. Many of the questions have been incorporated into the preparation of the project charter Project Management Plan “Project management plan” is a formal document approved by the executive sponsor and the Department and developed in the plan phase used to manage project execution, control, and project close. The primary uses of the project plan are to document planning assumptions and decisions, facilitate communication among stakeholders, and documents approved scope, cost and schedule baselines. A project plan includes at least other plans for issue escalation, change control, communications, deliverable review and acceptance, staff acquisition, and risk management plan. IV&V Contract & Reports IT Service Contracts “Independent verification and validation (IV&V)” means the process of evaluating a project to determine compliance with specified requirements and the process of determining whether the products of a given development phase fulfill the requirements established during the previous stage, both of which are performed by an organization independent of the lead agency. Independent verification and validation assessment reporting. The Department requires all projects subject to oversight to engage an independent verification and validation contractor unless waived by the Department. The Department of Information Technology and the State Purchasing Division of General Services have established a template for all IT related contracts. PAGE 10 PROJECT CHARTER - NMCD OFFENDER MANAGEMENT SYSTEM (OMS) REPLACEMENT Risk Assessment and management 11 The DoIT Initial PROJECT RISK ASSESSMENT template which is meant to fulfill the following requirement: “Prepare a written risk assessment report at the inception of a project and at end of each product development lifecycle phase or more frequently for large high-risk projects. Each risk assessment shall be included as a project activity in project schedule.” Project Oversight Process memorandum Project Schedule A tool used to indicate the planned dates, dependencies, and assigned resources for performing activities and for meeting milestones. The defacto standard is Microsoft Project Monthly Project Status Reports to DoIT Project status reports. For all projects that require Department oversight, the lead agency project manager shall submit an agency approved project status report on a monthly basis to the Department. Project Closeout Report This is the Template used to request that the project be officially closed. Note that project closure is the last phase of the certification process 3.1.2 PRODUCT DELIVERABLES The product deliverable documents listed here are only used for illustration purposes Requirements Documents The remaining modules that do not have updated requirements documents will be completed in Phase I – Planning: Classification, Discipline/Grievance, Caseload Management, Security, Housing/Bed Management, Visitation, Inmate Trust Accounting, and Investigation Gang Management. These will thoroughly outlined as part of the RFP. PAGE 11 PROJECT CHARTER - NMCD OFFENDER MANAGEMENT SYSTEM (OMS) REPLACEMENT 12 Design Documents As the application will be a commercial, off-the shelf product, full design documents will not be required. To the extent that system modifications will be required to support the business for our particular agency and state, these will be documented as part of a gap analysis, along with business requirements, system specifications and client configuration needs. Although these will be partially outlined as part of the RFP, the specific client configuration needs and gap analysis will not be completely known until after the RFP is awarded and the Offender Management System (OMS) Replacement application selected. Systems Specifications The IT department typically combine requirements and technical system specifications in one document. Therefore, these topics will be included as part of the requirements/specifications. Data and Infrastructure / Architecture As part of the data planning process, the goal is to replicate existing data and data structures from Informix to a NIEM and GRA-compliant data format, to ease migration to new Offender Management System (OMS) Replacement. The replication of production data to a separate environment is for the purpose of disaster recovery, reporting, statistical analysis and business intelligence efforts and is independent of what Offender Management System (OMS) Replacement application is selected. As part of the infrastructure planning process, documentation will be created to outline the requirements and layout of the infrastructure required to host and support the application. A virtual environment is envisioned to provide for high-availability, increased reliability, redundancy and streamlined administration of the Offender Management System (OMS) Replacement. Data and infrastructure planning and preparation will be completed during Phase I – Initiation and Planning portion of the project. PAGE 12 PROJECT CHARTER - NMCD OFFENDER MANAGEMENT SYSTEM (OMS) REPLACEMENT System and Acceptance Testing 13 Module testing. A formal document and process will be executed to ensure industry