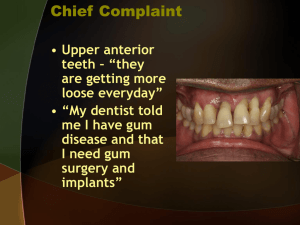
Periodont.diseases
advertisement

The name of the module: 1 Periodontal diseases. Etioology, pathogenesis. Classifications. Clinic, diagnostic, treatment and privention. Test tasks: 1. Osteolizys this: A. Pathological process, accompanied by a decrease in bone trabeculae per unit volume B. Pathological process, accompanied by functional and structural changes ZSCHS C. Pathological process, accompanied by an increase in bone trabeculae per unit volume D. * Pathological process, accompanied by complete resorption of the bone without any manifestations of its replacement E. There is no right answer 2. Objective simple hinhivektomiyi? A. Correction of defects of the alveolar process of the jaws B. * Elimination of periodontal pocket C. Conducting vacuum curettage D. Holding open curettage E. Eliminate bone pocket 3. Disadvantages hinhivektomiyi operations are: A. hyperesthesia bare roots to thermal stimuli B. cosmetic defect after removal of gingival papillae C. necks baring teeth D. hyperesthesia bare roots to chemical stimuli E. * All of the above is true 4. Hinhivotomiya - is: A. Removing ash to a depth of periodontal pockets B. * Autopsy gum C. Open curettage D. Stool periodontal abscess E. Disclosure of a single deep periodontal pockets 5. Determination of traumatic occlusion carried out using: A. Iodine solution B. Magenta C. * Wax plates D. Desmodometra E. Ehoosteometra 6. In what year was clinically proven ability periodontal relationships grow into the space between the membrane and the surface of the root A. 1,982 B. 1,981 C. 1,985 D. * 1984 E. 1,990 7. Indications for use of the method of selective pryshlifovuvannya teeth: A. Detection of premature tooth contacts in the central occlusion B. Installing premature contacts and the presence of contacts only some teeth when closing the jaws in any of the 4 occlusions C. Lack of contact between groups of teeth-antagonists D. Establishing contacts with premature closing of the jaws in the lateral and central occlusion. E. * All of the above is true 8. Removing tartar pid'yasennoho conduct: A. By curettage of periodontal pockets B. * During curettage of periodontal pockets C. After the curettage pockets D. A week before curettage E. There is no right answer 9. Kalamkari recommended to detect and eliminate premature contacts in position: A. Only the central occlusion B. Central and distal C. Distal and anterior D. Central and anterior E. * In all three positions occlusion 10. Curettage procedure recommended not more than: A. 4 times a year B. 5 times a year C. * 2 times a year D. 3 times a year E. 1 every year 11. What limited number of teeth operation hinhivektomiyi in the side area? A. * 3.2 B. 4.6 C. 6.8 D. 2.1 E. 4.3 12. The advantages of vacuum curettage is: A. opportunity to process deeper pockets B. opportunity to process bottom gingival pocket and adjacent bone C. visual inspection complete curettage D. relatively bloodless operative field E. * All of the above is true 13. What are the basic principles of sampling with grinding teeth? A. Zishlifovuvannya tissues within the thickness of the enamel layer, narrowing the chewing surfaces, while providing expressiveness equator; B. Zishlifovuvannya hard tissue on the occlusal surface is not made in the teeth, which are the backbone that hold interalveolar distance C. Teeth - antagonists in central occlusion should keep multiple buhorkovi - fisurnyy contact. D. Consider the position of teeth not only in the central occlusion E. * All answers are correct 14. The literature curettage operation is called: A. Real Viydmana-Neumann B. Real-Viydmana Tseshynskoho C. Real Tseshynskoho-Neumann D. * Method Jünger-registrar E. Real Znamenskoye 15. Local therapy of periodontal disease include: A. Training (control) patients the right care for your teeth. B. Eliminating local irritating factors. C. Treatment of systemic hyperesthesia, increased abrasion of hard tooth tissues. D. Local application means that improve the trophic and microcirculation. E. * All answers are correct 16. Indications for the kriokyuretazhu are: A. Periodontal pocket depth of 5-7 mm B. Hypertrophic gingivitis C. Severe gum hypertrophy in periodontitis D. Periodontal pockets with significant granulation E. * All of the above is true 17. Over time passes epithelization operated sites at diathermocoagulation? A. 7 days B. 21 days C. * For 10 - 14 days D. Over 20 days E. 30 days 18. Which of the following is the manipulation stages patchwork operation? A. vidseparuvannya muco-oxide flap of vestibular and language (palate) sides B. cutting edge modified gums, granulation, and curettage C. mobilization of mucous-oxide graft, stop bleeding D. suture in each interdental spaces and vertical sections E. * All of the above is true 19. What requirements must comply with barrier membrane? A. have tissue integration B. be impermeable to cells C. maintain prolonged action to regenerate new tissue D. inflammatory reaction that accompanies biorezorbtsiyu these membranes should be minimal and reversible E. * All of the above is true 20. With deep pockets of more than 5 mm is advisable to: A. * Loskutnu operation B. Vacuum curettage C. Closed curettage D. Open curettage E. Kriokyuretazh 21. Osteodystrophy is: A. Pathological process, accompanied by a decrease in bone trabeculae per unit volume B. * Pathological process, accompanied by functional and structural changes ZSCHS C. Pathological process, accompanied by an increase in bone trabeculae per unit volume D. Pathological process, accompanied by complete resorption of the bone without any manifestation of its replacement E. There is no right answer 22. Objective scrappy operations periodontium: A. Eliminate inflammation and inhibition of degeneration of periodontal tissue B. * Elimination of periodontal pockets and correction of defects in alveolar bone C. Eliminate bone pockets and stimulation of trophic disorders D. All answers are correct E. There is no right answer 23. The degree of traumatic occlusion is defined by: A. Odontoparodontohramy B. Panoramic x-rays C. * Oklyuzohramy D. Elektrorenthenohramy E. Telerenthenohrafiyi 24. Temporary splinting is done to: A. Stabilization of mobile teeth before the permanent prosthesis B. * Immobilization mobile teeth during therapeutic and surgical treatment C. Creating conditions gingival fixing bandages for highly mobile and lonely standing teeth D. Destabilization of moving teeth before surgery. E. There is no right answer 25. What drug is held neutralization hlornovatystokysloho sodium in periodontal pockets? A. 5% solution of acetic acid B. 5% solution of phosphoric acid C. * 5% citric acid solution D. 5% solution of hydrochloric acid E. 5% solution of nitric acid 26. In one class of premature contacts on Jankelson include: A. * Premature contacts on the vestibular surfaces of the buccal hillocks lower lateral vestibular surface of the teeth and lower front teeth. B. Contacts on oral surfaces hillocks upper palatal lateral teeth. C. Premature contacts on the vestibular surfaces of palatal tubercles upper lateral teeth. D. Premature contacts on the cutting edge E. All answers are correct 27. Jankelson recommended to detect and eliminate premature contacts in position: A. * Only the central occlusion B. Central and distal C. Distal and anterior D. Central and anterior E. In all three positions occlusion 28. With deep pockets to 4 mm is advisable to: A. Loskutnu operation B. Loskutnu operation using osteoplastychnyhyaterialiv C. * Closed curettage D. Open curettage E. By directing tissue regeneration 29. What incisions performed at flap operation? A. Continuous hirlyandopodibnyy cut B. Oblique incision interdental papillae C. Two vertical incisions in the direction of the transition folds on top of interdental papillae D. * Two vertical incisions in the direction of the transition folds passing interdental papillae E. There is no right answer 30. Interval between curettage various groups of teeth is: A. 1-2 days B. * 2-3 days C. 3-4 days D. 5-6 days E. 10 days 31. In the course of local therapy in the treatment of periodontal disease systemic hyperesthesia use: A. * Electrophoresis 2% solution of sodium fluoride B. Electrophoresis solution vitamin D C. Electrophoresis Tren tal D. Electrophoresis AESCUSAN E. Electrophoresis maraslavinu 32. When performing open curettage conduct: A. oblique incision interdental papillae to the bottom pocket only vestibular side B. oblique incision interdental papillae to the bottom pocket only Oral C. * Oblique incision interdental papillae to the bottom pockets on both sides D. hirlyandopodibnyy cut gums E. vertical incision papillae of Oral 33. Who is the world's first operation applied curettage? A. Junger B. Registrar C. Znamensky D. * Rigg E. Tseshynskyy 34. Who first proposed the use of chemical curettage surgery? A. Junger B. Registrar C. * Kenny D. Rigg E. Tseshynskyy 35. What made treatment of hard tissues of teeth with kriokyuretazhi to prevent their damage? A. Eugenol B. Sea buckthorn oil C. Vitamin E D. * Vaseline E. Metrogyl-Dent 36. Time coagulation in the treatment of periodontal pockets is: A. 1-2 sec. B. 30 seconds. C. * 02.04 sec. D. 5-10 seconds. E. 20-40 sec. 37. Orthodontic treatment of periodontal disease is aimed at solving specific problems, namely: A. * Removal of traumatic occlusion B. eliminate abnormal motion C. prevent displacement of teeth D. combining into a single unit all teeth E. all of the above is true 38. Because of time spend removing nerozsmoktuyuchyh membranes? A. After 2 weeks B. After 3 weeks C. After 5 weeks D. After 6 weeks E. * 3 months 39. Your tactics in the first 24-48 hours after an kriokyuretazhu periodontal pockets: A. Assign spray with halaskorbinom 6-8 times a day B. Hold intensive processing antiseptic C. Circulation insulating periodontal bandage D. * Apply enzymes and antibiotics E. There is no right answer 40. In a simple operation carried hinhivektomiyi excision of gum at a certain depth of periodontal pockets, namely: A. At ½ pocket depth B. At 1/3 the depth of the pocket C. At 2/3 the depth of the pocket D. * At the depth of the pocket E. There is no right answer 41. The basic principles curettage are: A. complete anesthesia operated tissues; B. careful attitude to the tissues in the area of manipulation: C. organization of blood clot and his defense: D. perfect compliance with the rules of hygiene in the postoperative period. E. * All answers are correct 42. In the treatment of periodontal disease carried hyperbaric oxygenation. This method involves: A. * Introduction submucous transitional folds 5 ml of oxygen B. Introduction submucous transitional folds 10 ml of oxygen C. Introduction submucous transitional folds trypsin D. Introduction submucous transitional folds prodektynu E. Introduction submucous transitional folds mevakoru 43. Over time passes epithelization operated sites at kriokyuretazhi? A. 7 days B. 21 days C. * For 14 days D. 10 days E. 30 days 44. The goal of periodontal surgery: A. Anti-inflammatory and desensitizing effect B. Removal of foci intoxication C. * Elimination of periodontal pockets and creating conditions for the stabilization process in the periodontal tissues D. Creating the conditions for the regeneration of alveolar bone. E. There is no right answer 45. In Class 2 premature contacts on Jankelson include: A. Premature contacts on the vestibular surfaces of buccal hillocks lower lateral vestibular surface of the teeth and lower front teeth. B. * Contacts on oral surfaces hillocks upper palatal lateral teeth C. Premature contacts on the vestibular surfaces of palatal tubercles upper lateral teeth. D. Premature contacts on the cutting edge E. All answers are correct 46. Osteosclerosis is: A. Pathological process, accompanied by a decrease in bone trabeculae per unit volume B. Pathological process, accompanied by functional and structural changes ZSCHS C. * Pathological process, accompanied by an increase in bone trabeculae per unit volume D. Pathological process, accompanied by complete resorption of the bone without any manifestation of its replacement E. There is no right answer 47. In the presence of abnormal mobility of teeth to create a calm periodontal tissues using: A. Closed curettage B. Selective pryshlifuvannya C. Suction curettage D. Loskutnu operation E. * Temporary splinting 48. Which of the following is the manipulation stages curettage? A. processing operating margins yodvmisnymy solutions B. remove tartar and tooth damaged cement C. deepithelization pocket D. curettage of bone edge alveoli E. * All answers are correct 49. What limited number of teeth operation hinhivektomiyi in frontal area? A. 2.3 B. * 4.6 C. 6.8 D. 2.1 E. 4.3 50. In what year was the first held scraping content periodontal pockets? A. 1,892 B. 1,902 C. 1,909 D. * 1867 E. 1,899 51. In what year was the first operation conducted chemical curettage? A. * 1981 B. 1,902 C. 1,971 D. 1,867 E. 1,899 52. Sulfanilamide drugs prescribed for: A. Mild periodontitis B. * Exacerbative periodontitis, which is accompanied by fever and symptoms of intoxication C. Localized periodontitis D. Periodontitis medium severity E. In remission 53. Application sulfanilamides conduct: A. Under the supervision reoparoontohrafiyi B. Under the control of X-ray C. * A dynamic control of clinical blood D. Under the control of urinalysis E. There is no correct answer 54. Which of the below listed drugs is not an antibiotic? A. Rovamitsyn B. Rondomitsyn C. * Levamisole D. Lincomycin E. Penicillin 55. Patients with aggressive forms of periodontitis, women with periodontal zaahvoryuvannyamy against menopause prescribe medication Fosfamaks: A. * On 1 tab. daily for 6 months B. At 3 tab. daily for 6 months C. At 2 tab. daily for 6 months D. On 1 tab. a day for 1 - year E. On 1 tab. per day for 1 - month 56. Effects of the drug Fosfamaks in the treatment of periodontitis is: A. Osteoklastychnoyi decrease bone resorption B. Improve bone mineral density by 8-12% C. Stimulation of reparative osteogenesis alveolar bone D. * Improvement of bone E. All of the above is true 57. What is the main biological effect of calcitonin? A. Stimulation of metabolism B. * Inhibition of bone resorption by inhibiting osteoklastychnoyi activity and reduce the number of osteoclasts C. Reduced permeability and capillary fragility D. Speeds up wound healing E. It stimulates the production of antibodies 58. What is the daily requirement of vitamin B15 for adults with periodontal disease? A. 10-20 mg B. 5-10 mg C. 100-200 mg D. 200-300 mg E. * 100-300 mg 59. Symptomatic treatment prodontu includes: A. Pain relief B. Treatment hyperesthesia of hard tissues of teeth C. * Eliminating local travmuyuchchyh factors D. That's right E. Selective pryshlifovuvannya teeth 60. Daily requirement for vitamin E in the treatment of periodontal disease are: A. 100 - 200 mg B. 50-100 mg C. * 15-20 mg D. 50-60 mg E. 10-15 mg 61. The daily requirement of vitamin B5 for the treatment of periodontitis is: A. 200 mg B. 100 mg C. 150 mg D. * 0-12 mg E. 60-70 mg 62. The daily requirement of vitamin B6 for the treatment of periodontitis is: A. * 2-2.5 mg B. 20-30 mg C. 40-50 mg D. 30-40 mg E. 10-20 mg 63. Pathogenetic treatment of periodontal disease include: A. Anti-inflammatory treatment B. The effect on local factors regulating bone resorption alveolar bone C. The effect on local factors of bone resorption D. Incentive processes of reparative regeneration of periodontal tissue E. * All answers are correct 64. Kaltsemin - a drug that belongs to the: A. * Drugs that regulate calcium homeostasis B. Antiviral drugs C. Antiprotozoa drug D. Groups vzantyrezorbtsiynoyu drug action E. Groups of drugs that stimulate bone formation 65. Etiotropic treatment of periodontal disease include: A. Removal of dental plaque B. Normalization oral cavity and gastro - intestinal tract C. Antibiotic therapy D. Treatment of somatic pathology with other medical specialties E. * All of the above is true 66. Patients aged 22 years treats acute periodontitis. What is the treatment of periodontitis has primarily to be? A. Symptomatic B. Pathogenic C. * Etiotropic D. Orthopaedic E. Drug 67. The aim of local treatment of periodontitis is: A. Normalization of the microflora of the digestive system B. Stimulation of the functional activity of the salivary glands C. Treatment of physical and odontogenic infection D. * Eliminating annoying factors, removing inflammation, normalize blood circulation in the periodontal tissues E. All answers are correct 68. General therapy of patients with periodontitis directed to: A. Eliminating irritating factors B. Normalization of blood circulation in the periodontal tissues C. * Normalization reactivity organisms and regenerative processes of periodontal tissues, treatment of somatic pathology D. Treatment of odontogenic infection E. Nutrition 69. Start topical treatment of periodontitis: A. Antibiotic B. Splinting of teeth C. Installations antiseptic intermediaries D. * Elimination of dental accretions defective orthopedic constructions E. Anti-inflammatory therapy 70. Which of the following methods do not consider the methods of removing and pidyasenevoho tartar. A. Mechanical B. Chemical C. Physical D. Combined E. * Biological 71. What tools are used for mechanical removal method over and pidyasenevoho tartar? A. Scalers. B. 15% solution of EDTA C. Saturated solution of hydroquinone D. * Sickle hooks E. 5% solution of ascorbic acid, 72. What tools are used in chemical methods of removal and pidyasenevoho tartar? A. Scalers. B. * 15% solution of EDTA C. Rashpilni Smoothers D. Sickle hooks E. Excavators 73. What tools are used for physical removal method over and pidyasenevoho tartar? A. * Scalers. B. 15% solution of EDTA C. Rubber cup using pastes D. Sickle hooks E. 5% solution of ascorbic acid, 74. Which of the following tools is used for mechanical removal method over and pidyasenevoho tartar? A. Rubber cup using pastes B. Rashpilni Smoothers C. * Scalers D. Excavator E. Sickle hooks 75. What is the daily requirement for vitamin B12 in the treatment of periodontal disease? A. 10-20 mg B. * 0.01-0.02 mg C. 0.5 - 0.7 mg D. 20-30 mg E. 40-50 mg 76. When treating patients with periodontitis vitamins are usually administered in stock: A. * Multivitamin preparations B. Antihistamines C. Hormonal drugs D. Antibacterials E. Immunomodulatory drugs 77. When generalized periodontitis treatment multivitamin preparations is: A. 5-6 weeks B. 2 months C. 6 months D. * 3-4 weeks E. 4 months 78. The indications for the use of vitamin U (metylmetioninsulfaniyu chloride) are: A. * Generalized periodontitis, which occurs against the background of the alimentary canal B. Generalized periodontitis that occurs on the background of diseases of the cardiovascular system C. Generalized periodontitis medium severity D. Localized periodontitis E. Periodontal Disease 79. Treatment immunomodulating drugs conducted: A. * Under the control of immunological parameters B. Under the supervision of a general analysis of blood C. Do not hold control parameters D. Under the control of biochemical analysis of blood E. Under the supervision zahaalnoho urinalysis 80. Curative treatment the drug Miakaltsykperedbachaaye its intranasal administration of 1 dose. How many DoD active substance contained in 1 dose of this drug? A. 500 IU B. * 200 IU C. 300 IU D. 400 IU E. 100 IU 81. Methods of treatment of periodontal disease: A. Anti-inflammatory and desensitizing therapy B. Surgical treatment and cryotherapy C. * Osteotropic and remineralization therapy D. Sclerotherapy E. Antibacterial and immunostimulatory therapy. 82. Purpose curettage? A. Remove vrostayuchi strands of epithelium B. The elimination of periodontal pockets C. * Erasing periodontal pocket D. Create conditions for anti-inflammatory therapy E. Remove abnormal granulation 83. What temperature creates a cryoprobe in periodontal pockets during kriokyuretazhi? A. * -60 - 1400S B. -20 - 1000 C C. -50 - 800 C D. - 45 - 1050 C E. - 140 - 2200 C 84. Exposure time cryoprobe is: A. 50 seconds. twice with an interval of 5 minutes B. * 30 sec. twice with an interval of 5 minutes C. 10 seconds. twice with an interval of 5 minutes D. 40 seconds. twice with an interval of 5 minutes E. 20 seconds. twice with an interval of 5 minutes 85. That includes a preoperative preparation before the flap operation for 2-4 weeks? A. teaching oral care B. elimination of traumatic occlusion C. conservative treatment of periodontitis, after which the surgery is carried out not earlier than 2 weeks and not later than 3 months D. dental health: replacement of substandard seals E. * All of the above is true 86. Temporary bus must meet certain requirements, such as: A. evenly distribute pressure on carts chewing teeth B. not interfere medicamentous and surgical treatment C. not to injure the mucosa D. reliably capture all moving teeth E. * All of the above is true 87. What is the role of biological membranes? A. create the possibility of regeneration for periodontal ties B. prevent apical migration of epithelium C. restrict the germination of gingival tissue in the defect area D. create the possibility of regeneration of the adjacent alveolar bone E. * All of the above is true 88. How many groups are divided calcium supplements that are used in the treatment of periodontal zayihvoryuvan? A. 2 B. 4 C. 5 D. * 3 E. 1 89. Which of the manipulation operation is simple hinhivektomiyi stages:? A. remove gum from the edge of Language (palatal) and vestibular sides parallel gingival margin with regard to uneven depth pockets B. stop the bleeding C. open curettage of granulation and pathologically altered bone alveolar process D. pid'yasennoho removal of tartar E. * All of the above is true 90. Indications for the operation curettage: A. Severe periodontitis B. Mild form of periodontal disease C. Deep pockets clinical and bone D. Ineffectiveness of conservative treatment of periodontal pockets of 5 mm. E. * All answers are correct 91. Local hypothermia in the treatment of periodontal disease include: A. Use cooled gas mixture of oxygen and nitrogen at a temperature of 12-14 1:9 0 B. * The use of cooled gas mixture of oxygen and nitrogen at a temperature of 12-14 9:1 0 C. Use cooled gas mixture of oxygen and nitrogen at a temperature of 20-25 9:1 0 D. Use cooled gas mixture of oxygen and nitrogen at a temperature of 20-25 1:9 0 E. Use cooled gas mixture of oxygen and nitrogen 9:1 at 16 92. In violation of the uniformity of physiological attrition occlusal surface of teeth is used: A. Closed curettage B. * Selective pryshlifuvannya C. Suction curettage D. Loskutnu operation E. Temporary splinting 93. Hinhivotomiya - is: A. Removing ash to a depth of periodontal pockets B. * Autopsy gum C. Open curettage D. Stool periodontal abscess E. Disclosure of a single deep periodontal pockets 94. In combination with surgical treatment of periodontitis apply: A. Sclerotherapy B. Stimulant therapy C. Immunosuppressive therapy D. * Antibiotic therapy E. Proteolytic enzymes. 95. Up to 3 classes of premature contacts on Jankelson include: A. Premature contacts on the vestibular surfaces of buccal hillocks lower lateral vestibular surface of the teeth and lower front teeth. B. Contacts on oral surfaces hillocks upper palatal lateral teeth. C. * Premature contacts on the vestibular surfaces of palatal tubercles upper lateral teeth D. Premature contacts on the cutting edge E. All answers are correct 96. Deepithelization pocket is: A. Remove the damaged cement B. * Removal of granulation and ingrown pocket epithelium C. treatment of periodontal pockets yodvmisnymy solutions D. periodontal pocket irrigation with antiseptic solutions under pressure E. no right answer 97. What limited number of teeth operation hinhivektomiyi in the side area? A. * 3.2 B. 4.6 C. 6.8 D. 2.1 E. 4.3 98. What drug used for chemical curettage? A. A solution of potassium hlornovatystokysloho B. * A solution of sodium hlornovatystokysloho C. A solution of magnesium hlornovatystokysloho D. A solution of calcium hlornovatystokysloho E. Solution hlornovatystokysloho iron 99. On that day after surgery is exclusion zone of necrosis at kriokyuretazhi? A. At 1-2 days B. At 3-4 days C. * At 4-5 days D. For 6-7 days E. For 8-9 days 100. Which of the following is used for replanting in periodontal pockets with flap operation? A. "Collapan" B. "Hapkol" C. "Kerhap" D. "BioResorb E. * All of the used 101. In what year was clinically proven ability periodontal relationships grow into the space between the membrane and the surface of the root A. 1,982 B. C. D. E. 102. A. B. C. D. 1,981 1,985 * 1984 1,990 Any of the following definitions describes osteolizys? Pathological process, accompanied by a decrease in bone trabeculae per unit volume Pathological process, accompanied by functional and structural changes ZSCHS Pathological process, accompanied by an increase in bone trabeculae per unit volume * Pathological process, accompanied by complete resorption of the bone without any manifestations of its replacement E. There is no right answer 103. What is the purpose relates to physician when performing simple hinhivektomiyi? A. Correction of defects of the alveolar process of the jaws B. * Elimination of periodontal pocket C. Conducting vacuum curettage D. Holding open curettage E. Eliminate bone pocket 104. Patient hinhivektomiyi intended operation. The disadvantages of this surgery are: A. hyperesthesia bare roots to thermal stimuli B. cosmetic defect after removal of gingival papillae C. necks baring teeth D. hyperesthesia bare roots to chemical stimuli E. * All of the above is true 105. Operation hinhivotomiyi is: A. Removing ash to a depth of periodontal pockets B. * Autopsy gum C. Open curettage D. Stool periodontal abscess E. Disclosure of a single deep periodontal pockets 106. What aids are used in the process of determining traumatic occlusion: A. Iodine solution B. Magenta C. * Wax plates D. Desmodometra E. Ehoosteometra 107. Property periodontal relationships grow into the space between the membrane and the surface of the root has been proven A. 1,982 B. 1,981 C. 1,985 D. * 1984 E. 1,990 108. Specify the indications for use of the method of selective pryshlifovuvannya teeth: A. Detection of premature tooth contacts in the central occlusion B. Installing premature contacts and the presence of contacts only some teeth when closing the jaws in any of the 4 occlusions C. Lack of contact between groups of teeth-antagonists D. Establishing contacts with premature closing of the jaws in the lateral and central occlusion. E. * All of the above is true 109. At that time spend pid'yasennoho remove tartar: A. By curettage of periodontal pockets B. * During curettage of periodontal pockets C. After the curettage pockets D. A week before curettage E. There is no right answer 110. In the situation where occlusion recommended to detect and eliminate premature contacts Kalamkari: A. Only the central occlusion B. Central and distal C. Distal and anterior D. Central and anterior E. * In all three positions occlusion 111. How many times a year is permissible to carry out the procedure curettage? A. 4 times a year B. 5 times a year C. * 2 times a year D. 3 times a year E. 1 every year 112. Operation hinhivektomiyi in lateral areas of the jaws such limited number of teeth: A. * 3.2 B. 4.6 C. 6.8 D. 2.1 E. 4.3 113. Which of the following can be considered the positive aspects of vacuum curettage: A. opportunity to process deeper pockets B. opportunity to process bottom gingival pocket and adjacent bone C. visual inspection complete curettage D. relatively bloodless operative field E. * All of the above is true 114. Patients show selective prpotsedura pryshlifovuvannya teeth. The basic principles of this prpotsedury are: A. Zishlifovuvannya tissues within the thickness of the enamel layer, narrowing the chewing surfaces, while providing expressiveness equator; B. Zishlifovuvannya hard tissue on the occlusal surface is not made in the teeth, which are the backbone that hold interalveolar distance C. Teeth - antagonists in central occlusion should keep multiple buhorkovi - fisurnyy contact. D. Consider the position of teeth not only in the central occlusion E. * All answers are correct 115. Operation curettage was first described in the literature: A. Viydmanom-Neumann B. Viydmanom-Tseshynskym C. Tseshynskym-Neumann D. * Junger-registrar E. Znamenskoye 116. Treatment of periodontal disease consists of general and local. Local therapy includes: A. Training (control) patients the right care for your teeth. B. Eliminating local irritating factors. C. Treatment of systemic hyperesthesia, increased abrasion of hard tooth tissues. D. Local application means that improve the trophic and microcirculation. E. * All answers are correct 117. Patient recommend surgery kriokyuretazhu. Indications for conducting this intervention are: A. Periodontal pocket depth of 5-7 mm B. Hypertrophic gingivitis C. Severe gum hypertrophy in periodontitis D. Periodontal pockets with significant granulation E. * All of the above is true 118. Woman '29 held diathermocoagulation. Over time passes epithelization operated this site? A. 7 days B. 21 days C. * For 10 - 14 days D. Over 20 days E. 30 days 119. The stages of flap operation are: A. vidseparuvannya muco-oxide flap of vestibular and language (palate) sides B. cutting edge modified gums, granulation, and curettage C. mobilization of mucous-oxide graft, stop bleeding D. suture in each interdental spaces and vertical sections E. * All of the above is true 120. The barrier membrane used in scrappy operations shall meet the following requirements: A. have tissue integration B. be impermeable to cells C. maintain prolonged action to regenerate new tissue D. inflammatory reaction that accompanies biorezorbtsiyu these membranes should be minimal and reversible E. * All of the above is true 121. 2 Generalized periodontitis severity characterized by the presence of periodontal pockets deeper than 5 mm. In this case it is advisable to: A. * Loskutnu operation B. Vacuum curettage C. Closed curettage D. Open curettage E. Kriokyuretazh 122. Specify the optimal concentration of F ions in toothpastes according to WHO recommendations: A. * 0.1% B. 0.7% C. 0.2% D. 0.5% E. 0.8% 123. According to the WHO maximum allowable concentration of fluoride ions in toothpastes replies A. 0.9%; B. 0.5%; C. 0.4% D. 0.7% E. * 0.1% 124. Which group includes toothpastes containing vitamins and enzymes: A. * The anti-inflammatory treatment and prevention; B. By against caries prevention and treatment. C. To medical D. By hygienic E. There is no right answer 125. Content enzymes and vitamins in toothpastes provides: A. Against caries preventive medical action. B. Remedial action C. Hygienic effect D. * Anti-inflammatory treatment and preventive action E. There is no right answer 126. Which toothpaste is recommended for use in periodontal disease: A. Hygiene; B. * Anti-inflammatory treatment and prevention; C. Protykariozni treatment and prevention. D. Therapeutic E. There is no right answer 127. The patient on examination revealed pathology of the periodontal tissues. What tooth paste can recommend in this case? A. * Anti-inflammatory treatment and prevention; B. Protykariozni treatment and prevention. C. Therapeutic D. Hygiene E. There is no right answer 128. Protykarioznu action toothpaste creates added to their composition: A. * Sodium fluoride B. Monoftorfosfaty sodium C. Bikarbonaty sodium D. Aminoftorydu E. Silica 129. Plasticity and uniform consistency of toothpaste provided components: A. Abrasive B. Foam C. * Binding D. Scented E. Preservatives 130. Which of these components are added to the toothpastes to of plasticity and uniformity? A. Foam B. * Binding C. Scented D. Preservatives E. Abrasives 131. Hygienic toothpastes contain in its composition: A. Abrasive components B. * Salt Supplements C. Extracts of medicinal plants D. Fluoride. E. All answers are correct 132. What components are part of the hygienic toothpaste? A. Compounds of fluorine B. Medicinal the means C. Abrasive D. * Salt Supplements E. There is no correct answer 133. To reduce gum bleeding patients should use toothpaste that contains: A. Sodium fluoride; B. Calcium carbonate; C. * Extracts of medicinal plants; D. Urea. E. There is no right answer 134. The patient bleeding gums Class. What are the components of toothpastes will provide hemostatic effect? A. * Extracts of medicinal plants B. Calcium carbonate C. Compounds of fluorine D. Urea E. There is no right answer 135. As abrasive ingredients in toothpaste composition comprises: A. Sodium monofluorophosphate; B. * Silicon Dioxide; C. Pyrophosphate. D. Sodium bicarbonate E. Sodium Fluoride 136. Whitening toothpastes have a high degree of abrasiveness. What substances provide this? A. Sodium Fluoride B. Sodium monofluorophosphate; C. Pyrophosphate. D. * Silicon Dioxide; E. Sodium bicarbonate 137. As the foam forming component in the composition of toothpastes include: A. Dicalcium phosphate; B. * Sodium Lauryl Sulfate; C. Polyethylene glycol; D. Hydrocolloids. E. There is no right answer 138. Modern toothpastes in contact with water in the mouth hard foam. What substances provide this property? A. Hydrocolloids. B. Polyethylene glycol; C. * Sodium Lauryl Sulfate D. Dicalcium phosphate; E. There is no right answer 139. Sewage treatment capacity toothpaste provided such components that are in its composition: A. Binding; B. * Abrasive; C. Foam; D. Flavoring. E. Preservatives 140. Content of compounds responsible for cleaning pastes property? A. * Abrasive; B. Flavoring. C. Foam; D. Binding; E. Preservatives 141. Fluoride toothpaste is recommended for children with A. 1.5 - 2 years B. * 3 - 4 years C. 5-6 years D. 10-12 years E. '15 142. At what age children are allowed to use toothpaste with fluoride? A. * 3 - 4 years B. 7-8 years C. 11-12 years D. 1.5 - 2 years E. '15 143. Children 2 years is best used for cleaning teeth A. Dentifrice B. Pastes based on chalky C. * Gel toothpaste D. Mouthwash E. There is no right answer 144. What toothpaste can recommend patients 1.5-2 years? A. * Gel toothpaste B. Pastes based on chalky C. Dentifrice D. Mouthwash E. There is no right answer 145. What amount of fluoride recommended in the composition of children's toothpaste? A. 0.2% B. 0.1% C. 0.01% D. * 0.023% E. 0.05% 146. According to the recommendations of the WHO maximum allowable concentration of fluoride ions in children's toothpastes replies A. * 0.023% B. 0.025% C. 0.1% D. 0.01% E. 0.05% 147. Which group includes toothpastes containing Ca and F: A. By hygienic; B. By anti-inflammatory treatment and prevention; C. * By protykarioznyh healthcare. D. To medical E. There is no right answer 148. Which toothpaste is recommended for children with a high index of CPV? A. Hygiene B. Anti-inflammatory treatment and prevention C. * Protykariozni prevention and treatment D. Therapeutic E. There is no right answer 149. During the inspection revealed that the baby high index index CPV. What toothpaste can recommend in this case? A. * Protykarioznu preventive medical B. Anti-inflammatory treatment and prevention C. Therapeutical D. Sanitarily E. There is no right answer 150. Calcium carbonate and silicon compounds added to toothpaste composition as: A. Frother B. Preservatives C. * Abrasives D. Moisturizer E. Antisepsis 151. How are compounds of silicon and calcium in toothpastes? A. * Abrasives B. Moisturizer C. Frother D. Preservatives E. Antisepsis 152. Lauryl sulfate in toothpastes serves A. * Frother B. Preservatives C. Abrasive D. Moisturizer E. Antisepsis 153. Which function is provided by the addition of the toothpastes lauryl? A. Damping B. Better storage C. Bleaching D. * Foaming E. Antisepsis 154. What is the purpose of the toothpastes injected zv'yazuyuchihelepodibni compound? A. To clean teeth B. * To obtain a homogeneous mixture C. For a pleasant odor D. For foaming E. There is no right answer 155. Zv'yazuyuchihelepodibni compounds in toothpastes serve as: A. Deodorizing B. Foaming C. * Getting a homogeneous mixture D. Cleaning teeth E. There is no right answer 156. Which of the following is used as a binder components A. * Sodium alginate B. Lauryl C. Calcium carbonate D. Silicon dioxide E. Xylitol 157. Which of these compounds can be used for in toothpastes homogenous? A. Triclosan B. Calcium citrate C. Silicon Dioxide D. * Sodium alginate E. Sorbitol 158. Why in toothpastes is xylitol and sorbitol? A. For foaming B. For cleaning C. * To improve the taste properties D. As an antiseptic E. As a moisturizer 159. The packaging of toothpaste states that it contains in its composition xylitol. Reason for this compound is introduced into the composition? A. Deodorization B. Foaming C. A homogeneous mixture D. Cleaning teeth E. * Improved taste 160. Chlorhexidine and Triclosan function: A. Frother B. * Antiseptic C. Abrasive D. Preservatives E. Moisturizer 161. What is the role of toothpastes given chlorhexidine and triclosan? A. * Antiseptic B. Abrasive C. Preservatives D. Frother E. Moisturizer 162. For how long after the release of toothpaste should contain in its composition of microorganisms A. 1 year B. 4 years C. 3 years D. * 2 years E. 5 years 163. Maximum storage toothpaste not containing microorganisms is: A. * 2 years B. 5 years C. 4 years D. 3 years E. 6 years 164. How many groups of action divided toothpaste A. 2 B. 4 C. * 3 D. 5 E. no right answer 165. Classification of toothpaste on their mode of action involves the division into: A. into 5 groups B. into 4 groups C. into 2 groups D. * Into 3 groups E. no right answer 166. For what age period intended for children toothpaste? A. 1 to 4 years B. from 2 to 6 years C. from 3 to 10 years D. * 1 to 6 years E. no right answer 167. Kids toothpaste used children this age: A. * 1 - 6 years B. 3 - 6 years C. 5 - 10 years D. 2 - 4 years E. 1.8 years 168. Patient with sensitive teeth the best fit: A. Toothpaste Anti-Plaque Type B. * Type Sensitive Toothpaste C. paste type Smokers D. no right answer E. all answers are correct 169. Toothpaste can recommend what type of patient with sensitive teeth? A. Herbal B. Anti-Plaque C. Smokers D. * Sensitive E. no right answer 170. What type of toothpaste designed Smokers A. For daily use B. * For professional teeth cleaning C. For patients with hypersensitivity D. For patients with high CPV E. There is no right answer 171. Toothpaste marked Smokers used for: A. * Professional teeth cleaning B. Daily use C. In patients with high CPV D. With increased sensitivity E. There is no right answer 172. Treatment - prophylactic toothpastes containing calcium compounds are used to influence: A. Periodontal B. Mucosa C. * Decomposition of enamel D. All answers are correct E. Reduced sensitivity 173. Compounds of calcium injected into the composition treatment - preventive pastes to influence: A. * Enamel B. Mucosa C. All answers are correct D. Periodontal E. Dentine 174. Treatment - prophylactic toothpastes with exposure to periodontal often contain: A. Compounds of potassium B. Compounds of strontium C. Compounds of fluorine D. * Anti-inflammatory agents E. Compounds of calcium 175. Toothpastes with treatment - preventive effect on periodontal incorporates often contain: A. Antibiotics B. * Anti-inflammatory C. Sorbents D. Enzymes E. Compounds of calcium 176. Which of the following compounds can be used in toothpastes for sensitive A. * 10% strontium chloride or potassium B. sodium fluoride C. tin fluoride D. calcium carbonate E. potassium carbonate 177. For sensitive teeth and gums in toothpaste often introduced: A. Calcium citrate B. sodium fluoride C. potassium carbonate D. tin fluoride E. * Potassium Chloride 178. Which band toothpastes can recommend a patient with multiple wedge-shaped defects? A. protykarioznu therapeutic - prophylactic paste B. anti-inflammatory treatment - preventive paste C. Smokers D. Anti-Plaque E. * Sensitive 179. The patient's teeth are a significant number of dental plaque, oral hygiene is very poor. What kind of toothpaste should be used? A. protykarioznu therapeutic - prophylactic paste B. anti-inflammatory treatment - preventive paste C. * Smokers D. Anti-Plaque E. Sensitive 180. By your use toothpaste share on: A. 2 groups B. * 3 groups C. 4 groups D. 5 groups E. 6 groups 181. Classification toothpastes according to your use involves their division into: A. 6 groups B. 5 groups C. 2 groups D. * 3 groups E. 7 groups 182. With long-term use of toothpastes with chlorhexidine possible side effects. What is it? A. Increased tooth sensitivity B. * Changing Color C. Changes in taste sensation D. Loss of enamel natural shine E. There is no right answer 183. What side effects of chlorhexidine manifested in its continued use? A. * Dysbacteriosis B. Loss of enamel natural shine C. Changes in taste sensation D. Increased tooth sensitivity E. There is no right answer 184. Mint flavor is contraindicated for children's toothpastes because: A. There is a strong allergen B. It is addictive effect C. Reduces the effectiveness of D. * Brings strong rvotnyy reflex E. All answers are correct 185. From below listed select contraindications to the use of mint flavoring in children's toothpastes: A. * Brings strong rvotnyy reflex B. Reduces the effectiveness of C. There is a strong allergen D. It is addictive effect E. All answers are correct 186. As a flavoring within children's toothpastes often used: A. Mint flavor B. Menthol flavor C. Eucalyptus flavor D. * Fruit flavor E. There is no right answer 187. What aromatic compound often used in children's toothpastes? A. Eucalyptic B. Mint C. * Fruit D. Menthol E. There is no right answer 188. What is the best pasta recommend pregnant patient with hypertrophy of the gums? A. Sanitarily B. * Anti-inflammatory treatment and