The Age of Exploration
advertisement

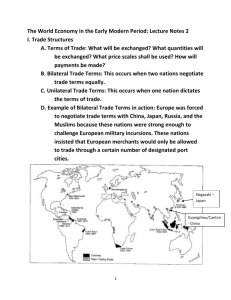
The Age of Exploration I. Europe Gets Ready to Explore - after the collapse of the Mongol Empire, local rulers taxed merchants who used the Silk Road - the Ottoman Turks conquered the Byzantine Empire and blocked Italian merchants from entering the Black Sea - Europeans wanted spices and silk from Asia. Having to trade with the Turks for these goods drove prices higher - In the 1400s, new technology allowed the Europeans to navigate the Atlantic Ocean. Increased trade and strong governments made expensive trips possible - By the end of the 1400s, Spain, Portugal, England, and France were anxious to discover a water route to Asia - Europeans discovered maps of the world drawn by Claudius Ptolemy and printed them in 1475. Ptolemy’s system of latitude and longitude is still used today - Europeans also discovered a book written by an Arab geographer, al-Idrisi that showed the geography of East Africa and the Indian Ocean. Explorers hoped that they could find a route to Asia by sailing around Africa II. Exploring the World - Henry the Navigator was a Portuguese prince who set up a research center for cartography and shipbuilding - The Portuguese began mapping Africa’s coastline and trading with African kingdoms, and then took control of the Azores, Madeira, and Cape Verde Islands - The Portuguese brought enslaved Africans to their islands to work in the sugarcane fields - Vasco da Gama sailed around the tip of Africa and across the Indian Ocean in 1497 - Christopher Columbus, an Italian sea captain, received funding from the rulers of Spain to search for a route to Asia by crossing the Atlantic Ocean. In 1492, Columbus landed in the Caribbean and explored the area, thinking he had reached Asia. - Ferdinand Magellan discovered what became known as the Strait of Magellan, the passageway south of South America. Magellan was later killed by natives in the Philippines, and his crew continued on to Spain. They were the first known people to circumnavigate, or sail around the world. - In 1497, the English captain John Cabot sailed along the coast of Canada. He was searching for a northern route to Asia - Giovanni da Verrazano, an explorer sailing for France, mapped America’s coast while searching for a route to Asia - Jacques Cartier, while attempting to find a northern route to Asia, explored the St. Lawrence River - Spain built a large empire in America, enslaving Africans and Native Americans to work farms in the new land. Spanish conquistadors conquered Native American peoples while searching for riches - England and Spain became enemies after the Protestants in the Netherlands rebelled against Catholic Spain, and England aided the Dutch people - Privateers were privately owned ships that had a license from the government to attack ships from other countries - The king of Spain sent the Spanish Armada, a huge fleet of ships, to invade England, but the Armada failed III. The Commercial Revolution - the Portuguese defeated the Muslim merchants in the Indian Ocean. Then they established trading posts in Asia - to become rich, the Europeans came up with the idea of mercantilism. Mercantilism is the idea that a country gains power by building up its supply of gold and silver. To do this, a country exports, or sells to other countries, more goods than it imports, or buys from other countries. - A colony is a settlement of people living in a new territory controlled by their home country. Europe set up colonies in Asia and the Americas - Commerce is the buying and selling of goods in large amounts over long distances. Merchants had to change the way they did business to participate in commerce. This new type of businessperson was called an entrepreneur. - Some business deals were so large that many entrepreneurs joined together to form a joint-stock company that invested in a business - The merchants, frustrated with the guilds, asked peasants to make goods for them. This system is called the cottage industry. IV. A Global Exchange - the Columbian Exchange refers to the exchange of people, technology, ideas, and even diseases that occurred between Europe and America during the Age of Exploration - crops and animals were exchanged with countries around the globe. Native Americans of the Great Plains began using horses to hunt buffalo. - People also moved as a part of the Exchange. Millions of enslaved Africans were sent to the Americas to work on plantations. The East India Company of England built an empire in India, and the Dutch East India Company built an empire in Indonesia. - Asian society was also changed. Using European weapons, the shogun was able to reunite Japan. - Not all changes were good. Many Native Americans were killed by various diseases brought over by the Europeans. V. Tidbit - the Renaissance and the Reformation were going on during a large portion of the Age of Exploration -