standard testing methodologies are planned and all functional and business process requirements are thoroughly tested prior to acceptance and production go live activities. All system and acceptance testing efforts and documentation will occur in Phase II and any subsequent phases, after the RFP is conducted, awarded and the Offender Management System (OMS) Replacement application selected. Software Implementation Plan Formal plans will be executed throughout the implementation process. Prior to go live activities a formal software implementation plan will be developed which will define implementation activities and provide quality measures for assessment of project. The implementation plan will be written in Phase II after the RFP is conducted, awarded and the Offender Management System (OMS) Replacement application selected. 3.2 SUCCESS AND QUALITY METRICS Below are the initial success and quality metrics of the Offender Management System (OMS) Replacement project. NUMBER DESCRIPTION QM-1 Monthly cost variance report delivered to Executive Steering Committee and IT Management on last day of each project month. QM-2 Monthly schedule variance report delivered to Executive Steering Committee and IT Management on last day of each project month. QM-3 Monthly earned value reports delivered to Executive Steering Committee and IT Management on the last day of each project month. QM-4 Bi-annual customer experience survey distributed to all project and business team members and business owners. QM-5 Quarterly estimate to completion report delivered to Executive Steering Committee and IT Management on the last day of each project quarter. PAGE 13 PROJECT CHARTER - NMCD OFFENDER MANAGEMENT SYSTEM (OMS) REPLACEMENT 14 4.0 SCHEDULE ESTIMATE Below is the estimated schedule for Phase I – Project Initiation and Planning. NMCD COTS OMS Project – Phase I 4/23/2015 - 4/23/2015 PCC Initiation Tollgate 6/30/2016 - 6/30/2016 TARC Review 9/1/2015 - 12/31/2015 RFP COTS OMS 4/24/2015 - 5/31/2015 Recruit Contract PM 1/1/2016 - 4/30/2016 Infrastructure Planning IV&V 7/1/2015 10/1/2015 4/22/2015 6/1/2015 - 12/31/2015 Project Planning 4/24/2015 - 8/31/2015 RFI System Alternatives 1/1/2016 4/1/2016 6/30/2016 11/2/2015 - 4/30/2016 Data Planning 4/1/2016 - 6/30/2016 Phase II Prep and Kickoff 1/28/2016 - 1/29/2016 PCC Planning Tollgate 5.0 BUDGET ESTIMATE At the point that an RFI and RFP are conducted/awarded for the procurement of the Offender Management System (OMS) Replacement application a full project budget can be estimated. At this point, only initiation and planning phase are estimated. 5.1 FUNDING SOURCE(S) SOURCE AMOUNT ASSOCIATED RESTRICTIONS Laws of 2015, Chapter 101, Section 7 (22) $500,000.00 Completion of an RFI, RFP, Project Management Plan and high-level project schedule and budget. PAGE 14 PROJECT CHARTER - NMCD OFFENDER MANAGEMENT SYSTEM (OMS) REPLACEMENT 5.2. BUDGET BY MAJOR DELIVERABLE OR TYPE OF EXPENSE IT E M COST ESTIMATE Contract PM $50,000 Phase I - Initiation RFI Activities $25,000 Phase I - Initiation Writing/Management of RFP $50,000 Phase I - Initiation Project Planning – PMP, project schedule, budget $25,000 Phase I – Initiation and Planning Data Planning $25,000 Phase I – Initiation and Planning Infrastructure Planning $25,000 Phase I – Initiation and Planning Requirements Analysis and Documentation $50,000 Phase I – Initiation and Planning Contract Resources – Data and Infrastructure $50,000 Phase I - Planning To be requested as part of project planning certification Data Replication / Migration $100,000 Phase I – Planning To be requested as part of project planning certification Infrastructure Preparation $100,000 Phase I – Planning To be requested as part of project planning certification 5.3 BUDGET BY PROJECT PHASE OR CERTIFICATION PHASE IT E M COST ESTIMATE Project Initiation (Phase I) $250,000 Project Planning $250,000 PAGE 15 15 PROJECT CHARTER - NMCD OFFENDER MANAGEMENT SYSTEM (OMS) REPLACEMENT IT E M (Phase I) COST ESTIMATE Project Execution / Implementation (Phase II – x) TBD 16 6.0 PROJECT AUTHORITY AND ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE 6.1 STAKEHOLDERS Below are the major stakeholders/types of stakeholders for the OFFENDER MANAGEMENT SYSTEM (OMS) REPLACEMENT project. NAME STAKE IN PROJECT ORGANIZATION T IT L E Gregg Marcantel Executive Leadership NMCD Secretary of Corrections Joe Booker Executive Leadership NMCD Deputy Secretary, Operations Mark Myers Executive Leadership NMCD Acting Deputy Secretary, Administration Jerry Roark Business Division Leadership NMCD Director, Adult Prisons Rose Bobchak Business Division Leadership NMCD Acting Director, Probation and Parole Timothy Oakeley Information Technology NMCD Chief Information Officer Cathy Catanach Business NMCD Bureau Chief, Offender Management Services Victoria Lounello Business NMCD Region Manager, Probation and Parole PAGE 16 PROJECT CHARTER - NMCD OFFENDER MANAGEMENT SYSTEM (OMS) REPLACEMENT NAME STAKE IN PROJECT ORGANIZATION T IT L E Francine Garcia Business NMCD Victim Services Administrator Micaela Cadena Business NMCD Recidivism Reduction Bureau Chief Tony Ortiz Statistical Analysis of NMCD data