prevention C. Protykarioznu medical - preventive D. Therapeutical E. There is no right answer 189. As divided toothbrushes in the class according to the classification Ulitkovskoho? A. In manual and mechanical B. On the mechanical and electrical C. * The manual, mechanical and electrical D. In manual and electric E. There is no right answer 190. According to the classification Ulitovskoho toothbrushes in the class are divided into: A. On the mechanical and electrical B. * The manual, mechanical and electrical C. In manual and mechanical D. In manual and electric E. There is no right answer 191. Toothbrush marked "Dencher" - is A. Brush with a V-shaped groove in the center of the field schitochnoho B. Brush with very soft bristles C. * Brush, whose head has two sided bristles D. Brush with a narrow head, which has two rows of 10 bristle bundles E. There is no right answer 192. Select from the options characteristic toothbrush "Dencher": A. Brush with very hard bristles B. * Brush, whose head has two sided bristles C. Brush with a narrow head, which has three rows of bristles with 10 beams D. Brush with a V-shaped groove in the center of the field schitochnoho E. Brush with a narrow head, which has two rows of bristles with 10 beams 193. What is the size of the brush work for adults? A. * 25-30 mm B. 30-40 mm C. 10-15 mm D. 10-20 mm E. 40 - 50 mm 194. Length of the working part of toothbrush for adults to meet: A. 5-10 mm B. 35-40 mm C. 20-25 mm D. * 25-30 mm E. 40 - 50 mm 195. What is the size of the working part of the toothbrush for children 2-5 years? A. 3 cm B. 2.5 cm C. 1 cm D. * 2 cm E. 5 cm 196. Length of the working part of toothbrush for children 2-5 years is: A. 1.5 cm B. * 2 cm C. 3.5 cm D. 2.5 cm E. 4 cm 197. Since then proposed provisions brushes corresponding method charter? A. Perpendicular to the axis of the tooth B. At an angle of 900 to the axis of the tooth C. At an angle of 450 to the axis of the tooth D. * Along the axis of the tooth E. There is no right answer 198. When brushing method to brush charter should include: A. * Along the axis of the tooth B. At an angle of 900 to the axis of the tooth C. Perpendicular to the axis of the tooth D. At an angle of 450 to the axis of the tooth E. There is no right answer 199. Active recess two-level bristles designed for cleaning: A. * Chewing surfaces B. Vestibular tooth surfaces C. Gingival groove D. Pear-shaped space gingival groove E. There is no right answer 200. Some toothbrushes have an active recess two-level bristles that designed to: A. Cleaning pear-shaped space gingival groove B. Cleaning gingival groove C. * Cleaning chewing surfaces D. Cleaning vestibular tooth surfaces E. There is no right answer 201. Method of cleaning known as "from red to white," "from the gums to the tooth" - a A. Method charter B. Method Background C. Method Stilmana modified D. * Method Leonard E. Method Stilmana 202. As to the author calls a method of teeth cleaning, which is used in periodontal diseases, the method "from red to white," "from the gums to the teeth?" A. * Method Leonard B. Method Stilmana C. Method Stilmana modified D. Method charter E. Method Background 203. For people with periodontal pathology recommended brushes: A. Soft B. * Average stiffness C. Hard D. Very soft E. Very tough 204. What type of hardness brush is recommended for patients with periodontal pathology? A. Very soft B. Soft C. Hard D. * Average stiffness E. Very tough 205. The scope of the toothbrush "Tang" are: A. Cleaning orthopedic constructions B. Cleaning teeth skuchenyh C. Clean interdental spaces D. * Cleaning the tongue E. Clean palate 206. Reason for use toothbrushes "Tang"? A. * Cleaning the tongue B. Cleaning teeth skuchenyh C. To clean the palate D. For cleaning interdental spaces E. For the treatment of orthopedic structures 207. What is the average angle range electric toothbrush? A. 500 B. 50-550 C. * 60-750 D. 80-900 E. 1,000 208. Electric Toothbrush has an average radius of which is: A. 80-900 B. 500 C. 1,000 D. * 60-750 E. 50-550 209. The width of the working part of the adult toothbrush A. * 10-12 mm B. 10.9 mm C. 8.9 mm D. 7-9 mm E. 40 mm 210. In adult toothbrush maximum width of the working part should be: A. 40 mm B. * 10-12 mm C. 7-9 mm D. 8.9 mm E. 10.9 mm 211. By tightening bristle toothbrushes are divided into A. Grade 4 B. * 5 degrees C. Grade 3 D. 6 Degrees E. 8 degrees 212. A. B. C. D. E. 213. A. B. C. D. E. 214. A. B. C. D. E. 215. A. B. C. D. E. 216. A. B. C. D. E. 217. A. B. C. D. E. 218. A. B. C. D. E. 219. A. B. C. D. E. 220. A. B. C. D. E. Classification bristle toothbrushes in their division provides rigidity to: Grade 4 6 Degrees 8 degrees Grade 3 * 5 degrees Brush Special "Taft" - is Rough brush round and crescent shapes Brush with a V-shaped groove in the center of the field schitochnoho * Brush with a 7-beam bristles on the head Brush, whose head has two sided bristles Brush oval Describe toothbrush "Taft" * Brush with a 7-beam bristles on the head Brush with a V-shaped groove in the center of the field schitochnoho Brush with 5-beam bristles on the head Rough brush round and crescent shapes Brush with a 6-beam bristles on the head For ages designed toothbrush ORAL-B Stage 4 From 2 to 4 years From 5 to 7 years * From 8 years From 6 to 24 months There is no right answer ORAL-B Stage 4 - a toothbrush designed for children: * Older than 8 years 2 - 4 years 5 - 7 years Up to 6 months 6 - 24 months For ages designed toothbrush ORAL-B Stage 1? From 2 to 4 years From 5 to 7 years From 8 years * From 6 to 24 months There is no right answer Kids of all ages can recommend a toothbrush ORAL-B Stage 1? Older than 8 years 2 - 4 years 5 - 7 years Up to 6 months * 6 - 24 months Toothbrush ORAL-B Stage 2 is designed to: * 2 to 4 years From 5 to 7 years From 8 years From 6 to 24 months There is no right answer What age group of children covered by using a toothbrush ORAL-B Stage 2? Kids older than 8 years * Kids 2 - 4 years Kids 5 - 7 years Kids up to 6 months Kids 6 - 24 months 221. Kids ages designed toothbrush ORAL-B Stage 3? A. From 2 to 4 years B. * 5 to 7 years C. From 8 years D. From 6 to 24 months E. There is no right answer 222. What patients prescribed toothbrush ORAL-B Stage 3? A. Kids older than 8 years B. Kids 2 - 4 years C. * Kids 5 - 7 years D. Kids up to 6 months E. Kids 6 - 24 months 223. Brushes whose firmness recommended for children 4.2 years of age? A. Soft and medium hardness B. * Soft and very soft C. Central D. That's right E. There is no right answer 224. The stiffness of toothbrushes used by kids aged 2-4 years should be: A. That's right B. Average C. * Soft and very soft D. Mild and medium E. There is no right answer 225. What is the size of the working part of the toothbrush for children 5-7 years? A. * 2.5 cm B. 3 cm C. 2 cm D. 1.5 cm E. 4 cm 226. Working part toothbrushes recommended for children 5-7 years should have a length: A. 2 cm B. 3.5 cm C. * 2.5 cm D. 1.5 cm E. 4.5 cm 227. What is the size of the working part of the toothbrush for children 7-10 years A. 2.5 cm B. 2 cm C. * 3 cm D. 1.5 cm E. 4 cm 228. The recommended length of the working part of toothbrushes for children 7-10 years: A. 2.9 cm B. * 3 cm C. 2.5 cm D. 3.5 cm E. 4.5 cm 229. Power projection brush ORAL-B clears: A. * Pear-shaped space and interdental spaces B. Chewable surface and interdental spaces C. Vestibular and oral surfaces D. E. 230. A. B. C. D. E. 231. A. B. C. D. E. 232. A. B. C. D. E. 233. A. B. C. D. E. 234. A. B. C. D. E. 235. A. B. C. D. E. 236. A. B. C. D. E. 237. A. B. C. D. E. 238. A. B. C. Fissures of the chewing surfaces That's right The function of the power brush performance ORAL-B are: Cleaning vestibular and oral surfaces Clean the chewing surfaces and interdental spaces * Cleaning pear-shaped space and interdental spaces Clean the chewing surfaces of fissures That's right Synthetic bristle toothbrushes divided into: Safety and hygiene Sanitary and hygienic conditional Prophylactic, hygienic and conditionally hygienic * There is no right answer That's right In their functional synthetic bristle toothbrushes divided into: Prophylactic, hygienic and conditionally hygienic Safety and hygiene Sanitary and hygienic conditional That's right * There is no right answer What is the optimal lifetime toothbrush? 1 month * 3-4 months 2-3 months 1-2 months 6 months How long you can use a toothbrush? 6 months 1 month 2-3 months 1-2 months * 3-4 months What is the toothbrush "Sensitiv"? Cleaning orthodontic constructions Cleaning the tongue Cleaning surgical apparatus mouth * Cleaning sensitive teeth There is no right answer Toothbrush marked "Sensitiv" is used for: Cleaning surgical apparatus mouth * Cleaning sensitive teeth Cleaning orthodontic constructions Cleaning the tongue There is no right answer What is the position relative to the surface of the tooth brush in Bas method? Along the axis of the tooth Perpendicular to the axis of the tooth * At an angle of 450 to the axis of the tooth At an angle of 900 to the axis of the tooth There is no right answer In the method of cleaning teeth by toothbrush Basu position should be as follows: * At an angle of 450 to the axis of the tooth At an angle of 900 to the axis of the tooth Perpendicular to the axis of the tooth D. Along the axis of the tooth E. There is no right answer 239. What are the optimal brush to use for those with healthy periodontium A. * Average stiffness B. Soft and medium hardness C. Hard D. Soft E. Very soft 240. Patients with clinically healthy periodontium for daily use is optimal toothbrushes: A. Very soft B. Hard C. Soft and medium hardness D. Soft E. * Average stiffness 241. At what age can use an electric toothbrush? A. From 2 years B. * From 3 years C. From 5 years D. With 10 years E. From 15 years 242. Electric toothbrush permitted for use with: A. With 8 years of age B. With 2 years of age C. With 6 years of age D. * From 3 years old E. From 14 years old 243. In which clinical situations used toothbrush "Monotaft" A. Clean interdental spaces B. * Cleaning skuchenyh teeth and necks bare teeth C. Cleaning orthodontic constructions D. Cleaning the tongue E. Clean palate 244. "Monotaft" - a toothbrush that is used to: A. Cleaning the tongue B. Cleaning palate C. Cleaning interdental spaces D. Cleaning orthodontic constructions E. * Skuchenyh cleaning teeth and necks bared teeth 245. Terms of dentition and are scouring motions using the method Charters meet: A. Pidmitayuchy movements with that extended jaws B. Circular movements with that extended jaws C. Pulsating movement in the jaws of closed D. * Rotating movements with that extended jaws E. There is no right answer 246. From below listed then cleaning movements and position dentition that corresponding method Charters: A. * Rotating movements with that extended jaws B. Circular movements with that extended jaws C. Pulsating movement in the jaws of closed D. Pidmitayuchy movements with that extended jaws E. There is no right answer 247. What is the position relative to the surface of the tooth brush using the method Stilmana? A. Along the axis of the tooth B. Perpendicular to the axis of the tooth C. * At an angle of 450 to the axis of the tooth D. At an angle of 900 to the axis of the tooth E. There is no right answer 248. Specify the position of the toothbrush using the method of cleaning the Stilmanu: A. Perpendicular to the axis of the tooth B. Along the axis of the tooth C. There is no right answer D. At an angle of 900 to the axis of the tooth E. * At an angle of 450 to the axis of the tooth 249. When used toothbrush "Travel"? A. Cleaning surgical apparatus mouth B. * During Trip C. Cleaning of complete and partial dentures D. Cleaning orthodontic constructions E. Clean palate 250. Toothbrush "Travel" is used by patients with: A. Purification of full and partial dentures B. Cleaning orthodontic constructions C. Cleaning surgical apparatus mouth D. Clean palate E. * During Trip 251. In the method of Leonard's position relative to the surface of the tooth brush as follows: A. At an angle of 450 to the axis of the tooth B. Along the axis of the tooth C. * Perpendicular to the axis of the tooth D. At an angle of 900 to the axis of the tooth E. That's right 252. What is the position relative to the surface of the tooth brush should be using the method "from gum to the tooth "? A. * Perpendicular to the axis of the tooth B. At an angle of 500 to the axis of the tooth C. Along the axis of the tooth D. At an angle of 450 to the axis of the tooth E. That's right 253. Which of the following methods of cleaning is recommended for diseases periodontal A. Method Stilmana B. Method Background C. Method Leonard D. * Method Bass E. Method charter 254. How far apart are the bristles in your toothbrush A. 3-3.5 mm B. 1-1.5 mm C. 1.5-2 mm D. * 2-2.5 mm E. 4 - 4.5 mm 255. The distance between the bristles of your toothbrush should be: A. * 2-2.5 mm B. 4 - 4.5 mm C. 1-1.5 mm D. 1.5-2 mm E. 3-3.5 mm 256. As classified by type of toothbrush according to the classification Ulitkovskoho A. In manual and mechanical B. On the mechanical and electrical C. In the manual, mechanical and electrical D. * In children, adolescents and adults E. There is no right answer 257. In some cases, the dentist participates in the clinical examination of children with chronic diseases of internal organs and systems? A. in the case of high prevalence and intensity of caries; B. in the case of high prevalence and intensity of malocclusion; C. in the case of marginal periodontal diseases; D. in the case of defects of the jaws and face; E. * All true. 258. The main objective of the first phase of clinical examination are: A. * Full coverage dental health total child population serviced clinic; B. use of primary caries prevention, expanding arsenal of means and methods of secondary caries prevention; C. of group and individual prevention group based child health, her physical development and condition of the oral cavity; D. distribution of the subject population of children after primary research; E. all true. 259. The main objective of the second phase of the clinical examination are: A. full coverage dental health total child population serviced clinic; B. * The use of primary caries prevention, expanding arsenal of means and methods of secondary caries prevention; C. of group and individual prevention group based child health, her physical development and condition of the oral cavity; D. distribution of the subject population of children after primary research; E. all true. 260. The main objective of the third phase of clinical examination are: A. full coverage dental health total child population serviced clinic; B. use of primary caries prevention, expanding arsenal of means and methods of secondary caries prevention; C. * Conducting group and individual prevention group based child health, her physical development and condition of the oral cavity; D. distribution of the subject population of children after primary research; E. all true 261. The main objective of the fourth stage of clinical examination are: A. full coverage dental health total child population serviced clinic; B. use of primary caries prevention, expanding arsenal of means and methods of secondary caries prevention; C. of group and individual prevention group based child health, her physical development and condition of the oral cavity; D. * Distribution of the subject population of children after primary research; E. all true 262. Mast cells synthesize connective tissue gum: A. Mukoproteyidy B. * Heparin and histamine C. Serotonin D. Collagen and E. Antibodies 263. Bunches of fibers which form the basis of actual mucosal gums? A. Oksytalanovyh B. Argyrophil C. * Collagen D. Rubbery E. There is no right answer 264. In the papillae of gum are: A. Bundles of collagen fibers B. Bunches of argyrophil fibers C. * Bunches of elastic fibers D. Bunches oksytalanovyh fibers E. There is no right answer 265. The method of examination in which the conduct tap the tooth tip or tweezers is: A. palpation B. termodiahnostyka C. * Percussion D. electroodontodiagnosis E. no right answer 266. Standard set for oral examination includes: A. mirror trowel B. probe, tweezers C. * Mirror probe tweezers D. spatula, probe, mirror E. no right answer 267. Submandibular lymph nodes examined by: A. Percussion B. * Palpation C. Auscultation D. probe E. radiography 268. Which of the following indexes is hygienic? A. Index KPI B. Index PMA C. Index SRITN D. * Index Fedorova - has been received E. all answers are correct 269. Satisfactory level of oral hygiene by Fedorov - has been received corresponding value: A. 1,1-1,5 B. * 1,6-2,0 C. 2,1-2,5 D. 2,6-3,4 E. all answers are correct 270. Whereby the indices hygiene by Green Vermilyonom? A. * Using a cotton swab with iodine-potassium solution B. visually using dental forceps and probe C. using a cotton swab with a solution Loholya D. visually using a probe and mirror E. no right answer 271. The value of the modified index Fedorova has been received is 1.9 points. Which level of care meets the figure A. good B. * Satisfactory C. poor D. bad E. very poor 272. Index PMA determines the severity: A. periodontitis B. * Gingivitis C. periodontitis D. periodontitis E. pulpitis 273. Haemorrhages in probing the gingival groove in the interdental gingival papilla on Myulemanu replies A. 0 points B. * 1 point C. 2 balls D. 3 balls E. 4 balls 274. How is the index at which spend photographing stained sections with subsequent transfer to the paper A. PMA B. NRC C. RFRI D. API E. * Amim 275. Index RI determines the severity A. * Periodontitis B. Periodontitis C. Pulpitis D. Caries E. There is no right answer 276. What surface evaluated by the simplified gingival sulcus bleeding index A. * Vestibular surfaces of the first and third quadrants and tongue surface of the second and fourth B. vestibular surface of the second and fourth quadrants of the tongue surface and the first and third C. vestibular surface of the first and second quadrants of the tongue surface and the third and fourth D. vestibular surface of the third and fourth quadrants and tongue surface of the first and second E. no right answer 277. The appearance of color changes due to gum inflammation, bleeding in probing occurs, you may experience a pronounced inflammatory edema. Myulemanu index gingival sulcus bleeding in this case says: A. 1 degree B. 2 degrees C. Grade 3 D. * 4 degree E. Grade 5 278. How many tooth surfaces involved in determining the index Tureski A. 4 B. * 2 C. 3 D. 6 E. 7 279. Which teeth examined in determining KPI in children 3-4 years A. * 55, 51, 65, 75, 85 B. 54, 54, 64, 74, 84 C. 55, 51, 64, 74, 85 D. 52, 51, 65, 72, 85 E. 53, 51, 65, 73, 85 280. What dye is used in determining the index Quigley and Nein A. Solution Bismarck B. * Solutions erytrozynu, methylene blue C. A solution of fuchsin D. Alcoholic solution of iodine E. There is no right answer 281. Which of the following indices include the fourth group? A. indices that assess an area of plaque B. indexes to evaluate the thickness of plaque C. indices that assess the weight of plaque D. * Indices that assess physical, chemical and microbiological parameters of plaque E. indexes to evaluate the area of tartar 282. To determine the index NRC tooth surface is divided into: A. 2 B. 3 C. 4 D. * 5 E. 6 areas 283. Periodontal - is: A. tooth, gums, periodontal B. tooth, gums, cement root C. gums, periodontal bone alveolus D. * Gums, periodontal bone alveoli tooth E. periodontal bone alveoli tooth 284. Bottom clinical gingival pockets are: A. * Pie ligament tooth B. Oblique fibers periodontal C. Rezorbovana bone D. Gingival-bone ligament E. There is no right answer 285. In determining the index Green - Vermilyona found that the level of hygiene is very poor. Which is a numeric value corresponding to A. 1.0 - 1.3 B. 1.4 - 1.9 C. 2,0 -2,1 D. * More than 2.6 E. no right answer 286. Index Green Vermilyona used to determine: A. Intensity decay B. * Plaque, tartar C. Bleeding gums D. Periodontal pockets E. Mobility of teeth 287. To determine the number of dental CPITN index is divided into: A. 2 B. 4 C. * 6 D. 8 E. 10 Sextant 288. What aids are used in determining the intensity of selection index gingival fluid A. litmus paper B. * Strips of filter paper C. indicators purulent processes D. caries-markers E. no right answer 289. Mobility tooth vestibular-oral and lateral directions replies A. 1 degree of mobility B. * 2 degrees of mobility C. 3 degrees of mobility D. 4 degrees of mobility E. 5 degrees of motion 290. Which of the following is one of the additional methods of examination A. * Radiography, biomicroscopy B. definition of bite C. Depth prysinka mouth D. determine the degree of mobility E. all answers are correct 291. Third grade gum recession's class Miller answers: A. condition in which the recession becomes muco-gingival border B. * Condition in which the recession leads to loss of gingival papillae C. condition in which the recession does not reach the muco-gingival border D. condition in which the recession leads to a breach of the tooth E. no right answer 292. The method of in vivo blood-based registration pulse oscillation is A. * Rheography B. Fluorescent diagnostics C. test Kulazhenko D. electroodontodiagnosis E. polarography 293. What is the method of quantifying bone jaws A. tomography B. elektrorenthenohrafiya C. * Ehoosteometriya D. panoramic radiography E. Radioviziohrafiya 294. During a routine inspection of the patient revealed 2 degree bleeding gums. It says: A. * Bleeding during brushing B. bleeding during consumption of solid food C. spontaneous bleeding D. no right answer E. bleeding during probing 295. Which radiological examination methods based on filmless computer technology to take pictures? A. tomography B. panoramic radiography C. * Radioviziohrafiya D. radiography vprykus E. no right answer 296. Hematoma formation in the mucosa when gum gingivitis is for: A. * 15-25 s. B. 5.10 s. C. 50-80S. D. 25-30 s. E. 10-15s. 297. Furkatsiya be prozondovana more than 3 mm in the horizontal direction. According to the classification Hampi responds: A. First Class B. * Second class C. Third-class D. Fourth Class E. Fifth grade 298. Degenerative changes in the epithelium occur: A. Mucoid swelling B. Osteoporosis and osteosclerosis C. Hyalinosis and sclerosis D. * Vakuolnoyu dystrophy E. Fragmentation 299. Periodontal gap in periodontitis: A. sharply narrowed B. * Extended C. atrophied D. no E. no right answer 300. Using a method can determine the species composition and quantitative characteristics of mucosal microflora? A. Tomography B. * Microbiological studies C. Radioviziohrafiyi D. Fotopletyzmohrafiyi E. Polarography 301. Species composition and quantitative characterization of microflora mucosa studied by means of: A. Ehoosteometriyi B. Polarography C. Fluorescent diagnostics D. Fotopletyzmohrafiyi E. * Microbiological studies 302. Microbiological research allows you to explore: A. * Species composition and quantitative characteristics of mucosal microflora B. Quantitative and qualitative composition of the cellular elements of the blood and epithelial cells C. Cyclical changes of stratified squamous epithelium of the oral cavity D. Saturation mucosal ascorbic acid E. That's right 303. The first category of changes in the composition of microflora on mucosal Khazanov is: A. Dysbacteriosis and II degree B. Dysbacteriosis third degree C. Dysbacteriosis fourth degree D. * Dysbiotic shift E. There is no right answer 304. The second category of changes in the composition of microflora on mucosal Khazanov is: A. * Dysbacteriosis and II degree B. Dysbacteriosis third degree C. Dysbacteriosis fourth degree D. Dysbiotic shift E. There is no right answer 305. The third category of changes in the composition of microflora on mucosal Khazanov is: A. Dysbacteriosis and II degree B. * Dysbacteriosis third degree C. Dysbacteriosis fourth degree D. Dysbiotic shift E. There is no right answer 306. The fourth category changes in the composition of microflora on mucosal Khazanov is: A. Dysbacteriosis and II degree B. Dysbacteriosis third degree C. * Dysbacteriosis fourth degree D. Dysbiotic shift E. There is no right answer 307. Which category changes of mucosal microflora responsible dysbiotic shift? A. * First B. Third C. Second D. Fourth E. no right answer 308. Which category of changes in the composition of microflora mucosal overgrowth meets I-II degree? A. First B. Third C. * Second D. Fourth E. no right answer 309. Which type of changes in the composition of microflora mucosa characterized by dysbiosis third degree? A. First B. * Third C. Second D. Fourth E. no right answer 310. Which type of changes in the composition of microflora mucosa characterized by dysbiosis fourth degree? A. First B. Third C. Second D. * Fourth E. no right answer 311. For a study in patients taking swab - scraping? A. Fluorescent diagnostics B. Microbiological studies C. X-ray study D. * Biomikroskopichnoho research E. There is no right answer 312. How many colonies of microorganisms per 1 cm2 identify with chronic diseases? A. 56 B. 26 C. * 36 D. 16 E. 2.1 313. What is the method by which study the quantitative and qualitative composition of the cellular elements of the blood and epithelial cells? A. Tomography B. C. D. E. 314. A. B. Microbiological research Ehoosteometriya Polarography * Exfoliative cytology Exfoliative cytology method allows you to explore: Species composition and quantitative characteristics of mucosal microflora * Quantitative and qualitative composition of the cellular elements of the blood and epithelial cells C. Cyclical changes of stratified squamous epithelium of the oral cavity D. Saturation mucosal ascorbic acid E. That's right 315. Using a method can determine the index keratinization? A. Fotopletyzmohrafiyi B. Microbiological studies C. * Exfoliative cytology D. Polarography E. Radiography 316. When conducting a study can determine the index keratinization? A. Microbiological studies B. Radiography C. Polarography D. Fotopletyzmohrafiyi E. * Exfoliative cytology 317. With which are material for cytology? A. Thematic glasses B. * Rubber cube C. Sterile loop D. Tweezers E. There is no right answer 318. The patient is recommended to conduct oral tsytodiahnostyku. Material for the study will be taken from: A. * Mucosa cheeks, above the interdigitation B. Mucosa in the region of the angle of the mouth C. Mucosa floor of the mouth D. Mucosa cheek below the interdigitation E. There is no correct answer 319. The place for the taking of material for oral tsytodiahnostyky are: A. The mucous membrane of the cheeks, below the interdigitation B. The mucous membrane of floor of the mouth C. Mucosa in the region of the angle of the mouth D. * The mucous membrane of the cheeks, above the interdigitation E. There is no correct answer 320. The first step of estrogen saturation is characterized by: A. The mean degree of estrogen deficiency B. * Cutting estrogen deficiency C. Moderate decrease in estrogen D. A good estrogen saturation E. There is no correct answer 321. Second degree estrogen saturation is characterized by: A. * Average degree of estrogen deficiency B. Abrupt estrogen deficiency C. Moderate decrease in estrogen D. A good estrogen saturation E. There is no correct answer 322. A. B. C. D. E. 323. A. B. C. D. E. 324. A. B. C. D. E. 325. A. B. C. D. E. 326. A. B. C. D. E. 327. A. B. C. D. E. 328. A. B. C. D. E. 329. A. B. C. D. E. 330. A. B. C. Third stage estrogen saturation is characterized by: Average degree of estrogen deficiency Abrupt estrogen deficiency * Moderate decrease in estrogen A good estrogen saturation There is no correct answer The main signs of periodontal disease: The presence of periodontal pockets, pioreya, mobility of teeth * Lack of inflammation in periodontal stability teeth, horizontal resorption of alveolar bone, the absence of clinical pocket Atrophy of gums, bone destruction of the alveolar ridge, mobility and displacement of teeth The presence of symptomatic gingivitis, periodontal pockets, tooth mobility. There is no right answer According to the classification of aggressive periodontitis forms are divided into: Localized and generalized * Juvenile, prepubertal and quickly progressing Juvenile and prepubertal Prepubertal and quickly progressing Juvenile and rapidly progressive One of the first symptoms quickly progressing periodontitis are: Bleeding gums Pain in teeth Swelling of the gums * Mobility of teeth Anemichnist gum Feature clinical course quickly progressing periodontitis are: Pronounced bleeding gums * Lack of inflammation The lack of mobility of teeth Pain from thermal and chemical stimuli Strong pastoznost gum First of all, clinically manifested juvenile periodontitis: * Loss 16, 26, 11, 21 teeth + Loss 12, 22, 36, 46 teeth Loss 36, 46, 31, 41, teeth Loss 16, 26, 41, 31 teeth There is no right answer For ages typical juvenile periodontitis? 6-12 years * 12-17 years 17-25 years 25-35 years After 45 years A characteristic feature of quickly progressing periodontitis forms are: Slow bone loss * Massive destruction of bone with loss of teeth over 5 years No bone destruction with pronounced inflammation Massive destruction of bone combined with a strong bleeding There is no right answer For what age group characteristic rapidly progressive periodontitis? 6-12 years 12-17 years * 17-25 years D. 25-35 years E. After 45 years 331. First degree mobility tooth mobility is in A. vestibular - oral and mediodystalnomu directions B. vestibular - oral and vertical directions C. and vertical directions mediodystalnomu D. * Vestibular - oral direction E. no right answer 332. The examination determined that the rate of complex periodontal index of 3.7. What kind of condition of periodontal tissues can be seen in this case A. Mild periodontitis B. average degree of periodontitis C. * Severe periodontitis D. very severe degree of periodontitis E. very mild degree of periodontitis 333. Periodontal index in the survey was 4, 2. What decryption can be given in this case A. severe stage of periodontitis B. light stage periodontitis C. secondary stage of periodontitis D. * Very severe stage of periodontitis E. no right answer 334. The emergence of periodontal disease on the theory E.E.Platonova occurs: A. * As a result of trophic disorders of the central or peripheral nervous system B. As a result of circulatory disorders periodontal tissue C. As a result of metabolism, accompanied by a sharp delay in the synthesis of protein D. As a result of the imbalance between the processes of osteosynthesis and osteolizysu E. Because immunological changes of periodontal tissues (autoagression). 335. The emergence of the theory A.I.Yevdokimova periodontitis occurs as A. Corollary hypovitaminosis C B. Metabolic disorders, which is accompanied by a sharp delay in the synthesis of proteins C. * Primary-degenerative process of bone due to periodontal atherosclerosis D. Imbalance between processes osteosynthesis and osteolizysu E. Because trophic disorders of the central or peripheral nervous system. 336. What are the pathological processes underlying osteodystrophy: A. Pathological process, accompanied by a decrease in bone trabeculae per unit volume B. * Pathological process, accompanied by functional and structural changes ZSCHS C. Pathological process, accompanied by an increase in bone trabeculae per unit volume D. Pathological process, accompanied by complete resorption of the bone without any manifestation of its replacement E. There is no right answer 337. What are the criteria for the effectiveness of curettage gingival and periodontal pockets? A. Lack pid'yasennoho tartar B. * Lack of severe bleeding, lack pid'yasennoho tartar, granulation and epithelial vrosshoho C. Complete absence of bleeding D. Clear tightly to the teeth E. Lack of granulation and epithelial vrosshoho 338. One kind of treatment of periodontal pathology is holding scrappy operations. The purpose of data on periodontal surgery are: A. Eliminate inflammation and inhibition of degeneration of periodontal tissue B. * Elimination of periodontal pockets and correction of defects in alveolar bone C. Eliminate bone pockets and stimulation of trophic disorders D. E. 339. A. B. C. D. E. 340. A. B. C. All answers are correct There is no right answer Through a study of the degree of traumatic occlusion? Odontoparodontohramy Panoramic x-rays * Oklyuzohramy Elektrorenthenohramy Telerenthenohrafiyi The purpose of the temporary splinting are: Stabilization of mobile teeth before the permanent prosthesis * Immobilization mobile teeth during therapeutic and surgical treatment Creating conditions gingival fixing bandages for highly mobile and lonely standing teeth D. Destabilization of moving teeth before surgery. E. There is no right answer 341. Neutralization hlornovatystokysloho sodium in periodontal pockets during chemical curettage is performed using: A. 5% solution of acetic acid B. 5% solution of phosphoric acid C. * 5% citric acid solution D. 5% solution of hydrochloric acid E. 5% solution of nitric acid 342. What neutralizes acid sodium hlornovatystokyslyy for chemical curettage? A. * 5% citric acid solution B. 5% solution of phosphoric acid C. 5% solution of acetic acid D. 5% solution of hydrochloric acid E. 5% solution of nitric acid 343. Before conducting the procedure pryshlifuvannyam selective definition of premature contacts. Up to 1 class a Jankelson include: A. A. * Premature contacts on the vestibular surfaces of the buccal hillocks lower lateral vestibular surface of the teeth and lower front teeth. B. Contacts on oral surfaces hillocks upper palatal lateral teeth. C. Premature contacts on the vestibular surfaces of palatal tubercles upper lateral teeth. D. Premature contacts on the cutting edge E. All answers are correct 344. Identify and eliminate premature contacts Jankelson recommends situation: A. * Only the central occlusion B. Central and distal C. Distal and anterior D. Central and anterior E. In all three positions occlusion 345. The depth of periodontal pockets in periodontitis to 4 mm. What treatment is recommended in this case? A. Loskutnu operation B. Loskutnu operation using osteoplastychnyhyaterialiv C. * Closed curettage D. Open curettage E. By directing tissue regeneration 346. When flap surgery, the surgeon holds the following sections: A. Continuous hirlyandopodibnyy cut B. Oblique incision interdental papillae C. Two vertical incisions in the direction of the transition folds on top of interdental papillae D. D. * Two vertical incisions in the direction of the transition folds passing interdental papillae E. There is no right answer 347. The patient is recommended to curettage. Interval for this operation in the area of different groups of teeth is: A. 1-2 days B. * 2-3 days C. 3-4 days D. 5-6 days E. 10 days 348. Treatment of systemic hyperesthesia conducted by: A. * Electrophoresis 2% solution of sodium fluoride B. Electrophoresis solution vitamin D C. Electrophoresis Tren tal D. Electrophoresis AESCUSAN E. Electrophoresis maraslavinu 349. What is the cut operation is carried out at an open curettage: A. oblique incision interdental papillae to the bottom pocket only vestibular side B. oblique incision interdental papillae to the bottom pocket only Oral C. * Oblique incision interdental papillae to the bottom pockets on both sides D. hirlyandopodibnyy cut gums E. vertical incision papillae of Oral 350. Operation curettage was first held: A. Junger B. Registrar C. Znamensky D. * Rigg E. Tseshynskyy 351. Chemical curettage was first proposed: A. Junger B. Registrar C. * Kenny D. Rigg E. Tseshynskyy 352. To protect the hard tissue of teeth with kriokyuretazhi cultivated? A. Eugenol B. Sea buckthorn oil C. Vitamin E D. * Vaseline E. Metrogyl-Dent 353. Over time passes coagulation in periodontal pockets? A. 1-2 sec. B. 30 seconds. C. * 02.04 sec. D. 5-10 seconds. E. 20-40 sec. 354. Solving problems which poses a orthopedic treatment of periodontal disease? A. * Removal of traumatic occlusion B. eliminate abnormal motion C. prevent displacement of teeth D. combining into a single unit all teeth E. all of the above is true 355. Membranes that are not biodegradable removed because: A. After 2 weeks B. After 3 weeks C. After 5 weeks D. After 6 weeks E. * After months of 356. The patient had kriokyuretazh periodontal pockets. What tactics doctor in the first 24-48 hours after the procedure? A. Assign spray with halaskorbinom 6-8 times a day B. Hold intensive processing antiseptic C. Circulation insulating periodontal bandage D. * Apply enzymes and antibiotics E. There is no right answer 357. What is the depth of carving gum periodontal pockets during operation simple hinhivektomiyi? A. At ½ pocket depth B. At 1/3 the depth of the pocket C. At 2/3 the depth of the pocket D. * At the depth of the pocket E. There is no right answer 358. When the transaction curettage doctor should follow the following basic principles: A. complete anesthesia operated tissues; B. careful attitude to the tissues in the area of manipulation: C. organization of blood clot and his defense: D. perfect compliance with the rules of hygiene in the postoperative period. E. * All answers are correct 359. What type of curettage most effective in generalized periodontitis III. gravity? A. Outdoor and vacuum - curettage B. * Vacuum - curettage, cryo - curettage C. Open curettage D. Closed curettage E. Open and closed curettage 360. What is the method of hyperbaric oxygenation? A. * Introduction submucous transitional folds 5 ml of oxygen B. Introduction submucous transitional folds 10 ml of oxygen C. Introduction submucous transitional folds trypsin D. Introduction submucous transitional folds prodektynu E. Introduction submucous transitional folds mevakoru 361. A patient with periodontal disease will be carried out by hyperbaric oxygenation. The basis of this method is: A. * Introduction submucous transitional folds 5 ml of oxygen B. Introduction submucous transitional folds 10 ml of oxygen C. Introduction submucous transitional folds trypsin D. Introduction submucous transitional folds prodektynu E. Introduction submucous transitional folds mevakoru 362. After the operation kriokyuretazhuepitelizatsiya section is operated by: A. 7 days B. 21 days C. * For 14 days D. 10 days E. 30 days 363. Periodontal surgery is intended to: A. Anti-inflammatory and desensitizing effect B. Removal of foci intoxication C. * Elimination of periodontal pockets and creating conditions for the stabilization process in the periodontal tissues D. E. 364. A. Creating the conditions for the regeneration of alveolar bone. There is no right answer Premature contacts in Class 2 Jankelson, is: Premature contacts on the vestibular surfaces of buccal hillocks lower lateral vestibular surface of the teeth and lower front teeth. B. * Contacts on oral surfaces hillocks upper palatal lateral teeth C. Premature contacts on the vestibular surfaces of palatal tubercles upper lateral teeth. D. Premature contacts on the cutting edge E. All answers are correct 365. The phenomenon of osteosclerosis is a pathological process that: A. Accompanied by a decrease in bone trabeculae per unit volume B. Accompanied by functional and structural changes ZSCHS C. * Accompanied by an increase in bone trabeculae per unit volume D. Accompanied by a full bone resorption without any manifestations of its replacement E. There is no right answer 366. What method of treatment used for the pathologic tooth mobility in order to stabilize them? A. Closed curettage B. Selective pryshlifuvannya C. Suction curettage D. Loskutnu operation E. * Temporary splinting 367. Operation curettage performed strictly in certain stages, namely: A. processing operating margins yodvmisnymy solutions B. remove tartar and tooth damaged cement C. deepithelization pocket D. curettage of bone edge alveoli E. * All answers are correct 368. Operation hinhivektomiyi in the frontal area is limited to: A. 2.3 teeth B. * 4-6 teeth C. 6.8 teeth D. 2.1 teeth E. 4.3 teeth 369. Content curettage of periodontal pockets was first held in: A. 1892, B. 1902, C. 1909, D. * 1867 E. 1899, 370. First operation of chemical curettage was performed in A. * 1981 B. 1902, C. 1971, D. 1867, E. 1899, 371. Periodontal disease can be treated with: A. Anti-inflammatory and desensitizing therapy B. Surgical treatment and krioterapiyiyi C. * Osteotropic and remineralization therapy D. Sclerotherapy E. Antibacterial and immunostimulatory therapy. 