KW Mineral Packet
advertisement

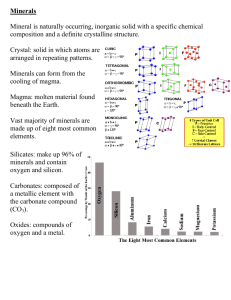
Name: ___________________________ Block: ________ KW Mineral Packet A mineral is a naturally occurring inorganic solid with a distinct chemical composition and crystalline structure. The five characteristics a substance must have to be classified as a mineral are: 1. It occurs naturally (not man made) 2. It is solid 3. It has a definite chemical composition 4. Its atoms are arranged in an orderly pattern (like a crystal) 5. It is inorganic (was never alive) The two most abundant mineral-making elements are oxygen and silicon. Minerals form from molten rock. As magma cools, the atoms, molecules and ions move closer together and form chemical bonds that create compounds. The size of the crystals is determined by the rate at which magma cools. If the magma cools quickly, the crystals do not have much time to form, so they are very small. If the magma cools slowly, then the crystals have enough time to grow and become large. A crystal is a regular geometric solid with smooth surfaces. There are six basic shapes of crystals including cubic and hexagonal. Minerals can also form from evaporation. Evaporate minerals are those that form by coming out of solution when seawater and the waters of large lakes evaporate. Halite forms when water evaporates from a solution of salt and water. Figure 3.23: The limestone towers are made mostly of calcite deposited in the salty and alkaline water of Mono Lake, in California. These rocks formed under water when calcium-rich spring water at the bottom of the lake bubbled up into the alkaline lake, forming these calcite "tufa" towers. If the lake level drops, the tufa towers appear in interesting formations. Types of minerals: Silicate Minerals - minerals that contain a combination of silicon and oxygen. They make up 90% of the Earth's crust. Families of silicates include: Quartz Feldspars Pyroxenes Mica Amphibole Kaolinite and the Olivine group Nonsilicate Minerals - minerals that do not contain a combination of the elements silicon and oxygen. There are six classes of these elements. Six classes of nonsilicate minerals: 1. Native elements - minerals that are composed of only one element. 2. Carbonates - minerals that contain combinations of carbon and oxygen. 3. Halides - compounds that are formed when atoms of the elements fluorine, chlorine, iodine, or bromine combine with sodium, potassium, or calcium. 4. Oxides - compounds that are formed when an element, such as aluminum or iron, combines chemically with oxygen. 5. Sulfates - contains sulfur and oxygen. 6. Sulfides - minerals that contain one or more elements, such as lead, iron, or nickel, combine with sulfur. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TwgGPtqZnQc Non-silicates 5:01 Identifying Minerals – Different Properties COLOR is the least useful property in mineral identification because many minerals have similar colors. Impurities can turn colorless minerals into colored minerals. Metallic minerals have distinct colors Nonmetallic minerals display a variety of colors LUSTER is the way the mineral shines in light. Two main classifications of luster are metallic (looks like metal) and nonmetallic. Nonmetallic luster is further divided into (but not limited to): Vitreous – Looks like glass (quartz) Adamantine – Brilliant like a diamond Resinous – Looks like resin or tree sap Pearly – Looks like a pearl (mica) Silky – Having a fibrous silk-like luster Earthy or dull – Looks like dirt https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MuJN-H52mGM https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rtc7XJdFiE4 Chumley – Gold vs. Fool’s Gold Quartz – Vitreous Luster Barite – Pearly luster Anglesite – Adamantine Luster Sphalerite - Resinous Luster Actinolite – Silky Luster Azurite – Earthy Luster CLEAVAGE is the tendency to break along definite planes and is determined by crystal structure. Some minerals cleave in sheets and some cleave leaving flat sides. Some minerals have cleavage in more than one direction. Some minerals have no cleavage at all. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cxtIvxUd4DY FRACTURE is the way a mineral breaks when it does not have cleavage. Kinds of fracture: Conchoidal- bowl shaped structures like the inside of a clam shell; like obsidian Fibrous or splintery- fractured surface shows fibers or splinters; like asbestos Uneven- this surface is rough and irregular; like basalt Obsidian – Conchoidal Fracture Chrysotile – splintery fracture Talc – uneven fracture https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=eeT068wxsVQ STREAK is the color of a mineral’s powder. It is tested by rubbing the mineral on an unglazed white tile called a streak plate. The streak is often a different color from the mineral. Streak is much more consistent than color for the purpose of identification. The streak of a metallic mineral is at least as dark as the specimen. The streaks of nonmetallic minerals are usually colorless or white. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wENW59poN8Q HARDNESS measures the ability of a mineral to resist scratching by another mineral or object of known hardness. Hardness depends on chemical structure. A diamond is carbon atoms arranged in a tetrahedral pattern. Graphite is carbon atoms arranged in sheets. MOH’S HARDNESS SCALE Moh’s Hardness Scale is a scale used to measure the relative hardness of a mineral by its resistance to scratching, made up of ten minerals arranged in decreasing hardness; 1 is the softest and 10 is the hardest. Objects with higher value on the Mohs' scale are capable of scratching objects with lower values. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=R-bw7_u3gSQ SPECIFIC GRAVITY is the ratio of a mineral’s mass to the mass of an equal volume of water. Density is mass divided by volume. D = M/V. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yGnNE-MWDV4 SPECIAL PROPERTIES Calcite can be tested with hydrochloric acid (HCL) because it fizzes when it comes in contact Fluorescence is a property of certain minerals: when you shine an ultraviolet "black light" on them in a darkened place, they respond by glowing in strangely bright colors. Double refraction splits light rays that pass through it such as Iceland Spar calcite. Magnetite is attracted by a magnet. Taste Smell https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AK_Z63UvQjE https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iS0pWYHSh84 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xrR14fBXpsM MINERAL Calcite Copper Diamond Feldspar Galena Graphite Gypsum Halite Hematite Muscovite Mica Quartz Silver Sulfur Talc HCL Black light Magnetite USES Medicine, toothpaste, building materials Tubing, Wires Cutting Tools Ceramic, Porcelain, Found in granite Lead Pencils, Lubricants in Machines Wall board Salt Iron Electrical insulators, Cosmetics Glass, Radios, Watches Jewelry, Photography Fungicides, Medicine, Vulcanizes Rubber Fertilizer, Coal & fuel, Baby powder, Gymnastics to grasp bars https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SqSOskpMsxM