Contractor for analysis for prison population projections and myriad other data projects. New Mexico Sentencing Commission (NMSC) Director 17 6.2 PROJECT GOVERNANCE PLAN Oversight of this project will occur through the following channels: 1 2 3 4 Executive Steering Committee – Overall project guidance and direction. Change Review Board – all change requests over $10,000 will be voted upon by committee. Major shift in scope or schedule also will be voted upon. Project Certification Committee – Release of legislative funds for major project lifecycle phases via certification tollgates. Independent Verification and Validation (IVV) – 3rd party vendor will be hired to conduct audits, suggest best practice, and document necessary corrective action throughout course of project. Department of Information Technology (DoIT) Enterprise Project Management Office (EPMO) – Provide IT Management Lifecycle policies, methodologies and templates for information technology (IT) initiatives to promote quality and success and report regularly to Executive, Legislative, and ITC on the status of the State's IT Project Portfolio; Provide support, guidance and oversight of the project to promote improved outcomes; receives monthly project status report. A graphical representation for project governance appears below. PAGE 17 PROJECT CHARTER - NMCD OFFENDER MANAGEMENT SYSTEM (OMS) REPLACEMENT 18 Gregg Marcantel Project Sponsor Executive Steering Committee Contract Project Manager IVV Vendor IT Leadership Timothy Oakeley, CIO Jerry Brinegar, Deputy CIO/PMO Manager Pamela Smyth Business Analysis Manager Bu siness An alyst Bu siness An alyst Deepa Makkar, Applications Manager State Project Manager Lilly Martin, Infrastructure Manager Vendor Project Manager IT Architect Vendor Systems Architect Systems Manager Vendor Database Architect Applications Developer Database Administrator Vendor Developer Vendor Busines s Analyst Not every position is listed at this time; rather, the major roles are defined. After the vacant positions are filled or contracted (indicated by the circles without people), and the RFP is negotiated and awarded, this project organization chart will be further elaborated and refined. Also, as this is a phased approach, the organization for Phase I – Initiation and Planning may be different than that for Phase II - Project Execution and Implementation. 6.3 PROJECT MANAGER 6.3.1 PROJECT MANAGER CONTACT INFORMATION NAME ORGANIZATION PHONE #(S) EMAIL Jerry Brinegar, PMP NMCD (505) 827-8605 jerry.brinegar@state.nm.us Contractor PM (TBD) TBD State PM (TBD) NMCD – Currently PAGE 18 PROJECT CHARTER - NMCD OFFENDER MANAGEMENT SYSTEM (OMS) REPLACEMENT NAME ORGANIZATION in the recruiting process. Vendor PM (TBD) TBD - Dependent upon RFP award PHONE #(S) 19 EMAIL 6.3.2 PROJECT MANAGER BACKGROUND Mr. Brinegar has been a certified project manager since 2009, holding certifications of Certified Associate of Project Management (CAPM #1235663 from 2009 through 2014) and Project Management Professional (PMP #1269268 from 2009 to current and certification extended through 2018). He holds degrees in Operations Management and Computer Programming and has more than 25 years’ experience in Information Technology and Project Management. Prior to his current role as Deputy Chief Information Officer, he was the Business/Research Analysis Manager for 3 years, and a Project Manager for 3 years prior to that for NMCD. He has a good grasp of the business of NMCD, as well as the technology and project management methodology. As other project managers are hired for this project effort, Mr. Brinegar will continue to provide direction and guidance to the other project managers and the overall project team. 6.4 PROJECT TEAM ROLES AND RESPONSIBILITIES ROLE RESPONSIBILITY Project Sponsor Provide top-level guidance and direction. Ensure that project resources are available to the project. Lead Project Manager/PMO Manager Provide direction and management of project management staff; ensure that necessary processes are in place and being followed per agency policy and PMO procedures. Ensures that project timelines, resources, installations, etc., are managed appropriately across all active projects. Oversees the RFP process. State Project Manager Once the RFP process is complete and the vendor selected, handles contract and vendor management. Manages the day-today project activities of project staff. Provides status reporting to executive structure and works with IVV vendor for auditing purposes. Manages the project scope, schedule and budget. Vendor Project Manager Manages the writing of the RFP and RFP process, completes project planning documentation and tasks. Once RFP is awarded, manages the vendor contract staff. Provides weekly status reports to State Project Manager. PAGE 19 PROJECT CHARTER - NMCD OFFENDER MANAGEMENT SYSTEM (OMS) REPLACEMENT ROLE Business Analyst Business Analysis Manager Application Developer Database Administrator Applications Manager Infrastructure System Architect Infrastructure Manager Subject Matter Expert 20 RESPONSIBILITY Ensures that the customer requirements are translated into specifications that developers