372. Objectives of curettage: A. Remove vrostayuchi strands of epithelium B. The elimination of periodontal pockets C. * Erasing periodontal pocket D. Create conditions for anti-inflammatory therapy E. Remove abnormal granulation 373. In a kriokyuretazhu in periodontal pockets cryoprobe creates such temperature: A. * -60 - 1400 C B. -20 - 1000 C C. -50 - 800 C D. - 45 - 1050 C E. - 140 - 2200 C 374. Kriokyuretazh involves the use of cryoprobe. Exposure time during the procedure: A. 50 seconds. twice with an interval of 5 minutes B. * 30 sec. twice with an interval of 5 minutes C. 10 seconds. twice with an interval of 5 minutes D. 40 seconds. twice with an interval of 5 minutes E. 20 seconds. twice with an interval of 5 minutes 375. Each patient is assigned a flap operation should undergo preoperative preparation for 2-4 weeks. What does it include? A. teaching oral care B. elimination of traumatic occlusion C. conservative treatment of periodontitis, after which the surgery is carried out not earlier than 2 weeks and not later than 3 months D. dental health: replacement of substandard seals E. * All of the above is true 376. When periodontal disease using temporary splinting. What requirements must they meet? A. evenly distribute pressure on carts chewing teeth B. not interfere medicamentous and surgical treatment C. not to injure the mucosa D. reliably capture all moving teeth E. * All of the above is true 377. Biological membranes perform a role, namely: A. create the possibility of regeneration for periodontal ties B. prevent apical migration of epithelium C. restrict the germination of gingival tissue in the defect area D. create the possibility of regeneration of the adjacent alveolar bone E. * All of the above is true 378. Preparations of calcium used in the treatment of periodontal disease are divided into: A. 2 groups B. 4 groups C. 5 groups D. * 3 groups E. 1 group 379. Operation is simple hinhivektomiyi has several stages. Which of the following applies to them? A. remove gum from the edge of Language (palatal) and vestibular sides parallel gingival margin with regard to uneven depth pockets B. stop the bleeding C. open curettage of granulation and pathologically altered bone alveolar process D. pid'yasennoho removal of tartar E. * All of the above is true 380. When diagnosed with chronic generalized periodontitis II severity recommended surgery. What does it take into account when choosing surgery? A. The depth of periodontal pockets B. C. D. E. Complaints patient Duration of disease Age of the patient * The depth of periodontal pockets, the general condition of the patient, the patient's age 381. Operation curettage performed at: A. Severe forms of periodontitis B. Mild forms of periodontal disease C. Profound clinical and bone pockets D. Failure of conservative treatment of periodontal pockets of 5 mm. E. * All answers are correct 382. The method of local hypothermia in the treatment of periodontal disease based on :: A. Use cooled gas mixture of oxygen and nitrogen at a temperature of 12-14 1:9 0 B. * Use cooled gas mixture of oxygen and nitrogen at a temperature of 12-14 9:1 0 C. Use cooled gas mixture of oxygen and nitrogen at a temperature of 20-25 9:1 0 D. Use cooled gas mixture of oxygen and nitrogen at a temperature of 20-25 1:9 0 E. Use cooled gas mixture of oxygen and nitrogen 9:1 at 16 383. When periodontal disease often occur premature contacts. Their treatment is carried out by :: A. Closed curettage B. * Sample pryshlifuvannya C. Suction curettage D. Loskutnoyi operation E. Temporary splinting 384. An indication of the effectiveness of curettage gingival and periodontal pockets in the implementation are: A. Lack pid'yasennoho tartar B. * Lack of severe bleeding, lack pid'yasennoho tartar, granulation and epithelial vrosshoho C. Complete absence of bleeding D. Clear tightly to the teeth E. Lack of granulation and epithelial vrosshoho 385. Operation hinhivotomiyi is: A. Removing ash to a depth of periodontal pockets B. * Autopsy gum C. Open curettage D. Stool periodontal abscess E. Disclosure of a single deep periodontal pockets 386. Surgical treatment of periodontitis applies to: A. Sclerotherapy B. Stimulant therapy C. Immunosuppressive therapy D. * Antibiotic therapy E. Proteolytic enzymes. 387. In Jankelson there are 3 classes of premature contacts. Up to 3 classes are: A. Premature contacts on the vestibular surfaces of buccal hillocks lower lateral vestibular surface of the teeth and lower front teeth. B. Contacts on oral surfaces hillocks upper palatal lateral teeth. C. * Premature contacts on the vestibular surfaces of palatal tubercles upper lateral teeth D. Premature contacts on the cutting edge E. All answers are correct 388. Operation of deepithelization pocket is: A. Remove the damaged cement B. * Removal of granulation and ingrown pocket epithelium C. treatment of periodontal pockets yodvmisnymy solutions D. periodontal pocket irrigation with antiseptic solutions under pressure E. no right answer 389. In the lateral area of operation is limited hinhivektomiyi so many teeth? A. * 3.2 B. 4.6 C. 6.8 D. 2.1 E. 4.3 390. Which of the following is used for chemical curettage? A. A solution of potassium hlornovatystokysloho B. * A solution of sodium hlornovatystokysloho C. A solution of magnesium hlornovatystokysloho D. A solution of calcium hlornovatystokysloho E. Solution hlornovatystokysloho iron 391. The exclusion zone of necrosis at kriokyuretazhi passes after surgery: A. At 1-2 days B. At 3-4 days C. * At 4-5 days D. For 6-7 days E. For 8-9 days 392. What preparation take a seat in periodontal pockets with flap operation? A. "Collapan" B. "Hapkol" C. "Kerhap" D. "BioResorb E. * All of the used 393. When was the ability of periodontal relationships grow into the space between the membrane and the surface of the root A. 1,982 B. 1,981 C. 1,985 D. * 1984 E. 1,990 394. Depending on the nature of the process, the causes and mechanisms of development of periodontitis treatment may be: A. Causal B. Pathogenetic C. Symptomatic D. Pathogenetic combined with symptomatic E. * All answers are correct 395. Treatment of periodontal disease should be directed to: A. Elimination of inflammation in periodontal B. Strengthening overall health C. Increasing the body's defenses D. Removing the causes of disease E. * All answers are correct 396. Regardless of the form and stage of the pathological process in periodontal topical treatment begins with: A. * Thorough removal of dental plaque B. Appointment of antibiotics C. Treatment of somatic pathology D. Appointment of antihistamines E. Conducting correction of the gastrointestinal tract 397. Local treatment of periodontal disease include: A. Elimination of defects fillings and prosthetics B. Clinical observation of the patient C. * That's right D. Consultation gastroenterologist E. Consultation endocrinologist 398. Local treatment of periodontal disease include: A. Remove excess filling material from interdental spaces B. Removing improperly manufactured dental bridges C. Removal of crowns that go deep under the gums D. Timely replacement E. * That's right 399. Contraindications to the use of immunotherapy: A. Cardio - vascular insufficiency B. Leukemia C. Mental Illness D. * All of the above is true E. Neoplasm 400. General treatment of periodontitis include: A. Treatment of somatic pathology B. Regulation of reactivity C. Generall therapy D. Activation of metabolic processes E. * All of the above is true 401. Treatment somatic diseases carried by dentists with: A. Gastroenterologist B. Neurologist C. Cardiologist D. Endocrinologist E. * All the experts 402. In terms of antimicrobial treatment for acute periodontitis with symptoms of abscess designate A. Vitamins B. Tranquilizers C. Hormones D. * Antibiotics E. Stimulants 403. Which course of drug treatment Biosed that is a biogenic stimulator? A. 5.1 Injection B. 2 injections C. * 25-30 injections D. 20 injections E. 30 injections 404. How many injections provides treatment Plasmol? A. 2 B. 5 C. 7 D. * 10 E. 15 405. Immunal - is: A. A. * immunomodulators of plant origin B. Biogenic stimulator C. Antihistamine D. Antibiotic E. Steroidal anti-inflammatory drug 406. Diet therapy consisting of combined treatment of periodontitis are: A. * Mandatory B. Optionally C. Partially necessary D. In certain cases E. There is no right answer 407. What drug is prescribed to patients with periodontitis and concomitant hypertension 1 degree? A. Tavegil B. Suprastin C. * Clonidine with hypothiazide D. Levamisole E. Clotrimazole 408. According to the pathological changes that are gingivitis belongs to: A. * Inflammatory diseases B. Inflammatory and degenerative diseases C. Degenerative diseases D. Tumor diseases E. There is no right answer 409. During a routine inspection, the patient revealed catarrhal gingivitis. What is the earliest clinical sign of inflammation in the gums? A. * Warp gingival papillae B. Cyanosis gum C. Gingival pocket to 3 mm D. Bleeding in probing E. Puffiness gum 410. Inflammatory periodontal tissues characterized by the emergence of false pockets. Within the tissue it is located: A. * Ash B. Ash and periodontal C. Ash, periodontal and bone alveolus D. Periodontal bone and alveoli E. There is no right answer. 411. Clinical edematous form of hypertrophic gingivitis characterized by gingival pockets. Within the tissue they are located in this disease: A. * Within the gums B. Within the gingival and periodontal C. Within the gums, periodontal and bone alveolus D. Within periodontal and bone alveolus E. There is no right answer. 412. The clinical picture of granulating form hypertrophic gingivitis occurs: A. Morbidity and rozpushenist gum B. Significant bleeding gums C. Pronounced gingival cyanosis D. Desquamation of the epithelium gingival papillae E. * All of the above 413. The clinical picture of ulcerative-necrotic gingivitis occurs: A. Pain gums B. Bad Breath C. Necrotic phenomena in the gums D. Enlargement of regional lymph nodes E. * All of the above 414. Patient undergoing treatment hypertrophic gingivitis. A time to repeat injection during deep sklerotyzatsiyi: A. Day B. * Week C. Month D. 1 time in 2 weeks E. 1 every three days 415. What is the minimum course of treatments with superficial sklerotyzatsiyivahotylom A. 6 days B. Week C. * 3 days D. Month E. 2 months 416. Surface application by Ovrutskom this: A. Applications vagotilom B. Applications celandine C. Applications glucose D. * Applications neotsydu E. Applications hlorfilipt 417. What course of treatments with superficial sklerotyzatsiyi celandine on Udovytska O. A. 20 procedures B. * 10 sessions C. 30 procedures D. 40 procedures E. 15 procedures 418. According topography - the anatomical structure of the alveolar part of the gums - is: A. Gingival papilla and gums around the tooth B. Naturally, the surrounding tooth C. * Clear, covering alveolar bone D. Gingival groove E. There is no right answer 419. The final phase of treatment of ulcerative gingivitis characterized using keratoplasty. Which of the following drugs belongs to this group: A. Trypsin B. Chymotrypsin C. Trihopol D. * Eugenol E. Chlorhexidine 420. In patients diagnosed with ulcerative-necrotic gingivitis. Clinical and morphological characteristics of a given zahvoryuyutsya occur due to: A. * Alteration and necrosis B. Proliferation C. Edema and inflammatory infiltration D. All answers are correct E. There is no right answer 421. Treatment of any disease has causal, pathogenetic and symptomatic therapy. Symptomatic therapy is: A. Medicamentous influence on pathophysiological links inflammation B. Identify and address local exogenous factors C. * Elimination of certain symptoms of periodontal disease D. There is no right answer E. All answers are correct 422. X-ray picture of acute catarrhal gingivitis medium severity: A. Cortical plate interdental septum rozrushena B. Cortical plate and bone interdental septum is preserved, osteosclerosis C. Loss of interdental bone septum ½ lengths on the roots of teeth D. * No changes E. There is no right answer 423. For which of these therapies used these drugs vagotilom, maraslavin, celandine? A. Causal treatment B. Pathogenetic therapy C. Symptomatic therapy D. * Sclerotherapy E. There is no right answer 424. In hypertrophic gingivitis perform operation hinhivektomiyi. At what angle to the axis of the tooth hold the cut at this surgical intervention? A. 450 B. 500 C. * 600 D. 900 E. 300 425. A patient diagnosed with hypertrophic gingivitis (swelling form). Morphologically, the disease manifests itself: A. Fibroblast proliferation, parakeratosis phenomena B. * Vasodilatation, edema of the connective tissue elements C. Lymphocytic infiltration, coarsening of collagen fibers D. Vasoconstriction, acanthosis mucosa. E. All answers are correct 426. X-ray picture of acute ulcerative necrotic gingivitis light severity: A. * Cortical plate and bone interdental septum saved B. Cortical plate interdental septum is preserved, bone loss at 1/3 the length of the root C. Cortical plate interdental septum rozrushena, bone loss at ½ the length of the root D. All answers are correct E. There is no right answer 427. Surface sklerotyzatsiyi Udovytska the method is: A. Processing pockets vagotilom B. Processing pockets celandine and putting in your pocket honsurydu C. * Processing pockets celandine D. Processing pockets maraslavinom E. There is no right answer 428. A patient diagnosed with puffy shape hypertrophic gingivitis. Morphologically feature under persistent edema are: A. * Slowly disappearing recess in place of the pressure with a blunt object B. Thickening of collagen fibers C. Phenomena couple keratosis D. Proliferation of fibroblasts E. There is no right answer 429. X-ray picture of acute catarrhal gingivitis is characterized by: A. Resorption top interdental partitions B. Serednovohnyschevym osteoporosis C. * No changes of bone D. Osteolizysom. E. All answers are correct 430. Patient delivered dentist diagnosed acute catarrhal gingivitis. What are the main complaints with the will of the patient: A. Swelling of the gums B. Pain C. Violation of chewing D. Bleeding E. * All answers are correct 431. Treatment of any disease has causal, pathogenetic and symptomatic therapy. Causal treatment is: A. * Medicamentous influence on pathophysiological links inflammation B. Identify and address local exogenous factors C. Eliminate some symptoms of periodontal disease D. There is no right answer E. All answers are correct 432. In the study of smears taken from surface ulcers in a patient with ulcerative necrotic gingivitis find: A. Staphylococci and spirochete B. * Spirochetes and fuzobakteriyi C. Fuzobakteriyi and lactobacilli D. Spirochetes and lactobacilli E. Lactobacillus and Staphylococcus 433. Patient delivered dentist diagnosis puffy form hypertrophic gingivitis. What are the main complaints with the will of the patient: A. Deformation gingival papillae B. Cutting congestion gingival papillae C. Swelling D. Bleeding E. * All answers are correct 434. Patient delivered dentist diagnosed fibrous form of hypertrophic gingivitis. What are the signs while the patient will: A. Elephantiasis gum B. Lack of bleeding C. Hyperplasia gingival papillae D. Roundness gingival papillae E. * All of the above 435. On examination, the patient was determined PMA index. Which severity of gingivitis will match the index of 31-60%? A. Very easy B. light C. * Average D. heavy E. very difficult 436. Morphologically all clinical signs in catarrhal gingivitis occur due to: A. Alteration and necrosis B. Proliferation C. * Edema and inflammatory infiltration D. All answers are correct E. There is no right answer 437. What formations occur in edematous form of hypertrophic gingivitis as a result of late edema and hyperplasia: A. Periodontal pockets B. Ulcers C. Syphiloma D. * Gingival pockets E. Papilloma 438. Which of the following diseases characterized by false pockets: A. Periodontitis B. Periodontal Disease C. * Hypertrophic gingivitis D. Epulisu E. Syndrome Papiyona-Lefebvre 439. When treating gingivitis used indoor and outdoor treatments. Outdoor treatment is: A. Hardening gingival bandages B. * Intensive care without imposing gingival dressings C. Therapeutic gingival bandages D. Elektoforeziosteotropnyh drugs. E. There is no right answer 440. Which numeric value corresponds to the normal gingival sulcus depth? A. 1-1.5 mm B. 0.2-0.5 mm C. * 0.5-1 mm D. 2-3 mm E. 3-5 mm. 441. What is the cause of the ulcer-necrotic stomatitis? A. Periostitis B. * Perykoronaryt C. Periodontitis D. Caries E. Pulpitis 442. Gingivitis manifested form false pockets. Pocket defined by: A. Radiologically B. Morphologically C. Microscopically D. Histologically E. * Clinically 443. In which of the following diseases is most common ulcer-necrotic gingivitis: A. Syphilis B. Sugar diabetes C. Gastric D. Pyelonephritis E. * HIV 444. PMA index equal to 75%. Which severity of gingivitis meets this value? A. Very easy B. light C. average D. * Heavy E. very difficult 445. Bleeding during the initial stages of chronic catarrhal gingivitis appears: A. Without permission B. When eating C. * When the mechanical stress D. With a slight touch E. When brushing teeth 446. Which of the following gingivitis observed pronounced breath of sweet taste? A. Hypertrophic fibrous form B. Hypertrophic, puffy shape C. * Ulcer-necrotic D. Catarrhal E. Deskvamativny 447. Which of the following is used in the treatment of ulcerative-necrotic gingivitis as keratoplasty? A. Furatsillina B. Furadonin C. Peroxide D. Vagotilom E. * Sea buckthorn oil 448. Ulcer-necrotizing gingivitis well to treatment. However, no effect of treatment recommended a blood test: A. In sugar B. Biochemical C. C-reactive protein D. * The HIV E. In lactate dehydrogenase 449. According to the pathological changes that are gingivitis belongs to: A. * Inflammatory diseases B. Inflammatory and degenerative diseases C. Degenerative diseases D. Tumor diseases E. There is no right answer 450. The clinical picture of granulating form hypertrophic gingivitis occurs: A. Morbidity and rozpushenist gum B. Significant bleeding gums C. Pronounced gingival cyanosis D. Desquamation of the epithelium gingival papillae E. * All of the above 451. The clinical picture of ulcerative-necrotic gingivitis occurs: A. Pain gums B. Bad Breath C. Necrotic phenomena in the gums D. Enlargement of regional lymph nodes E. * All of the above 452. Patient undergoing treatment hypertrophic gingivitis. A time to repeat injection during deep sklerotyzatsiyi: A. Day B. * Week C. Month D. 1 time in 2 weeks E. 1 every three days 453. Patient undergoing treatment hypertrophic gingivitis. A time to repeat injection during surface sklerotyzatsiyivahotylom: A. * Day B. Week C. Month D. 1 time in 2 weeks E. 1 every three days 454. What is the minimum course of treatments with superficial sklerotyzatsiyivahotylom A. 6 days B. Week C. * 3 days D. Month E. 2 months 455. Surface application by Ovrutskom this: A. Applications vagotilom B. Applications celandine C. Applications glucose D. * Applications neotsydu E. Applications hlorfilipt 456. What course of treatments with superficial sklerotyzatsiyi celandine on Udovytska O. A. 20 procedures B. * 10 sessions C. 30 procedures D. 40 procedures E. 15 procedures 457. According topography - the anatomical structure of the alveolar part of the gums - is: A. Gingival papilla and gums around the tooth B. Naturally, the surrounding tooth C. * Clear, covering alveolar bone D. Gingival groove E. There is no right answer 458. The final phase of treatment of ulcerative gingivitis characterized using keratoplasty. Which of the following drugs belongs to this group: A. Trypsin B. Chymotrypsin C. Trihopol D. * Eugenol E. Chlorhexidine 459. In patients diagnosed with ulcerative-necrotic gingivitis. Clinical and morphological characteristics of a given zahvoryuyutsya occur due to: A. * Alteration and necrosis B. Proliferation C. Edema and inflammatory infiltration D. All answers are correct E. There is no right answer 460. Treatment of any disease has causal, pathogenetic and symptomatic therapy. Symptomatic therapy is: A. Medicamentous influence on pathophysiological links inflammation B. Identify and address local exogenous factors C. * Elimination of certain symptoms of periodontal disease D. There is no right answer E. All answers are correct 461. X-ray picture of acute catarrhal gingivitis medium severity: A. Cortical plate interdental septum rozrushena B. Cortical plate and bone interdental septum is preserved, osteosclerosis C. Loss of interdental bone septum ½ lengths on the roots of teeth D. * No changes E. There is no right answer 462. For which of these therapies used these drugs vagotilom, maraslavin, celandine? A. Causal treatment B. Pathogenetic therapy C. Symptomatic therapy D. * Sclerotherapy E. There is no right answer 463. In hypertrophic gingivitis perform operation hinhivektomiyi.Pid angle to the axis of the tooth hold the cut at this surgical intervention? A. 450 B. 500 C. * 600 D. 900 E. 300 464. A patient diagnosed with hypertrophic gingivitis (swelling form). Morphologically this zahvoryuvnnya shown: A. Fibroblast proliferation, parakeratosis phenomena B. * Vasodilatation, edema of the connective tissue elements C. Lymphocytic infiltration, coarsening of collagen fibers D. Vasoconstriction, acanthosis mucosa. E. All answers are correct 465. X-ray picture of acute ulcerative necrotic gingivitis light severity: A. * Cortical plate and bone interdental septum saved B. Cortical plate interdental septum is preserved, bone loss at 1/3 the length of the root C. Cortical plate interdental septum rozrushena, bone loss at ½ the length of the root D. All answers are correct E. There is no right answer 466. Surface sklerotyzatsiyi Udovytska the method is: A. Processing pockets vagotilom B. Processing pockets celandine and putting in your pocket honsurydu C. * Processing pockets celandine D. Processing pockets maraslavinom E. There is no right answer 467. A patient diagnosed with puffy shape hypertrophic gingivitis. Morphologically feature under persistent edema are: A. * Slowly disappearing recess in place of the pressure with a blunt object B. Thickening of collagen fibers C. Phenomena couple keratosis D. Proliferation of fibroblasts E. There is no right answer 468. Renthenolohina picture of acute catarrhal gingivitis is characterized by: A. Resorption top interdental partitions B. Serednovohnyschevym osteoporosis C. * No changes of bone D. Osteolizysom. E. All answers are correct 469. Patient delivered dentist diagnosed acute catarrhal gingivitis. What are the main complaints with the will of the patient: A. Swelling of the gums B. Pain C. Violation of chewing D. Bleeding E. * All answers are correct 470. Treatment of any disease has causal, pathogenetic and symptomatic therapy. Causal treatment is: A. * Medicamentous influence on pathophysiological links inflammation B. Identify and address local exogenous factors C. Eliminate some symptoms of periodontal disease D. There is no right answer E. All answers are correct 471. In the study of smears taken from surface ulcers in a patient with ulcerative necrotic gingivitis find: A. Staphylococci and spirochete B. * Spirochetes and fuzobakteriyi C. Fuzobakteriyi and lactobacilli D. Spirochetes and lactobacilli E. Lactobacillus and Staphylococcus 472. Patient delivered dentist diagnosis puffy form hypertrophic gingivitis. What are the main complaints with the will of the patient: A. Deformation gingival papillae B. Cutting congestion gingival papillae C. Swelling D. Bleeding E. * All answers are correct 473. Patient delivered dentist diagnosed fibrous form of hypertrophic gingivitis. What are the signs while the patient will: A. Elephantiasis gum B. Lack of bleeding C. Hyperplasia gingival papillae D. Roundness gingival papillae E. * All of the above 474. On examination, the patient was determined PMA index. Which severity of gingivitis will match the index of 31-60%? A. Very easy B. light C. * Average D. heavy E. very difficult 475. Morphologically all clinical signs in catarrhal gingivitis occur due to: A. Alteration and necrosis B. Proliferation C. * Edema and inflammatory infiltration D. All answers are correct E. There is no right answer 476. What formations occur in edematous form of hypertrophic gingivitis as a result of late edema and hyperplasia: A. Periodontal pockets B. Ulcers C. Syphiloma D. * Gingival pockets E. Papilloma 477. Which of the following diseases characterized by false pockets: A. Periodontitis B. Periodontal Disease C. * Hypertrophic gingivitis D. Epulisu E. Syndrome Papiyona-Lefebvre 478. When treating gingivitis used indoor and outdoor treatments. Outdoor treatment is: A. Hardening gingival bandages B. * Intensive care without imposing gingival dressings C. Therapeutic gingival bandages D. Elektoforeziosteotropnyh drugs. E. There is no right answer 479. Which numeric value corresponds to the normal gingival sulcus depth? A. 1-1.5 mm B. 0.2-0.5 mm C. * 0.5-1 mm D. 2-3 mm E. 3-5 mm. 480. Treatment of any disease has causal, pathogenetic and symptomatic therapy. Pathogenetic therapy is: A. * Medicamentous influence on pathophysiological links inflammation B. Identify and address local exogenous factors C. Eliminate some symptoms of periodontal disease D. There is no right answer E. All answers are correct 481. What is the cause of the ulcer-necrotic stomatitis? A. Periostitis B. * Perykoronaryt C. Periodontitis D. Caries E. Pulpitis 482. Gingivitis manifested form false pockets. Pocket defined by: A. Radiologically B. Morphologically C. Microscopically D. Histologically E. * Clinically 483. In which of the following diseases is most common ulcer-necrotic gingivitis: A. Syphilis B. Sugar diabetes C. Gastric D. Pyelonephritis E. * HIV 484. PMA index equal to 75%. Which severity of gingivitis meets this value? A. Very easy B. light C. average D. * Heavy E. very difficult 485. Bleeding during the initial stages of chronic catarrhal gingivitis appears: A. Without permission B. When eating C. * When the mechanical stress D. With a slight touch E. When brushing teeth 486. Which of the following gingivitis observed pronounced breath of sweet taste? A. Hypertrophic fibrous form B. Hypertrophic, puffy shape C. * Ulcer-necrotic D. Catarrhal E. Deskvamativny 487. Which of the following is used in the treatment of ulcerative-necrotic gingivitis as keratoplasty? A. Furatsillina B. Furadonin C. Peroxide D. Vagotilom E. * Sea buckthorn oil 488. Ulcer-necrotizing gingivitis well to treatment. However, no effect of treatment recommended a blood test: A. In sugar B. Biochemical C. C-reactive protein D. * The HIV E. In lactate dehydrogenase 489. On a glass plate physician mixed chloramphenicol, sulfadimezin, calcium gluconate, zinc oxide and vitamin E. What type of bandage is put on the patient? A. Netverdiyucha B. * Hardening C. Elastic D. Therapeutic E. There is no right answer 490. Hardening periodontal dressings zamishuyutsya to: A. Lanolin-petrolatum base B. Water C. Isotonic D. Impression materials E. * Oil solution 491. The structure of periodontal dressings must enter an antibacterial agent. Which of the following is included in this group? A. Methyluracil B. Calcium gluconate C. * Chloramphenicol D. Sulphadimezin E. Chlorhexidine 492. The value of health-protective dressings in treatment of periodontitis: A. Create conditions for stabilizing mobile teeth B. Leading to rapid cure periodontitis C. * Ensure a long-term effect of medicines on periodontal tissue and create conditions of calm in the affected area D. Warns of atrophic and hyperplastic processes in periodontal tissues. E. That's right 493. According to the method of curing periodontal dressings are divided into: A. Therapeutic and insulating B. Isolation and elastic C. * Elastic, hardening and netverdiyuchi D. Thermal and elastic E. Hardening and netverdiyuchi 494. On a glass plate doctor mixed in equal proportions methyluracil, metrogil and zinc oxide to rare - plastic consistency. What type of bandage is put on the patient? A. Elastic B. Hardening C. * Netverdiyucha D. Therapeutic E. There is no right answer 495. At what minimum time imposed medical gingival dressing? A. At 2:00 B. B. * The period during which inhibited the growth of pathogenic organisms C. At 4:00 D. At the time allocation therapeutic dose ingredient. E. That's right 496. Elastic bandages periodontal zamishuyutsya to: A. Oil solution B. Water C. Isotonic D. * Impression materials E. Eugenol 497. How long after blending is correction dressings in the mouth? A. After 1 Guolin B. After 2-3 hours C. * After 15-20 minutes D. After 40 minutes E. Not held 498. Absolute contraindications to the use of the closed method of treatment of periodontal inflammation: A. Severe hypersensitivity hard tissues B. * Availability of dental plaque C. The presence of erosive and ulcerative lesions D. Significant purulent discharge from the periodontal pockets E. Acute course of the inflammatory process in the periodontium. 499. Hardening periodontal dressings imposed on: A. * 5-6 days B. 2-3 hours C. 1 week D. 10 days E. 14 days 500. Netverdiyuchi periodontal dressings imposed on: A. 5-6 days B. * 2-3 hours C. 1 week D. 10 days E. 14 days 501. Netverdiyuchi periodontal dressings zamishuyutsya to: A. * Lanolin-petrolatum base B. Water C. Isotonic D. Impression materials E. Oil solution 502. On a glass plate doctor mixed in equal proportions methyluracil, metrogil and upin. What type of bandage is put on the patient? A. Netverdiyucha B. Hardening C. * Elastic D. Therapeutic E. There is no right answer 503. How many groups are divided periodontal dressings on curing method? A. 4 B. 5 C. 6 D. 2 E. * 3 504. The structure of periodontal dressings must enter sulfanilamides. Which of the following is included in this group? A. Chloramphenicol B. Calcium gluconate C. * Sulphadimezin D. Tetracycline E. Chlorhexidine 505. What drugs are used to stimulate epiteleutvorennya with gingivitis? A. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory B. Antiseptics C. * Keratoplasty D. Immunomodulators E. Proteolytic enzymes 506. Which of the following drugs are used as a means nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory in the treatment of catarrhal gingivitis? A. Furatsillina B. Peroxide C. Chlorhexidine D. Yodinola E. * Mefenaminat sodium 507. Which of the following applies antiseptic to nitrofuran drugs? A. Peroxide B. Yodinola C. Potassium permanganate D. * Furatsillina E. There is no right answer 508. Drugs which groups used in the final stage of the treatment of ulcerative gingivitis: A. anesthetics; B. enzymes; C. sulfonamides; D. * Keratoplasty; E. no correct answer. 509. Which of the following antiseptic with prolonged use causes overgrowth? A. Peroxide B. Yodinola C. Potassium permanganate D. Furatsillina E. * Chlorhexidine 510. Which of the following groups of drugs used to facilitate the rejection of necrotic tissue? A. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory B. Antiseptics C. Anesthetic D. Immunomodulators E. * Proteolytic enzymes 511. Which of the following drugs used in the final stage of treatment vyrazk.hinhivitu: A. trypsin; B. chymotrypsin; C. trihopol; D. * Sea buckthorn oil; E. no correct answer. 512. Symptomatic therapy is: A. Medicamentous influence on pathophysiological links inflammation B. Identify and address local exogenous factors C. * Elimination of certain symptoms of periodontal disease D. There is no right answer E. All answers are correct 513. Pathogenetic therapy is: A. * Medicamentous influence on pathophysiological links inflammation B. Identify and address local exogenous factors C. Eliminate some symptoms of periodontal disease D. There is no right answer E. All 514. Depending on the nature of the process, the causes and mechanisms of development of periodontitis treatment may be: A. Causal B. Pathogenetic C. Symptomatic D. Pathogenetic combined with symptomatic E. * All answers are correct 515. Treatment of periodontal disease should be directed to: A. Elimination of inflammation in periodontal B. Strengthening overall health C. Increasing the body's defenses D. Removing the causes of disease E. * All answers are correct 516. Regardless of the form and stage of the pathological process in periodontal topical treatment begins with: A. * Thorough removal of dental plaque B. Appointment of antibiotics C. Treatment of somatic pathology D. Appointment of antihistamines E. Conducting correction of the gastrointestinal tract 517. Local treatment of periodontal disease include: A. Elimination of defects fillings and prosthetics B. Clinical observation of the patient C. * That's right D. Consultation gastroenterologist E. Consultation endocrinologist 518. Local treatment of periodontal disease include: A. Remove excess filling material from interdental spaces B. Removing improperly manufactured dental bridges C. Removal of crowns that go deep under the gums D. Timely replacement E. * That's right 519. Contraindications to the use of immunotherapy: A. Cardio - vascular insufficiency B. Leukemia C. Mental Illness D. * All of the above is true E. Neoplasm 520. General treatment of periodontitis include: A. Treatment of somatic pathology B. Regulation of reactivity C. Generall therapy D. Activation of metabolic processes E. * All of the above is true 521. Treatment somatic diseases carried by dentists with: A. Gastroenterologist B. Neurologist C. Cardiologist D. Endocrinologist E. * All the experts 522. In terms of antimicrobial treatment for acute periodontitis with symptoms of abscess designate A. Vitamins B. Tranquilizers C. Hormones D. * Antibiotics E. Stimulants 523. Which course of drug treatment Biosed that is a biogenic stimulator? A. 5.1 Injection B. 2 injections C. * 25-30 injections D. 20 injections E. 30 injections 524. How many injections provides treatment Plasmol? A. 2 B. 5 C. 7 D. * 10 E. 15 525. Immunal - is: A. * Immunomodulators of plant origin B. Biogenic stimulator C. Antihistamine D. Antibiotic E. Steroidal anti-inflammatory drug 526. Diet therapy consisting of combined treatment of periodontitis are: A. * Mandatory B. Optionally C. Partially necessary D. In certain cases E. There is no right answer 527. What drug is prescribed to patients with periodontitis and concomitant hypertension 1 degree? A. Tavegil B. Suprastin C. * Clonidine with hypothiazide D. Levamisole E. Clotrimazole 528. In what year D.Ye.Kindiy and R.U.Anischenko proposed treatment of periodontitis in patients with chronic gastritis by a special scheme A. 1,901 B. * 1990 C. 1,932 D. 1,963 E. 1,978 529. Who of the research results the authors developed a special scheme for treatment of periodontitis in patients with chronic gastritis A. * D.Ye.Kindiy and R.U.Anischenko B. E.V.Borovskyy C. Yu.M.Maksymovskyy D. V.S.Ivanov E. V.F.Danylevskyy 530. Who are the scientists proposed a method of treatment in patients with periodontitis y diabetes using medical paast Clotrimazole - Troxevasin - insulin? A. * T.M.Kozub B. D.E.Kindiy C. R.I.Anischenko D. V.I.Kalinin E. E.V.Borovskyy 531. Sulfanilamide drugs prescribed for: A. Mild periodontitis B. * Exacerbative periodontitis, which is accompanied by fever and symptoms of intoxication C. Localized periodontitis D. Periodontitis medium severity E. In remission 532. Application sulfanilamides conduct: A. Under the supervision reoparoontohrafiyi B. Under the control of X-ray C. * A dynamic control of clinical blood D. Under the control of urinalysis E. There is no correct answer 533. Which of the below listed drugs is not an antibiotic? A. Rovamitsyn B. Rondomitsyn C. * Levamisole D. Lincomycin E. Penicillin 534. Patients with aggressive forms of periodontitis, women with periodontal zaahvoryuvannyamy against menopause prescribe medication Fosfamaks: A. * On 1 tab. daily for 6 months B. At 3 tab. daily for 6 months C. At 2 tab. daily for 6 months D. On 1 tab. a day for 1 - year E. On 1 tab. per day for 1 - month 535. Effects of the drug Fosfamaks in the treatment of periodontitis is: A. Osteoklastychnoyi decrease bone resorption B. Improve bone mineral density by 8-12% C. Stimulation of reparative osteogenesis alveolar bone D. * Improvement of bone E. All of the above is true 536. What is the main biological effect of calcitonin? A. Stimulation of metabolism B. * Inhibition of bone resorption by inhibiting osteoklastychnoyi activity and reduce the number of osteoclasts C. Reduced permeability and capillary fragility D. Speeds up wound healing E. It stimulates the production of antibodies 537. What is the daily requirement of vitamin B15 for adults with periodontal disease? A. 10-20 mg B. 5-10 mg C. 100-200 mg D. 200-300 mg E. * 100-300 mg 538. What is the daily requirement for vitamin B12 in the treatment of periodontal disease? A. : In B. 10-20 mg C. * 0.01-0.02 mg D. 0.5 - 0.7 mg E. 20-30 mg 539. When treating patients with periodontitis vitamins are usually administered in stock: A. * Multivitamin preparations B. Antihistamines C. Hormonal drugs D. E. 540. A. B. C. D. E. 541. A. Antibacterials Immunomodulatory drugs When generalized periodontitis treatment multivitamin preparations is: 5-6 weeks 2 months 6 months * 3-4 weeks 4 months The indications for the use of vitamin U (metylmetioninsulfaniyu chloride) are: * Generalized periodontitis, which occurs against the background of the alimentary canal B. Generalized periodontitis that occurs on the background of diseases of the cardiovascular system C. Generalized periodontitis medium severity D. Localized periodontitis E. Periodontal Disease 542. Treatment immunomodulating drugs conducted: A. * Under the control of immunological parameters B. Under the supervision of a general analysis of blood C. Do not hold control parameters D. Under the control of biochemical analysis of blood E. Under the supervision zahaalnoho urinalysis 543. Curative treatment the drug Miakaltsyk peredbachaaye its intranasal administration of 1 dose. How many DoD active substance contained in 1 dose of this drug? A. 500 IU B. * 200 IU C. 300 IU D. 400 IU E. 100 IU 544. Miakaltsyk drug has the following effect: A. Regulates calcium homeostasis B. Regulates bone metabolism C. Has anti-inflammatory effect D. Has aanalhetychnu and antihistamine action E. * All of the above is true 545. Which way the drug Miakaltsyk? A. Intralihamentarno B. Orally C. * Intranasal D. Subcutaneous E. Intramuscular 546. What are the possible side effects in patients using the drug at Miakaltsyk? A. Redness of skin B. Headache C. Dizziness D. * All possible E. Nausea 547. What are the contraindications to the drug Miakaltsyk? A. Reduced reactivity B. Hypersensitivity to the drug and hypocalcemia C. Reduced sensitivity to the drug D. Hypercalcemia E. * That's right 548. What is the effect of the drug Miakaltsyk in treatment of generalized periodontitis in acute A. Normalizes bone metabolism and skeletal alveolar bone B. Inhibits bone resorption interdental membranes C. Stimulates processes reosyfikatsiyi D. Promotes clinical stabilization of the pathological process in the periodontal tissues E. * All of the above is true 549. Symptomatic treatment prodonta includes: A. Pain relief B. Treatment hyperesthesia of hard tissues of teeth C. * Eliminating local travmuyuchchyh factors D. That's right E. Selective pryshlifovuvannya teeth 550. Daily requirement for vitamin E in the treatment of periodontal disease are: A. 100 - 200 mg B. 50-100 mg C. * -20 Mg D. 50-60 mg E. 10-15 mg 551. The daily requirement of vitamin B5 for the treatment of periodontitis is: A. 200 mg B. 100 mg C. 150 mg D. * 10-12 mg E. 60-70 mg 552. The daily requirement of vitamin B6 for the treatment of periodontitis is: A. * 2-2.5 mg B. 20-30 mg C. 40-50 mg D. 30-40 mg E. 10-20 mg 553. Drug Korberon are: A. * Drug fluoride B. Calcium supplementation C. Potassium preparations D. Enzyme preparations E. Antibacterials 554. What group of drugs belonging Ossyn: A. Groups of drugs that regulate calcium homeostasis B. Groups of drugs with antyrezorbtsiynoyu action C. * Groups of drugs that stimulate bone formation D. Antiviral drugs E. Antifungal drugs 555. Korberon drug belongs to: A. Prytyhrybkovyh drugs B. Groups of drugs with antyrezorbtsiynoyu action C. * Groups of drugs that stimulate bone formation D. Antiviral drugs E. Antifungal drugs 556. Pathogenetic treatment of periodontal disease include: A. Anti-inflammatory treatment B. The effect on local factors regulating bone resorption alveolar bone C. The effect on local factors of bone resorption D. Incentive processes of reparative regeneration of periodontal tissue E. * All answers are correct 557. Kaltsemin - a drug that belongs to the: A. * Drugs that regulate calcium homeostasis B. Antiviral drugs C. Antiprotozoa drug D. Groups drug VZ antyrezorbtsiynoyu action E. Groups of drugs that stimulate bone formation 558. Etiotropic treatment of periodontal disease include: A. Removal of dental plaque B. Normalization oral cavity and gastro - intestinal tract C. Antibiotic therapy D. Treatment of somatic pathology with other medical specialties E. * All of the above is true 559. Contraindications to the use of immunotherapy: A. Cardio - vascular insufficiency B. Leukemia C. Mental Illness D. Neoplasm E. * All answers are correct 560. The daily requirement of vitamin B2 are: A. 5-6 mg B. * 2.5-3mg C. 11-15 mg D. 120-130 mg E. 1-3mg 561. Patients aged 22 years treats acute periodontitis. What is the treatment of periodontitis has primarily to be? A. Symptomatic B. Pathogenic C. * Etiotropic D. Orthopaedic E. Drug 562. The aim of local treatment of periodontitis is: A. Normalization of the microflora of the digestive system B. Stimulation of the functional activity of the salivary glands C. Treatment of physical and odontogenic infection D. * Eliminating annoying factors, removing inflammation, normalize blood circulation in the periodontal tissues E. All answers are correct 563. General therapy of patients with periodontitis directed to: A. Eliminating irritating factors B. Normalization of blood circulation in the periodontal tissues C. * Normalization reactivity organisms and regenerative processes of periodontal tissues, treatment of somatic pathology D. Treatment of odontogenic infection E. Nutrition 564. Start topical treatment of periodontitis: A. Antibiotic B. Splinting of teeth C. Installations antiseptic intermediaries D. * Elimination of dental accretions defective orthopedic constructions E. Anti-inflammatory therapy 565. Which of the following methods do not consider the methods of removing and pidyasenevoho tartar. A. Mechanical B. Chemical C. Physical D. Combined E. * Biological 566. What tools are used for mechanical removal method over and pidyasenevoho tartar? A. Scalers. B. 15% solution of EDTA C. Saturated solution of hydroquinone D. * Sickle hooks E. 5% solution of ascorbic acid, 567. What tools are used in chemical methods of removal and pidyasenevoho tartar? A. Scalers. B. * 15% solution of EDTA C. Rashpilni Smoothers D. Sickle hooks E. Excavators 568. What tools are used for physical removal method over and pidyasenevoho tartar? A. * Scalers. B. 15% solution of EDTA C. Rubber cup using pastes D. Sickle hooks E. 5% solution of ascorbic acid, 569. Which of the following tools is used for mechanical removal method over and pidyasenevoho tartar? A. Rubber cup using pastes B. Rashpilni Smoothers C. C. * scalers D. Excavator E. Sickle hooks 570. Which of the following vehicles are not used in the chemical method of removing and pidyasenevoho tartar? A. 5% solution of citric acid. B. 15% solution of EDTA C. Saturated solution of hydroquinone D. * Rubber cup using pastes E. 5% solution of ascorbic acid, 571. Patients aged 33 years treats acute periodontitis. The doctor plans to Application anesthesia. What preparation of the following are the most appropriate to use? A. 3-5% solution of sodium salicylate B. B. * 5-20% oily solutions anestezina C. 1% solution of potassium permanganate D. 0.2% hlorheksedynu bigluconate E. 1% trihopolom 572. PATIENTS '35 treats acute periodontitis. The doctor plans to Application anesthesia solution of propolis and dikaina. What preparation of listed below should be added to potentiation of anesthesia? A. * Dimeksida B. Hlorheksedyn C. 0.1% epinephrine D. Diphenhydramine E. Trihopol 573. PATIENTS '42 treats acute periodontitis. The doctor plans to Application anesthesia butadionovoyu 5% ointment, which group related drugs phenylbutazone? A. Steroidal anti-inflammatory B. Narcotic analgesics C. * Non-narcotic analgesics D. Local anesthetic, esters E. Local anesthetic, amides 574. On admission clinical periodontal patient doctor plans to Application anesthesia 5% solution of sodium salicylate which group drugs include sodium salicylate? A. Narcotic analgesics B. Steroidal anti-inflammatory C. Local anesthetic, esters D. * Non-narcotic analgesics E. Local anesthetic, amides 575. On admission clinical periodontal patient doctor plans to anesthesia. From history we know that the patient is allergic to volatile anesthetics that drug from listed below should be used in this clinical situation? A. Procaine. B. Novocaine. C. Dikain. D. Anestezin. E. * Mepivakayin. 