Cells and the Cell Theory
advertisement

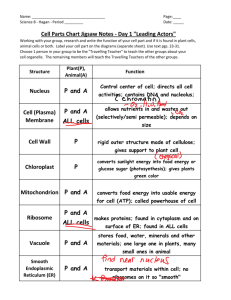
Cells and the Cell Theory Academic Biology I. II. III. Name_______________ Intro A. Most organisms are made of billions or trillions of cells. Adult human has 35 trillion cells. B. Organisms differ from each other in cell structure. 1. certain features common to all: cell membrane, cytoplasm 2. certain processes are necessary for all cells: metabolism, reproduction, creating energy, removing wastes, getting nutrients Invention of the microscope enabled scientists to view cells. A. Anton von Leeuwenhoek (dutch merchant) 1. developed first working microscope 2. first to view microorganisms and living cells B. British scientist Hook viewed cork cells 1. coined the term cells as they looked like monastery cells. C. Schleiden 1. German botanist – 1838 2. studied plant cells 3. discovered that all organisms are made of fully individualized, independent, separate beings (cells) D. Schwann 1. German zoologist – 1939 2. studied animal cells 3. found that the cell is the cellular basis of all life E. Virchow 1. Discovered that the animal only arises from an animal and the plant only from a plant 2. contradicted the idea of spontaneous generation Cell Theory A. The combined work of Schleiden, Schwann, and Virchow led to the Cell Theory 1. Cells are the basic unit of life. 2. All organisms are made of cells. 3. All cells arise from pre-existing cells. IV. Parts of a cell A. Cell membrane 1. thin double layer of lipids and proteins separating the cell’s contents from its environment 2. microns thick (10,000 cell membranes is as thick as a piece of paper) 3. Mostly made of phospholipids a. polar molecule b. hydrophilic c. hydrophobic 4. Fluid mosaic model – proteins are embedded in the cell membrane that allow materials to come in and out. They move in through the proteins which can move around and change shape for all materials to enter through. (Find a cell membrane and draw it and label it.) B. Nucleus 1. 2. 3. 4. V. control center of the cell prokaryotic cell – no nucleus, DNA is found in the center eukaryotic cell – has a membrane bound nucleus surrounded by a double layer membrane called a nuclear envelope. 5. lots of pores are found in the membrane 6. contains DNA a. long thin strands are called chromatin b. condenses into thick strands called chromosomes during cell division c. contains coded blueprints that control cell activity 7. has at least one nucleolus which make ribosomes which build proteins C. cytoplasm 1. everything between the cell membrane and the nuclear membrane 2. Two main components a. cytosol which is jellylike, mostly water, with proteins, carbohydrates, and organic compounds – biological reactions occur b. Organelles are structures that work like miniature organs that carry out specific functions in a cell Organelles A. ribosomes 1. make proteins 2. found free floating or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum B. Endoplasmic reticulum 1. intracellular transport (highway) 2. connects nuclear membrane to cell membrane 3. detoxifies chemicals in cytoplasm 4. rough ER is studded with ribosome’s – processes proteins 5. smooth ER has no ribosomes – processes lipids and carbohydrates C. Golgi Apparatus 1. packages and secretes cell products D. E. F. G. VI. 2. series of flat, membrane-bound sacs stacked like pancakes called cristae mitochondria 1. powerhouse of the cell 2. releases energy contained in food 3. folded inner membrane increases the surface area 4. makes ATP through cellular respiration lysosomes 1. contains enzymes to digest food particles inside the cell 2. enzymes are produced by the golgi apparatus vacuoles 1. membrane bound sac in cell membrane 2. stores food, cell products, or wastes Other cell parts: Cell Diversity Structure Cell membrane Cell wall nucleus chromosomes ribosomes ER Golgi apparatus lysosomes vacuoles mitochondria chloroplasts cytoskeleton Prokaryotic cells No Yes No Yes No No No No No No No Yes eukaryotic Animal Yes No Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes No eukaryotic plant yes yes Yes yes yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes yes No A. Plant cells 1. have a cell wall and a cell membrane 2. cell wall has cellulose which makes it rigid. 3. Plastids: chromoplasts, chloroplasts, leucoplasts, and other plastids.