will use to code the system. Tests all code and is responsible for identifying and documenting code issues. Assists in training end users. Lead for ensuring that all requirements are appropriately documented and meet business need. Manage the day-to-day tasks of the Business Analysts. Responsible for coding system functionality based on specifications provided by Business Analysts. Ensures that the back-end database structure exists and that needed tables and columns are created to appropriately store data necessary in the system. Lead for ensuring that the system provides the necessary functionality based on identified requirements and specifications. Manage the day-to-day tasks of Applications Developer and Database Administrator. Ensure that all infrastructure necessary for the application exists, servers, backups, etc. Ensures that all application infrastructure, networking, etc. are in place to support the application needs of the end-users. Manage the day-to-day activities of the Infrastructure Systems Architect. Provide guidance on what specific rules should be in place in order to meet business goals. Assist in testing, identifying issues, and training. Executive Steering Committee Member Provide necessary high-level input and sets high level project priorities. Votes on change request and scope shifts as necessary. IVV Vendor Provides independent validation and verification of project activities at regular intervals throughout the project life cycle. Submits reports outlining status to project sponsor, NMCD lead project manager and IT leadership, and the Department of Information Technology (DoIT) Enterprise Project Management Office (EPMO). 6.5 PROJECT MANAGEMENT METHODOLOGY The project will consist of a mixed organization structure, as there will be lines of authority both from the project management/PMO and from functional managers for project PAGE 20 PROJECT CHARTER - NMCD OFFENDER MANAGEMENT SYSTEM (OMS) REPLACEMENT 21 participants. Depending on the level of the project manager, functional managers may be at peer level or management level. Lead Project Manager/PMO Manager will be the line of authority over both project and functional managers assigned to the project. Where possible, the project will utilize an Agile approach to define requirements, configure and test smaller, more manageable components to the COTS system, while the certification, funding release, and overall timeline of the project will follow a traditional waterfall method. Three major roles will exist in this project: Leader - provides leadership and guidance to the team and takes responsibility for the results of teamwork. This consists of the following roles: o o o o Member - involved in doing assigned tasks. Team members directly access the project and actively evolve its processes. This includes the following roles: o o o o o o o o Project Sponsor Lead Project Manager/PMO Manager State Project Manager Vendor Project Manager Business Analyst Business Analysis Manager Developer Data Architect Applications Manager Infrastructure/Systems Architect Infrastructure Manager Subject Matter Expert Contributor - participates in teamwork but is not actually involved in performing tasks and carrying out project team responsibilities. This will include: o o o Executive Steering Committee members Other Subject Matter Experts IVV Auditor 7.0 CONSTRAINTS NUMBER DESCRIPTION C-001 Full future funding to procure a OFFENDER MANAGEMENT SYSTEM PAGE 21 PROJECT CHARTER - NMCD OFFENDER MANAGEMENT SYSTEM (OMS) REPLACEMENT 22 NUMBER DESCRIPTION (OMS) REPLACEMENT application. C-002 Full project team staffing, by filling internal vacancies where possible and utilizing staff augmentation to implement an Offender Management System (OMS) Replacement application. C-003 The new offender management system must be a commercial-off-the-shelf system, not an internally developed or inherited system. 8.0 DEPENDENCIES Below are the project dependencies associated with Phase I – Project Initiation and Planning and to move the project forward to Phase II – Project Execution and Implementation. Mandatory dependencies are dependencies that are inherent to the work being done. D- Discretionary dependencies are dependencies defined by the project management team. This may also encompass particular approaches because a specific sequence of activities is preferred, but not mandatory in the project life cycle. E-External dependencies are dependencies that involve a relationship between project activities and nonproject activities such as purchasing/procurement NUMBER DESCRIPTION TYPE M,D,E DEP-001 Successful certification by PCC to initiate the project. E DEP-002 Ability to successfully contract project management resources to complete Phase I – Initiation and Planning activities and documentation. M DEP-003 Successful completion of RFI activities so that project may progress into the RFP process. D DEP-004 Successful completion and award of RFP so that the project may progress into the phases of project execution and implementation. M DEP-005 Successful certification by PCC to move the project into the planning phase. E DEP-006 Future legislative