576. On admission clinical periodontal patient doctor plans to spend 10% pain relief ointment oil solution anestezina which group drugs include benzocaine? A. Narcotic analgesics B. * Local anesthetic esters C. Steroidal anti-inflammatory D. Local anesthetic, amides E. Non-narcotic analgesics 577. Periodontal patient doctor plans to apply for pain solution narcotic analgesics, the below listed products belongs to this group A. * Mefenamova acid B. Dikain C. Mepivakayin D. Articaine E. Salicylic acid 578. Periodontal patient doctor plans to apply for anesthesia ester local anesthetic agent of the below listed products belongs to this group A. Mefenamova acid B. * Dikain C. Mepivakayin D. Salicylic acid E. Articaine 579. Periodontal patient doctor plans to apply for pain medication amide local anesthetic agent of the below listed products belongs to this group A. Dikain B. Mefenamova acid C. Novocaine D. * Articaine E. Salicylic acid 580. Periodontal patient doctor plans to use anesthesia. Which of the below listed biogenic stimulants have anesthetic effect. A. Aloe B. Juice of Kalanchoe C. * Propolis D. SOLCOSERYL E. Aktovehil 581. When hyperesthesia naked neck teeth or exposed roots covered: A. * Fluoride varnish B. Lidokayinovym spray C. Novocaine D. Crowns E. Dentin for bandages 582. What drugs should be used a woman 40 years at the final stage of treatment of ulcernecrotic gingivitis moderately. A. Keratolityky B. * Keratoplasty C. Vitamins D. Proteolytic enzymes E. Antibiotics 583. During microscopic examination content periodontal pockets patient showed symbiosis fuzobakteriy and trichomonads which drug the following to apply for this patient? A. Lincomycin B. Ribonuclease C. * Metronidazole D. Nimesulide E. Chloramphenicol 584. What organic acid from the following acids using pre-softening mineralized plaque to facilitate their removal: A. * Lemon B. Peroxide C. Salt D. Bourne E. Salicylic 585. When exposed necks of teeth and appearance hyperesthesia appoint electrophoresis: A. Potassium iodide and dikaina B. Dimeksida, fluorine and vitamin. PP C. Dikainom, calcium and vitamin. B1 D. * Calcium and fluorine, novocaine and vitamin. B1 E. Dimeksida, potassium iodide 586. When severe bleeding and stagnation in the gums recommended electrophoresis A. Potassium, Vit. C and P B. Potassium iodide C. * Calcium, vitamin C and P D. Vit. A & E E. Calcium chloride. 587. In patients aged S0 years diagnosed with acute ulcerative gingivitis moderately. Which drugs should be applied to remove necrotic plaque: A. Solution furatsilinom B. * Iruksol C. A solution of hydrogen peroxide D. A solution of potassium permanganate E. Chlorhexidine solution? 588. A patient aged S0 years diagnosed with acute ulcerative gingivitis moderately. Drugs which group to apply the final stage of the treatment of this disease: A. Keratolytic B. Antibiotics C. Antioxidants D. * Keratoplastychni E. Proteolytic enzymes? 589. Periodontal patient planning to apply for instillation of periodontal pockets antiseptic herbal the below listed antiseptics in this case should be used? A. Furatsillina B. * Khlorophilipt C. Chlorhexidine D. Hypochlorite E. Chloramine 590. Edema form of hypertrophic gingivitis doctor plans to use decongestants and caustic agents such as instillation that preparations listed below should be used? A. * Vagotilom, dimeksid B. Hypochlorite, iodine C. Chlorhexidine, alcohol D. Salicyl alcohol, EDTA E. Aloe, hypochlorite 591. Periodontal patient planning to use sclerotherapy that preparations listed below should be used? A. * 50% glucose, novembyhin B. Calcium, Aloe C. Potassium aloe D. Vit. B1, iruksol E. Vit. D, zinc oxide 592. On a glass plate physician mixed chloramphenicol, sulfadimezin, calcium gluconate, zinc oxide and vitamin E. What type of bandage is put on the patient? A. Netverdiyucha B. * Hardening C. Elastic D. Therapeutic E. There is no right answer 593. Hardening periodontal dressings zamishuyutsya to: A. Lanolin-petrolatum base B. Water C. Isotonic D. Impression materials E. * Oil solution 594. The value of health-protective dressings in treatment of periodontitis: A. Create conditions for stabilizing mobile teeth B. Leading to rapid cure periodontitis C. * Ensure a long-term effect of medicines on periodontal tissue and create conditions of calm in the affected area D. Warns of atrophic and hyperplastic processes in periodontal tissues. E. That's right 595. According to the method of curing periodontal dressings are divided into: A. Therapeutic and insulating B. Isolation and elastic C. * Elastic, hardening and netverdiyuchi D. Thermal and elastic E. Hardening and netverdiyuchi 596. On a glass plate doctor mixed in equal proportions methyluracil, metrogil and zinc oxide to rare - plastic consistency. What type of bandage is put on the patient? A. Elastic B. Hardening C. * Netverdiyucha D. Therapeutic E. 597. A. B. C. D. E. 598. A. B. C. D. E. 599. A. B. C. D. E. 600. A. B. C. D. There is no right answer At what minimum time imposed medical gingival dressing? At 2:00 * The period during which inhibited the growth of pathogenic organisms At 4:00 At the time allocation therapeutic dose ingredient. That's right How long after blending is correction dressings in the mouth? After 1 hour After 2-3 hours * After 15-20 minutes After 40 minutes Not held Elastic bandages periodontal zamishuyutsya to: Oil solution Water Isotonic * Impression materials Eugenol Osteolizys this: Pathological process, accompanied by a decrease in bone trabeculae per unit volume Pathological process, accompanied by functional and structural changes ZSCHS Pathological process, accompanied by an increase in bone trabeculae per unit volume * Pathological process, accompanied by complete resorption of the bone without any manifestations of its replacement E. There is no right answer 601. Objective simple hinhivektomiyi? A. Correction of defects of the alveolar process of the jaws B. * Elimination of periodontal pocket = C. Conducting vacuum curettage D. Holding open curettage E. Eliminate bone pocket 602. Disadvantages hinhivektomiyi operations are: A. hyperesthesia bare roots to thermal stimuli B. cosmetic defect after removal of gingival papillae C. necks baring teeth D. hyperesthesia bare roots to chemical stimuli E. * All of the above is true 603. Hinhivotomiya - is: A. Removing ash to a depth of periodontal pockets B. * Autopsy gum C. Open curettage D. Stool periodontal abscess E. Disclosure of a single deep periodontal pockets 604. Determination of traumatic occlusion carried out using: A. Iodine solution B. Magenta C. * Wax plates D. Desmodometra E. Ehoosteometra 605. In what year was clinically proven ability periodontal relationships grow into the space between the membrane and the surface of the root A. 1,982 B. 1,981 C. D. E. 606. A. B. C. D. E. 607. A. B. C. D. E. 608. A. B. C. D. E. 609. A. B. C. D. E. 610. A. B. C. D. E. 611. A. B. C. D. E. 612. A. B. C. D. E. 613. A. B. C. 1,985 D. * 1984 1,990 Indications for use of the method of selective pryshlifovuvannya teeth: Detection of premature tooth contacts in the central occlusion Installing premature contacts and the presence of contacts only some teeth when closing the jaws in any of the 4 occlusions Lack of contact between groups of teeth-antagonists Establishing contacts with premature closing of the jaws in the lateral and central occlusion. * All of the above is true Removing tartar pid'yasennoho conduct: By curettage of periodontal pockets * During curettage of periodontal pockets After the curettage pockets A week before curettage There is no right answer Kalamkari recommended to detect and eliminate premature contacts in position: Only the central occlusion Central and distal Distal and anterior Central and anterior * In all three positions occlusion Curettage procedure recommended not more than: 4 times a year 5 times a year * 2 times a year 3 times a year 1 every year What limited number of teeth operation hinhivektomiyi in the side area? * 3.2 4.6 6.8 2.1 4.3 The advantages of vacuum curettage is: opportunity to process deeper pockets opportunity to process bottom gingival pocket and adjacent bone visual inspection complete curettage relatively bloodless operative field * All of the above is true What are the basic principles of sampling with grinding teeth? Zishlifovuvannya tissues within the thickness of the enamel layer, narrowing the chewing surfaces, while providing expressiveness equator; Zishlifovuvannya hard tissue on the occlusal surface is not made in the teeth, which are the backbone that hold interalveolar distance Teeth - antagonists in central occlusion should keep multiple buhorkovi - fisurnyy contact. Consider the position of teeth not only in the central occlusion * All answers are correct The literature curettage operation is called: Real Viydmana-Neumann Real-Viydmana Tseshynskoho Real Tseshynskoho-Neumann D. E. 614. A. B. C. D. E. 615. A. B. C. D. E. 616. A. B. C. D. E. 617. A. B. C. D. E. 618. A. B. C. D. * Method Jünger-registrar Real Znamenskoye Local therapy of periodontal disease include: Training (control) patients the right care for your teeth. Eliminating local irritating factors. Treatment of systemic hyperesthesia, increased abrasion of hard tooth tissues. Local application means that improve the trophic and microcirculation. * All answers are correct Indications for the kriokyuretazhu are: Periodontal pocket depth of 5-7 mm Hypertrophic gingivitis Severe gum hypertrophy in periodontitis Periodontal pockets with significant granulation * All of the above is true Over time passes epithelization operated sites at diathermocoagulation? 7 days 21 days * For 10 - 14 days Over 20 days 30 days Which of the following is the manipulation stages patchwork operation? vidseparuvannya muco-oxide flap of vestibular and language (palate) sides cutting edge modified gums, granulation, and curettage C. mobilization of mucous-oxide graft, stop bleeding suture in each interdental spaces and vertical sections * All of the above is true What requirements must comply with barrier membrane? have tissue integration be impermeable to cells maintain prolonged action to regenerate new tissue D. inflammatory reaction that accompanies biorezorbtsiyu these membranes should be minimal and reversible E. * All of the above is true 619. With deep pockets of more than 5 mm is advisable to: A. * Loskutnu operation B. Vacuum curettage C. Closed curettage D. Open curettage E. Kriokyuretazh 620. Osteodystrophy is: A. Pathological process, accompanied by a decrease in bone trabeculae per unit volume B. * Pathological process, accompanied by functional and structural changes ZSCHS C. Pathological process, accompanied by an increase in bone trabeculae per unit volume D. Pathological process, accompanied by complete resorption of the bone without any manifestation of its replacement E. There is no right answer 621. Patient M., 32 years old need to curettage gingival and periodontal pockets. The criterion of efficiency curettage gingival and periodontal pockets in the implementation are: A. Lack pid'yasennoho tartar B. * Lack of severe bleeding, lack pid'yasennoho tartar, granulation and epithelial vrosshoho C. Complete absence of bleeding D. Clear tightly to the teeth E. 622. A. B. C. D. E. 623. A. B. C. D. E. 624. A. B. C. Lack of granulation and epithelial vrosshoho Objective scrappy operations periodontium: Eliminate inflammation and inhibition of degeneration of periodontal tissue * Elimination of periodontal pockets and correction of defects in alveolar bone Eliminate bone pockets and stimulation of trophic disorders All answers are correct There is no right answer The degree of traumatic occlusion is defined by: Odontoparodontohramy Panoramic x-rays * Oklyuzohramy Elektrorenthenohramy Telerenthenohrafiyi Temporary splinting is done to: Stabilization of mobile teeth before the permanent prosthesis * Immobilization mobile teeth during therapeutic and surgical treatment Creating conditions gingival fixing bandages for highly mobile and lonely standing teeth D. Destabilization of moving teeth before surgery. E. There is no right answer 625. What drug is held neutralization hlornovatystokysloho sodium in periodontal pockets? A. 5% solution of acetic acid B. 5% solution of phosphoric acid C. * 5% citric acid solution D. 5% solution of hydrochloric acid E. 5% solution of nitric acid 626. In one class of premature contacts on Jankelson include: A. * Premature contacts on the vestibular surfaces of the buccal hillocks lower lateral vestibular surface of the teeth and lower front teeth. B. Contacts on oral surfaces hillocks upper palatal lateral teeth. C. Premature contacts on the vestibular surfaces of palatal tubercles upper lateral teeth. D. Premature contacts on the cutting edge E. All answers are correct 627. Jankelson recommended to detect and eliminate premature contacts in position: A. * Only the central occlusion B. Central and distal C. Distal and anterior D. Central and anterior E. In all three positions occlusion 628. With deep pockets to 4 mm is advisable to: A. Loskutnu operation B. Loskutnu deal with osteoplastic yaterialiv C. * Closed curettage D. Open curettage E. By directing tissue regeneration 629. What incisions performed at flap operation? A. Continuous hirlyandopodibnyy cut B. Oblique incision interdental papillae C. Two vertical incisions in the direction of the transition folds on top of interdental papillae D. * Two vertical incisions in the direction of the transition folds passing interdental papillae E. There is no right answer 630. Interval between curettage various groups of teeth is: A. 1-2 days B. * 2-3 days C. 3-4 days D. 5-6 days E. 10 days 631. In the course of local therapy in the treatment of periodontal disease systemic hyperesthesia use: A. * Electrophoresis 2% solution of sodium fluoride B. Electrophoresis solution vitamin D C. Electrophoresis Tren tal D. Electrophoresis AESCUSAN E. Electrophoresis maraslavinu 632. When performing open curettage conduct: A. oblique incision interdental papillae to the bottom pocket only vestibular side B. oblique incision interdental papillae to the bottom pocket only Oral C. * Oblique incision interdental papillae to the bottom pockets on both sides D. hirlyandopodibnyy cut gums E. vertical incision papillae of Oral 633. Who is the world's first operation applied curettage? A. Junger B. Registrar C. Znamensky D. * Rigg E. Tseshynskyy 634. Who first proposed the use of chemical curettage surgery? A. Junger B. Registrar C. * Kenny D. Rigg E. Tseshynskyy 635. What made treatment of hard tissues of teeth with kriokyuretazhi to prevent their damage? A. Eugenol B. Sea buckthorn oil C. Vitamin E D. * Vaseline E. Metrogyl-Dent 636. Time coagulation in the treatment of periodontal pockets is: A. 1-2 sec. B. 30 seconds. C. * 02.04 sec. D. 5-10 seconds. E. 20-40 sec. 637. Orthodontic treatment of periodontal disease is aimed at solving specific problems, namely: A. * Removal of traumatic occlusion B. eliminate abnormal motion C. prevent displacement of teeth D. combining into a single unit all teeth E. all of the above is true 638. Because of time spend removing nerozsmoktuyuchyh membranes? A. After 2 weeks B. After 3 weeks C. After 5 weeks D. After 6 weeks E. * After months of 639. Your tactics in the first 24-48 hours after an kriokyuretazhu periodontal pockets: A. Assign spray with halaskorbinom 6-8 times a day B. Hold intensive processing antiseptic C. Circulation insulating periodontal bandage D. * Apply enzymes and antibiotics E. There is no right answer 640. In a simple operation carried hinhivektomiyi excision of gum at a certain depth of periodontal pockets, namely: A. At ½ pocket depth B. At 1/3 the depth of the pocket C. At 2/3 the depth of the pocket D. * At the depth of the pocket E. There is no right answer 641. The basic principles curettage are: A. complete anesthesia operated tissues; B. careful attitude to the tissues in the area of manipulation: C. organization of blood clot and his defense: D. perfect compliance with the rules of hygiene in the postoperative period. E. * All answers are correct 642. In the treatment of periodontal disease carried hyperbaric oxygenation. This method involves: A. * Introduction submucous transitional folds 5 ml of oxygen B. Introduction submucous transitional folds 10 ml of oxygen C. Introduction submucous transitional folds trypsin D. Introduction submucous transitional folds prodektynu E. Introduction submucous transitional folds mevakoru 643. Over time passes epithelization operated sites at kriokyuretazhi? A. 7 days B. 21 days C. * For 14 days D. 10 days E. 30 days 644. The goal of periodontal surgery: A. Anti-inflammatory and desensitizing effect B. Removal of foci intoxication C. * Elimination of periodontal pockets and creating conditions for the stabilization process in the periodontal tissues D. Creating the conditions for the regeneration of alveolar bone. E. There is no right answer 645. In Class 2 premature contacts on Jankelson include: A. Premature contacts on the vestibular surfaces of buccal hillocks lower lateral vestibular surface of the teeth and lower front teeth. B. * Contacts on oral surfaces hillocks upper palatal lateral teeth C. Premature contacts on the vestibular surfaces of palatal tubercles upper lateral teeth. D. Premature contacts on the cutting edge E. All answers are correct 646. Osteosclerosis is: A. Pathological process, accompanied by a decrease in bone trabeculae per unit volume B. Pathological process, accompanied by functional and structural changes ZSCHS C. * Pathological process, accompanied by an increase in bone trabeculae per unit volume D. Pathological process, accompanied by complete resorption of the bone without any manifestation of its replacement E. There is no right answer 647. In the presence of abnormal mobility of teeth to create a calm periodontal tissues using: A. Closed curettage B. Selective pryshlifuvannya C. Suction curettage D. Loskutnu operation E. * Temporary splinting 648. Which of the following is the manipulation stages curettage? A. processing operating margins yodvmisnymy solutions B. remove tartar and tooth damaged cement C. deepithelization pocket D. curettage of bone edge alveoli E. *all answers are correct 649. What limited number of teeth operation hinhivektomiyi in frontal area? A. 2.3 B. * 4.6 C. 6.8 D. 2.1 E. 4.3 650. In what year was the first held scraping content periodontal pockets? A. 1,892 B. 1,902 C. 1,909 D. * 1867 E. 1,899 651. In what year was the first operation conducted chemical curettage? A. * 1981 B. 1,902 C. 1,971 D. 1,867 E. 1,899 652. Methods of treatment of periodontal disease: A. Anti-inflammatory and desensitizing therapy B. Surgical treatment and cryotherapy C. * Osteotropic and remineralization therapy D. Sclerotherapy E. Antibacterial and immunostimulatory therapy. 653. Purpose curettage? A. Remove vrostayuchi strands of epithelium B. The elimination of periodontal pockets C. * Erasing periodontal pocket D. Create conditions for anti-inflammatory therapy E. Remove abnormal granulation 654. What temperature creates a cryoprobe in periodontal pockets during kriokyuretazhi? A. * -60 - 1400S B. -20 - 1000 C C. -50 - 800 C D. - 45 - 1050 C E. - 140 - 2200 C 655. Exposure time cryoprobe is: A. 50 seconds. twice with an interval of 5 minutes B. C. D. E. 656. A. B. C. * 30 sec. twice with an interval of 5 minutes 10 seconds. twice with an interval of 5 minutes 40 seconds. twice with an interval of 5 minutes 20 seconds. twice with an interval of 5 minutes That includes a preoperative preparation before the flap operation for 2-4 weeks? teaching oral care elimination of traumatic occlusion C. conservative treatment of periodontitis, after which the surgery is carried out not earlier than 2 weeks and not later than 3 months D. dental health: replacement of substandard seals E. * All of the above is true 657. Temporary bus must meet certain requirements, such as: A. evenly distribute pressure on carts chewing teeth B. not interfere medicamentous and surgical treatment C. not to injure the mucosa D. reliably capture all moving teeth E. * All of the above is true 658. What is the role of biological membranes? A. create the possibility of regeneration for periodontal ties B. prevent apical migration of epithelium C. restrict the germination of gingival tissue in the defect area D. create the possibility of regeneration of the adjacent alveolar bone E. * All of the above is true 659. How many groups are divided calcium supplements that are used in the treatment of periodontal zayihvoryuvan? A. 2 B. 4 C. 5 D. * 3 E. 1 660. Which of the manipulation operation is simple hinhivektomiyi stages:? A. remove gum from the edge of Language (palatal) and vestibular sides parallel gingival margin with regard to uneven depth pockets B. stop the bleeding C. open curettage of granulation and pathologically altered bone alveolar process D. pid'yasennoho removal of tartar E. * All of the above is true 661. Indications for the operation curettage: A. Severe periodontitis B. Mild form of periodontal disease C. Deep pockets clinical and bone D. Ineffectiveness of conservative treatment of periodontal pockets of 5 mm. E. * All answers are correct 662. Local hypothermia in the treatment of periodontal disease include: A. Use cooled gas mixture of oxygen and nitrogen at a temperature of 12-14 1:9 0 B. * Cooled gas mixture of oxygen and nitrogen 9:1 at a temperature of 12-14 0 C. Use cooled gas mixture of oxygen and nitrogen at a temperature of 20-25 9:1 0 D. Use cooled gas mixture of oxygen and nitrogen at a temperature of 20-25 1:9 0 E. Use cooled gas mixture of oxygen and nitrogen 9:1 at 16 663. In violation of the uniformity of physiological attrition occlusal surface of teeth is used: A. Closed curettage B. * Selective pryshlifuvannya C. Suction curettage D. Loskutnu operation E. Temporary splinting 664. Patient M., 32 years old need to curettage gingival and periodontal pockets. The criterion of efficiency curettage gingival and periodontal pockets in the implementation are: A. Lack pid'yasennoho tartar B. * Lack of severe bleeding, lack pid'yasennoho tartar, granulation and epithelial vrosshoho C. Complete absence of bleeding D. Clear tightly to the teeth E. Lack of granulation and epithelial vrosshoho 665. Hinhivotomiya - is: A. Removing ash to a depth of periodontal pockets B. * Autopsy gum C. Open curettage D. Stool periodontal abscess E. Disclosure of a single deep periodontal pockets 666. In combination with surgical treatment of periodontitis apply: A. Sclerotherapy B. Stimulant therapy C. Immunosuppressive therapy D. * Antibiotic therapy E. Proteolytic enzymes. 667. Up to 3 classes of premature contacts on Jankelson include: A. Premature contacts on the vestibular surfaces of buccal hillocks lower lateral vestibular surface of the teeth and lower front teeth. B. Contacts on oral surfaces hillocks upper palatal lateral teeth. C. * Premature contacts on the vestibular surfaces of palatal tubercles upper lateral teeth D. Premature contacts on the cutting edge E. All answers are correct 668. Deepithelization pocket is: A. Remove the damaged cement B. * Removal of granulation and ingrown pocket epithelium C. treatment of periodontal pockets yodvmisnymy solutions D. periodontal pocket irrigation with antiseptic solutions under pressure E. no right answer 669. What limited number of teeth operation hinhivektomiyi in the side area? A. * 3.2 B. 4.6 C. 6.8 D. 2.1 E. 4.3 670. What drug used for chemical curettage? A. A solution of potassium hlornovatystokysloho B. * A solution of sodium hlornovatystokysloho C. A solution of magnesium hlornovatystokysloho D. A solution of calcium hlornovatystokysloho E. Solution hlornovatystokysloho iron 671. On that day after surgery is exclusion zone of necrosis at kriokyuretazhi? A. At 1-2 days B. At 3-4 days C. * At 4-5 days D. For 6-7 days E. For 8-9 days 672. Which of the following is used for replanting in periodontal pockets with flap operation? A. "Collapan" B. "Hapkol" C. "Kerhap" D. "BioResorb E. * All of the used 673. In what year was clinically proven ability periodontal relationships grow into the space between the membrane and the surface of the root A. 1,982 B. 1,981 C. 1,985 D. * 1984 E. 1,990 674. Which toothpaste is recommended for use in periodontal disease: A. Hygiene; B. * Anti-inflammatory treatment and prevention C. Protykariozni prevention and treatment D. Therapeutic E. There is no right answer 675. To reduce gum bleeding patients should use toothpaste that contains: A. Sodium fluoride; B. Calcium carbonate; C. * Extracts of medicinal plants; D. Urea. E. There is no right answer 676. Since then proposed provisions brushes corresponding method charter? A. Perpendicular to the axis of the tooth B. At an angle of 900 to the axis of the tooth C. C. * At an angle 450 to the axis of the tooth D. Along the axis of the tooth E. E. There is no correct answer 677. For people with periodontal pathology recommended brushes: A. Soft B. * Average stiffness C. Hard D. Very soft E. Very tough 678. For those in the postoperative period after loskutnyh operations recommended brushes: A. * Soft B. Central rigidity C. Hard D. Very soft E. Very tough 679. In the method BASA provisions denture cleansers and movements are as follows: A. Pulsating movement in the half-open mouth B. Pidmitayuchy movements with that extended jaws C. Circular movements with the jaws of closed D. * Pulsating movement with that extended jaws E. There is no right answer 680. What is the position relative to the surface of the tooth brush in Bas method? A. * Along the axis of the tooth B. Perpendicular to the axis of the tooth C. At an angle of 450 to the axis of the tooth D. At an angle of 900 to the axis of the tooth E. There is no right answer 681. What are the optimal brush to use for those with healthy periodontium A. * Average stiffness B. Soft and medium hardness C. Hard D. Soft E. Very soft 682. Terms of dentition and which cleaning method movements correspond charter: A. Pidmitayuchi movements with that extended jaws B. Circular movements with that extended jaws C. Pulsating movement in the jaws of closed D. * Rotating movements with that extended jaws E. There is no right answer 683. Which of the following methods of cleaning is recommended for periodontal disease A. Method Stilmana B. Method Background C. Method Leonard D. D. * Method Bass E. Method charter 684. The standard method Pakhomov position denture cleansers and movements are as follows: A. * Pidmitayuchi motions half-open mouth B. Circular movements with that extended jaws C. Light vibrating movements with half-open mouth D. Pulsating movement with that extended jaws E. There is no right answer 685. People with a healthy periodontium can recommend brushing teeth by: A. * Method Stilmana modified B. Method Background C. Method Bass D. Method charter E. That's right 686. The standard method of cleaning teeth is a method A. Bass B. Background C. Charter D. * Pakhomov E. Stilmana 687. Which of the following is a clinical contraindication to the use of electric brushes A. * Hypertrophic gingivitis B. Catarrhal gingivitis C. Available in the mouth braces - systems. D. Periodontitis E. There is no right answer 688. The standard method of brushing duration of the procedure is: A. 1 min B. 2 min C. * 3 min D. 4 min E. 5 min 689. Where to begin brushing method Pakhomov A. * Upper right posterior teeth B. C. D. E. 690. A. B. C. D. E. 691. A. B. C. D. E. 692. A. B. The upper left posterior teeth Lower right posterior teeth Lower left posterior teeth There is no right answer Improper position of the toothbrush according to the method Bas can lead to: Pathological abrasion of enamel Wedge-shaped defects * Violation of epithelial connection Erosion of enamel Gingivitis What movements finish brushing method by Pakhomov Back-translational Gyratory * Circular Pidmitayuchymy There is no right answer Secondary prevention of periodontal disease include: Combined treatment of severe parodontopathies * Treatment ranih manifestations of pathological changes of the teeth and periodontal tissues C. Training Techniques individual oral hygiene D. Distribution of patients in clinical group E. Preventing the emergence and development of periodontal disease 693. A must in the prevention of periodontal diseases in children are: A. Hygienic study of oral care B. * Prevention of malocclusion C. Detection and correction anomalyynoho attaching soft tissue to bone skeleton person D. All of the above E. There is no right answer 694. Most effective for the prevention of periodontal diseases associated with the development of hormonal status are: A. The period of early childhood B. Antenatalnыy period C. Peredpubertatnyy period D. D. * Puberty + E. The period of late childhood 695. Most important in the maintenance of oral hygiene A. take plenty of water and thoroughly rinse your mouth B. regularly attend dental hygienist C. carefully brushing and flossing use at least 1 time per day D. use antiseptic mouthwashes E. * All of the above 696. Recommendations for change in nutrition in patients with periodontal disease A. limit the carbohydrates, especially before going to bed and in the end a meal to end a meal raw fruits and vegetables is good clean surface of teeth B. excluded from receiving chatter, sharp, kysluyu, cold, stimulating nerve endings in the bare necks of teeth C. to exclude fried, fatty D. needed milk and vegetable diet E. * All of the above 697. In order to prevent periodontal disease should brush your teeth A. once in the morning B. twice - morning and evening C. only at night D. E. 698. A. B. C. D. E. 699. A. B. C. D. E. 700. A. B. C. D. E. 701. A. B. C. D. E. 702. A. B. C. D. E. 703. A. B. C. D. E. 704. A. B. C. D. E. 705. A. B. C. D. E. 706. A. B. C. three times * 3-5 times For daily brushing to recommend brush with natural bristles * With artificial bristles does not matter tough soft Keep your toothbrush recommended in case * With soapy bristles in hypertonic salt solution no case in soda solution Most effective in cleaning tooth surfaces aproksymalnыh toothbrush * Thread (flosses) Water Jet toothpick rinsing procedure Massive social and preventive measures are carried out mainly: separately by each person Dentist in mouth * State health authorities comprehensively, all listed by no right answer Treatment and prevention activities are conducted mainly: separately by each person * Dentist in the mouth State health authorities comprehensively, all listed by no right answer Individual preventive measures are carried out mainly: * Separate each person Dentist in mouth State health authorities comprehensively, all listed by no right answer By massive social and preventive measures are: elimination of internal diseases rational regime of work and rest of children water fluoridation * Breastfeeding her baby all of the above By preventive measures include: dental health removal of dental plaque treatment of anomalies of position of individual teeth treatment of inflammatory diseases * All of the above By individual preventive measures include: thorough brushing Use dental floss rinse antiseptic rinses D. E. 707. A. B. C. D. E. 708. A. B. C. D. E. 709. A. B. C. D. E. 710. A. B. Use toothpicks * All of the above How many offices must unite periodontic department? 2 3 6 *4 5 Objective clinical examination: Detection of early forms of the disease Identifying risk factors Comprehensive preventive measures Conducting socio-sanitary measures * All of the above In a selection for clinical records addresses the following questions? Diagnosis of early forms of the disease Definition of medical tactics Recommendations for rehabilitation * All of the above Conducting dynamic observation Clinical examination subject entities: At the age of 30 years without clinical signs of disease Regardless of age in the presence of chronic gingivitis, the initial degree of periodontitis C. At the age of 50 years if developed forms of generalized periodontitis, periodontitis D. Individuals with idiopathic disease E. * All of the persons 711. Based on the age psychological characteristics as primary school students are invited to study the methods of oral hygiene? A. * 10.07 B. 5.4 C. 2.3 D. 12.11 E. 6.5 712. Based on the age psychological characteristics of many middle schools are invited to study the methods of oral hygiene? A. 7.10 B. * 4.5 C. 2.3 D. 12.11 E. 6.5 713. How many hours per academic year is given to hygiene lessons for students in the first grade? A. 2 B. 1 C. * 3 D. 4 E. 5 714. How many hours per academic year is given to hygiene lessons for students of classes IX-2.3? A. * 2 B. 1 C. 3 D. 4 E. 5 715. How many hours per academic year is given to hygiene lessons for students 04.10 -'s classes? A. 2 B. * 1 C. 3 D. 4 E. 5 716. At what age children are taught to rinse your mouth with water after eating? A. From 2-3 years B. * With 1.5-2 years C. With 4 years D. From 3 years E. From 5 years 717. How old do children learn self-clean teeth with a toothbrush? A. * With 2-3 years B. With 1.5-2 years C. With 4 years D. From 3 years E. From 5 years 718. At what age children vchatchystyty using toothpaste? A. From 2-3 years B. With 1.5-2 years C. From 3 years D. * With 4-5 years E. From 6 years 719. Who We teach oral health care of children attending kindergartens? A. Dentist B. Parents C. * Mentor D. Doctor - Pediatrician E. There is no right answer 720. At what stage of a clinical examination of children in the periodontist? A. * In five B. In three C. In six D. In four E. In two 721. What made the first stage of clinical examination? A. Comprehensive survey B. Dynamic observation of clinical patients C. * Selection of dispensary groups of patients D. Preparation of a comprehensive treatment plan E. Implementation of a comprehensive treatment plan drawn up 722. What made the second phase of clinical examination? A. * Comprehensive survey B. Dynamic observation of clinical patients C. Selection of dispensary groups of patients D. Preparation of a comprehensive treatment plan E. Implementation of a comprehensive treatment plan drawn up 723. What made the third stage of clinical examination? A. Comprehensive survey B. Dynamic observation of clinical patients C. Selection of dispensary groups of patients D. * Preparation of a comprehensive treatment plan E. Implementation of a comprehensive treatment plan drawn up 724. Conducted on chetvetromu stage dispensary? A. Comprehensive survey B. Dynamic observation of clinical patients C. Selection of dispensary groups of patients D. Preparation of a comprehensive treatment plan E. * Performing compiled a comprehensive treatment plan 725. What is held on the fifth stage of clinical examination? A. Comprehensive survey B. * Dynamic observation of clinical patients C. Selection of dispensary groups of patients D. Preparation of a comprehensive treatment plan E. Implementation of a comprehensive treatment plan drawn up 726. One of the criteria for evaluating the effectiveness of clinical examination is stabilizing. These are: A. Short-term stabilization within one year B. Treatment does not lead to stabilization or deterioration process C. Strengthening and progression D. * The stabilization process for 1.5 - 2 years E. There is no right answer 727. One of the criteria for evaluating the effectiveness of clinical examination is in remission. These are: A. * Short-term stabilization within one year B. Treatment does not lead to stabilization or deterioration process C. Strengthening and progression D. The stabilization process for 1.5 - 2 years E. There is no right answer 728. One of the criteria for evaluating the effectiveness of clinical examination is worsening. These are: A. Short-term stabilization within one year B. Treatment does not lead to stabilization or deterioration process C. * Strengthening and progression D. The stabilization process for 1.5 - 2 years E. There is no right answer 729. One of the criteria for evaluating the effectiveness of clinical examination of the concept is the same. These are: A. Short-term stabilization within one year B. * Treatment does not lead to stabilization or deterioration process C. Strengthening and progression D. The stabilization process for 1.5 - 2 years E. There is no right answer 730. The main signs of periodontal disease: A. The presence of periodontal pockets, pioreya, mobility of teeth B. * Lack of inflammation in periodontal stability teeth, horizontal resorption of alveolar bone, the absence of clinical pocket C. Atrophy of gums, bone destruction of the alveolar ridge, mobility and displacement of teeth D. The presence of periodontal pockets, traumatic occlusion E. Atrophy of gums pioreya, horizontal alveolar bone resorption 731. On the basis of clinical signs is carried out differential diagnosis of periodontal disease and periodontitis? A. * The presence or absence of periodontal pockets and symptomatic gingivitis B. The degree of mobility and displacement of teeth, the nature of the inflammatory process C. The extent and nature of destruction of bone tissue D. The presence or absence of inflammation in the gums, pioreyi E. The degree of traumatic occlusion 732. Whereby the indices hygiene by Green Vermilyonom? A. * Using a cotton swab with iodine-potassium solution B. visually using dental forceps and probe C. using a cotton swab with a solution Loholya D. visually using a probe and mirror E. no right answer 733. The value of the modified index Fedorova has been received is 1.9 points. Which level of care meets the figure A. good B. * Satisfactory C. poor D. bad E. very poor 734. The appearance of color changes due to gum inflammation, bleeding occurs in probing, possible occurrence of pronounced inflammatory edema. Myulemanu index gingival sulcus bleeding in this case says: A. 1 degree B. 2 degrees C. Grade 3 D. * 4 degree E. Grade 5 735. In the pathogenesis of periodontal disease leading role of the masses: A. Local trauma periodontal tissue B. Endocrine changes in the body C. * Violation of the blood supply and metabolism of periodontal tissues D. Imbalance of local and systemic immunity E. Endotoxin dental plaque 736. Index Green Vermilyona used to determine: A. Intensity decay B. * Plaque, tartar C. Bleeding gums D. Periodontal pockets E. Mobility of teeth 737. At what minimum time imposed medical gingival dressing? A. At 2:00 B. The period during which inhibited growth patohyei. yuyi microflora C. At 4:00 D. * At the time allocation therapeutic dose ingredient; .. E. At 30 minutes 738. Absolute contraindications to the use of the closed method of treatment of periodontal inflammation: A. Severe hypersensitivity hard tissues B. The presence of dental plaque C. The presence of erosive and ulcerative lesions D. * Significant purulent discharge from the periodontal pockets E. Acute course of inflammation in periodontal 739. The value of health-protective dressings in treatment periodontitis: A. Create conditions for stabilizing mobile teeth B. Leading to rapid cure periodontitis C. D. E. 740. A. B. C. D. E. 741. A. B. C. D. E. 742. A. B. C. D. E. 743. A. B. C. D. E. 744. A. B. C. D. E. 745. A. B. C. D. E. 746. A. B. C. D. E. 747. A. B. C. D. E. * Provide long medkamentiv effect on periodontal tissue and create conditions of calm in the affected area Warns of atrophic and hyperplastic processes in Bottom clinical gingival pockets are: * Pie ligament tooth Oblique fibers periodontal Rezorbovana bone Gingival-bone ligament There is no right answer Temporary splinting is done to: Stabilization of mobile teeth before the permanent prosthesis * Immobilization mobile teeth during therapeutic treatment and hirurhichnoh Creating conditions gingival fixing bandages for highly mobile and solitary standing teeth Stabilization of mobile teeth after surgery Removal of traumatic occlusion Indications for use of the method of selective pryshlifovuvannya teeth: Detection of premature tooth contacts in the central occlusion * Set premature contacts and the presence of contacts only some teeth when closing the jaws in any of the 4 occlusions Lack of contact between groups of teeth-antagonists Establishing contacts with premature closing of the jaws in the lateral and central occlusion The presence of primary traumatic occlusion To determine the number of dental CPITN index is divided into: 2 4 *6 8 10 Sextant What aids are used in determining the intensity of selection index gingival fluid litmus paper * Strips of filter paper indicators purulent processes caries-markers no right answer Mobility tooth vestibular-oral and lateral directions replies 1 degree of mobility * 2 degrees of mobility 3 degrees of mobility 4 degrees of mobility 5 degrees of motion The subjective test is based on: local data view * Patient complaints additional methods of examination intraoral examination results all answers are correct Indications for the operation curettage: Severe periodontitis Mild form of periodontal disease Deep pockets clinical and bone * Ineffectiveness of conservative treatment in periodontal pockets up to 5 mm Periodontal abscess 748. Solution erytrozynu used for: A. * Display plaque B. detection of focal demineralization C. detection of gum disease D. All of the above E. no right answer 749. What is the biologically active substance has a positive test-Shiller Pisarev A. * Glycogen B. Histamine C. Bradykinin D. There is no right answer E. All answers are correct 750. Contraindications to the operation suction curettage A. Gingival hyperplasia B. Bone pockets deeper periodontal pockets 4 mm C. * Periodontal Disease D. Periodontal abscess E. Ulcer-necrotic processes in the gums 751. In combination with surgical treatment of periodontitis apply: A. Sclerotherapy B. Stimulant therapy C. Immunosuppressive therapy D. * Antibiotic therapy E. Proteolytic enzymes 752. In the formation of periodontal pockets i> irishalns chonnya has: A. Status of local immunity B. Local traumatic factors C. * Endotoxin and proteazy'zubnoyi plaques D. The nature and severity of inflammation in periodontal E. Violation microcirculation in periodontal tissues 753. What volume of work performed UTO doctor periodontist, having curettage of periodontal pockets in section 4 teeth and put it on operative field gingival bandage? A. 2.5 B. * 3.0 C. C 4.0 D. 5.5 E. 6.0 754. What drugs are used to stimulate epiteleutvorennya with gingivitis? A. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory B. Antiseptics C. * Keratoplasty D. Immunomodulators E. Proteolytic enzymes 755. Sclerotherapy carried out at: A. * Hypertrophic gingivitis B. Sharp catarrhal gingivitis C. Ulcer-necrotizing gingivitis D. Deskvamativny gingivitis E. Atrophic gingivitis 756. Which of the following surgical procedures carried out in the treatment of hypertrophic gingivitis? A. Cryosurgery B. Diathermocoagulation C. Hinhivektomiya D. Hinhivotomiya E. * All of the above 757. According to the classification, MF Danilevsky (1994) gingivitis refer to: A. * Inflammatory diseases B. productive processes (parodontomy) C. degenerative diseases D. dystrophic and inflammatory diseases E. progressive idiopathic diseases 758. The root cause of gingivitis: A. Pathological changes in vessel walls B. Crowding of teeth C. * Microbial plaque D. Hereditary factor. E. There is no right answer 759. How UTO (contingent labor units) completed a medical periodontist, following removal of tartar from teeth lsih patient periodontitis mechanically: A. 2.0 B. 6.0 C. * 4.0 D. 4.5 E. 3.5 760. Generalized severe periodontitis in the acute stage (abscess). What treatment plan: A. Medication (antibiotics) and physical therapy (UHF) band effect on abscesses, and after the elimination of acute inflammation - surgery, stimulating therapy, splinting B. Hinhivoektomiya, antibiotic therapy, rational prosthesis C. * Disclosure periodontal abscesses, anti-inflammatory and antibiotic therapy, removal of traumatic factors shred operation, orthopedic D. Disclosure of periodontal abscesses, after the elimination of purulent inflammatory process curettage pockets, stimulating therapy E. Hinhivotomiya, antibiotic therapy, physiotherapy, splinting 761. In hypertrophic gingivitis clinical and morphological features occur due to: A. Alteration and necrosis B. * Proliferation C. Edema and inflammatory infiltration D. All answers are correct E. There is no right answer 762. Stability of capillaries in the gums catarrhal gingivitis in Kulazhenko A. Pp. 50-60 B. * 15-25 s C. Pp. 30-40 D. Pp. 35-60 E. 5.10 s 763. Which of the following drugs are used as a means nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory in the treatment of catarrhal gingivitis? A. Furatsillina B. Peroxide C. Chlorhexidine D. Yodinola E. * Mefenaminat sodium 764. Which of the following clinical signs typical of ulcerative-necrotic gingivitis? A. Swelling and redness of the mucous membrane B. Dirty, gray fibrin plaque on the gums C. Necrosis interdental papillae D. The plight of the patient E. 765. A. B. * That's right Plan local treatment of generalized periodontitis light severity: Removal of dental plaque, anti-inflammatory therapy, curettageperiodontal pockets * Remediation, anti-inflammatory therapy, surgery, removal traumatic occlusion, physiotherapy C. Removal of dental plaque, curettage of periodontal pockets anti-inflammatory and sclerotherapy D. The irrigation of the mouth, curettage of periodontal pockets anti-inflammatory and stimulating therapy E. Oral health, surgical treatment, and anti-inflammatory therapyphysiotherapy 766. The goal of periodontal surgery: A. Anti-inflammatory and desensitizing effect B. Removal of foci intoxication C. * Elimination of periodontal pockets and creating the conditions for stabilization D. process in the periodontal tissues E. Creating the conditions for the regeneration of alveolar bone 767. Basic principles of treatment of generalized periodontitis: A. Eliminate inflammation in periodontal stimulation defenses B. body, eliminating traumatic factors C. Eliminating traumatic factors, anti-inflammatory therapy, curettage D. periodontal pockets, rational prosthesis E. * Elimination of clinical signs of periodontitis using therapeutic, surgical and orthopedic treatments 768. Generalized periodontitis differentiate: A. In catarrhal gingivitis, periodontitis, marginal periodontitis, papillitis B. In hypertrophic gingivitis, gum fibromatosis, papillitis, eosinophilic granuloma C. * With gingivitis, eosinophilic granuloma, periodontitis D. With periodontal disease, catarrhal and hypertrophic gingivitis, odontogenic abscess E. In chronic gingivitis, epulis, gingival fibromatosis 769. Chronic hypertrophic gingivitis edematous forms: A. * Cortical plate and bone interdental septum saved B. Cortical plate interdental septum is preserved, bone loss at 1/3 the length of the root C. Cortical plate interdental septum rozrushena, bone loss at ½ the length of the root D. All answers are correct E. There is no right answer 770. In the clinical course of these gingivitis which can be identified erosion, erythematous, and bullous forms? A. Hypertrophic gingivitis B. Sharp catarrhal gingivitis C. Ulcer-necrotizing gingivitis D. * Deskvamativny gingivitis E. Atrophic gingivitis 771. Surface sklerotyzatsiyi by Kovalevsky method is: A. * Processing vagotilom pockets and putting in your pocket honsurydu B. Processing pockets celandine and putting in your pocket honsurydu C. Processing vagotilom pockets and putting in your pocket glucose D. Processing maraslavinom pockets and putting in your pocket honsurydu E. There is no right answer 772. What processes take place in the tissues during diathermocoagulation: A. Irreversible coagulation of tissue proteins B. Coagulation vascular C. Clotting D. Fulling vessels in the wound E. * All of the above is true 773. X-ray picture moderate periodontitis: A. Destruction compact plate uniform horizontal resorption mezhalveolyarnyh partitions on 1/3 B. * Osteoporosis spongy bone, horizontal and vertical alveolar bone resorption to 1/3 height partitions between teeth, periodontal expansion slots C. Lack of cortical plate, horizontal resorption alveolar bone to 1/2 the height of interdental partitions, events and osteoporosis osteosclerosis D. Destruction and lysis of alveolar ridge E. Vertical bone destruction from the presence of cystic defects 774. The main features of generalized periodontitis in any its clinical course: A. Bleeding gums, osteoporosis and vertical alveolar bone destruction, tooth mobility, traumatic occlusion B. Symptomatic gingivitis, tooth mobility, horizontal bone destruction of the alveolar ridge C. * Symptomatic gingivitis, the presence of periodontal pockets horizontal and vertical alveolar ridge resorption, traumatic occlusion, tooth mobility D. Symptomatic gingivitis, osteoporosis and vertical resorption of alveolar bone E. Bleeding gums, presence of periodontal pockets, horizontal and vertical resorption of interdental partitions pioreya 775. Osteolizys this: A. Pathological process, accompanied by a decrease in bone trabeculae per unit volume B. Pathological process, accompanied by functional and structural changes ZSCHS C. Pathological process, accompanied by an increase in bone trabeculae per unit volume D. * Pathological process, accompanied by complete resorption of the bone without any manifestations of its replacement E. There is no right answer 776. Objective simple hinhivektomiyi? A. Correction of defects of the alveolar process of the jaws B. * Elimination of periodontal pocket = C. Conducting vacuum curettage D. Holding open curettage E. Eliminate bone pocket 777. Disadvantages hinhivektomiyi operations are: A. hyperesthesia bare roots to thermal stimuli B. cosmetic defect after removal of gingival papillae C. necks baring teeth D. hyperesthesia bare roots to chemical stimuli E. * All of the above is true 778. Hinhivotomiya - is: A. Removing ash to a depth of periodontal pockets B. * Autopsy gum C. Open curettage D. Stool periodontal abscess E. Disclosure of a single deep periodontal pockets 779. Determination of traumatic occlusion carried out using: A. Iodine solution B. Magenta C. * Wax plates D. Desmodometra E. Ehoosteometra 780. In what year was clinically proven ability periodontal relationships grow into the space between the membrane and the surface of the root A. 1,982 B. 1,981 C. 1,985 D. * 1984 E. 1,990 781. Which dodaktovyh survey methods necessary to establish the severity of periodontitis? A. Probing the depths of steam, iontalnyh pockets B. Determination of mobility zuby1. C. * Renthendiahnostyka D. Determination of bleeding gums E. Trial of Parma 782. Methods of treatment of periodontal disease: A. Anti-inflammatory and desensitizing therapy B. Surgical treatment and cryotherapy C. * Osteotropic and remineralization therapy D. Sclerotherapy E. Antibacterial and immunostimulatory therapy 783. Indications for use of the method of selective pryshlifovuvannya teeth: A. Detection of premature tooth contacts in the central occlusion B. Installing premature contacts and the presence of contacts only some teeth when closing the jaws in any of the 4 occlusions C. Lack of contact between groups of teeth-antagonists D. Establishing contacts with premature closing of the jaws in the lateral and central occlusion. E. * All of the above is true 784. Removing tartar pid'yasennoho conduct: A. By curettage of periodontal pockets B. * During curettage of periodontal pockets C. After the curettage pockets D. A week before curettage E. There is no right answer 785. Kalamkari recommended to detect and eliminate premature contacts in position: A. Only the central occlusion B. Central and distal C. Distal and anterior D. Central and anterior E. * In all three positions occlusion 786. What are the physical methods of treatment are shown in the postoperative period in patients with periodontitis? A. Vacuum therapy B. The anode-galvanization C. Electrophoresis D. * UHF-therapy E. Microwave therapy 787. Contraindications for the massage at zai aleyni periodontal A. The presence of stagnation in periodontal B. * Purulent discharge from periodontal pockets C. Mobility of teeth D. Hypertrophy of gums E. Bleeding gums 788. Indications for balneotherapy in generalized periodontitis: A. Only in remission B. At all stages of treatment, in addition to postoperative C. * At all stages of treatment D. In the postoperative period E. During medical treatment 789. Which toothpaste is recommended for use in periodontal disease: A. Hygiene; B. * Anti-inflammatory treatment and prevention C. Protykariozni prevention and treatment D. Therapeutic E. There is no right answer 790. To reduce gum bleeding patients should use toothpaste that contains: A. Sodium fluoride; B. Calcium carbonate; C. * Extracts of medicinal plants; D. Urea. E. There is no right answer 791. Contraindications to the use of electrophoresis in patients parodontitis A. Hypertrophic processes in the gums B. The presence of teeth hyperesthesia C. * Violation of intact epithelial mucosa D. Bleeding gums E. The presence of bone pockets 792. For people with periodontal pathology recommended brushes: A. Soft B. * Average stiffness C. Hard D. Very soft E. Very tough 793. For those in the postoperative period after loskutnyh operations recommended brushes: A. * Soft B. Central rigidity C. Hard D. Very soft E. Very tough 794. In the method BASA provisions denture cleansers and movements are as follows: A. Pulsating movement in the half-open mouth B. Pidmitayuchy movements with that extended jaws C. Circular movements with the jaws of closed D. * Pulsating movement with that extended jaws E. There is no right answer 795. What is the position relative to the surface of the tooth brush in Bas method? A. * Along the axis of the tooth B. Perpendicular to the axis of the tooth C. At an angle of 450 to the axis of the tooth D. At an angle of 900 to the axis of the tooth E. There is no right answer 796. What are the optimal brush to use for those with healthy periodontium A. * Average stiffness B. Soft and medium hardness C. Hard D. Soft E. Very soft 797. Fluctuarization and darsonvalization vykorystuyutsya in periodontitis: A. In order to anesthesia B. To reduce bleeding and swelling of periodontal tissue C. * To accelerate microcirculation and epithelialization, improved D. E. 798. A. B. C. D. E. 799. A. B. C. D. E. 800. A. B. C. D. E. 801. A. B. C. D. E. 802. A. B. C. D. E. 803. reparative processes in periodontal To relieve inflammation in the gums Which factor is crucial in the emergence of diseases periodontal? * Infection Injury Malocclusions Violation of immunity Somatic Diseases The emergence of periodontal disease on the theory E.E.Platonova occurs: * As a result of trophic disorders of the central or peripheral regions nervous system As a result of circulatory disorders periodontal tissue As a result of metabolism, accompanied by a sharp delay in the synthesis of protein As a result of the imbalance between the processes and osteysyntezu osteolizysu Because immunological changes of periodontal tissues (autoagression) The emergence of the theory A.I.Yevdokimova periodontitis occurs as Corollary hypovitaminosis C Metabolic disorders, which is accompanied by a sharp delay the synthesis of proteins * Primary-degenerative process of bone tissue due to atherosclerosis periodontal Imbalance between processes and osteosynthesis osteolizysu Because trophic disorders of the central or peripheral partsnervous system Which of the following is a clinical contraindication to the use of electric brushes * Hypertrophic gingivitis Catarrhal gingivitis Available in the mouth braces - systems. Periodontitis There is no right answer The standard method of brushing duration of the procedure is: 1 min 2 min * 3 min 4 min 5 min In histological preparation determined the formation of oral mucosa is presented, which is part of the free and attached firmly adherent to the periosteum. Multilayered epithelium, flat, rohoviyuchyy. Own plate forming long nipples are jutting out into the deep epithelium. Call it education: 804. A. cheeks B. hard palate C. * Gums D. lip E. tongue At a reception at the dentist when viewed from the patient revealed that prysinka depth is 4.5 mm. It says: A. Very shallow B. Middle prysinku C. Deep prysinku D. Very deep E. 805. 806. 807. * Milka prysinku When viewed prysinka oral patient revealed that its depth is 9 mm. It says: A. Milka prysinku B. * Middle prysinku C. Deep prysinku D. Norm E. There is no right answer When viewed prysinka oral patient revealed that its depth is 9 mm. It says: A. shallow prysinku B. * Average prysinku C. deep prysinku D. Normally E. no right answer On examination of children in '15 hemorrhage detected in 35% of cases. How can I describe this figure 808. A. low B. high C. * Moderate D. very low E. very high The patient complained of bleeding gums when consuming solid food. What degree of bleeding in this patient 809. A. 2 degree B. * 1 degree C. 3 degree D. 4 degree E. 5th level An examination of the wall in front of the mouth are paying attention to the mucous membrane of the cheek in the area of six upper teeth. Which anatomical formation is taken into account in this case? 810. A. excretory duct submandibulars salivary gland B. * Excretory duct parotid salivary gland C. infraorbitalnyy channel D. maxillary sinus E. all answers are correct During a routine inspection of the patient revealed 2 degree bleeding gums. It says: 811. A. * Bleeding during brushing B. bleeding during consumption of solid food C. spontaneous bleeding D. no right answer E. bleeding during probing The examination revealed that the recession becomes muco-gingival border. Which class recession according to the classification of Miller responds: 812. A. 1 class B. * Class 2 C. Class 3 D. Class 4 E. no right answer The examination revealed that due to gum recession was losing gingival papillae. Which class recession according to the classification of Miller responds: 813. A. 1 class B. Class 2 C. * Class 3 D. Class 4 E. no right answer The examination revealed that due to gum recession was losing gingival papillae and disrupted the position of the tooth. Which class recession according to the classification of Miller responds: 814. A. 1 class B. Class 2 C. Class 3 D. * Class 4 E. no right answer This clinical picture: the appearance of color changes due to inflammation of the gums, bleeding in probing occurs, may cause spontaneous bleeding gums and erosions of the epithelium. In Myulemanu index gingival sulcus bleeding in this case says: A. 1 degree of inflammation B. 2 degrees of inflammation C. Grade 4 inflammation D. 3 degrees of inflammation E. * 5 degree of inflammation 815. The patient chronic generalized periodontitis in remission. When microbiological study content pockets were seeded microorganisms. How many of their colonies per 1 cm2 thus found? 816. A. * 36 B. 26 C. 46 D. 6 E. 2.1 In women diagnosed with exacerbation of chronic generalized periodontitis. When microbiological study content pockets were seeded microorganisms. How many of their colonies per 1 cm2 thus found? 817. A. 460 B. * 360 C. 560 D. 1-60 E. 1-20 The patient is recommended to conduct oral tsytodiahnostyku. Material for the study will be taken from: 818. A. * Mucosa cheeks, above the interdigitation B. Mucosa in the region of the angle of the mouth C. Mucosa floor of the mouth D. Mucosa cheek below the interdigitation E. There is no correct answer When the reaction of adsorption of microorganisms found that PAM is 83%. Describe the nonspecific resistance in this indicator: 819. A. Poor B. Poor C. Satisfactory D. Very good E. * Good The reaction of adsorption of microorganisms found that PAM is 36%. Describe the nonspecific resistance in this indicator: A. Poor B. Poor C. Very good D. * Satisfactory E. 820. Good Patient 5 years of complaining about bad mouth, gum overgrowth. In the history of epilepsy, the patient systematically taking hydantoin (difenin). On examination, hyperemia and edema of the gums, gums covering teeth crowns for 1/2, palpation bleed. Blood and urine tests are normal. What is the most likely diagnosis? 821. A. Juvenile gingivitis B. * Difeninovyy gingivitis C. Bismuth gingivitis D. Mercury gingivitis E. Gingivitis is pregnant The patient in the treatment of catarrhal gingivitis over three weeks spent oral bath with antiseptic solution. This notice discoloration crowns. What antiseptic is able to cause this? 822. A. Peroxide B. Yodinola C. Potassium permanganate D. Furatsillina E. * Chlorhexidine A patient diagnosed with ulcerative-necrotic gingivitis. Which of the following clinical signs are characteristic of this disease? 823. A. Swelling and redness of the mucous membrane B. Dirty, gray fibrin plaque on the gums C. Necrosis interdental papillae D. The plight of the patient E. * That's right The patient in '28 diagnosed with ulcerative-necrotic gingivitis moderately. An objective examination revealed: 824. A. Swollen lymph nodes B. Dirty, gray fibrin plaque on the gums C. Necrosis interdental papillae D. Edema and hyperemia of the mucosa E. * That's right To the doctor turned patient 39. The complaints of general weakness, fever, pain in the mouth, rapid bleeding gums, putrefactive breath for 4-nights. On examination: the patient was pale, regional lymph nodes are enlarged, painful on palpation, mucous membrane of the gums on both jaws swollen, flushed, covered with gray bloom that is easily removed, sharply painful and bleeding. Which of the following diagnoses is most likely? 825. A. * Ulcer-necrotizing gingivitis B. Catarrhal gingivitis C. Merkurialnyy gingivitis D. Herpetic hinhivostomatyt E. Generalized periodontitis The patient diagnosed with hypertrophic gingivitis. Established that the cause of the disease was the change in the internal organs. What pererahovnoho caused? 826. A. * Endocrine pathology B. Hypertension C. Cardiac glycosides D. Ulcer E. Chronic cholecystitis Patients with hypertrophic gingivitis shows the operation hinhivektomiyi. Which route will be cut at a given surgical intervention? 827. A. Horizontal B. * Continuous hirlyandopodibnyy C. Intermittent Garland similar D. Oval E. There is no right answer The patient in '34 diagnosed ulcerative-necrotic gingivitis. When microbiological study of plaque from the gum found at: 828. A. Fuzobakteriyi B. Spirochaete C. Actinomycetes D. Hromomitsety E. * That's right The patient was diagnosed thipertrofichnyy gingivitis puffy shape. What will manifest clinically in this patient as a result of late edema and hyperplasia? A. Periodontal pockets B. Ulcers C. Syphiloma D. * Gingival pockets E. Papilloma 829. At the reception appealed patient with catarrhal gingivitis moderately. How much ash is included in the inflammatory process in this case: 830. A. Of papillary B. * Papillary and marginal C. Marginal and alveolar D. Alveolar, marginal, papillary E. There is no right answer Patient diagnosed with hypertrophic gingivitis. The doctor decided to sklerotyzatsiyi procedure. What single dose of the drug during deep sklerotyzatsiyi? 831. A. 0.2-0.4 ml B. 0.3-0.5 ml C. 0.4-0.5 ml D. * 0.1-0.2 ml E. 0.7 ml Patients with periodontal diseases subject to mandatory medical examination Patients with catarrhal gingivitis should be attributed to: 832. A. Group 1 clinical patients B. 3 groups of clinical patients C. * 2 groups of clinical patients D. 4 groups of clinical patients E. 5 groups of clinical patients The patient came to the doctor for the final phase of treatment of ulcerative gingivitis. Which of the following groups of drugs used in this case? 833. A. Anesthetic B. Enzymes C. Sulfonamide D. * Keratoplasty E. There is no right answer. The patient came to the doctor for the final phase of treatment of ulcerative gingivitis. Which of the following drugs used in this case? A. Metronidazole B. Chlorhexidine C. Biseptol D. Trypsin E. * A solution of vitamin A 834. On admission to a pediatric dentist parents brought a girl 7 years. Complaints child for bad breath, gum overgrowth. In the history of epilepsy, the patient systematically taking hydantoin (difenin). On examination, hyperemia and edema of the gums, gums covering teeth crowns for 1/2, palpation bleed. Blood and urine tests are normal. What is the most likely diagnosis? 835. A. Juvenile gingivitis B. * Difeninovyy gingivitis C. Bismuth gingivitis D. Mercury gingivitis E. Gingivitis is pregnant On the advice of child's dentist parents came 10 year old boy. The boy complains sprawl gums, bad breath. The patient consistently taking antiepileptic drug difenin. Objectively redness and swelling of the gums, gums cover the crowns of teeth in 1/3, palpation bleed. Blood and urine tests are normal. What is the preliminary diagnosis? 836. A. Juvenile gingivitis B. Gingivitis is pregnant C. Bismuth gingivitis D. * Mercury gingivitis E. Difeninovyy gingivitis Patient complains of '46 bleeding gums, hnoyetechu, tooth mobility. Sick for 10 years. On examination: clear the upper and lower jaws are congested, swollen, with dotorkuvanni bleed. In the 42, 41, 32, 31 teeth periodontal pockets up to 7 mm with purulent discharge, the mobility of II degree, the remaining teeth and degree. The X-ray - resorption mezhalveolyarnyh partitions in 42, 41, 31, 32 2/3 the length of the root, the phenomenon of osteoporosis. Which of the following methods most indicated for surgical treatment of this disease? 837. A. Kriokyuretazh B. * Patchwork operation C. Curettage D. Hinhivotomiya E. Hinhivektomiya Patient G. that dispensary diagnosed with generalized periodontitis, and the extent to chronic under examination [X-ray] at 6 months showed bone lonely pocket between 24 and 25 teeth, reaching 1/2 interalveolar height. The 24 tooth with amalgam filling goes deeply into the interdental space. Your tactics regarding bone pockets after correction fillings? 838. A. Hold course lincomycin in transition folds 24 and 25 teeth № 7-10 B. * Will hold open curettage C. Hold hinhivektomiyu D. Hold hinhivotomiyu E. Hold a series of periodontal dressings metroqyl-denta Patient M., 32 years old need to curettage gingival and periodontal pockets. The criterion of efficiency curettage gingival and periodontal pockets in the implementation are: A. Lack pid'yasennoho tartar B. * Lack of severe bleeding, lack pid'yasennoho tartar, granulation and epithelial vrosshoho 839. C. Complete absence of bleeding D. Clear tightly to the teeth E. Lack of granulation and epithelial vrosshoho Patient Y. The diagnosis "generalized periodontitis degree, chronic." What will be the first session of the local treatment? 840. A. * Temporary splinting B. Treatment of symptomatic gingivitis C. Anti-inflammatory therapy D. Curettage periodontal pockets E. Antiseptic treatment and removal of dental plaque Woman '45 complains of bad breath, bleeding gums and pain that intensified when eating. OBJECTIVE: catarrhal gingivitis degree, periodontal pockets reach neck 4 mm, containing a moderate amount of serous - pus. It is noted delaying tartar and plaque in nad'yasneviy and pid'yasneviy parts of the tooth. Mobility of teeth Class. Radiological findings: cortical plate impaired resorption of alveolar bone reaches half the height mezhalveolyarnyh membranes. Diagnosed chronic generalized periodontitis second degree. Where to begin treatment? 841. A. Appointment of mud applications B. * Removal of dental plaque. C. Purpose of the means of anti-inflammatory D. Conducting temporary splinting E. The planned operation In the Clinic Preventive Dentistry appealed patient aged 40 years., Who diagnosed acute generalized periodontitis III. severity. What type of curettage can be used in this nosology 842. A. Outdoor and vacuum - curettage B. * Vacuum - curettage, cryo - curettage C. Open curettage D. Closed curettage E. Open and closed curettage The patient, in '41, diagnosed with generalized periodontitis 2 degrees of severity, sharp course with abscess formation. Which methods of general treatment should be appointed in the first place? 843. A. Stimulant therapy B. Hyposensitization therapy C. Physiotherapy D. * Antibiotic E. Vitamin The patient, 46 years old, diagnosed with generalized periodontitis 2 degrees of severity, sharp course. Recently, the patient noted deterioration, skin itch, dryness in the mouth. Which methods of additional tests should be used before embarking on treatment? 844. A. Total blood B. Urinalysis C. Determination of vitamin C in the blood D. * Determination of blood sugar E. Immunological studies of blood The patient appealed to the dentist with complaints of persistent spontaneous pain, swelling of the gums in 26 and 27 teeth for 2 days. An examination of the lips of the upper and lower jaws of a large number of soft and hard plaque. At 26 and 27 teeth adjacent large fillings, contact checkbox, clear congested, swollen, on alveolar part of the protrusion, palpation painful, tooth-gingival pocket 6 mm with purulent exudate. What is the primary tactic local drug treatment? 845. A. Closed curettage tools gingival pockets B. * Removal of dental plaque, periodontal abscess disclosure C. Removal of dental plaque, application of medicines to clear D. Open curettage of periodontal pockets E. Rinse antiseptic Appointment The patient complains of '55 bad breath, bleeding gums and pain that intensified when eating. OBJECTIVE: catarrhal gingivitis degree, periodontal pocket depth of 4 mm, containing a moderate amount of serous - pus. It is noted delaying tartar and plaque in nad'yasneviy and pid'yasneviy parts of the tooth. Mobility of teeth Class. Radiological findings: cortical plate impaired resorption of alveolar bone reaches half the height mezhalveolyarnyh membranes. Diagnosed chronic generalized periodontitis second degree. Where to begin treatment? 846. A. Appointment of mud applications B. * Removal of dental plaque. C. Purpose of the means of anti-inflammatory D. Conducting temporary splinting E. The planned operation Patient A., 35 years old with a diagnosis of chronic generalized periodontitis II severity, need to surgery. The criterion for selection of surgical intervention in treatment parodotytu are: A. The depth of periodontal pockets B. Complaints patient C. Duration of disease D. Age of the patient E. * The depth of periodontal pockets, the general condition of the patient, the patient's age 847. Patient M., 32 years old need to curettage gingival and periodontal pockets. The criterion of efficiency curettage gingival and periodontal pockets in the implementation are: A. Lack pid'yasennoho tartar B. * Lack of severe bleeding, lack pid'yasennoho tartar, granulation and epithelial vrosshoho 848. C. Complete absence of bleeding D. Clear tightly to the teeth E. Lack of granulation and epithelial vrosshoho On admission the patient came in '36 with complaints of bleeding gums, hnoyetechu, tooth mobility. Sick for 10 years. On examination: clear the upper and lower jaws are congested, swollen, with dotorkuvanni bleed. In the 42, 41, 32, 31 teeth periodontal pockets up to 7 mm with purulent discharge, the mobility of II degree, the remaining teeth and degree. The X-ray - resorption mezhalveolyarnyh partitions in 42, 41, 31, 32 2/3 the length of the root, the phenomenon of osteoporosis. Which of the following methods most indicated for surgical treatment of this disease? A. Kriokyuretazh B. * Patchwork operation 849. C. Curettage D. Hinhivotomiya E. Hinhivektomiya In consultation addressed patient in '42 with complaints bleeding gums, hnoyetechu gums, tooth mobility. Sick 8 years. OBJECTIVE: gums on the upper and lower jaws hyperemic, edematous, with dotorkuvanni bleed. In the 32, 31, 42, 41 teeth periodontal pockets up to 6.5 mm with purulent discharge, the mobility of II degree, the remaining teeth and degree. The X-ray - resorption mezhalveolyarnyh partitions in 42, 41, 31, 32 2/3 the length of the root, the phenomenon of osteoporosis. Which of the following methods most indicated for surgical treatment of this disease? 850. A. Kriokyuretazh B. Curettage C. * Patchwork operation D. Hinhivotomiya E. Hinhivektomiya Woman '38 complains hnoyetechu and bleeding gums, tooth mobility. OBJECTIVE: gums on the upper and lower jaws hyperemic, edematous, with dotorkuvanni bleeding, periodontal pocket of 6 mm with purulent discharge, the mobility of the second degree. The X-ray - resorption mezhalveolyarnyh walls on 2/3 the length of the root, the phenomenon of osteoporosis. Which of the following most indicated for surgical treatment of this disease? 851. A. Kriokyuretazh B. Curettage C. * Patchwork operation D. Hinhivotomiya E. Hinhivektomiya A patient with periodontal pathology recommended surgery - operation hinhivektomiyi. The operation will be conducted in the right side area of the upper jaw. What number of teeth will obmezhovuvatys operative field? 852. A. * 3.2 B. 4.6 C. 6.8 D. 2.1 E. 4.3 When examining a patient with a diagnosis of chronic generalized periodontitis and severity discovered bone lonely pocket between 24 and 25 teeth, reaching 1/2 interalveolar height. The 24 tooth with amalgam filling goes deeply into the interdental space. Your tactics regarding bone pocket after correction fillings? 853. A. Hold course lincomycin in transition folds 24 and 25 teeth № 7-10 B. * Will hold open curettage C. Hold hinhivektomiyu D. Hold hinhivotomiyu E. Hold a series of periodontal dressings metroqyl-denta On the advice appealed woman, 35 years. The woman is on the records with a diagnosis of chronic generalized periodontitis and severity. The examination revealed bone lonely pocket between 13 and 14 teeth, reaching 1/2 interalveolar height. The 14 tooth set a seal that goes deeply into the interdental space. Your tactics regarding bone pocket after correction fillings? A. Hold a course of antibiotics for a transitional folds 24 and 25 teeth № 7-10 854. B. * Will hold open curettage C. Hold hinhivektomiyu D. Hold closed curettage E. Hold a series of periodontal dressings metroqyl-denta Patient in '40 is on the records with a diagnosis of chronic generalized periodontitis and severity. At the planned examination revealed bone lonely pocket between 14 and 15 teeth, reaching 1/2 interalveolar height. What treatment should be in this case? A. Hold a course of antibiotics for a transitional folds 24 and 25 teeth № 7-10 855. B. * Will hold open curettage C. Hold hinhivektomiyu D. Hold closed curettage E. Hold a series of periodontal dressings metroqyl-denta Patient doctor prescribed brushing toothpaste containing calcium and fluoride. Which group includes this toothpaste? A. * The group protykarioznyh medical toothpastes B. The group therapeutic toothpastes C. The group hygienic toothpaste D. The group of anti-inflammatory treatment and prevention toothpaste E. There is no right answer 856. In determining the index Fedorova - has been received revealed that the state of oral hygiene is very poor, with multiple dental plaque. What kind of toothpaste should be used in this case 857. A. * Type Smokers Toothpaste B. Toothpaste Anti-Plaque Type C. paste type Sensitive D. protykarioznu therapeutic - prophylactic paste E. no right answer An examination of the patient revealed multiple wedge-shaped defects. Which band toothpastes can recommend this patient 858. A. paste type Smokers B. Toothpaste Anti-Plaque Type C. * Type Sensitive Toothpaste D. protykarioznu therapeutic - prophylactic paste E. no right answer In vah'itnoyi patient hypertrophic gingivitis. What toothpaste can recommend in this case? 859. A. * Anti-inflammatory treatment and prevention B. Therapeutical C. Protykarioznu medical - preventive D. Sanitarily E. There is no right answer The patient was diagnosed pathology of periodontal tissues. What method of cleaning can be recommended in this case? 860. A. * Method Bass B. Method charter C. Method Background D. Method Stilmana E. Method Leonard The patient chronic generalized periodontitis in remission. When microbiological study content pockets were seeded microorganisms. How many of their colonies per 1 cm2 thus found? A. * 36 B. 26 C. 46 D. 1-6 E. 861. 2.1 In women diagnosed with exacerbation of chronic generalized periodontitis. When microbiological study content pockets were seeded microorganisms. How many of their colonies per 1 cm2 thus found? 862. A. 460 B. * 360 C. 560 D. 1-60 E. 1-20 Patient R., 22 years old, diagnosed - ulcerative-necrotic stomatitis Vincent. During the surface treatment of ulcers necrotic plaque is removed from the effort. What are the medications most appropriate solution for the raid? 863. A. Antifungal drugs B. * Proteolitichni enzymes C. Antiseptic drugs D. Keratoplasty E. Keratolityky After suffering ARI patient appealed to the dentist complaining of pain in the gums, bad breath, inability to eat, general weakness. OBJECTIVE: clear congested, swollen, covered with fibrinous coating, which occurs when removing the bleeding. Microbiological research gum tissue revealed a large number of cocci, bacilli, and spirochetes fuzobakteriy. Specify drug treatment etiotropic 864. A. Karotolina B. Haloskorbin C. Potassium permanganate D. Trypsin E. * Metronidazole Patient '17 complains of pain in the mouth, bleeding gums sharp, putrefactive breath, general weakness within 3 days. On examination: the patient is pale, regional lymph nodes are enlarged, painful on palpation, mucous membrane of the gums on both jaws swollen, flushed, covered with gray bloom that is easily removed, sharply painful and bleeding. Which of the following diagnoses is most likely? A. * Ulcer-necrotizing gingivitis B. Catarrhal gingivitis C. Merkurialnyy gingivitis D. Herpetic hinhivostomatyt E. 865. Generalized periodontitis Patient complains of '17 bleeding gums and pain within six months. On examination gingival papillae in the frontal area of the upper and lower jaws swollen, hyperemic. Relief gingival margin broken, papillae cover crowns on teeth 1/2, palpation bleed, false pocket depth of 4 mm, nad'yasenevi dental plaque. What interventions are most effective for local treatment of this disease 866. A. Diathermocoagulation hypertrophied papillae B. Sclerotherapy 50% glucose solution C. Overlay tsyklofosfanovoyi paste D. Phonophoresis Heparin ointment E. * Anti-inflammatory therapy, excision of gum Patient complains of '16 overgrowth of gums, their bleeding, pain when eating. Complaints during the year. The examination is marked skuchenist teeth on the lower jaw. Gingival papillae on the lower jaw increased in size, covering the crowns of teeth on 1/2, bright red, bleeding when touched, nad'yasenevi dental plaque. On radiographs unchanged. Applications which feed you want to assign to the local anti-inflammatory therapy? 867. A. Etoniyevoyi B. * Hinozolovoyi C. Metatsylovoyi D. Furatsylinovoyi E. Heparin Pregnant '20 complains overgrowth of gums, bleeding and pain when consuming food or cleaning teeth. Objectively: the gingival papillae on the upper and lower jaws are congested, cover the crowns of teeth on the 1/2, bleeding, painful. Festonchastist gingival margin broken. What is the most likely diagnosis in pregnant? 868. A. Aggravation of periodontitis B. Acute catarrhal gingivitis. C. Chronic catarrhal gingivitis. D. * Hypertrophic gingivitis, puffy shape. E. There is no right answer Patient '23 complains of pain in the mouth, bad breath, fever up to 38C. Patient pale, adynamic, regional lymph nodes are enlarged, painful. Interdental papillae and marginal part gums swollen, hyperemic, in ulcers, covered with necrotic plaque on teeth tartar deposits nad'yasenevoho and soft plaque. What additional research needs to be undertaken for diagnosis of this condition? 869. A. * Total blood B. Fluorescent C. Bacteriological D. Immunological E. Cytological Patient complains of '16 overgrowth of gum in front teeth upper and lower jaws. Diagnosed hypertrophic gingivitis medium severity. Pathology which system is important in the etiology of this disease? 870. A. Digestive B. * Endocrine C. Vascular D. Immune E. Nervous Patient, 20 years old, grumbles overgrowth of gums and bleeding when brushing teeth. OBJECTIVE: proliferation of gingival papillae at all teeth that 1/2 override crown height of teeth, gums, bright red, painful on palpation. What pathogenetic treatment should be applied here? 871. A. Stimulant B. Anti-inflammatory C. Antimicrobial D. * Sclerosing E. Remineralization. The patient in '23 was diagnosed: "Hypertrophic gingivitis, fibrous shape, average severity." What is the most rational treatment? 872. A. * Surgical B. Diathermocoagulation. C. Anti-inflammatory therapy. D. Sclerotherapy E. There is no right answer Patient, 26 years old, appealed with complaints about the proliferation of gum. OBJECTIVE: In section 14 of the tooth gums fungous growths limited form dense, dark red with cyanotic tinge. 14 tooth mobility in the vestibular-oral direction. Abnormal formation of patient noted a year ago, and connects with pregnancy. What is the most likely diagnosis? A. Gingival fibromatosis B. * Epulit, anheomatozna form 873. C. Hypertrophic gingivitis, swelling form D. Acute localized periodontitis of moderate severity E. Hypertrophic gingivitis, fibrous form. Patient 19, a driver complains of malaise, fever, sore gums, bad breath. Objectively: the gingival papillae and gingival edge grayish, friable, easily removed with uncovering ulcers, bleeding and sharply painful surface. Oral mucosa pink. What is the most likely diagnosis in the patient? 