Name
advertisement

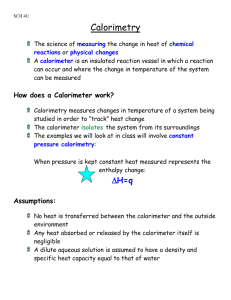
Name____________________________ Cp Problems Date_____________ 1. If the same amount of heat is added to 1.00 g of each of the following substances, which substance will undergo the largest temperature change? Substance Specific Heat (J/g·ºC) Al(s) 0.90 Cl2(g) 0.48 C6H6(l) 1.7 H2O(l) 4.2 NaCl(s) 0.87 a. Al(s) b. Cl2(g) c. C6H6(l) d. H2O(l) e. NaCl(s) 2. Aluminum has a specific heat of 0.902 J/g·ºC. How many joules of heat are required to change the temperature of 8.50 grams of aluminum from 25.0ºC to 93.4ºC? a. 7.67 J c. 192 J e. 524 J b. 71.7 J d. 483 J 3. Copper has a specific heat of 0.382 J/g·ºC. If 2.51 g of copper absorbs 2.75 J of heat, what is the change in temperature? a. 0.419ºC c. 2.87ºC e. 6.90ºC b. 2.63ºC d. 4.12ºC 4. Copper has a specific heat of 0.382 J/g·ºC. The temperature of an unknown mass of copper increases by 4.50ºC when it absorbs 3.97 J of heat. What is the mass of the copper? a. 2.31 g c. 6.82 g e. 46.8 g b. 4.90 g d. 8.85 g 5. The heat capacity of 5.00 grams of iron is 2.23 J/ºC. How much heat is required to heat the iron by 50.0ºC? a. 0.223 J c. 112 J e. 612 J b. 22.3 J d. 558 J 6. If 35.0 J is required to heat 50.3 g Hg by 5.00ºC, what is the specific heat of mercury? a. 0.139 J/g·ºC c. 0.572 J/g·ºC e. 1.49 J/g·ºC b. 0.250 J/g·ºC d. 0.878 J/g·ºC 7. Water has a specific heat of 4.18 J/g·ºC. If 35.0 g of water at 98.8ºC loses 4.94 kJ of heat, what is the final temperature of the water? a. 32.0ºC c. 47.2ºC e. 65.0ºC b. 46.2ºC d. 57.2ºC 8. A coffee-cup calorimeter contains 50.0 g of water at 60.51ºC. A 12.4 g piece of graphite at 24.21ºC is placed in the calorimeter. The final temperature of the water and the carbon is 59.02ºC. Calculate the specific heat of carbon. The specific heat of water is 4.18 J/g·ºC. a. 0.328 J/g·ºC c. 0.692 J/g·ºC e. 1.39 J/g·ºC b. 0.639 J/g·ºC d. 0.721 J/g·ºC 9. A coffee-cup calorimeter contains 10.0 g of water at 59.00ºC. If 3.00 g Au at 15.20ºC is placed in the calorimeter, what is the final temperature of the water in the calorimeter? The specific heat of water is 4.18 J/g·ºC; the specific heat of gold is 0.128 J/g·ºC. a. 55.37ºC c. 59.40ºC e. 64.19ºC b. 58.60ºC d. 60.80ºC 10. When 2.50 g of potassium bromide dissolves in 1.00 102 g of water in a calorimeter, the temperature drops from 22.657ºC to 21.661ºC. What is the heat change per gram of potassium bromide dissolved in water? Assume that all the heat comes from the water (c = 4.18 J/g·ºC) a. 0.0671 J c. 26.0 J e. 167 J b. 2.08 J d. 87.0 J 11. When 1.75 g of CaCl2 dissolves in 125 g of water in a coffee-cup calorimeter, the temperature increases by 2.44ºC. What is the heat change per mole of CaCl2 dissolved in water? Assume that all the heat is absorbed by the water (c = 4.18 J/g·ºC). a. -11.3 kJ c. -1.13 kJ e. -91.9 kJ b. -728 J d. -80.9 kJ 12. Commercial cold packs consist of solid ammonium nitrate and water. NH4NO3 absorbs 330 J of heat per gram dissolved in water. In a coffee-cup calorimeter, 4.00 g of NH4NO3 is dissolved in 75.0 g H2O. Assuming that all the heat is lost from the water (c = 4.18 J/g·ºC), what is the temperature change of the water? a. 4.2ºC c. 11ºC e. 19ºC b. 8.4ºC d. 13ºC 13. A chemical reaction in a bomb calorimeter raises the temperature of the calorimeter from 20.22ºC to 23.14ºC. If the heat capacity of the calorimeter is 8.44 kJ/ºC, calculate the heat evolved in the reaction. a. 2.89 kJ c. 9.12 kJ e. 24.6 kJ b. 5.52 kJ d. 11.36 kJ 14. A chemical reaction in a bomb calorimeter evolves 3.15 kJ of heat. If the temperature of the calorimeter is raised from 19.19ºC to 22.03ºC, what is the heat capacity of the calorimeter? a. 1.11 kJ/ºC c. 8.95 kJ/ºC e. 69.4 kJ/ºC b. 2.01 kJ/ºC d. 14.5 kJ/ºC 15. A 2.50 g sample of ethanol, C2H5OH, is combusted in a bomb calorimeter. The temperature of the calorimeter increases by 14.2ºC. If the heat capacity of the calorimeter is 5.22 kJ/ºC, what is the heat evolved per mole of ethanol combusted? a. 29.6 kJ/mol c. 4.02 kJ/mol e. 1370 kJ/mol b. 6.77 kJ/mol d. 74.1 kJ/mol 16. If 25.0 g H2O at 85.0ºC is mixed in a coffee-cup calorimeter with 15.0 g H2O at 20.0ºC, what is the final temperature of the mixture? The specific heat of water is 4.18 J/g·ºC. a. 45.6ºC c. 60.6ºC e. 183ºC b. 52.5ºC d. 68.4ºC 17. 10.0 g of ice at 0.00ºC is mixed with 25.0 g of water at 35.00ºC in a coffee-cup calorimeter. What is the final temperature of the mixture? The specific heat of water is 4.18 J/g·ºC; the heat of fusion of water is 333 J/g. a. 0.00ºC c. 5.22ºC e. 47.8ºC b. 2.24ºC d. 25.0ºC 18. 30.0 g H2O at an unknown temperature is mixed with 27.0 g of water at 15.8ºC in a coffeecup calorimeter. If the final temperature of the mixture is 29.1ºC, what is the initial temperature of the water? a. 23.7ºC c. 39.7ºC e. 46.7ºC b. 31.1ºC d. 41.1ºC 1. ANS: B 2. ANS: E 3. ANS: C 4. ANS: A 5. ANS: C 6. ANS: A 7. ANS: E 8. ANS: D 9. ANS: B 10. ANS: E 11. ANS: D 12. ANS: A 13. ANS: E 14. ANS: A 15. ANS: E 16. ANS: C 17. ANS: B 18. ANS: D