funding to procure a Offender Management System (OMS) Replacement application and complete future phases of project execution and implementation. E PAGE 22 PROJECT CHARTER - NMCD OFFENDER MANAGEMENT SYSTEM (OMS) REPLACEMENT 9.0 ASSUMPTIONS NUMBER DESCRIPTION A-001 That a State IT Project Manager can be successfully hired in a timely fashion at the agency to handle the day-to-day operations of the project and to interface with the contract project manager and other contracted resources. A-002 That contract resources can be successfully obtained in a timely fashion to meet the dependencies outlined above to meet the requirements of the initiation and planning phase. A-003 That all requirements contingent on legislative funding will be successfully completed and communicated appropriately. A-004 That future funding will be awarded to ensure the forward momentum of the project. 10.0 SIGNIFICANT RISKS AND MITIGATION STRATEGY Below are the initial significant risks for both the project and the agency if the project is not successfully funded and completed. INABILITY TO CONTINUE FUTURE MODIFICATION OF THE POWERBUILDER SOURCE CODE Probability - Certain Impact - Very High Description - The only operating system that the source code of the legacy system may be modified on is Windows XP. Since this operating system is no longer supported by Microsoft, with no future security patches or fixes, the agency faces the inability to modify the source code in any way at some point in the future, and complete stagnation to meet future changing laws and internal agency policy and procedure adjustments. Mitigation Strategy – This risk cannot be fully or adequately mitigated in a status-quo scenario. Contingency Plan - The IT department is keeping multiple XP machines on the shelf to continue the ability to modify the PowerBuilder source code as a temporary measure. PAGE 23 23 PROJECT CHARTER - NMCD OFFENDER MANAGEMENT SYSTEM (OMS) REPLACEMENT INABILITY TO PROVIDE ADEQUATE PUBLIC SAFETY Probability - Expected Description - The ability to correctly project an inmate’s release date is a toplevel agency goal in ensuring public safety. If an inmate is released early, additional time and resources are necessary to apprehend and re-incarcerate the inmate, and additional crimes could be committed while the inmate is out. If an inmate is released late, the NMCD spends unnecessarily on incarceration. The inmate has a legal right to be released as specified by both the calculated sentence and the good time applied while incarcerated. 24 Impact - Very High Mitigation Strategy – Providing the Offender Management System (OMS) Replacement project with the necessary resources mitigates this risk. Contingency Plan - The agency will continue to project inmate release date through manual calculations. Although tedious, the centralization of records functions in the Offender Management Services group at the Plaza Maya building in Albuquerque lessens the risk of improper release. NO OR INADEQUATE MANAGEMENT COMMITMENT AND SUPPORT Description - Management commitment of time and resources is key to successful implementation effort. In previous development cycles, IT has requested that subject matter experts be assigned to the project to ensure that the business requirements and rules, testing, training and implementation is successful. This approach has been only partly successful, as those assigned to the project also had their normal daily responsibilities. Probability - Unlikely Impact - Very High Mitigation Strategy – The agency plans to backfill positions utilizing a contract staffing augmentation strategy to support the legacy system so that permanent resources, both technical and subject matter experts will be committed to successfully complete the project. Contingency Plan - Extend project timeline IMPROPER MANAGEMENT OF OFFENDER FROM INCARCERATION THROUGH COMMUNITY SUPERVISION Description - If the offender is not provided the correct mix of programming and services that address their specific criminogenic needs, the likelihood of recidivism increases. The 15-year old client-server system does not have the Probability - Expected Impact - High Mitigation Strategy – Providing an entire Offender Management System (OMS) Replacement solution based on both new technology and business requirements that quantifies and tracks program success helps the agency ensure that the inmate’s transition back to society has a higher likelihood of success. PAGE 24 PROJECT CHARTER - NMCD OFFENDER MANAGEMENT SYSTEM (OMS) REPLACEMENT capabilities to support the shift to evidence-based programming. 