874. A. Acute ulcerative gingivitis. B. Acute leukemia C. Lead gingivitis D. Gangrenous gingivitis E. Chronic ulcerative gingivitis Patient complains of '30 overgrowth of gum in 22, 23, 24 teeth, which is noticed more than 3 months ago. On examination: the contact surfaces 22, 23, 24 teeth deep cavities, interdental contacts violated ash papillae increased in volume, covering the crowns of teeth on 1/3 at dotorkuvanni bleeding on the radiograph changes not. Which of the following diagnoses is most likely? 875. A. * Localized hypertrophic gingivitis B. Chronic papillitis C. Nad'yasenevyy epulis D. Localized periodontitis E. Generalized hypertrophic gingivitis The patient in '18 revealed the diagnosis "chronic catarrhal gingivitis." When X-ray revealed alveolar bone osteoporosis. What pathogenetic therapy lead to eradication of the disease. 876. A. * Immunomodulatory therapy. B. Antihistamine therapy. C. Antibiotic. D. Vitamin. E. Electrophoresis calcium supplements During the examination, the patient R., 25 years old, diagnosed - ulcerative-necrotic stomatitis Vincent. During processing poverhen ulcers necrotic plaque is removed from the effort. What are the medications most appropriate solution for the raid? A. Antifungal drugs B. * Proteolitichni enzymes C. Antiseptic drugs 877. D. Keratoplasty E. Keratolityky On the advice of the patient turned 38 years old. Patient after suffering a cold. Complaints of pain in the gums, bad breath, inability to eat, general weakness. OBJECTIVE: clear congested, swollen, covered with fibrinous coating, which occurs when removing the bleeding. Microbiological research gum tissue revealed a large number of cocci, bacilli, and spirochetes fuzobakteriy. Specify drug treatment etiotropic 878. A. Karotolina B. Haloskorbin C. Potassium permanganate D. Trypsin E. * Metronidazole On the advice of the patient came 28 years after suffering a cold. Complaints of pain in the gums, bad breath, inability to eat, general weakness. OBJECTIVE: clear congested, swollen, covered with fibrinous coating, which occurs when removing the bleeding. Microbiological research gum tissue revealed a large number of cocci, bacilli, and spirochetes fuzobakteriy. Select a drug for general etiotropic treatment for this patient 879. A. Karotolina B. Halaskorbin C. Potassium permanganate D. Trypsin E. * Metronidazole Patient '27 complains of pain in the mouth, bleeding gums sharp, putrefactive breath, general weakness within 3 days. Objective: the patient is pale, regional lymph nodes are enlarged, painful on palpation, mucous membrane of the gums on both jaws swollen, flushed, covered with gray bloom that is easily removed, sharply painful and bleeding. Which of the following diagnoses is most likely? 880. A. * Ulcer-necrotizing gingivitis B. Catarrhal gingivitis C. Merkurialnyy gingivitis D. Herpetic hinhivostomatyt E. Generalized periodontitis To the doctor turned patient 19. Complaints of pain in the mouth, rapid bleeding gums, putrefactive breath, general weakness within 3 days. On examination: the patient was pale, regional lymph nodes are enlarged, painful on palpation, mucous membrane of the gums on both jaws swollen, flushed, covered with gray bloom that is easily removed, sharply painful and bleeding. Which of the following diagnoses is most likely? 881. A. * Ulcer-necrotizing gingivitis B. Catarrhal gingivitis C. Merkurialnyy gingivitis D. Herpetic hinhivostomatyt E. Generalized periodontitis To the doctor turned sick in '19 with complaints of bleeding and sore gums within six months. On examination gingival papillae in the frontal area of the upper and lower jaws swollen, hyperemic. Relief gingival margin broken, papillae cover crowns on teeth 1/2, palpation bleed, false pocket depth of 4 mm, nad'yasenevi dental plaque. What interventions are most effective for local treatment of this disease 882. A. Diathermocoagulation hypertrophied papillae B. Sclerotherapy 50% glucose solution C. Overlay tsyklofosfanovoyi paste D. Phonophoresis Heparin ointment E. * Anti-inflammatory therapy, excision of gum The patient complains of '29 bleeding and sore gums during 6 months. On examination gingival papillae in areas of the upper and lower jaws swollen, hyperemic. Relief gingival margin broken, papillae cover crowns on teeth 1/2, palpation bleed, false pocket depth of 4 mm, nad'yasenevi dental plaque. What is the preliminary diagnosis 883. A. Ulcer-necrotizing gingivitis B. Merkurialnyy gingivitis C. Periodontal Disease D. * Hypertrophic gingivitis 2 severity E. Generalized periodontitis The patient complains of '32 bleeding and sore gums during 6 months. OBJECTIVE: gingival papillae in parts of the upper and lower jaws swollen, hyperemic. Relief gingival margin broken, papillae cover crowns of teeth in 1/3, palpation bleed, false pocket depth of 2 mm, nad'yasenevi dental plaque. What is the preliminary diagnosis A. Ulcer-necrotizing gingivitis B. * Hypertrophic gingivitis 1 degree of severity C. Periodontal Disease D. Hypertrophic gingivitis 2 severity E. Generalized periodontitis 884. To the doctor turned patient in '29 with complaints of bleeding and sore gums within six months. On examination gingival papillae in the frontal area of the upper and lower jaws swollen, hyperemic. Relief gingival margin broken, papillae cover crowns on teeth 1/2, palpation bleed, false pocket depth of 4 mm, nad'yasenevi dental plaque. What is the preliminary diagnosis 885. A. Ulcer-necrotizing gingivitis B. Merkurialnyy gingivitis C. Periodontal Disease D. * Hypertrophic gingivitis E. Generalized periodontitis The patient in '34 diagnosed acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis-mild severity. What data radiographs in this case: A. * Cortical plate and bone interdental septum saved B. Cortical plate interdental septum is preserved, bone loss at 1/3 the length of the root C. Cortical plate interdental septum rozrushena, bone loss at ½ the length of the root 886. D. All answers are correct E. There is no right answer On admission the patient filed in '18 complaining of gingival overgrowth, their bleeding, pain when eating. Complaints during the year. An examination observed that gingival papillae on the lower jaw increased in size, covering crowns on teeth 1/2, bright red, bleeding when touched, nad'yasenevi dental plaque, skuchenist teeth on the lower jaw. On radiographs unchanged. Applications which feed you want to assign to the local anti-inflammatory therapy? 887. A. Etoniyevoyi B. * Hinozolovoyi C. Metatsylovoyi D. Furatsylinovoyi E. Heparin On admission the patient filed in '17 complaining of gingival overgrowth, their bleeding, pain when eating. Complaints over six months. An examination observed that gingival papillae on the lower jaw increased in size, covering crowns on teeth 1/2, bright red, bleeding when touched, nad'yasenevi dental plaque, skuchenist teeth on the lower jaw. On radiographs unchanged. What is the preliminary diagnosis? A. Ulcer-necrotizing gingivitis 888. B. Catarrhal gingivitis C. * Hypertrophic gingivitis D. Herpetic hinhivostomatyt E. Generalized periodontitis To the doctor turned patient in '16 complaining of gingival overgrowth, their bleeding, pain when eating. These complaints within six months. OBJECTIVE: gingival papillae increased in size, covering the crowns of teeth on the 1/2, bright red, bleeding when touched, nad'yasenevi dental plaque, skuchenist teeth on the lower jaw. On radiographs unchanged. What is the preliminary diagnosis? 889. A. Ulcer-necrotizing gingivitis B. Catarrhal gingivitis C. * Hypertrophic gingivitis, swelling form D. Herpetic hinhivostomatyt E. Hypertrophic gingivitis, fibrous form An objective examination of the patient vstnovleno that a clear bright red, polished color. Which of the following gingivitis characterized this picture? 890. A. Hypertrophic gingivitis B. Sharp catarrhal gingivitis C. Ulcer-necrotizing gingivitis D. * Deskvamativny gingivitis E. Atrophic gingivitis Pregnant '25 complains overgrowth of gums, bleeding and pain when consuming food or cleaning teeth. Objectively: the gingival papillae on the upper and lower jaws are congested, cover the crowns of teeth on the 1/3, bleeding, painful. Festonchastist gingival margin broken. What is the preliminary diagnosis in pregnant? 891. A. Aggravation of periodontitis B. Acute catarrhal gingivitis. C. Chronic catarrhal gingivitis. D. * Hypertrophic gingivitis, puffy shape. E. There is no right answer At the doctor appealed pregnant in '28 with complaints overgrowth of gums, bleeding and pain when consuming food or cleaning teeth. On examination: the gingival papillae on the upper and lower jaws are congested, cover the crowns of teeth on the 1/3, bleeding, painful. Festonchastist gingival margin broken. What is the most likely diagnosis in pregnant? A. Aggravation of periodontitis 892. B. Acute catarrhal gingivitis. C. Chronic catarrhal gingivitis. D. * Hypertrophic gingivitis, puffy shape. E. There is no right answer At the doctor turned patsiyenka '25 complaining overgrowth of gums, bleeding and pain when consuming food or cleaning teeth. The patient at 27 weeks gestation. On examination: the gingival papillae on the upper and lower jaws are congested, cover the crowns of teeth on the 1/2, bleeding, painful. Festonchastist gingival margin broken. What is the most likely diagnosis? 893. A. Aggravation of periodontitis B. Acute catarrhal gingivitis. C. * Hypertrophic gingivitis, puffy shape of the second severity. D. Hypertrophic gingivitis, the first form of edema severity. E. There is no right answer Patient '26 complains of pain in the mouth, bad breath, fever up to 38 C. On examination: the patient was pale, adynamic, regional lymph nodes are enlarged, painful. Interdental papillae and marginal part gums swollen, hyperemic, in ulcers, covered with necrotic plaque on teeth tartar deposits nad'yasenevoho and soft plaque. What additional research needs to be undertaken for diagnosis of this condition? 894. A. * Total blood B. Fluorescent C. Bacteriological D. Immunological E. Cytological At the doctor turned patient in '29 with complaints of pain in the mouth, bad breath, fever up to 38, 5 C. Objectively: the patient was pale, adynamic, regional lymph nodes are enlarged, painful. Interdental papillae and marginal part gums swollen, hyperemic, in ulcers, covered with necrotic plaque on teeth tartar deposits nad'yasenevoho and soft plaque. Put previous daahnoz-ulcerative-necrotic gingivitis. What additional research needs to be undertaken for diffusion. diagnosis of this condition? A. * A blood test for HIV. B. Fluorescent C. Bacteriological D. Immunological E. Cytological 895. By dentist turned sick 15 years. Complaints overgrowth of gum in front teeth upper and lower jaws. Delivered preliminary diagnosis hypertrophic gingivitis medium severity. Changes in the system which are important in the etiology of this disease? 896. A. Digestive B. * Endocrine C. Vascular D. Immune E. Nervous Patient complains of '47 aching pain, especially when eating in section 36 of the tooth. OBJECTIVE: on the medial surface 36 tooth hanging end seals, pin point missing, smoothing kokontura gum papilla, papilla bluish tint, swollen, bleeding when touched. Put diagnosis 897. A. acute catarrhal papillitis; B. * Chronic catarrhal papillitis; C. hypertrophic papillitis; D. ulcerative papillitis; E. the correct answer. In histological preparation determined the formation of oral presentation of the mucous membrane, which has a free part and attached firmly adherent to the periosteum. Multilayered epithelium, flat, keratinizing. Own plate forming long nipples are jutting out into the deep epithelium. Call it education: 898. A. cheeks; B. hard palate; C. clear; D. lip; E. tongue. Parents of children 8 years appealed to the dentist for oral rehabilitation of the child. The examination revealed high intensity caries process (kp + CPV = 7), the index has been received Fedorov-3, 0 points. Which assessment meets the hygienic condition of the mouth of the child: A. satisfactory; B. very bad; C. unsatisfactory; D. good; E. bad. 899. Patient in '25 turned to the doctor complaining of severe bleeding gums, dry mouth, mobility and change the position of teeth, hnoyetechu gums, bad breath. Patient considers himself about 2 months. What research is necessary to conduct primarily for diagnosis: 900. A. analysis in blood sugar; B. revmoproby; C. allergic test; D. serological studies; E. immunological research. Child '14 complains bleeding gums when brushing your teeth for a year. OBJECTIVE: gingival papillae swollen, cyanotic, slightly increased in size. What additional research is necessary to clarify the diagnosis: 901. A. blood; B. sample Yasinovka; C. reoparodontohrafiya; D. radiography; E. sample Schiller-Pisarev. The patient complains of '30 jam food between 46 and 47 teeth, appeared two weeks ago. OBJECTIVE: 46.47 teeth intact, percussion painless teeth, the gum papilla between 46-47 teeth somewhat defined small amount of fibrous food residue. What type of research should be used for concealed cavities: 902. A. fluorescent diagnostics; B. electroodontodiagnosis; C. transilyuministsentnu diagnosis; D. radiographic studies; E. welcome color. Patient '45 complains of pain in the region of 37 teeth. Objectively, 37 tooth covered mytalevoyu crown, ash bud in section 37 and 36 teeth swollen and hyperemic underneath swollen with cyanotic tinge bleeds when touched. Put diagnosis A. acute catarrhal papillitis; B. chronic catarrhal papillitis; C. Acute hypertrophic papillitis; D. chronic hypertrophic papillitis; E. no correct answer. 903. Patient '45 complains of pain in the region of 37 teeth. Objectively, 37 tooth covered mytalevoyu crown, ash bud in section 37 and 36 teeth swollen with cyanotic tinge bleeds when touched. Diagnosed, chronic catarrhal papillitis. Your treatment strategy: 904. A. replacement crowns; B. UHF-therapy; C. requires no treatment; D. rinse medicines; E. electrophoresis-potassium iodine. The patient complains of education in the area of tooth 46. Objectively ash papilla between 46 i47 hyperplastic teeth, bleeding when touched, overlapping crowns on teeth 1/2. In 46 deep tooth cavity. Put diagnosis 905. A. hypertrophic papillitis and art.; B. hypertrophic papillitis second century.; C. hypertrophic papillitis III.; D. chronic catarrhal papillitis; E. chronic ulcerative papillitis. The patient complains of education in the area of tooth 46. Objectively ash papilla between 46 i47 hyperplastic teeth, bleeding when touched, overlapping crowns of teeth on 2/3. In 46 deep tooth cavity. Put diagnosis 906. A. hypertrophic papillitis and art.; B. hypertrophic papillitis second century.; C. hypertrophic papillitis III.; D. chronic catarrhal papillitis; E. chronic ulcerative papillitis. The patient complains of education in the area of tooth 46. OBJECTIVE: ash papilla between 46 i47 hyperplastic teeth, bleeding when touched, overlapping crowns of teeth on 1/3. In 46 deep tooth cavity. Put diagnosis 907. A. hypertrophic papillitis and art.; B. hypertrophic papillitis second century.; C. hypertrophic papillitis III.; D. chronic catarrhal papillitis; E. chronic ulcerative papillitis. Patient 33 years skarzhytsya of pain in the region of 37 teeth. OBJECTIVE: in 37 deep tooth cavity, ash bud in section 37 vyrazkuvatyy covered with gray bloom, bleeding when touched, abundant plaque left lymph nodes are enlarged, painful on palpation. Put diagnosis 908. A. acute catarrhal papillitis; B. ulcerative papillitis; C. atrophic papillitis; D. hypertrophic papillitis; E. no correct answer. Patient 32 years complains of bleeding gums and pain in the area of tooth 35. OBJECTIVE: on the distal surface 35 of the tooth hanging edge seals, ash bud hyperemic, swollen, bleeding when touched. Put diagnosis 909. A. chronic catarrhal papillitis; B. acute catarrhal papillitis; C. atrophic papillitis; D. hypertrophic papillitis; E. no correct answer. Patient 32 years complains of bleeding gums and pain in the area of tooth 35. OBJECTIVE: on the distal surface 35 of the tooth hanging edge seals, ash bud hyperemic, swollen, bleeding when touched. Diagnosed, acute catarrhal papillitis. Your tactics: 910. A. UHF-therapy; B. requires no treatment; C. pereplombuvannya; D. rinse; E. no correct answer. Patient 32 years complains of bleeding gums and pain in the area of tooth 35. OBJECTIVE: on the distal surface 35 of the tooth hanging edge seals, ash papilla swollen, cyanotic hue bleeds when touched. Put diagnosis 911. A. chronic catarrhal papillitis; B. acute catarrhal papillitis; C. Acute hypertrophic; D. chronic hypertrophic; E. no right answer; Patient 32 years complains of bleeding gums and pain in the area of tooth 35. OBJECTIVE: on the distal surface 35 of the tooth hanging edge seals, ash papilla swollen, cyanotic hue bleeds when touched. Your tactics: A. UHF-therapy; B. requires no treatment; C. pereplombuvannya; 912. D. rinse; E. no right answer; To the dentist asked the patient complaining of bleeding gums and pain in diyantsi 46 tooth. OBJECTIVE: on the distal surface 46 of the tooth hanging edge seals, ash bud hyperemic, swollen, bleeding when touched. Put diagnosis A. acute catarrhal papillitis; B. hypertrophic papillitis; C. chronic catarrhal papillitis; D. atrophic papillitis; E. no correct answer. SITUATIONAL TASKS 1. In histological preparation determined the formation of oral mucosa is presented, which is part of the free and attached firmly adherent to the periosteum. Multilayered epithelium, flat, rohoviyuchyy. Own plate forming long nipples are jutting out into the deep epithelium. Call it education: A. cheeks B. hard palate C. * Gums D. lip E. tongue 2. At a reception at the dentist when viewed from the patient revealed that prysinka depth is 4.5 mm. It says: A. Very shallow B. Middle prysinku C. Deep prysinku D. Very deep E. * Milka prysinku 3. When viewed prysinka oral patient revealed that its depth is 9 mm. It says: A. Milka prysinku B. * Middle prysinku C. Deep prysinku D. Norm E. There is no right answer 4. When viewed prysinka oral patient revealed that its depth is 9 mm. It says: A. shallow prysinku B. * Average prysinku C. deep prysinku D. Normally E. no right answer 5. On examination of children in '15 hemorrhage detected in 35% of cases. How can I describe this figure A. low B. high C. * Moderate D. very low E. very high 6. The patient complained of bleeding gums when consuming solid food. What degree of bleeding in this patient A. 2 degree B. * 1 degree C. 3 degree D. 4 degree E. 5th level 7. An examination of the wall in front of the mouth are paying attention to the mucous membrane of the cheek in the area of six upper teeth. Which anatomical formation is taken into account in this case? A. excretory duct submandibulars salivary gland B. * Excretory duct parotid salivary gland C. infraorbitalnyy channel D. maxillary sinus E. all answers are correct 8. During a routine inspection of the patient revealed 2 degree bleeding gums. It says: A. * Bleeding during brushing B. bleeding during consumption of solid food C. spontaneous bleeding D. no right answer E. bleeding during probing 9. The examination revealed that the recession becomes muco-gingival border. Which class recession according to the classification of Miller responds: A. B. C. D. E. 1 class * Class 2 Class 3 Class 4 no right answer 10. The examination revealed that due to gum recession was losing gingival papillae. Which class recession according to the classification of Miller responds: A. 1 class B. Class 2 C. * Class 3 D. Class 4 E. no right answer 11. The examination revealed that due to gum recession was losing gingival papillae and disrupted the position of the tooth. Which class recession according to the classification of Miller responds: A. 1 class B. Class 2 C. Class 3 D. * Class 4 E. no right answer 12. This clinical picture: the appearance of color changes due to inflammation of the gums, bleeding in probing occurs, may cause spontaneous bleeding gums and erosions of the epithelium. In Myulemanu index gingival sulcus bleeding in this case says: A. 1 degree of inflammation B. 2 degrees of inflammation C. Grade 4 inflammation D. 3 degrees of inflammation E. * 5 degree of inflammation 13. The patient chronic generalized periodontitis in remission. When microbiological study content pockets were seeded microorganisms. How many of their colonies per 1 cm2 thus found? A. * 36 B. 26 C. 46 D. 6 E. 2.1 14. In women diagnosed with exacerbation of chronic generalized periodontitis. When microbiological study content pockets were seeded microorganisms. How many of their colonies per 1 cm2 thus found? A. 460 B. * 360 C. 560 D. 1-60 E. 1-20 15. The patient is recommended to conduct oral tsytodiahnostyku. Material for the study will be taken from: A. * Mucosa cheeks, above the interdigitation B. Mucosa in the region of the angle of the mouth C. Mucosa floor of the mouth D. Mucosa cheek below the interdigitation E. There is no correct answer 16. When the reaction of adsorption of microorganisms found that PAM is 83%. Describe the nonspecific resistance in this indicator: A. Poor B. Poor C. Satisfactory D. Very good E. * Good 17. The reaction of adsorption of microorganisms found that PAM is 36%. Describe the nonspecific resistance in this indicator: A. Poor B. Poor C. Very good D. * Satisfactory E. Good 18. Patient 5 years of complaining about bad mouth, gum overgrowth. In the history of epilepsy, the patient systematically taking hydantoin (difenin). On examination, hyperemia and edema of the gums, gums covering teeth crowns for 1/2, palpation bleed. Blood and urine tests are normal. What is the most likely diagnosis? A. Juvenile gingivitis B. * Difeninovyy gingivitis C. Bismuth gingivitis D. Mercury gingivitis E. Gingivitis is pregnant 19. The patient in the treatment of catarrhal gingivitis over three weeks spent oral bath with antiseptic solution. This notice discoloration crowns. What antiseptic is able to cause this? A. Peroxide B. Yodinola C. Potassium permanganate D. Furatsillina E. * Chlorhexidine 20. A patient diagnosed with ulcerative-necrotic gingivitis. Which of the following clinical signs are characteristic of this disease? A. Swelling and redness of the mucous membrane B. Dirty, gray fibrin plaque on the gums C. Necrosis interdental papillae D. The plight of the patient E. * That's right 21. The patient in '28 diagnosed with ulcerative-necrotic gingivitis moderately. An objective examination revealed: A. Swollen lymph nodes B. Dirty, gray fibrin plaque on the gums C. Necrosis interdental papillae D. Edema and hyperemia of the mucosa E. * That's right 22. To the doctor turned patient 39. The complaints of general weakness, fever, pain in the mouth, rapid bleeding gums, putrefactive breath for 4-nights. On examination: the patient was pale, regional lymph nodes are enlarged, painful on palpation, mucous membrane of the gums on both jaws swollen, flushed, covered with gray bloom that is easily removed, sharply painful and bleeding. Which of the following diagnoses is most likely? A. * Ulcer-necrotizing gingivitis B. Catarrhal gingivitis C. Merkurialnyy gingivitis D. Herpetic hinhivostomatyt E. Generalized periodontitis 23. The patient diagnosed with hypertrophic gingivitis. Established that the cause of the disease was the change in the internal organs. What pererahovnoho caused? A. * Endocrine pathology B. Hypertension C. Cardiac glycosides D. Ulcer E. Chronic cholecystitis 24. Patients with hypertrophic gingivitis shows the operation hinhivektomiyi. Which route will be cut at a given surgical intervention? A. Horizontal B. * Continuous hirlyandopodibnyy C. Intermittent Garland similar D. Oval E. There is no right answer 25. The patient in '34 diagnosed ulcerative-necrotic gingivitis. When microbiological study of plaque from the gum found at: A. Fuzobakteriyi B. Spirochaete C. Actinomycetes D. Hromomitsety E. * That's right 26. The patient was diagnosed thipertrofichnyy gingivitis puffy shape. What will manifest clinically in this patient as a result of late edema and hyperplasia? A. Periodontal pockets B. Ulcers C. Syphiloma D. * Gingival pockets E. Papilloma 27. At the reception appealed patient with catarrhal gingivitis moderately. How much ash is included in the inflammatory process in this case: A. Of papillary B. * Papillary and marginal C. Marginal and alveolar D. Alveolar, marginal, papillary E. There is no right answer 28. Patient diagnosed with hypertrophic gingivitis. The doctor decided to sklerotyzatsiyi procedure. What single dose of the drug during deep sklerotyzatsiyi? A. 0.2-0.4 ml B. 0.3-0.5 ml C. 0.4-0.5 ml D. * 0.1-0.2 ml E. 0.7 ml 29. Patients with periodontal diseases subject to mandatory medical examination Patients with catarrhal gingivitis should be attributed to: A. Group 1 clinical patients B. 3 groups of clinical patients C. * 2 groups of clinical patients D. 4 groups of clinical patients E. 5 groups of clinical patients 30. The patient came to the doctor for the final phase of treatment of ulcerative gingivitis. Which of the following groups of drugs used in this case? A. Anesthetic B. Enzymes C. Sulfonamide D. * Keratoplasty E. There is no right answer. 31. The patient came to the doctor for the final phase of treatment of ulcerative gingivitis. Which of the following drugs used in this case? A. Metronidazole B. Chlorhexidine C. Biseptol D. Trypsin E. * A solution of vitamin A 32. On admission to a pediatric dentist parents brought a girl 7 years. Complaints child for bad breath, gum overgrowth. In the history of epilepsy, the patient systematically taking hydantoin (difenin). On examination, hyperemia and edema of the gums, gums covering teeth crowns for 1/2, palpation bleed. Blood and urine tests are normal. What is the most likely diagnosis? A. Juvenile gingivitis B. * Difeninovyy gingivitis C. Bismuth gingivitis D. Mercury gingivitis E. Gingivitis is pregnant 33. On the advice of child's dentist parents came 10 year old boy. The boy complains sprawl gums, bad breath. The patient consistently taking antiepileptic drug difenin. Objectively redness and swelling of the gums, gums cover the crowns of teeth in 1/3, palpation bleed. Blood and urine tests are normal. What is the preliminary diagnosis? A. Juvenile gingivitis B. Gingivitis is pregnant C. Bismuth gingivitis D. * Mercury gingivitis E. Difeninovyy gingivitis 34. Patient complains of '46 bleeding gums, hnoyetechu, tooth mobility. Sick for 10 years. On examination: clear the upper and lower jaws are congested, swollen, with dotorkuvanni bleed. In the 42, 41, 32, 31 teeth periodontal pockets up to 7 mm with purulent discharge, the mobility of II degree, the remaining teeth and degree. The Xray - resorption mezhalveolyarnyh partitions in 42, 41, 31, 32 2/3 the length of the root, the phenomenon of osteoporosis. Which of the following methods most indicated for surgical treatment of this disease? A. Kriokyuretazh B. * Patchwork operation C. Curettage D. Hinhivotomiya E. Hinhivektomiya 35. Patient G. that dispensary diagnosed with generalized periodontitis, and the extent to chronic under examination [X-ray] at 6 months showed bone lonely pocket between 24 and 25 teeth, reaching 1/2 interalveolar height. The 24 tooth with amalgam filling goes deeply into the interdental space. Your tactics regarding bone pockets after correction fillings? A. Hold course lincomycin in transition folds 24 and 25 teeth № 7-10 B. * Will hold open curettage C. Hold hinhivektomiyu D. Hold hinhivotomiyu E. Hold a series of periodontal dressings metroqyl-denta 36. Patient M., 32 years old need to curettage gingival and periodontal pockets. The criterion of efficiency curettage gingival and periodontal pockets in the implementation are: A. Lack pid'yasennoho tartar B. * Lack of severe bleeding, lack pid'yasennoho tartar, granulation and epithelial vrosshoho C. Complete absence of bleeding D. Clear tightly to the teeth E. Lack of granulation and epithelial vrosshoho 37. Patient Y. The diagnosis "generalized periodontitis degree, chronic." What will be the first session of the local treatment? A. * Temporary splinting B. Treatment of symptomatic gingivitis C. Anti-inflammatory therapy D. Curettage periodontal pockets E. Antiseptic treatment and removal of dental plaque 38. Woman '45 complains of bad breath, bleeding gums and pain that intensified when eating. OBJECTIVE: catarrhal gingivitis degree, periodontal pockets reach neck 4 mm, containing a moderate amount of serous - pus. It is noted delaying tartar and plaque in nad'yasneviy and pid'yasneviy parts of the tooth. Mobility of teeth Class. Radiological findings: cortical plate impaired resorption of alveolar bone reaches half the height mezhalveolyarnyh membranes. Diagnosed chronic generalized periodontitis second degree. Where to begin treatment? A. Appointment of mud applications B. * Removal of dental plaque. C. Purpose of the means of anti-inflammatory D. Conducting temporary splinting E. The planned operation 39. In the Clinic Preventive Dentistry appealed patient aged 40 years., Who diagnosed acute generalized periodontitis III. severity. What type of curettage can be used in this nosology A. Outdoor and vacuum - curettage B. * Vacuum - curettage, cryo - curettage C. Open curettage D. Closed curettage E. Open and closed curettage 40. The patient, in '41, diagnosed with generalized periodontitis 2 degrees of severity, sharp course with abscess formation. Which methods of general treatment should be appointed in the first place? A. Stimulant therapy B. Hyposensitization therapy C. Physiotherapy D. * Antibiotic E. Vitamin 41. The patient, 46 years old, diagnosed with generalized periodontitis 2 degrees of severity, sharp course. Recently, the patient noted deterioration, skin itch, dryness in the mouth. Which methods of additional tests should be used before embarking on treatment? A. Total blood B. Urinalysis C. Determination of vitamin C in the blood D. * Determination of blood sugar E. Immunological studies of blood 42. The patient appealed to the dentist with complaints of persistent spontaneous pain, swelling of the gums in 26 and 27 teeth for 2 days. An examination of the lips of the upper and lower jaws of a large number of soft and hard plaque. At 26 and 27 teeth adjacent large fillings, contact checkbox, clear congested, swollen, on alveolar part of the protrusion, palpation painful, tooth-gingival pocket 6 mm with purulent exudate. What is the primary tactic local drug treatment? A. Closed curettage tools gingival pockets B. * Removal of dental plaque, periodontal abscess disclosure C. Removal of dental plaque, application of medicines to clear D. Open curettage of periodontal pockets E. Rinse antiseptic Appointment 43. The patient complains of '55 bad breath, bleeding gums and pain that intensified when eating. OBJECTIVE: catarrhal gingivitis degree, periodontal pocket depth of 4 mm, containing a moderate amount of serous - pus. It is noted delaying tartar and plaque in nad'yasneviy and pid'yasneviy parts of the tooth. Mobility of teeth Class. Radiological findings: cortical plate impaired resorption of alveolar bone reaches half the height mezhalveolyarnyh membranes. Diagnosed chronic generalized periodontitis second degree. Where to begin treatment? A. Appointment of mud applications B. * Removal of dental plaque. C. Purpose of the means of anti-inflammatory D. Conducting temporary splinting E. The planned operation 44. Patient A., 35 years old with a diagnosis of chronic generalized periodontitis II severity, need to surgery. The criterion for selection of surgical intervention in treatment parodotytu are: A. The depth of periodontal pockets B. Complaints patient C. Duration of disease D. Age of the patient E. * The depth of periodontal pockets, the general condition of the patient, the patient's age 45. Patient M., 32 years old need to curettage gingival and periodontal pockets. The criterion of efficiency curettage gingival and periodontal pockets in the implementation are: A. Lack pid'yasennoho tartar B. * Lack of severe bleeding, lack pid'yasennoho tartar, granulation and epithelial vrosshoho C. Complete absence of bleeding D. Clear tightly to the teeth E. Lack of granulation and epithelial vrosshoho 46. On admission the patient came in '36 with complaints of bleeding gums, hnoyetechu, tooth mobility. Sick for 10 years. On examination: clear the upper and lower jaws are congested, swollen, with dotorkuvanni bleed. In the 42, 41, 32, 31 teeth periodontal pockets up to 7 mm with purulent discharge, the mobility of II degree, the remaining teeth and degree. The X-ray - resorption mezhalveolyarnyh partitions in 42, 41, 31, 32 2/3 the length of the root, the phenomenon of osteoporosis. Which of the following methods most indicated for surgical treatment of this disease? A. Kriokyuretazh B. * Patchwork operation C. Curettage D. Hinhivotomiya E. Hinhivektomiya 47. In consultation addressed patient in '42 with complaints bleeding gums, hnoyetechu gums, tooth mobility. Sick 8 years. OBJECTIVE: gums on the upper and lower jaws hyperemic, edematous, with dotorkuvanni bleed. In the 32, 31, 42, 41 teeth periodontal pockets up to 6.5 mm with purulent discharge, the mobility of II degree, the remaining teeth and degree. The X-ray - resorption mezhalveolyarnyh partitions in 42, 41, 31, 32 2/3 the length of the root, the phenomenon of osteoporosis. Which of the following methods most indicated for surgical treatment of this disease? A. Kriokyuretazh B. Curettage C. * Patchwork operation D. Hinhivotomiya E. Hinhivektomiya 48. Woman '38 complains hnoyetechu and bleeding gums, tooth mobility. OBJECTIVE: gums on the upper and lower jaws hyperemic, edematous, with dotorkuvanni bleeding, periodontal pocket of 6 mm with purulent discharge, the mobility of the second degree. The X-ray - resorption mezhalveolyarnyh walls on 2/3 the length of the root, the phenomenon of osteoporosis. Which of the following most indicated for surgical treatment of this disease? A. Kriokyuretazh B. Curettage C. * Patchwork operation D. Hinhivotomiya E. Hinhivektomiya 49. A patient with periodontal pathology recommended surgery - operation hinhivektomiyi. The operation will be conducted in the right side area of the upper jaw. What number of teeth will obmezhovuvatys operative field? A. * 3.2 B. 4.6 C. 6.8 D. 2.1 E. 4.3 50. When examining a patient with a diagnosis of chronic generalized periodontitis and severity discovered bone lonely pocket between 24 and 25 teeth, reaching 1/2 interalveolar height. The 24 tooth with amalgam filling goes deeply into the interdental space. Your tactics regarding bone pocket after correction fillings? A. Hold course lincomycin in transition folds 24 and 25 teeth № 7-10 B. * Will hold open curettage C. Hold hinhivektomiyu D. Hold hinhivotomiyu E. Hold a series of periodontal dressings metroqyl-denta 51. On the advice appealed woman, 35 years. The woman is on the records with a diagnosis of chronic generalized periodontitis and severity. The examination revealed bone lonely pocket between 13 and 14 teeth, reaching 1/2 interalveolar height. The 14 tooth set a seal that goes deeply into the interdental space. Your tactics regarding bone pocket after correction fillings? A. Hold a course of antibiotics for a transitional folds 24 and 25 teeth № 7-10 B. * Will hold open curettage C. Hold hinhivektomiyu D. Hold closed curettage E. Hold a series of periodontal dressings metroqyl-denta 52. Patient in '40 is on the records with a diagnosis of chronic generalized periodontitis and severity. At the planned examination revealed bone lonely pocket between 14 and 15 teeth, reaching 1/2 interalveolar height. What treatment should be in this case? A. Hold a course of antibiotics for a transitional folds 24 and 25 teeth № 7-10 B. * Will hold open curettage C. Hold hinhivektomiyu D. Hold closed curettage E. Hold a series of periodontal dressings metroqyl-denta 53. Patient doctor prescribed brushing toothpaste containing calcium and fluoride. Which group includes this toothpaste? A. * The group protykarioznyh medical toothpastes B. The group therapeutic toothpastes C. The group hygienic toothpaste D. The group of anti-inflammatory treatment and prevention toothpaste E. There is no right answer 54. In determining the index Fedorova - has been received revealed that the state of oral hygiene is very poor, with multiple dental plaque. What kind of toothpaste should be used in this case A. * Type Smokers Toothpaste B. Toothpaste Anti-Plaque Type C. paste type Sensitive D. protykarioznu therapeutic - prophylactic paste E. no right answer 55. An examination of the patient revealed multiple wedge-shaped defects. Which band toothpastes can recommend this patient A. paste type Smokers B. Toothpaste Anti-Plaque Type C. * Type Sensitive Toothpaste D. protykarioznu therapeutic - prophylactic paste E. no right answer 56. In vah'itnoyi patient hypertrophic gingivitis. What toothpaste can recommend in this case? A. * Anti-inflammatory treatment and prevention B. Therapeutical C. Protykarioznu medical - preventive D. Sanitarily E. There is no right answer 57. The patient was diagnosed pathology of periodontal tissues. What method of cleaning can be recommended in this case? A. * Method Bass B. Method charter C. Method Background D. Method Stilmana E. Method Leonard 58. The patient chronic generalized periodontitis in remission. When microbiological study content pockets were seeded microorganisms. How many of their colonies per 1 cm2 thus found? A. * 36 B. 26 C. 46 D. 1 - 6 E. 2.1 59. In women diagnosed with exacerbation of chronic generalized periodontitis. When microbiological study content pockets were seeded microorganisms. How many of their colonies per 1 cm2 thus found? A. 460 B. * 360 C. 560 D. 1-60 E. 1-20 60. Patient R., 22 years old, diagnosed - ulcerative-necrotic stomatitis Vincent. During the surface treatment of ulcers necrotic plaque is removed from the effort. What are the medications most appropriate solution for the raid? A. Antifungal drugs B. * Proteolitichni enzymes C. Antiseptic drugs D. Keratoplasty E. Keratolityky 61. After suffering ARI patient appealed to the dentist complaining of pain in the gums, bad breath, inability to eat, general weakness. OBJECTIVE: clear congested, swollen, covered with fibrinous coating, which occurs when removing the bleeding. Microbiological research gum tissue revealed a large number of cocci, bacilli, and spirochetes fuzobakteriy. Specify drug treatment etiotropic A. Karotolina B. Haloskorbin C. Potassium permanganate D. Trypsin E. * Metronidazole 62. Patient '17 complains of pain in the mouth, bleeding gums sharp, putrefactive breath, general weakness within 3 days. On examination: the patient is pale, regional lymph nodes are enlarged, painful on palpation, mucous membrane of the gums on both jaws swollen, flushed, covered with gray bloom that is easily removed, sharply painful and bleeding. Which of the following diagnoses is most likely? A. * Ulcer-necrotizing gingivitis B. Catarrhal gingivitis C. Merkurialnyy gingivitis D. Herpetic hinhivostomatyt E. Generalized periodontitis 63. Patient complains of '17 bleeding gums and pain within six months. On examination gingival papillae in the frontal area of the upper and lower jaws swollen, hyperemic. Relief gingival margin broken, papillae cover crowns on teeth 1/2, palpation bleed, false pocket depth of 4 mm, nad'yasenevi dental plaque. What interventions are most effective for local treatment of this disease A. Diathermocoagulation hypertrophied papillae B. Sclerotherapy 50% glucose solution C. Overlay tsyklofosfanovoyi paste D. Phonophoresis Heparin ointment E. * Anti-inflammatory therapy, excision of gum 64. Patient complains of '16 overgrowth of gums, their bleeding, pain when eating. Complaints during the year. The examination is marked skuchenist teeth on the lower jaw. Gingival papillae on the lower jaw increased in size, covering the crowns of teeth on 1/2, bright red, bleeding when touched, nad'yasenevi dental plaque. On radiographs unchanged. Applications which feed you want to assign to the local anti-inflammatory therapy? A. Etoniyevoyi B. * Hinozolovoyi C. Metatsylovoyi D. Furatsylinovoyi E. Heparin 65. Pregnant '20 complains overgrowth of gums, bleeding and pain when consuming food or cleaning teeth. Objectively: the gingival papillae on the upper and lower jaws are congested, cover the crowns of teeth on the 1/2, bleeding, painful. Festonchastist gingival margin broken. What is the most likely diagnosis in pregnant? A. Aggravation of periodontitis B. Acute catarrhal gingivitis. C. Chronic catarrhal gingivitis. D. * Hypertrophic gingivitis, puffy shape. E. There is no right answer 66. Patient '23 complains of pain in the mouth, bad breath, fever up to 38C. Patient pale, adynamic, regional lymph nodes are enlarged, painful. Interdental papillae and marginal part gums swollen, hyperemic, in ulcers, covered with necrotic plaque on teeth tartar deposits nad'yasenevoho and soft plaque. What additional research needs to be undertaken for diagnosis of this condition? A. * Total blood B. Fluorescent C. Bacteriological D. Immunological E. Cytological 67. Patient complains of '16 overgrowth of gum in front teeth upper and lower jaws. Diagnosed hypertrophic gingivitis medium severity. Pathology which system is important in the etiology of this disease? A. Digestive B. * Endocrine C. Vascular D. Immune E. Nervous 68. Patient, 20 years old, grumbles overgrowth of gums and bleeding when brushing teeth. OBJECTIVE: proliferation of gingival papillae at all teeth that 1/2 override crown height of teeth, gums, bright red, painful on palpation. What pathogenetic treatment should be applied here? A. Stimulant B. Anti-inflammatory C. Antimicrobial D. * Sclerosing E. Remineralization. 69. The patient in '23 was diagnosed: "Hypertrophic gingivitis, fibrous shape, average severity." What is the most rational treatment? A. * Surgical B. Diathermocoagulation. C. Anti-inflammatory therapy. D. Sclerotherapy E. There is no right answer 70. Patient, 26 years old, appealed with complaints about the proliferation of gum. OBJECTIVE: In section 14 of the tooth gums fungous growths limited form dense, dark red with cyanotic tinge. 14 tooth mobility in the vestibular-oral direction. Abnormal formation of patient noted a year ago, and connects with pregnancy. What is the most likely diagnosis? A. Gingival fibromatosis B. * Epulit, anheomatozna form C. Hypertrophic gingivitis, swelling form D. Acute localized periodontitis of moderate severity E. Hypertrophic gingivitis, fibrous form. 71. Patient 19, a driver complains of malaise, fever, sore gums, bad breath. Objectively: the gingival papillae and gingival edge grayish, friable, easily removed with uncovering ulcers, bleeding and sharply painful surface. Oral mucosa pink. What is the most likely diagnosis in the patient? A. Acute ulcerative gingivitis. B. Acute leukemia C. Lead gingivitis D. Gangrenous gingivitis E. Chronic ulcerative gingivitis 72. Patient complains of '30 overgrowth of gum in 22, 23, 24 teeth, which is noticed more than 3 months ago. On examination: the contact surfaces 22, 23, 24 teeth deep cavities, interdental contacts violated ash papillae increased in volume, covering the crowns of teeth on 1/3 at dotorkuvanni bleeding on the radiograph changes not. Which of the following diagnoses is most likely? A. * Localized hypertrophic gingivitis B. Chronic papillitis C. Nad'yasenevyy epulis D. Localized periodontitis E. Generalized hypertrophic gingivitis 73. The patient in '18 revealed the diagnosis "chronic catarrhal gingivitis." When X-ray revealed alveolar bone osteoporosis. What pathogenetic therapy lead to eradication of the disease. A. * Immunomodulatory therapy. B. Antihistamine therapy. C. Antibiotic. D. Vitamin. E. Electrophoresis calcium supplements 74. During the examination, the patient R., 25 years old, diagnosed - ulcerative-necrotic stomatitis Vincent. During processing poverhen ulcers necrotic plaque is removed from the effort. What are the medications most appropriate solution for the raid? A. Antifungal drugs B. * Proteolitichni enzymes C. Antiseptic drugs D. Keratoplasty E. Keratolityky 75. On the advice of the patient turned 38 years old. Patient after suffering a cold. Complaints of pain in the gums, bad breath, inability to eat, general weakness. OBJECTIVE: clear congested, swollen, covered with fibrinous coating, which occurs when removing the bleeding. Microbiological research gum tissue revealed a large number of cocci, bacilli, and spirochetes fuzobakteriy. Specify drug treatment etiotropic A. Karotolina B. Haloskorbin C. Potassium permanganate D. Trypsin E. * Metronidazole 76. On the advice of the patient came 28 years after suffering a cold. Complaints of pain in the gums, bad breath, inability to eat, general weakness. OBJECTIVE: clear congested, swollen, covered with fibrinous coating, which occurs when removing the bleeding. Microbiological research gum tissue revealed a large number of cocci, bacilli, and spirochetes fuzobakteriy. Select a drug for general etiotropic treatment for this patient A. Karotolina B. Halaskorbin C. Potassium permanganate D. Trypsin E. * Metronidazole 77. Patient '27 complains of pain in the mouth, bleeding gums sharp, putrefactive breath, general weakness within 3 days. Objective: the patient is pale, regional lymph nodes are enlarged, painful on palpation, mucous membrane of the gums on both jaws swollen, flushed, covered with gray bloom that is easily removed, sharply painful and bleeding. Which of the following diagnoses is most likely? A. * Ulcer-necrotizing gingivitis B. Catarrhal gingivitis C. Merkurialnyy gingivitis D. Herpetic hinhivostomatyt E. Generalized periodontitis 78. To the doctor turned patient 19. Complaints of pain in the mouth, rapid bleeding gums, putrefactive breath, general weakness within 3 days. On examination: the patient was pale, regional lymph nodes are enlarged, painful on palpation, mucous membrane of the gums on both jaws swollen, flushed, covered with gray bloom that is easily removed, sharply painful and bleeding. Which of the following diagnoses is most likely? A. * Ulcer-necrotizing gingivitis B. Catarrhal gingivitis C. Merkurialnyy gingivitis D. Herpetic hinhivostomatyt E. Generalized periodontitis 79. To the doctor turned sick in '19 with complaints of bleeding and sore gums within six months. On examination gingival papillae in the frontal area of the upper and lower jaws swollen, hyperemic. Relief gingival margin broken, papillae cover crowns on teeth 1/2, palpation bleed, false pocket depth of 4 mm, nad'yasenevi dental plaque. What interventions are most effective for local treatment of this disease A. Diathermocoagulation hypertrophied papillae B. Sclerotherapy 50% glucose solution C. Overlay tsyklofosfanovoyi paste D. Phonophoresis Heparin ointment E. * Anti-inflammatory therapy, excision of gum 80. The patient complains of '29 bleeding and sore gums during 6 months. On examination gingival papillae in areas of the upper and lower jaws swollen, hyperemic. Relief gingival margin broken, papillae cover crowns on teeth 1/2, palpation bleed, false pocket depth of 4 mm, nad'yasenevi dental plaque. What is the preliminary diagnosis A. Ulcer-necrotizing gingivitis B. Merkurialnyy gingivitis C. Periodontal Disease D. * Hypertrophic gingivitis 2 severity E. Generalized periodontitis 81. The patient complains of '32 bleeding and sore gums during 6 months. OBJECTIVE: gingival papillae in parts of the upper and lower jaws swollen, hyperemic. Relief gingival margin broken, papillae cover crowns of teeth in 1/3, palpation bleed, false pocket depth of 2 mm, nad'yasenevi dental plaque. What is the preliminary diagnosis A. Ulcer-necrotizing gingivitis B. * Hypertrophic gingivitis 1 degree of severity C. Periodontal Disease D. Hypertrophic gingivitis 2 severity E. Generalized periodontitis 82. To the doctor turned patient in '29 with complaints of bleeding and sore gums within six months. On examination gingival papillae in the frontal area of the upper and lower jaws swollen, hyperemic. Relief gingival margin broken, papillae cover crowns on teeth 1/2, palpation bleed, false pocket depth of 4 mm, nad'yasenevi dental plaque. What is the preliminary diagnosis A. Ulcer-necrotizing gingivitis B. Merkurialnyy gingivitis C. Periodontal Disease D. * Hypertrophic gingivitis E. Generalized periodontitis 83. The patient in '34 diagnosed acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis-mild severity. What data radiographs in this case: A. * Cortical plate and bone interdental septum saved B. Cortical plate interdental septum is preserved, bone loss at 1/3 the length of the root C. Cortical plate interdental septum rozrushena, bone loss at ½ the length of the root D. All answers are correct E. There is no right answer 84. On admission the patient filed in '18 complaining of gingival overgrowth, their bleeding, pain when eating. Complaints during the year. An examination observed that gingival papillae on the lower jaw increased in size, covering crowns on teeth 1/2, bright red, bleeding when touched, nad'yasenevi dental plaque, skuchenist teeth on the lower jaw. On radiographs unchanged. Applications which feed you want to assign to the local anti-inflammatory therapy? A. Etoniyevoyi B. * Hinozolovoyi C. Metatsylovoyi D. Furatsylinovoyi E. Heparin 85. On admission the patient filed in '17 complaining of gingival overgrowth, their bleeding, pain when eating. Complaints over six months. An examination observed that gingival papillae on the lower jaw increased in size, covering crowns on teeth 1/2, bright red, bleeding when touched, nad'yasenevi dental plaque, skuchenist teeth on the lower jaw. On radiographs unchanged. What is the preliminary diagnosis? A. Ulcer-necrotizing gingivitis B. Catarrhal gingivitis C. * Hypertrophic gingivitis D. Herpetic hinhivostomatyt E. Generalized periodontitis 86. To the doctor turned patient in '16 complaining of gingival overgrowth, their bleeding, pain when eating. These complaints within six months. OBJECTIVE: gingival papillae increased in size, covering the crowns of teeth on the 1/2, bright red, bleeding when touched, nad'yasenevi dental plaque, skuchenist teeth on the lower jaw. On radiographs unchanged. What is the preliminary diagnosis? A. Ulcer-necrotizing gingivitis B. Catarrhal gingivitis C. * Hypertrophic gingivitis, swelling form D. Herpetic hinhivostomatyt E. Hypertrophic gingivitis, fibrous form 87. An objective examination of the patient vstnovleno that a clear bright red, polished color. Which of the following gingivitis characterized this picture? A. Hypertrophic gingivitis B. Sharp catarrhal gingivitis C. Ulcer-necrotizing gingivitis D. * Deskvamativny gingivitis E. Atrophic gingivitis 88. Pregnant '25 complains overgrowth of gums, bleeding and pain when consuming food or cleaning teeth. Objectively: the gingival papillae on the upper and lower jaws are congested, cover the crowns of teeth on the 1/3, bleeding, painful. Festonchastist gingival margin broken. What is the preliminary diagnosis in pregnant? A. Aggravation of periodontitis B. Acute catarrhal gingivitis. C. Chronic catarrhal gingivitis. D. * Hypertrophic gingivitis, puffy shape. E. There is no right answer 89. At the doctor appealed pregnant in '28 with complaints overgrowth of gums, bleeding and pain when consuming food or cleaning teeth. On examination: the gingival papillae on the upper and lower jaws are congested, cover the crowns of teeth on the 1/3, bleeding, painful. Festonchastist gingival margin broken. What is the most likely diagnosis in pregnant? A. Aggravation of periodontitis B. Acute catarrhal gingivitis. C. Chronic catarrhal gingivitis. D. * Hypertrophic gingivitis, puffy shape. E. There is no right answer 90. At the doctor turned patsiyenka '25 complaining overgrowth of gums, bleeding and pain when consuming food or cleaning teeth. The patient at 27 weeks gestation. On examination: the gingival papillae on the upper and lower jaws are congested, cover the crowns of teeth on the 1/2, bleeding, painful. Festonchastist gingival margin broken. What is the most likely diagnosis? A. Aggravation of periodontitis B. Acute catarrhal gingivitis. C. * Hypertrophic gingivitis, puffy shape of the second severity. D. Hypertrophic gingivitis, the first form of edema severity. E. There is no right answer 91. Patient '26 complains of pain in the mouth, bad breath, fever up to 38 C. On examination: the patient was pale, adynamic, regional lymph nodes are enlarged, painful. Interdental papillae and marginal part gums swollen, hyperemic, in ulcers, covered with necrotic plaque on teeth tartar deposits nad'yasenevoho and soft plaque. What additional research needs to be undertaken for diagnosis of this condition? A. * Total blood B. Fluorescent C. Bacteriological D. Immunological E. Cytological 92. At the doctor turned patient in '29 with complaints of pain in the mouth, bad breath, fever up to 38, 5 C. Objectively: the patient was pale, adynamic, regional lymph nodes are enlarged, painful. Interdental papillae and marginal part gums swollen, hyperemic, in ulcers, covered with necrotic plaque on teeth tartar deposits nad'yasenevoho and soft plaque. Put previous daahnoz-ulcerative-necrotic gingivitis. What additional research needs to be undertaken for diffusion. diagnosis of this condition? A. * A blood test for HIV. B. Fluorescent C. Bacteriological D. Immunological E. Cytological 93. By dentist turned sick 15 years. Complaints overgrowth of gum in front teeth upper and lower jaws. Delivered preliminary diagnosis hypertrophic gingivitis medium severity. Changes in the system which are important in the etiology of this disease? A. Digestive B. * Endocrine C. Vascular D. Immune E. Nervous 94. In histological preparation determined the formation of oral presentation of the mucous membrane, which has a free part and attached firmly adherent to the periosteum. Multilayered epithelium, flat, rohoviyuchyy. Own plate forming long nipples are jutting out into the deep epithelium. Call it education: A. cheeks; B. hard palate; C. clear; D. lip; E. tongue. 95. Parents of children 8 years appealed to the dentist for oral rehabilitation of the child. The examination revealed high intensity caries process (kp + CPV = 7), the index has been received Fedorov-3, 0 points. Which assessment meets the hygienic condition of the mouth of the child: A. satisfactory; B. very bad; C. unsatisfactory; D. good; E. bad. 96. Patient in '25 turned to the doctor complaining of severe bleeding gums, dry mouth, mobility and change the position of teeth, hnoyetechu gums, bad breath. Patient considers himself about 2 months. What research is necessary to conduct primarily for diagnosis: A. analysis in blood sugar; B. revmoproby; C. allergic test; D. serological studies; E. immunological research. 97. The patient complains of '30 stuck food between 46 and 47 teeth, appeared two weeks ago. OBJECTIVE: 46.47 teeth intact, percussion painless teeth, the gum papilla between 46-47 teeth slightly swollen and hyperemic beneath identified a small number of fibrous food residue. What type of research should be used for concealed cavities: A. fluorescent diagnostics; B. electroodontodiagnosis; C. transilyuministsentnu diagnosis; D. radiographic studies; E. welcome color. 98. Patient '45 complains of pain in the region of 37 teeth. Objectively, 37 tooth covered mytalevoyu crown, ash bud in section 37 and 36 teeth swollen with cyanotic tinge bleeds when touched. Put diagnosis A. acute catarrhal papillitis; B. chronic catarrhal papillitis; C. Acute hypertrophic papillitis; D. chronic hypertrophic papillitis; E. no correct answer. 99. Patient '45 complains of pain in the region of 37 teeth. Objectively, 37 tooth covered mytalevoyu crown, ash bud in section 37 and 36 teeth swollen with cyanotic tinge bleeds when touched. Diagnosed, chronic catarrhal papillitis. Your treatment strategy: A. replacement crowns; B. UHF-therapy; C. requires no treatment; D. rinse medicines; E. electrophoresis-potassium iodine. 100. The patient complains of education in the area of tooth 46. Objectively ash papilla between 46 i47 hyperplastic teeth, bleeding when touched, overlapping crowns on teeth 1/2. In 46 deep tooth cavity. Put diagnosis A. hypertrophic papillitis and art.; B. hypertrophic papillitis second century.; C. hypertrophic papillitis III.; D. chronic catarrhal papillitis; E. chronic ulcerative papillitis. 101. The patient complains of education in the area of tooth 46. Objectively ash papilla between 46 i47 hyperplastic teeth, bleeding when touched, overlapping crowns of teeth on 2/3. In 46 deep tooth cavity. Put diagnosis A. hypertrophic papillitis and art.; B. hypertrophic papillitis second century.; C. hypertrophic papillitis III.; D. chronic catarrhal papillitis; E. chronic ulcerative papillitis. 102. The patient complains of education in the area of tooth 46. OBJECTIVE: ash papilla between 46 i47 hyperplastic teeth, bleeding when touched, overlapping crowns of teeth on 1/3. In 46 deep tooth cavity. Put diagnosis A. hypertrophic papillitis and art.; B. hypertrophic papillitis second century.; C. hypertrophic papillitis III.; D. chronic catarrhal papillitis; E. chronic ulcerative papillitis. 103. Patient 33 years skarzhytsya of pain in the region of 37 teeth. OBJECTIVE: in 37 deep tooth cavity, ash bud in section 37 vyrazkuvatyy covered with gray bloom, bleeding when touched, abundant plaque left lymph nodes are enlarged, painful on palpation. Put diagnosis A. acute catarrhal papillitis; B. ulcerative papillitis; C. atrophic papillitis; D. hypertrophic papillitis; E. no correct answer. 104. Patient 32 years complains of bleeding gums and pain in the area of tooth 35. OBJECTIVE: on the distal surface 35 of the tooth hanging edge seals, ash bud hyperemic, swollen, bleeding when touched. Put diagnosis A. chronic catarrhal papillitis; B. acute catarrhal papillitis; C. atrophic papillitis; D. hypertrophic papillitis; E. no correct answer. 105. Patient 32 years complains of bleeding gums and pain in the area of tooth 35. OBJECTIVE: on the distal surface 35 of the tooth hanging edge seals, ash bud hyperemic, swollen, bleeding when touched. Diagnosed, acute catarrhal papillitis. Your tactics: A. UHF-therapy; B. requires no treatment; C. pereplombuvannya; D. rinse; E. no correct answer. 106. Patient 32 years complains of bleeding gums and pain in the area of tooth 35. OBJECTIVE: on the distal surface 35 of the tooth hanging edge seals, ash papilla swollen, cyanotic hue bleeds when touched. Put diagnosis A. chronic catarrhal papillitis; B. acute catarrhal papillitis; C. Acute hypertrophic; D. chronic hypertrophic; E. no right answer; 107. Patient 32 years complains of bleeding gums and pain in the area of tooth 35. OBJECTIVE: on the distal surface 35 of the tooth hanging edge seals, ash papilla swollen, cyanotic hue bleeds when touched. Your tactics: A. UHF-therapy; B. requires no treatment; C. pereplombuvannya; D. rinse; E. no right answer; 108. In papillitis goes lesions: A. soft periodontal tissues; B. soft tissue and periodontal bone alvolyarnoyi; C. only alvolyarnoyi bone; D. no lesions; E. no correct answer. 109. To the dentist asked the patient complaining of bleeding gums and pain in the area of tooth 46. OBJECTIVE: on the distal surface 46 of the tooth hanging edge seals, ash bud hyperemic, swollen, bleeding when touched. Put diagnosis A. acute catarrhal papillitis; B. hypertrophic papillitis; C. chronic catarrhal papillitis; D. atrophic papillitis; E. no correct answer. 110. Patient complains of '47 aching pain, especially when eating in section 36 of the tooth. OBJECTIVE: on the medial surface 36 tooth hanging end seals, pin point missing, smoothing the path gum papilla, papilla bluish tint, swollen, bleeding when touched. Put diagnosis A. acute catarrhal papillitis; B. chronic catarrhal papillitis; C. hypertrophic papillitis; D. ulcerative papillitis; E. no correct answer. 111. The boy in '15 complaints of weakness, pain when consuming food, bleeding gums, t ˚ body 38 S. OBJECTIVE: pale baby on cheek mucosa, hard and soft palate, point krovovylyvy.Yaki research methods should be undertaken for diagnosis: A. blood; B. prohba Kulazhenko; C. smear microscopy; D. tsytoskopichnyy; E. sample Schiller-Pisarev. 112. Patient skarzhytsya on cosmetic defect in the tooth on the upper jaw. Recognizes injury two years ago. OBJECTIVE: 11 tooth intact, changed in color, percussion painless. In the mucosa in a stretch of 11 tooth marked bone bulging wall. What additional examination is necessary to: A. X-ray; B. EDI; C. rheography; D. capillaroscopy; E. thermometry. 113. Patient skarzhytsya on short, spontaneous, periodic pain in the tooth on the upper left schylepi. OBJECTIVE: on the chewing surface of the tooth cavity 26 within bilyapulparnoho dentynu.Zonduvannya bottom sore. Pain from thermal stimuli lasts about 3 minutes. Diagnosed hyperemia of the pulp. What method is necessary to confirm the diagnosis: A. electroodontodiagnosis; B. renthendiahnostyka; C. TER-test; D. transilyuminatsiya; E. polarography. 114. Child '14 applied to rehabilitation of the mouth. Recognizes May 31 tooth two years ago. OBJECTIVE: 31 tooth intact, perkustsiya painless, mucous membrane in the region of 31 tooth is not changed. What additional method required for putting diagnosis: A. X-ray; B. EDI; C. reflective; D. rheography; E. polarography. 115. Patient skarzhytsya bleeding from the gums. Locally: interdental papillae nabryakshi, red, cyanotic tinge. There is crowding of teeth in the front area. Which method of research is required to determine the final diagnosis: A. definition of periodontal indices; B. determine the hygienic indices; C. X-ray; D. complete blood count; E. All answers are correct. 116. Patient 25 years old, appealed with complaints of bleeding gums during consumption of solid food. Prevalence of inflammation determined by? A. Index PMA; B. Index Green-Vermilona; C. periodontal index; D. Index Fedorova has been received; E. formalin test. 117. The patient filed a complaint for bleeding gums when brushing teeth and taking hard food. Seen from the marginal part of the gingival vestibular side on the upper and lower jaw swollen, hipermiyovana, deposition of gum stone index Fedorova has been received - 3.0. What method should be carried out: A. sample Schiller-Pisarev; B. determine the stability of the capillaries; C. thorough history taking; D. determining emigration of leukocytes; E. X-ray examination. 118. Patient in '46 complained to bleeding gums when teeth cleanings for 6 months, bad breath. On examination: Yassin papillae of the upper and lower jaw stagnant hyperemic, edematous, roofing in probing. Teeth fixed, deposits on the teeth above the gum stone. Periodontal pockets there. Which method of research is necessary to more accurate diagnosis: A. reoparodontohrafiya; B. complete blood count; C. blood sugar; D. panoramic radiography; E. Index hygiene by Fedorova has been received 119. To the dentist asked the patient complaining of bleeding gums and pain in the area of tooth 46. OBJECTIVE: on the distal surface 46 of the tooth hanging edge seals, ash bud hyperemic, swollen, bleeding when touched. Put diagnosis A. acute catarrhal papillitis; B. hypertrophic papillitis; C. chronic catarrhal papillitis; D. artofichnyy papillitis; E. no correct answer. 120. Patient complains of '47 aching pain, especially when eating in section 36 of the tooth. OBJECTIVE: on the medial surface 36 tooth hanging end seals, pin point missing, smoothing kokontura gum papilla, papilla bluish tint, swollen, bleeding when touched. Put diagnosis A. acute catarrhal papillitis; B. * Chronic catarrhal papillitis; C. hypertrophic papillitis; D. ulcerative papillitis; E. the correct answer. 121. In histological preparation determined the formation of oral presentation of the mucous membrane, which has a free part and attached firmly adherent to the periosteum. Multilayered epithelium, flat, keratinizing. Own plate forming long nipples are jutting out into the deep epithelium. Call it education: A. cheeks; B. hard palate; C. clear; D. lip; E. tongue. 122. Parents of children 8 years appealed to the dentist for oral rehabilitation of the child. The examination revealed high intensity caries process (kp + CPV = 7), the index has been received Fedorov-3, 0 points. Which assessment meets the hygienic condition of the mouth of the child: A. satisfactory; B. very bad; C. unsatisfactory; D. good; E. bad. 123. Patient in '25 turned to the doctor complaining of severe bleeding gums, dry mouth, mobility and change the position of teeth, hnoyetechu gums, bad breath. Patient considers himself about 2 months. What research is necessary to conduct primarily for diagnosis: A. analysis in blood sugar; B. revmoproby; C. allergic test; D. serological studies; E. immunological research. 124. Child '14 complains bleeding gums when brushing your teeth for a year. OBJECTIVE: gingival papillae swollen, cyanotic, slightly increased in size. What additional research is necessary to clarify the diagnosis: A. blood; B. sample Yasinovka; C. reoparodontohrafiya; D. radiography; E. sample Schiller-Pisarev. 125. The patient complains of '30 jam food between 46 and 47 teeth, appeared two weeks ago. OBJECTIVE: 46.47 teeth intact, percussion painless teeth, the gum papilla between 46-47 teeth somewhat defined small amount of fibrous food residue. What type of research should be used for concealed cavities: A. fluorescent diagnostics; B. electroodontodiagnosis; C. transilyuministsentnu diagnosis; D. radiographic studies; E. welcome color. 126. Patient '45 complains of pain in the region of 37 teeth. Objectively, 37 tooth covered mytalevoyu crown, ash bud in section 37 and 36 teeth swollen and hyperemic underneath swollen with cyanotic tinge bleeds when touched. Put diagnosis A. acute catarrhal papillitis; B. chronic catarrhal papillitis; C. Acute hypertrophic papillitis; D. chronic hypertrophic papillitis; E. no correct answer. 127. Patient '45 complains of pain in the region of 37 teeth. Objectively, 37 tooth covered mytalevoyu crown, ash bud in section 37 and 36 teeth swollen with cyanotic tinge bleeds when touched. Diagnosed, chronic catarrhal papillitis. Your treatment strategy: A. replacement crowns; B. UHF-therapy; C. requires no treatment; D. rinse medicines; E. electrophoresis-potassium iodine. 128. The patient complains of education in the area of tooth 46. Objectively ash papilla between 46 i47 hyperplastic teeth, bleeding when touched, overlapping crowns on teeth 1/2. In 46 deep tooth cavity. Put diagnosis A. hypertrophic papillitis and art.; B. hypertrophic papillitis second century.; C. hypertrophic papillitis III.; D. chronic catarrhal papillitis; E. chronic ulcerative papillitis. 129. The patient complains of education in the area of tooth 46. Objectively ash papilla between 46 i47 hyperplastic teeth, bleeding when touched, overlapping crowns of teeth on 2/3. In 46 deep tooth cavity. Put diagnosis A. hypertrophic papillitis and art.; B. hypertrophic papillitis second century.; C. hypertrophic papillitis III.; D. chronic catarrhal papillitis; E. chronic ulcerative papillitis. 130. The patient complains of education in the area of tooth 46. OBJECTIVE: ash papilla between 46 i47 hyperplastic teeth, bleeding when touched, overlapping crowns of teeth on 1/3. In 46 deep tooth cavity. Put diagnosis A. hypertrophic papillitis and art.; B. hypertrophic papillitis second century.; C. hypertrophic papillitis III.; D. chronic catarrhal papillitis; E. chronic ulcerative papillitis. 131. Patient 33 years skarzhytsya of pain in the region of 37 teeth. OBJECTIVE: in 37 deep tooth cavity, ash bud in section 37 vyrazkuvatyy covered with gray bloom, bleeding when touched, abundant plaque left lymph nodes are enlarged, painful on palpation. Put diagnosis A. acute catarrhal papillitis; B. ulcerative papillitis; C. atrophic papillitis; D. hypertrophic papillitis; E. no correct answer. 132. Patient 32 years complains of bleeding gums and pain in the area of tooth 35. OBJECTIVE: on the distal surface 35 of the tooth hanging edge seals, ash bud hyperemic, swollen, bleeding when touched. Put diagnosis A. chronic catarrhal papillitis; B. acute catarrhal papillitis; C. atrophic papillitis; D. hypertrophic papillitis; E. no correct answer. 133. Patient 32 years complains of bleeding gums and pain in the area of tooth 35. OBJECTIVE: on the distal surface 35 of the tooth hanging edge seals, ash bud hyperemic, swollen, bleeding when touched. Diagnosed, acute catarrhal papillitis. Your tactics: A. UHF-therapy; B. requires no treatment; C. pereplombuvannya; D. rinse; E. no correct answer. 134. Patient 32 years complains of bleeding gums and pain in the area of tooth 35. OBJECTIVE: on the distal surface 35 of the tooth hanging edge seals, ash papilla swollen, cyanotic hue bleeds when touched. Put diagnosis A. chronic catarrhal papillitis; B. acute catarrhal papillitis; C. Acute hypertrophic; D. chronic hypertrophic; E. no right answer; 135. Patient 32 years complains of bleeding gums and pain in the area of tooth 35. OBJECTIVE: on the distal surface 35 of the tooth hanging edge seals, ash papilla swollen, cyanotic hue bleeds when touched. Your tactics: A. UHF-therapy; B. requires no treatment; C. pereplombuvannya; D. rinse; E. no right answer; 136. To the dentist asked the patient complaining of bleeding gums and pain in diyantsi 46 tooth. OBJECTIVE: on the distal surface 46 of the tooth hanging edge seals, ash bud hyperemic, swollen, bleeding when touched. Put diagnosis A. acute catarrhal papillitis; B. hypertrophic papillitis; C. chronic catarrhal papillitis; D. atrophic papillitis; E. no correct answer. 137. Girl 17 years old complained of bleeding gums while brushing teeth and bad breath. OBJECTIVE: clear hyperemic with tsyanotychnym shade, bleeding on probing. Periodontal pockets of 5 mm above and pid'yasenevi SUPRADENTAL stratification, mobility of teeth 1 degree. On radiographs: irregular horizontal resorption mezhalveolyarnyh membranes for 1/3 the length of the root, minor signs of osteoporosis. Install the diagnosis. A. * Generalized periodontitis II degree, chronic B. Generalized periodontitis III degree, chronic C. Generalized periodontitis I level, chronic D. Generalized periodontitis III degree tapered course E. Generalized periodontitis II degree, tapered course 138. Boy in '16 complained of bleeding gums while brushing teeth and bad breath. OBJECTIVE: clear in the area of papillae and marginal land with hyperemic tsyanotychnym shade, bleeding on probing. Periodontal pockets to 3 mm, soft plaque, teeth fixed. On radiographs: destruction of compact plate tops interdental membranes. Install the diagnosis. A. * Generalized periodontitis I level, chronic B. Generalized periodontitis II degree, chronic C. Generalized periodontitis III degree, chronic D. Generalized periodontitis I degree tapered course E. Generalized periodontitis II degree, tapered course 139. Boy '16 complains of pain, bleeding gums, bad breath. OBJECTIVE: clear bright hyperemic, swollen, bleed easily. Periodontal pockets of 5 mm with purulent exudate over and pid'yasenevi SUPRADENTAL stratification, mobility of teeth 2 degrees. On radiographs: horizontal and vertical interdental resorption membranes to 1/2 the length of the root to form bone pockets, diffuse osteoporosis in intact tissue. Install the diagnosis. A. * Generalized periodontitis II degree, tapered course B. Generalized periodontitis III degree tapered course C. Generalized periodontitis I degree tapered course D. Generalized periodontitis III degree, chronic E. Generalized periodontitis II degree, chronic 140. Girl 17 years old complains of pain, bleeding gums, bad breath. OBJECTIVE: clear bright hyperemic, swollen, bleeding when touched. Periodontal pockets than 5 mm, filled with granulations and significant purulent content. Mobility of teeth 2 degrees. Radiological findings: horizontal and vertical alveolar bone resorption within 2/3 height of interdental partitions, diffuse zone osteoporosis bone. Install the diagnosis. A. * Generalized periodontitis III degree tapered course B. Generalized periodontitis II degree, tapered course C. Generalized periodontitis I degree tapered course D. Generalized periodontitis III degree, chronic E. Generalized periodontitis II degree, chronic 141. Boy in '16 complained of bleeding gums while brushing teeth, bad breath. OBJECTIVE: clear hyperemic with tsyanotychnym touch, swollen, bleeding on probing. Periodontal pockets than 5 mm with serous exudate over and pid'yasenevi SUPRADENTAL stratification, mobility of teeth 2 degrees. Radiological findings: horizontal and vertical alveolar bone resorption within 2/3 height of interdental membranes. Install the diagnosis. A. * Generalized periodontitis III degree, chronic B. Generalized periodontitis II degree, chronic C. Generalized periodontitis I level, chronic D. Generalized periodontitis III degree tapered course E. Generalized periodontitis II degree, tapered course 142. Boy '11 complains of pain in the gums, bleeding them. OBJECTIVE: clear in the area of all teeth bright hyperemic, swollen, bleeding on probing. Periodontal pocket depth of 3 mm, soft plaque, teeth fixed. The X-ray: diffuse osteoporosis in the upper third interdental membranes. Install the diagnosis. A. * Generalized periodontitis I degree tapered course B. Generalized periodontitis II degree, tapered course C. Generalized periodontitis III degree tapered course D. Generalized periodontitis I level, chronic E. Generalized periodontitis II degree, chronic 143. Patient in '38 to see a doctor. After history taking and examination revealed acute generalized periodontitis second degree. After elimination of local factors and after anti-inflammatory treatment should move to eliminate periodontal pockets. What method should be used? A. * Curettage B. Hinhivektomiya C. Hinhivotomiya D. Scrappy operation E. Tummy peredsinka 144. The patient in '40 diagnosed with generalized periodontitis 2 degrees, sharp course, tooth-ash pockets 5-6 mm with purulent exudate. What are the primary manipulation must hold a doctor? A. * Use applique anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial agents B. Closed curettage C. Use fibrolizuyuchi means D. Hold cryodestruction tools gum pockets E. Open curettage 145. Patient S., '50, addressed the periodontist complaining of swelling of the gums and spontaneous pain in the region of 46 and 47 teeth for 3 days. OBJECTIVE: soft and hard dental plaque. 46 and 47 tooth unsealed contact point is missing, gums swollen, hyperemic, in the area of alveolar bone squeezing palpation acutely painful toothgingival pocket (5-6 mm in the presence of purulent exudate. Which manipulations should be undertaken in the first place? A. * Removal of dental plaque and periodontal abscess disclosure B. Removal of dental plaque and deposition applications C. Open curettage of periodontal pockets D. Closed curettage of periodontal pockets E. Hinhivektomiya 146. Patient K., 50 years old, who has been diagnosed with diabetes, showed generalized periodontitis III severity in the acute stage. Which of these groups of drugs should be used for local therapy in the treatment of generalized periodontitis? A. Nitrofuran B. Sulfonamide C. * Antifungal D. D. Anymseptyky E. That's right 147. Patient A., 50 years, is hospitalized in parodolntolohichnomu department regarding CHD. Sick for the last 10years. An objective examination of RP marked edema and hyperemia of the gums, a large number of - and pid'yasennyh dental plaque, mobility of individual teeth second century. Parodontalnyhkyshen depth of 5-6 mm, bleeding gums, 2 tbsp. Test Kulazhenko in the frontal section 10c. What preparation is useful to introduce the complex pathology of periodontal tissue with immune method and for potentiation of antibacterial effect? A. Pentoxyl B. Prodihiozon C. * Immuno-tone D. Amizon E. Dekaris 148. Patient M., 20 years old, complained of bleeding gums when eating and brushing teeth. Ob-no: interdental papillae on the lower jaw swollen, congested, bleeding when touched. On radiographs: integrity compact interdental plate membranes are not compromised. What is the prognosis of the disease at the end of the treatment correctly? A. * Recovery B. Stabilization C. Progression D. Remission E. Aggravation 149. Patient, 20 years old, a few months complained of bleeding gums during brushing. OBJECTIVE: clear cyanotic, swollen, bite artohnatychnyy. GI-by Fedorov has been received is 2, Radiological pathological changes in periodontal tissues were found. From what measures do you think should start treating gingivitis? A. Sclerosing therapy B. * Occupational Hygiene C. Anti-inflammatory therapy D. Physiotherapy E. Clinical supervision 150. Patient complains of bleeding gums over the past 2 years. OBJECTIVE: diffuse chronic catarrhal gingivitis, tooth mobility and art., Pockets of 2-3 mm with a slight serous exudate expressed traumatic occlusion. On radiographs of the integrity of a compact plate expansion periodontitis cracks around peaks mezhalveolyarnyh partitions, osteoporosis, resorption within 1/3 height mezhalveolyarnyh partitions. Your diagnosis? A. * Generalized periodontitis, and the extent chronic B. Chronic catarrhal gingivitis C. Periodontal disease and degree D. Generalized periodontitis, and the degree tapered course E. Generalized periodontitis, the initial stage, chronic 151. Patient K., 48 years appealed to skrhamy of discomfort in the gums, their unusual appearance, mobility of individual teeth, bleeding gums when eating. Ob'ktyvno gums swollen, hyperemic, in probing bleed through the 30s. The depth of periodontal pockets 5-6 mm. gum recession at 1/3 the length of the root. Some teeth are moving-2 c. Panoramic x-rays observed diffuse resorption mezhalveolyarnyh partitions to 1/2 the length of their height, the vertical type, osteoporosis spongy substance. From history we know that the patient was suffering from rheumatism and chronic nefrolitioz. What preparation is recommended to use A. Osteohenon B. Kaltsemin C. Fosamoks D. * Kaltsemin Advans E. Chitin 152. Patient A., 35, complained of an unusual shape, form gums. OBJECTIVE: gingival papillae pale pink, tightly to the teeth, although slightly increased in size, do not bleed. Install the diagnosis. A. * Hypertrophic gingivitis and art. (Fibrous form) B. Hypertrophic gingivitis and art. (Granulating form) C. Desmodontoz gum D. Atrophic gingivitis E. Periodontal Disease 153. Patient A.. 50 years old, diagnosed with generalized periodontitis and extent chronic course. Specify one of the earliest diagnostic tests that detected radiographically. A. * Destruction of cortical plate B. Osteosclerosis cortical plvstynky C. Osteoporosis cortical plate D. Sequestration of bone E. Resorption mezhalveolyarnyh partitions 154. Patient L., 35r. complained to bleeding gums, bad breath, tooth mobility. OBJECTIVE: clear congested with cyanotic tinge, periodontal pocket-5mm, abnormal tooth mobility IIst. In the teeth of the observed and pid'yasennyy dental plaque, hygienic index-3 points. The diagnosis: chronic generalized periodontitis IIst. How many times a year to carry out a comprehensive treatment of this patient? A. 3 times B. 1 time C. * 2 times D. 5 times E. In case of complications 155. Patient S., '23, complaints sharp bleeding gums, bad breath that appeared 5 days ago. OBJECTIVE: interdental papilla and gingival edge everywhere loosened, bright red, swollen, painful and heavily bleeding on palpation. Gingival pocket 3 mm on the radiograph - expressive osteoporosis mezhalveolyarnyh membranes on? their height, periodontal expansion gap around the tops mezhalveolyarnyh membranes. The compact disc is not broken. Your diagnosis? A. Acute catarrhal gingivitis B. Acute leukemia C. Acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitisD. Generalized periodontitis, II degree, tapered course E. Hypovitaminosis C (skorbutna dentistry) 156. Patient A., 30, with the diagnosis of periodontal diseases, the initial stage, a chronic course, we need a filling two adjacent cavities in 46 and 47 teeth. How to restore contact point between 46 and 47? A. * Spot B. Planar to transverzali C. By planar and vertical transverzali D. Planar vertical E. No need to restore 157. Patient K., '25, complaints of bleeding gums, bad breath in the morning for 1 year. OBJECTIVE: Persistent teeth, periodontal pockets missing interdental papilla and gingival edge - with a bluish tinge. The X-ray - integrity compact plate impaired periodontal gap expanded around verhnivok mezhalveolyarnyh membranes, osteoporosis and resorption - minor. Your diagnosis? A. Periodontal syndrome B. Chronic catarrhal gingivitis C. Chronic necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis, Vincent, mild D. Hypovitaminosis C E. * Generalized periodontitis, the initial stage, chronic 158. On examination, 20-year old patient revealed thickened slightly cyanotic, compacted gum edge, overlapping crowns of all teeth for 1/2 their height. Hygienic code has been received by Fedorov-3.0. On radiographs of pathological changes in periodontal tissues were found. From history: over 5 years, the patient is treated in mental hospital about epilepsy Determine preliminary diagnosis. A. * Chronic hypertrophic gingivitis B. Aggravation catarrhal gingivitis C. Chronic catarrhal gingivitis D. Acute catarrhal gingivitis E. Aggravation of hypertrophic gingivitis 159. The patient, aged 45 years, diagnosed with generalized periodontitis second degree chronicity. According to the results of microscopic investigation of the periodontal pockets of the significant amount of yeast fungi of the genus Candida. Which of the following medications is most expedient to use for instillation? A. Diclofenac sodium B. Trihopol C. Dioxidin D. * Clotrimazole E. That's right 160. The patient, aged 49 years, complained of increased tooth sensitivity to temperature and chemical stimuli. OBJECTIVE: clear dense, anemic, the roots of teeth exposed for 3-4 mm, is klynopobidni defects within the dentin. The X-ray revealed a uniform decrease in height mezhalveolyarnyh partitions within 1/2 their height and osteosclerosis alveolar bone tissue. Define the diagnosis. A. * Periodontal Second Degree B. Periodontal disease and the degree of C. Atrophic gingivitis D. Generalized periodontitis second degree chronicity E. Generalized periodontitis and degree of chronicity 161. After suffering ARI patient appealed to the dentist complaining of pain in the gums, bad breath, inability to eat, general weakness. OBJECTIVE: clear congested, swollen, covered with fibrinous coating, which occurs when removing the bleeding. Microbiological research gum tissue revealed a large number of cocci, bacilli, and spirochetes fuzobakteriy. Specify drug treatment etiotropic A. Karotolina B. Haloskorbin C. Potassium permanganate D. Trypsin E. * Metronidazole 162. The patient in the treatment of catarrhal gingivitis over three weeks spent oral bath with antiseptic solution. This notice discoloration crowns. What antiseptic is able to cause this? A. Peroxide B. Yodinola C. Potassium permanganate D. Furatsillina E. * Chlorhexidine 163. K dentist obratylsya b-noy K., 23 years old, accounting for sostoyaschyy As HIVynfytsyrovannыy, p mourning into krovotochivost gums. Áûë put the diagnosis CHRONIC kataralnыy gingivitis. When snyatyy zubnыh postponed doctor travmyroval finger. What are profylaktycheskye action neobhodimo Run doctor after snyatyya gloves? A. Vыdavyt Blood of wounds, wound obrabotat 5 \% nastoykoy Yoda, vыmыt hands with mыlom, obrabotat s 70 \% p-rum alcohol B. The wound obrabotat 5 nastoykoy Yoda, vыmыt hands with mыlom, nalozhyt plasters C. Vыdavyt Blood of wound, wound and hands obrabotat 70 \% p-rum alcohol, nalozhyt plasters D. Vыdavyt Blood of wounds, wound obrabotat 5 \% nastoykoy iodine, hands obrabotat 0.2 \% p-rum hlorantoyna, nalozhyt E. Vыdavyt Blood of thumb, wound obrabotat 1 \% p-rum hloramyna, hands obrabotat 0.2 \% p-rum hlorantoyna, nalozhy 164. Bolnaya 45 years stradaet CHRONIC generalized periodontitis Class II severity. In the conduct of microbiological survey of the contents parodontalnыh Karmanov been been identified Much insemination trichomonads. Some kind of drugs most perechyslennыh tselesoobrazno Apply for instillyatsy in parodontalnыe pockets in dannoy Chao? A. Metrogil-dent. B. Chlorhexidine biglyukonata. C. Hlorofyllypt. D. Clotrimazole. E. Rotokan. 