25 Contingency Plan - Agency will continue to provide offender programming based on the knowledge, feelings and intuition of the officers. While not empirically quantified, this experience still provides many positive outcomes for offenders and recidivism. PROJECT FUNDING UNCERTAINTIES Probability - Possible Description - Fully funding this project is a critical success factor. Piece meal funding has created an environment where business functionality exists in multiple disparate systems. The IT staff has had to both support existing systems while trying to move new systems forward. This has had a negative impact on the success of the project and the agency overall, that expects results now. Impact - Very High Mitigation Strategy - Purchasing a Offender Management System (OMS) Replacement that has the majority of the application predeveloped and requiring only client configuration allows all modules to be more rapidly implemented. Contingency Plan - Continue internal development at the slow pace that it is currently going. Expected completion without funding with current staff is 2024. ORGANIZATIONAL READINESS Probability - Unlikely Description - The previous approach that NMCD took was a development approach. This approach has taken the modules through development and testing, but not through implementation. Since this is a change to an implementation approach, the agency needs to ensure that processes and people are in place that will be able to appropriately use the increased functionality provided by the new system. Statewide training, review and modification of necessary policies and possible redefinition of current job responsibilities and tasks are objectives that must be accomplished during this period. Impact - Very High Mitigation Strategy - The project timeline mitigates this risk by creating a lengthy implementation period early on to both adequately plan and accomplish the transition to production operations. The agency is ready for these changes and has support at all levels of management. Contingency Plan – Although the current administration is very supportive of this effort, this priority could change in future administrations if this project extends that far in the future. Rapid implementation of the project is the best contingency for this possibility. CHANGES IN STATE OR FEDERAL LAWS Description - Probability - Likely PAGE 25 Impact - Very High PROJECT CHARTER - NMCD OFFENDER MANAGEMENT SYSTEM (OMS) REPLACEMENT Since the Agency is operating in multiple system environments, any changes in state or federal laws create the potential for duplication of work. The organization of the current system does not lend itself well to changes. 26 Mitigation Strategy – One high-level goal of a Offender Management System (OMS) Replacement solution is to provide a client configuration layer that allows for the definition, creation and deprecation of rules, based on current law, such as the Earned Meritorious Deduction laws that have changed over time. Contingency Plan - If modification of current code set still possible, then these changes could be programmatically handled. If not, much manual intervention and business processing would have to be enacted. 11.0 COMMUNICATION PLAN FOR EXECUTIVE REPORTING Effective communication to all relevant project team stakeholders is extremely important in mitigating issues and realizing the project’s ultimate goal. Issues will be reported to the Project Manager and documented. In the event the issue requires escalation the Project Manager will escalate the issue to the appropriate level including the Lead Project Manager, Project Sponsor and/or the Executive Steering Committee (ESC). The Executive Steering Committee currently meets each month to prioritize IT efforts over a number of projects. The project manager for the Offender Management System (OMS) Replacement project will report to the ESC on all project status items and will convey any issues that require Executive level attention. As previously stated, all major scope and schedule changes will be voted on by the Change Review Board, which consists of ESC members, IT management and certain Business Owners. All changes in budget over $10,000 will also be voted upon by the CRB. Quality metrics will be calculated and communicated as previously outlined. Monthly reporting to the DoIT EPMO and NMCD IT management will occur. The approach to communication and a more formal communication plan will be further elaborated as part of the overall project management plan. 12.0 INDEPENDENT VERIFICATION AND VALIDATION - IV&V Below are the project and product areas identified and required for Phase I – Initiation and Planning activities. Some of the items that are listed as a ‘No’ cannot be reviewed until the RFP is conducted, awarded and the system is selected. As such, those listed as ‘No’ for Phase I would be included as part of a later phase and dependent upon future funding. PAGE 26 PROJECT CHARTER - NMCD OFFENDER MANAGEMENT SYSTEM (OMS) REPLACEMENT Project/Product Area Include –Yes/No Project Management Phase I - Yes Quality Management Phase I - Yes Training Phase I - No Requirements Management Phase I - Yes Operating Environment Phase I - No Development Environment Phase I - No Software Development Phase I - No System and Acceptance Testing Phase I - No Data Management Phase I - Yes Operations Oversight Phase I - No Business Process Impact Phase I - Yes 13.0 PROJECT CHARTER AGENCY APPROVAL SIGNATURES SIGNATURE EXECUTIVE SPONSOR BUSINESS OWNER AGENCY CIO/IT LEAD PROJECT MANAGER PAGE 27 DATE 27 PROJECT CHARTER - NMCD OFFENDER MANAGEMENT SYSTEM (OMS) REPLACEMENT 28 14.0 PROJECT CHARTER CERTIFICATION APPROVAL SIGNATURE SIGNATURE DOIT / PCC APPROVAL PAGE 28 DATE