165. In K. Chao, 28 years on Complaints putrid smell yzo PTA and soreness during a food. According DATA objectively Survey Chao áûë put the diagnosis: yazvennыy gingivitis. Physician Treatment began co snyatyya necrotic raid swab with furatsyllynom. Specify What are Pharmaceuticals sredstva contribute to the necrotic lyzyrovanyyu raid. A. Trypsin, chymotrypsin B. Soluble hloramyna C. Soluble hydrogen peroxide D. Soluble chlorhexidine E. Soluble antibiotic 166. Chao 29 years zhaluetsya on krovotochivost gums during a teeth cleaning, odor nepryyatnыy yzo PTA. Objectively: gum hyperemyrovanы, p tsyanotychnыm ottenkom, krovotochat at dotrahyvanyy, parodontalnыe pockets hlubynoy 3-3.5 mm with serous exudate. Ymeyutsya over s poddesnevыe zubnыe otlozhenyya. Panoramic x-rays - otrostka alveolar osteoporosis, resorption mezhalveolyarnыh partitions to 1 / Put diagnosis. A. Generalized periodontitis Class 1, hronycheskoe Flow B. Generalized periodontitis Primary Class, hronycheskoe Flow C. Generalized periodontitis 11 degrees hronycheskoe Flow D. Generalized periodontitis 11 degrees obostryvsheesya Flow E. Generalized periodontitis Class 1, obostryvsheesya Flow 167. Woman 40 years zhaluetsya on neznachytelnuyu soreness gums, teeth povыshennuyu chuvstvytelnost k temperaturnыm stimuli. Objectively: gum blednaya, plotnaya in the section of the Lower frontalnыh teeth observed retraction desnы s oholenyem sheek teeth. On radiographs - resorption mezhalveolyarnыh partitions on 1/3 dlynы roots. Put diagnosis. A. Periodontal 1 Class B. Periodontal 11 Class C. Periodontal Primary Class D. Kataralnыy gingivitis E. Lokalyzovannыy periodontitis 168. Boys 18 years obratylsya rolled dentist with mourning for soreness and krovotochivost gums, kotorыe appeared two days ago after acute respiratory disease. In Flow ïîñëåäíèé two years peryodychesky bespokoyt krovotochivost gums when teeth cleanings. Objectively: interdental papillae and marhynalnыy edge desnы sharply otechnы, bright-red color, and boleznennы krovotochat by palpation. Parodontalnыe pockets not opredelyayutsya. Hygienic post index by Fedorov-Volodkynoy - 3.3 Balla. In panoramnoy radiograph - kostnaya fabric alveolyarnыh otrostkov without pathological changes. Kakov most veroyatnыy diagnosis? A. Exacerbations of chronic catarrhal gingivitis B. Hypertrophic gingivitis, edematous form C. Generalized periodontitis initial degrees obostryvsheesya Flow D. Deskvamatyvnыy gingivitis, эrytematoznaya form E. Lokalyzovannыy periodontitis obostryvsheesya Flow 169. Girl 17 years obratylas with mourning into krovotochivost growths and gums. Objectively: desnы in the field frontalnыh Lower jaw teeth rыhlыe, hyperemyrovannыe, perekrыvayut crowns on teeth 1/3 heights, krovotochat at dotrahyvanyy. Opredelyayutsya parodontalnыe pockets to 3.5 mm. Zubnaya arc Lower jaw suzhena, skuchennost teeth vo frontal location. Hygienic post index by FedorovVolodkynoy - 3.5 Balla. Kakov most veroyatnыy diagnosis? A. Lokalyzovannыy periodontitis and degrees hronycheskoe Flow B. Generalized periodontitis initial degrees hronycheskoe Flow C. Hypertrophic gingivitis, edematous form and Class D. Deskvamatyvnыy gingivitis, эrytematoznaya form E. Exacerbations of chronic catarrhal gingivitis 170. A young man 20 years obratylsya rolled dentist with mourning into krovotochivost gums and soreness in the gums pryeme food. Objectively: gum in the field frontalnыh Lower jaw teeth valykoobrazno thickenings, edematous, hyperemic, zubы skuchenы. In region 42, 41, 31, 32 opredelyayutsya parodontalnыe pockets hlubynoy to 4 mm with sero-hnoynыm exudate. Bite on a straight radiograph: resorption mezhalveolyarnыh partitions in region 42, 41, 31, 32 to 1/3 dlynы roots. Kakov most veroyatnыy diagnosis? A. Lokalyzovannыy periodontitis and degrees obostryvsheesya Flow B. Generalized periodontitis Class II, obostryvsheesya Flow C. Generalized periodontitis and degrees hronycheskoe Flow D. Lokalyzovannыy periodontitis Class II, hronycheskoe Flow E. Exacerbations of chronic catarrhal gingivitis II Class 171. 171. Males 32 years old's laid diagnosis: yazvennыy gingivitis Class II severity. After antiseptics processing cavity under the PTA held a physician anestezyey Remove zubnыh postponed and necrotic raid. Plans to finish Visits Nalozhenye gingival povyazky. Kako drug etiotrop a necessary action to put into composition gingival povyazky? A. Metronidazole B. Kontrikal C. Methyluracil D. Pymafutsyn E. Terrylytyn 172. The patient, in '41, diagnosed with generalized periodontitis 2 degrees of severity, sharp course with abscess formation. Which methods of general treatment should be appointed in the first place? A. Stimulant therapy B. Hyposensitization therapy C. Physiotherapy D. * Antibiotic E. Vitamin 173. The patient, 46 years old, diagnosed with generalized periodontitis 2 degrees of severity, sharp course. Recently, the patient noted deterioration, skin itch, dryness in the mouth. Which methods of additional tests should be used before embarking on treatment? A. Total blood B. Urinalysis C. Determination of vitamin C in the blood D. * Determination of blood sugar E. Immunological studies of blood 174. The patient appealed to the dentist with complaints of persistent spontaneous pain, swelling of the gums in 26 and 27 teeth for 2 days. An examination of the lips of the upper and lower jaws of a large number of soft and hard plaque. At 26 and 27 teeth adjacent large fillings, contact checkbox, clear congested, swollen, on alveolar part of the protrusion, palpation painful, tooth-gingival pocket 6 mm with purulent exudate. What is the primary tactic local drug treatment? A. Closed curettage tools gingival pockets B. * Removal of dental plaque, periodontal abscess disclosure C. Removal of dental plaque, application of medicines to clear D. Open curettage of periodontal pockets E. Rinse antiseptic Appointment 175. Patients aged 22 years treats acute periodontitis. What is the treatment of periodontitis has primarily to be? A. Symptomatic B. Pathogenic C. * Etiotropic D. Orthopaedic E. Drug 176. Patients aged 33 years treats acute periodontitis. The doctor plans to Application anesthesia. What preparation of the following are the most appropriate to use? A. 3-5% solution of sodium salicylate B. B. * 5-20% oily solutions anestezina C. 1% solution of potassium permanganate D. 0.2% hlorheksedynu bigluconate E. 1% trihopolom 177. PATIENTS '35 treats acute periodontitis. The doctor plans to Application anesthesia solution of propolis and dikaina. What preparation of listed below should be added to potentiation of anesthesia? A. * Dimeksida B. Hlorheksedyn C. 0.1% epinephrine D. Diphenhydramine E. Trihopol 178. PATIENTS '42 treats acute periodontitis. The doctor plans to Application anesthesia butadionovoyu 5% ointment, which group related drugs phenylbutazone? A. Steroidal anti-inflammatory B. Narcotic analgesics C. * Non-narcotic analgesics D. Local anesthetic, esters E. Local anesthetic, amides 179. On admission clinical periodontal patient doctor plans to Application anesthesia 5% solution of sodium salicylate which group drugs include sodium salicylate? A. Narcotic analgesics B. Steroidal anti-inflammatory C. Local anesthetic, esters D. * Non-narcotic analgesics E. Local anesthetic, amides 180. On admission clinical periodontal patient doctor plans to anesthesia. From history we know that the patient is allergic to volatile anesthetics that drug from listed below should be used in this clinical situation? A. Procaine. B. Novocaine. C. Dikain. D. Anestezin. E. * Mepivakayin. 181. On admission clinical periodontal patient doctor plans to spend 10% pain relief ointment oil solution anestezina which group drugs include benzocaine? A. Narcotic analgesics B. * Local anesthetic esters C. Steroidal anti-inflammatory D. Local anesthetic, amides E. Non-narcotic analgesics 182. Patients aged 42 years treats acute periodontitis. The doctor plans to anesthesia solution Articaine which group of drugs is Articaine? A. Non-narcotic analgesics B. Narcotic analgesics C. Steroidal anti-inflammatory D. Local anesthetic, esters E. * Local anesthetic, amides 183. Husband 30 years, conducting the final phase of treatment of acute ulcerative necrotic gingivitis moderately. Drugs which group should be used in the final stage of treatment? A. * Keratoplasty B. Keratolityky C. Antioxidants D. Proteolytic enzymes E. Antibiotics 184. The patient was 43 years old diagnosed with chronic generalized periodontitis second degree. During microscopic examination content periodontal pockets revealed a significant coccal microflora Trichomonas. Which of the following measures should be applied medication for instillation? A. * Metronidazole B. Lincomycin C. Dioxin D. Nimesulide E. Dikain 185. During microscopic examination content periodontal pockets patient showed symbiosis fuzobakteriy and trichomonads which drug the following to apply for this patient? A. Lincomycin B. Ribonuclease C. * Metronidazole D. Nimesulide E. Chloramphenicol 186. Patient 41r. Complains of bleeding gums, mobility of teeth, bad breath. On radiographs: alveolar bone resorption more than 1/3 the length of the root. Diagnosis: generalized periodontitis degree, chronic course. How should begin treatment? A. Definition oklyuziohrammy B. * Removal of dental plaque C. Splinting D. Sample pryshlifovuvannya E. Applications antimicrobial 187. Patient 39r., Diagnosed generalized periodontitis II severity, sharp course doctor plans to appoint osteotropic antybiotok, the below mentioned antibiotics is osteotropic? A. Gentamicin. B. * Lincomycin C. Chloramphenicol D. Cefazolin E. Nystatin 188. In patients aged S0 years diagnosed with acute ulcerative gingivitis moderately. Which drugs should be applied to remove necrotic plaque: A. Solution furatsilinom B. * Iruksol C. A solution of hydrogen peroxide D. A solution of potassium permanganate E. Chlorhexidine solution? 189. A patient aged S0 years diagnosed with acute ulcerative gingivitis moderately. Drugs which group to apply the final stage of the treatment of this disease: A. Keratolytic B. Antibiotics C. Antioxidants D. * Keratoplastychni E. Proteolytic enzymes? 190. A woman aged 32 years complained of bleeding gums during the last 3 years. In the history of frequent Catarrhal diseases, surgery about a year ago mastitis. OBJECTIVE: clear frontal area jaws swollen, congested hyper-emiyovani, bleeding during tapping tool. Cervical teeth exposed to 1-1.5 mm. Periodontal pocket depth of 1-2 mm with minor secretions. Teeth fixed, Radiographs slight osteoporosis and resorption tops mizhkomirkovyh partitions within 1/3 of their height. That may be contraindications for appointment stimulation therapy patient data: A. Young age B. Sluggish flow process in periodontal C. * Operation on mastitis in history D. Early stage of development of dystrophic-inflammatory process in periodontal E. Frequent Cold disease in history 191. Dentist proyzvel vskrыtye periodontal abscess in region 11 and 21 patsyentke 48 years from diagnosis: generalized periodontitis Class II, abstsedyruyuschee Flow. In history: hyperatsydnыy gastritis, hypotension. Something of fyzyoterapevtycheskyh procedure can prescribe ýòîé Chao for acceleration resorption of inflammatory infiltrates? A. EUV-therapy. B. Mykrovolnovuyu (UHF) therapy. C. UHF therapy. D. Dyatermyyu. E. Electrophoresis with trypsin. 192. Patients 54 years proyzvedeno vskrыtye parodontalnыh abstsessov field in 34.35, promыvanye cavity abstsessov antiseptic. In history: generalized periodontitis Class II, stradaet Flow in 10 years, peryodychesky Disease obostryaetsya s education abstsessov. Because of concomitant diseases: CHRONIC gepatoholetsistite, dyskoydnaya Red erythematosus. Something of fyzyoterapevtycheskyh procedure can prescribe Told patient for relief voznyksheho exacerbations? A. UHF therapy. B. Dyatermyyu. C. Ynfrakrasnoe radiation (lamp "Solux"). D. UV irradiation (quartz tube). E. Electrophoresis with heparin. 193. In the Clinic Preventive Dentistry appealed patient K., 46 years old, complaining of pain in the gums, increased bleeding, bad breath, the mobility of individual teeth. Within 5 years suffering from chronic pyelonephritis. After the survey was diagnosed exacerbation of chronic generalized periodontitis II severity. What is the natural method of physical therapy should be the first day of treatment? A. Hydrotherapy B. UVR C. Pelotherapy D. Massage gums E. Paraffin 194. On examination of the oral cavity of the patient M., age 15, a dentist discovered cyanosis and edema of the gums of both jaws, gum overgrowth of papillae to 1/2 the height of crowns, ash pockets, a small number of dental nasharuvan.V history menstrual irregularities. What is physiotherapy treatment should be in this case? A. Spark method Darsonvalization B. UHF-therapy C. Helium-neon laser D. Phonophoresis hydrocortisone E. Hydromassage 195. B. The patient is diagnosed with exacerbation of chronic generalized periodontitis second century. severity recommended to conduct additional physiotherapy. What type of physiotherapy should you choose? A. Microwave therapy B. Electrophoresis of trypsin solution C. Darsonvalization D. Electrophoresis of vitamin C E. Vacuum therapy 196. K. Patient was complaining of bleeding gums when brushing teeth. An objective examination diagnosed with chronic generalized periodontitis and art. severity. What is the treatment plan? A. Comprehensive treatment including therapeutic interventions, closed curettage, physiotherapy B. Several sessions with aloe ultrofonoforezom C. Electrophoresis with a solution halaskorbinu (10 sessions) D. Electrophoresis with a solution of heparin (5seansiv) E. Removal of dental plaque and application of anti-inflammatory drugs. 197. What are the physical methods of treatment are shown in the postoperative period in patients with periodontitis? A. Vacuum therapy B. The anode-galvanization C. Electrophoresis D. UHF-therapy. E. No right answer 198. Contraindications to massage inflammation of periodontal A. The presence of stagnation in periodontal B. Purulent discharge from the periodontal pockets = C. Mobility of teeth D. Phase abscess. 199. Indications for balneotherapy in generalized periodontitis: A. Only in remission B. At all stages of treatment, in addition to postoperative C. At all stages of treatment = D. The period of exacerbation. 200. Contraindications to the use of electrophoresis in the periodontitis patients: A. Hypertrophic processes in the gums B. The presence of teeth hyperesthesia C. Violation of the integrity of the epithelium of the mucous membrane of the gums D. Bleeding gums. 201. Fluctuarization and d'Arsonvalizatsiya used in periodontitis: A. In order to anesthesia B. To reduce bleeding and swelling of periodontal tissue C. To accelerate microcirculation and enhance metabolism, improve D. reparative processes in the periodontium = E. In acute 202. Patient complains of '46 bleeding gums, hnoyetechu, tooth mobility. Sick for 10 years. On examination: clear the upper and lower jaws are congested, swollen, with dotorkuvanni bleed. In the 42, 41, 32, 31 teeth periodontal pockets up to 7 mm with purulent discharge, the mobility of II degree, the remaining teeth and degree. The Xray - resorption mezhalveolyarnyh partitions in 42, 41, 31, 32 2/3 the length of the root, the phenomenon of osteoporosis. Which of the following methods most indicated for surgical treatment of this disease? A. Kriokyuretazh B. * Patchwork operation C. Curettage D. Hinhivotomiya E. Hinhivektomiya 203. Patient G. that dispensary diagnosed with generalized periodontitis, and the extent to chronic under examination [X-ray] at 6 months showed bone lonely pocket between 24 and 25 teeth, reaching 1/2 interalveolar height. The 24 tooth with amalgam filling goes deeply into the interdental space. Your tactics regarding bone pockets after correction fillings? A. Hold course lincomycin in transition folds 24 and 25 teeth № 7-10 B. * Will hold open curettage C. Hold hinhivektomiyu D. Hold hinhivotomiyu E. Hold a series of periodontal dressings metroqyl-denta 204. Patient M., 32 years old need to curettage gingival and periodontal pockets. The criterion of efficiency curettage gingival and periodontal pockets in the implementation are: A. Lack pid'yasennoho tartar B. * Lack of severe bleeding, lack pid'yasennoho tartar, granulation and epithelial vrosshoho C. Complete absence of bleeding D. Clear tightly to the teeth E. Lack of granulation and epithelial vrosshoho 205. Patient Y. The diagnosis "generalized periodontitis degree, chronic." What will be the first session of the local treatment? A. * Temporary splinting B. Treatment of symptomatic gingivitis C. Anti-inflammatory therapy D. Curettage periodontal pockets E. Antiseptic treatment and removal of dental plaque 206. Woman '45 complains of bad breath, bleeding gums and pain that intensified when eating. OBJECTIVE: catarrhal gingivitis degree, periodontal pockets reach neck 4 mm, containing a moderate amount of serous - pus. It is noted delaying tartar and plaque in nad'yasneviy and pid'yasneviy parts of the tooth. Mobility of teeth Class. Radiological findings: cortical plate impaired resorption of alveolar bone reaches half the height mezhalveolyarnyh membranes. Diagnosed chronic generalized periodontitis second degree. Where to begin treatment? A. Appointment of mud applications B. * Removal of dental plaque. C. Purpose of the means of anti-inflammatory D. Conducting temporary splinting E. The planned operation 207. In the Clinic Preventive Dentistry appealed patient aged 40 years., Who diagnosed acute generalized periodontitis III. severity. What type of curettage can be used in this nosology A. Outdoor and vacuum - curettage B. * Vacuum - curettage, cryo - curettage C. Open curettage D. Closed curettage E. Open and closed curettage 208. The patient complains of '55 bad breath, bleeding gums and pain that intensified when eating. OBJECTIVE: catarrhal gingivitis degree, periodontal pocket depth of 4 mm, containing a moderate amount of serous - pus. It is noted delaying tartar and plaque in nad'yasneviy and pid'yasneviy parts of the tooth. Mobility of teeth Class. Radiological findings: cortical plate impaired resorption of alveolar bone reaches half the height mezhalveolyarnyh membranes. Diagnosed chronic generalized periodontitis second degree. Where to begin treatment? A. Appointment of mud applications B. * Removal of dental plaque. C. Purpose of the means of anti-inflammatory D. Conducting temporary splinting E. The planned operation 209. Patient A., 35 years old with a diagnosis of chronic generalized periodontitis II severity, need to surgery. The criterion for selection of surgical intervention in treatment parodotytu are: A. The depth of periodontal pockets B. C. D. E. Complaints patient Duration of disease Age of the patient * The depth of periodontal pockets, the general condition of the patient, the patient's age 210. Girl 18 years with prophylactic examination was diagnosed with hypertrophic gingivitis, edematous form of moderate severity. What method of brushing you suggest patients after treatment? A. Method Leonard B. * Method charter C. Standard Method D. Method Stylmana E. Method Rd 211. Patient B., 27 years old, suffering from diabetes, a course of treatment for generalized periodontitis of moderate severity. How often should a patient visit a dentist to prevent the progression of periodontal disease? A. * 3-4 times a year B. 2 times a year C. 1 every year D. Every 2 months E. As needed 212. Dentist conducted a comprehensive treatment of the patient with generalized hypertrophic gingivitis. Put the patient on clinical supervision. How long does your doctor should prescribe the patient for re-treatment? A. * After 6 months B. 4 months C. After 3 months D. After 1 month E. After 1 year 213. Dentist conducted a combined treatment of periodontitis P severity. Put the patient on clinical supervision. How long does your doctor should prescribe the patient for retreatment rate? A. * After 6 months B. After 1 misyatsi C. After 3 months D. After 1 year E. After 1.5 years 214. Dentist conducted a comprehensive treatment of patients with generalized periodontitis W severity. Put the patient on clinical supervision. How long does your doctor should prescribe the patient for re-treatment rate? A. * 3 months B. After 1 month C. After 6 months D. After 1 year E. After 1.5 years 215. Boy in '13 diagnosed with chronic catarrhal gingivitis held professional oral hygiene. After that time the teeth will be found dental plaque? A. 12:00 B. * 24 hours C. 36 hours D. 6:00 E. 48 hours. 216. The girl is 12 years with a diagnosis of chronic hypertrophic gingivitis held professional oral hygiene. During manipulation which, in your opinion, is removed dental plaque? A. * Professional removal of dental plaque B. Brushing C. Rinse elixir D. Eating solid food E. Clean interdental spaces flosses. 217. Patient K., 24 years old, complained of bleeding gums when cleaning teeth, taking hard food. OBJECTIVE: clear both jaws swollen, tsyanotychni, bleeding dotorkuvanni, no periodontal pockets, layering nadyasennoho tartar. What type of prevention shows patient? A. Local prevention B. * Secondary Prevention C. Primary Prevention D. Tertiary prevention E. Social prevention 218. When teaching the patient oral hygiene should be stressed that delaying plaque restored: how many hours of careful brushing it starts to grow and harmful impact on teeth and gums? A. 1 hour B. * 3 hours C. 6 hours D. 12 hours E. after 24 hours 219. Complaints of discomfort in the gums, increased tooth sensitivity to thermal stimuli. OBJECTIVE: naked neck teeth, wedge-shaped defects, mucous gums pale pink, tight to the teeth. Diagnosis. A. Chronic catarrhal gingivitis B. Periodontitis, mild C. * Mild form of periodontal disease D. Gingival fibromatosis E. Chronic hypertrophic gingivitis 220. When probing the gingival groove observed bleeding in the form of small spots, not flowing beyond the gingival groove, hanging drop. In Myulemanu bleeding replies A. 0 balls B. 1 point C. * 2 balls D. 3 balls E. 4 balls 221. The examination determined that the rate of complex periodontal index of 3.7. What kind of condition of periodontal tissues can be seen in this case A. Mild periodontitis B. average degree of periodontitis C. * Severe periodontitis D. very severe degree of periodontitis E. very mild degree of periodontitis 222. OBJECTIVE: swelling and redness of gums, their pain and bleeding when probing. Significant dental plaque. Periodontal pockets to 4 mm. Mobility of teeth Class. Radiological findings: expanding periodontal gap in the area of the necks of the teeth, resorption of interdental partitions to 1/3 height, osteoporosis. Diagnosis: A. Exacerbation of chronic catarrhal gingivitis B. Acute marginal periodontitis C. * Mild generalized periodontitis D. Generalized moderate periodontitis E. Periodontal disease, mild 223. Boy in '13 diagnosed with chronic catarrhal gingivitis held professional oral hygiene. After that time the teeth will be found dental plaque? A. 12:00 B. * 24 hours C. 36 hours D. 6:00 E. 48 hours. 224. The girl is 12 years with a diagnosis of chronic hypertrophic gingivitis held professional oral hygiene. During manipulation which, in your opinion, is removed dental plaque? A. * Professional removal of dental plaque B. Brushing C. Rinse elixir D. Eating solid food E. Clean interdental spaces flosses. 225. Complaints continued bleeding gums while brushing teeth, sensitivity to temperature, chemical irritants, discoloration of gums. The depth of periodontal pockets of 5 mm, sero-purulent discharge from the pockets, tooth mobility and degree, baring the necks of the teeth. What is the diagnosis of this pathology is responsible? A. Chronic generalized periodontitis, mild B. Acute catarrhal gingivitis, severe degree C. Syndrome Papiyona-Lefebvre D. * Exacerbation of chronic generalized periodontitis middle degree E. Exacerbation of chronic generalized periodontitis mild 226. On examination, the patient has catarrh interdental papillae, plenty of soft plaque above and pidyasennyy tartar, periodontal pocket depth of 3 mm. What is the X-ray picture is this pathology? A. Uniform horizontal resorption iyizhalveolyarnyh partitions on 1/3 height B. B. Horizontal alveolar bone resorption at 1/2 the height of the interdental partitions C. C. Expansion slot periodontitis D. Focal osteoporotic cancellous bone interdental partitions (Resorption compact interdental plates on the tops of walls, decrease in height partitions on 1/3) E. * There is no right answer 227. Patient, 26 years old, approached and complaints overgrowth of gum. OBJECTIVE: In section 14 of the tooth gums fungous growths limited form dense, dark red with cyanotic tinge. 14 tooth mobility in the vestibular-oral direction. Abnormal formation of patient noted a year ago, and connects with pregnancy. What is the most likely diagnosis? A. Gingival fibromatosis B. * Epulis, anheomatozna form C. Hypertrophic gingivitis, swelling form D. Acute localized periodontitis of moderate severity E. Hypertrophic gingivitis, fibrous form 228. As a man, 42 years old, when viewed oral dental therapist revealed multiple wedgeshaped defects on the tooth; stertist tubercles chewing surfaces of molars and premolars, k tremas same teeth, minor sediments nadyasennoho tartar. Slyzivka gums pale pink. There gingival retraction pa 2 - mm. On radiography - horizontal rezorbtsi mezhalveolyarnyh partitions to 1/3 the length of the roots, osteoporosis and osteosclerosis cancellous bone of the alveolar ridge. Diagnosis - gum, mild. Does the patient surgical treatment? A. Only the removal of the inflammatory process B. Only with deep pockets parontalnyh more than 5 mm C. In the presence of periodontal pockets D. If mobility of teeth E. * Does not require 229. Patient, 55 years old, asked about aching pain in the lower jaw gums itch. OBJECTIVE: clear upper and lower jaw pale, potonsheni, painless, the recession of the edge 2 mm, teeth intact, soft plaque and stone there. Which of the following physiotherapy expedient to apply? A. UHF-therapy B. Ultraviolet irradiation mennya C. * Phonophoresis with nicotinic acid vacuum therapy D. Aeroionotherapy E. Electrophoresis of trypsin solution 230. Choose the most appropriate sequence of treatment policy A. Splinting, anti-inflammatory therapy, surgery, B. physiotherapy C. * Anti-inflammatory therapy, splinting, surgical treatment, causal D. therapy, treatment zahalnoukriplyuyuche E. Eliminating mechanical stimuli, splinting, anti-inflammatory therapy, 231. Female, 40 years old, complained of slight pain in the gums and teeth cleaning to a new brush, increased tooth sensitivity to cold food, periodic discomfort in the gums, mainly in the area of mandibular incisors. OBJECTIVE: clear pale and thick, in the area of the front teeth observed their slight retraction of incisors and exposing necks clicks. When probing - no clinical pockets. The X-ray observed uniform decrease in height interdental section to 1/3 the length of roots, periodontal expansion slots. Which disease meets the clinical picture? A. Generalized periodontitis mild in remission B. * Periodontal disease, mild degree C. Atrophic gingivitis, mild degree D. Chronic generalized periodontitis, mild degree E. Periodontal disease, the average degree 232. Patient, 43 years old, complained of acute throbbing pain in the region of the upper jaw thing going second day, malaise, headache, body temperature 37,8 ° C. OBJECTIVE: inflammatory infiltrate rounded on the gums vestibular side in section 16 of the tooth. Tooth intact, driven II stage, the horizontal and vertical percussion positive periodontal pockets 4-5 mm. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis? A. Periostitis of the upper jaw to the right B. Exacerbation of chronic granulating periodontitis 16 tooth C. Acute pyeriodontyt 16 tooth D. * Exacerbation of chronic periodontitis severe degree E. Exacerbation of chronic gangrenous pulpitis 16 tooth 233. The patient, 40 years complains of bleeding, expressed pain gums. Mobility of the lower front teeth. He suffers from diabetes of 6 years. OBJECTIVE: clear hiporemiyovani, interdental papillae swollen, loosened, moving teeth, periodontal pockets of 5 mm with purulent content. On radiographs of the alveolar ridge in the region of the lower front Teeth determined degradation compact plate and spongy substance interdental membranes to 1/3 the length of the root. What is the most likely diagnosis? A. Catarrhal gingivitis, chronic B. * Localized periodontitis, chronic C. Localized periodontitis in acute D. Generalized periodontitis, chronic E. Generalized periodontitis, pointed 234. A woman, 38 years old, diagnosed with generalized periodontitis of moderate severity, abscesses flow. Objectively temperature 37,3 ° C, weakness, malaise. What additional tests would you have spent sick in the first place? A. Overall expanded blood B. * Determine the amount of sugar in the blood and urine C. Determination of capillary gum Kulazhenko D. Identification of tissue saturation with ascorbic acid E. Reoparodontohrafiya 235. Patient, 44 years old, an employee printing, complains nezychaynyy look and periodic bleeding gums. Complaints appeared a few years ago. He has kidney disease. Objectively: skin normal 'color, lips and oral mucosa anemic. Gingival papillae cyanotic, pasty, with dotorkuvanni bleed. On marginal land ash - gray rim that is not changed by erasure. Teeth fixed. Regional lymph nodes are not changed. Put the most likely diagnosis. A. Skorbut B. * Saturnism C. Merkurializm D. Pellagra E. Aryboflavinoz 236. The patient, 54 p., Complains of pain in the gums, their bleeding, bad breath, mobility jy6ie. Treated regularly. OBJECTIVE: clear in the teeth on the upper jaw smoothed with periodontal pockets excreted manure. Depth parodoptalnyh pockets 5-8 mm. Mobility of teeth II-III century. Teeth frontal area of the mandible shifted is defective dentition. The X-ray 21, 12 interdental septum absent for 1/2 the length of the roots. Please diagnosis. A. Chronic periodontitis heneralizs ized mild B. Chronic generalized periodontitis of moderate severity C. * Chronic generalized periodontitis heavy siupenya D. Chronic localized severe periodontitis E. Acute generalized periodontitis of moderate severity 237. Patient, 32 p., Complains of pain, bleeding gums, mobility of teeth, raising the temperature to 37,5 ° C. OBJECTIVE: clear bright hyperemic, swollen, painful on palpation. The roots of teeth exposed to 1/4 of their length, mobility 31, 32, 41, 42 -1 degree. Periodontal pockets - 3-4 mm sero-purulent exudate. Panoramic x-rays: irregular resorption interalveolar septum at 1/3 the length of the root, diffuse osteoporosis, periodontitis expansion slots. Therefore diagnosed select physiotherapy: A. Electrophoresis B. Darsonvalization C. Automasazh D. Laser Therapy E. * Cryodestruction 238. The patient, 45 p., Complaints of feeling itching gums. Clear dense normal color. There is an increased tooth sensitivity to cold. The X-ray revealed a defect compact plate on top of the interdental septum, osteoporosis interdental membranes. Put the most likely diagnosis. A. * Periodontal disease and degree B. Periodontal Degree II C. Periodontitis and degree D. Chronic catarrhal gingivitis E. Periodontal initial degree 239. Patient, 38 years old, asked two weeks ago to a dentist, who made a diagnosis of generalized periodontitis of moderate severity, acute stage. After a course of antiinflammatory therapy gums were normal color, periodontal pockets 4-5 mm from the serosal release. Which method of elimination of periodontal pockets you prefer in this case? A. Conservative method B. * Curettage C. Hinhivotomiya D. Hinhivektomiya E. Scrappy operation Questions to the pictures 1. Which anatomical and histological formation picture in figure 1? A. attached part gum B. connecting epithelium C. *dentine D. compact disc alveoli E. enamel 2. During that figure is depicted in Figure gum edge? A. *under number 2 B. in figure 1 C. under the number 3 D. in figure 4 E. not shown at all 3. Interdental papilla shown in figure: A. under number 2 B. *in figure 1 C. under the number 3 D. in figure 4 E. not shown at all 4. Gingival sulcus the picture below figure: A. under number 2 B. in figure 1 C. *under the number 3 D. in figure 4 E. not shown at all 5. Sticky gingival part shown on the picture under the number: A. under number 2 B. in figure 1 C. under the number 3 D. *in figure 4 E. not shown at all 6. What formation picture in figure 2? A. horny layer of the epithelium B. *granular layer of the epithelium C. ribbed layer of the epithelium D. basal layer of the epithelium E. own plate 7. In which figure in the picture capillaries? A. under number 2 B. in figure 1 C. *under the number 3 D. in figure 4 E. not shown at all 8. What is the point of contact in the picture under the letter A? A. plane B. plural C. *punctate D. parallel E. no correct answer 9. Which group of lymph nodes shown in the figure at number 1? A. *submandibular B. submental C. deep cervical D. superficial cervical E. parotid 10. What a survey shown in the picture? A. *polarography B. electroodontodiagnosis C. biomicroscopy D. test Kulazhenko E. tomography 11. What classification shown in the picture? A. *Classification of recessions on Miller B. Classification of recessions in Hamp C. Classification of recessions in Tarnow D. Classification of recessions on glacier E. no right answer 12. What class recession by Miller on this picture under number 1? A. *First class B. The second class C. third-class D. Fourth grade E. Fifth Grade 13. In Miller class recession shown in the figure by figure 2 ? A. First class B. *The second class C. third-class D. Fourth grade E. Fifth Grade 14. What class recession shown in the figure under number 3? A. First class B. The second class C. *third-class D. Fourth grade E. Fifth Grade 15. What is the picture? A. Garlands McCauley B. recession Miller C. *Cracks Schtilmana D. recession Hampi E. no right answer 16. Apparatus for which research is drawn in this picture? A. polarography B. electroodontodiagnosis C. biomicroscopy D. *Ehoosteometry E. There is no right answer 17. The figure shows: A. *Garlands McCauley B. recession Miller C. Cracks Schtilmana D. recession Hampi E. no right answer 18. What study painted in the picture? A. polarography B. electroodontodiagnosis C. *biomicroscopy D. tomography E. no right answer 19. 19. Apparatus for a survey in the picture is? A. polarography B. electroodontodiagnosis C. biomicroscopy D. Tomography E. *Samples Kulazhenko 20. What research on a picture? A. polarography B. electroodontodiagnosis C. biomicroscopy D. test Kulazhenko E. *tomography 21. In view of the teeth showed dental plaque, in the picture, namely: A. undergingival tartar B. *plaque C. subgingival tartar D. microbial plaque E. tartar 22. What Diagnostic Tool in the picture? A. pulptester B. apekslokator C. *registration leaflet D. apparatus Kulazhenko E. no right answer 23. Which bite on this picture? A. *ortognatic B. progenic C. prognathic D. deep E. cross 24. What is the procedure shown in Figure? A. determine the degree of mobility of teeth B. determine the width of the periodontal gap C. definition of bite D. *determine the depth of periodontal pockets E. no right answer 25. What research in the picture? A. determine the degree of mobility of teeth B. determine the width of the periodontal gap C. definition of bite D. *determine the depth of periodontal pockets E. no right answer 26. 26. Which index conducted in this picture? A. Fedorova has been received B. Green-Vermilien C. PMA D. KPI E. *Silnes-Loye 27. What index is shown in this picture? A. Index PMA B. Index KPI C. test-Shiller Pisarev D. index PI E. Index Silnes-Loye F. ANSWER: C 28. What a survey is shown in this picture? A. Depth of prysinka B. test-Shiller Pisarev C. *determine the degree of mobility of teeth D. palpation E. percussion 29. What research depicted in this picture? A. Depth of vestibulum oris B. test-Shiller Pisarev C. determine the degree of mobility of teeth D. *investigation of the pockets E. percussion 30. What research conducted in this picture? A. Depth of vestibulum oris B. sample-Shiller Pisarev C. formalin test D. investigation of the pockets E. *Selection contents of pockets 31. What traumatic factor is shown in Figure 1? A. incorrectly made crowns B. *cavities on the contact surfaces of the teeth C. violation spividnoshen contact between teeth D. cervical caries with growing of gingival papilla E. teeth erossion 32. What is the formation of the picture under number 1? A. pelicule B. plaque C. *cuticle D. microbial plaque E. tartar 33. What is deposition of the picture under number 1? A. *undergingival tartar B. plaque C. subgingival tartar D. microbial plaque E. tartar 34. What dye used for coloring of teeth in this picture? A. iodine solution B. methylene blue C. *erytrozyn D. Brilliant green E. fukurtsyn 35. The solution which the dye used for coloring of teeth on this picture? A. iodine solution B. *methylene blue C. erytrozyn D. Brilliant green E. fukurtsyn 36. What are the tools used for operations gingivectomy on the picture under the letter A? A. Universal blade holder 360 ° B. *Replacement blade scalpel C. Axe for gingivectomy Kirkland D. Excavators E. Knife for gingivectomy Orban 1/2. 37. Tools used for operations gingivectomy see in the image below in the letter is: A. Universal blade holder 360 ° B. Replacement blade scalpel C. *Axe for gingivectomy Kirkland D. Excavators E. Knife gingivectomy Orban 1/2. 38. In the letter B shows the following tools that are used for operations gingivectomy: A. *Universal blade holder 360 ° B. Replacement blade scalpel C. Axe for gingivectomy Kirkland D. Excavators E. Knife gingivectomy Orban 1/2. 39. Tools used for operations gingivectomy the picture under the letter G is: A. Universal blade holder 360 ° B. Replacement blade scalpel C. Axe for gingivectomy Kirkland D. Excavators E. *Knife for gingivectomy Orban 1/2. 40. In which operation shown the direction of the incission: A. Gibgivectomy B. curettage C. Criocurretage D. *Gingivotomy E. diathermocoagulation 41. What is the stabilization of the dentition is shown in Figure? A. *sagittal B. Frontal C. Frontosahitalna D. Parasahitalna E. In arc 42. What type of stabilization dentition shown in the figure? A. sagittal B. *Frontal C. Frontosahitalna D. Parasahitalna E. In arc 43. Stabilization dentition shown in figure is: A. sagittal B. Frontal C. *Frontosahitalna D. Parasahitalna E. In arc 44. The figure shows this stabilization dentition as: A. sagittal B. Frontal C. Frontsagittal D. *Parasagittal E. In arc 45. What stage curettage is shown in Figure? A. Removing undergingival plaque B. *Removing subgingival plaque C. Removing of bone lission D. curettage of granulation E. There is no right answer 46. The second stage of curettage is shown in Figure? A. Removing undergingival plaque B. Removing subgingival plaque C. *Removing of bone lission D. curettage of granulation E. There is no right answer 47. The third stage of curettage is shown in Figure? A. Removing undergingival plaque B. Removing subgingival plaque C. Removing of bone lission D. *curettage of granulation E. There is no right answer 48. What splints for temporary fixed upper jaw are shown in Figure? A. Circule splint B. A slint on artificial crowns with multi clammer C. wire splint with plastic lining D. *wire splint E. There is no right answer 49. What temporary removable splint for maxilla shown in Figure? A. *Circule splint B. A slint on artificial crowns with multi clammer C. wire splint with plastic lining D. wire splint E. There is no right answer 50. Which of fixed, temporary splints are used for mandible? A. Circule splint B. *A slint on artificial crowns with multi clammer C. wire splint with plastic lining D. wire splint E. There is no right answer 51. For the mandible used such a fixed, temporary splints: A. Circule splint B. A slint on artificial crowns with multi clammer C. *wire splint with plastic lining D. wire splint E. There is no right answer 52. Figures 1 marked areas blocking movement of the mandible at: A. *If movements in the sagittal direction B. When you change the degree of incisal overlap C. With the shift to the right D. With the shift to the left E. There is no right answer 53. Figure 2 marked areas, blocking movement of the mandible at: A. If movements in the sagittal direction B. *When you change the degree of incisal overlap C. With the shift to the right D. With the shift to the left E. There is no right answer 54. Figure 3 marked areas, blocking movement of the mandible at: A. If movements in the sagittal direction B. When you change the degree of incisal overlap C. *With the shift to the right D. With the shift to the left E. There is no right answer 55. Number 4 marked areas, blocking movement of the mandible at: A. If movements in the sagittal direction B. When you change the degree of incisal overlap C. With the shift to the right D. *With the shift to the left E. There is no right answer