File
advertisement

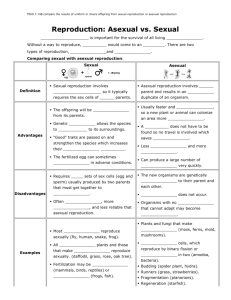
BIO 2 GO! 3215 Asexual and Sexual Reproduction In asexual reproduction, the offspring have the same DNA as the parent. In sexual reproduction, the offspring have a combination of DNA provided by 2 different parents, so they do not have the same DNA as their parents. Asexual and Sexual Reproduction 3.2.1.5 Upon successful completion of this unit, you should be able to do the following: 1. Explain and describe the similarities and differences between sexual and asexual reproduction. 2. List, describe, and explain the 3 types of asexual reproduction. 3. Explain the role of DNA in sexual and asexual reproduction. 4. Explain and describe the process of mitosis. 5. List and explain the 2 reasons that cells divide. 6. Explain and describe sexual reproduction in angiosperms, and mammals. 7. Be able to use the following words in their correct context: sexual reproduction sperm asexual reproduction egg binary fission zygote budding vegetative reproduction clone reproduction Asexual and Sexual Reproduction 3.2.1.5 Living organisms, both plant and animal, make more living organisms in a process called reproduction. The offspring of reproduction genetically resemble the parents. There are 2 types of reproduction: 1) Asexual 2) Sexual. ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION: In asexual reproduction, 1 parent produces offspring that are genetically identical to that parent. In other words, the offspring have exactly the same DNA as the parent. (Remember, DNA is located on the chromosomes.) The offspring are often called clones because they are the same as the parent. REMEMBER THIS !!! In asexual reproduction, the offspring have the same DNA as the parents. They are exact duplicates of the parents. In asexual reproduction, the new offspring is created by making new cells in the process called cell division. Whenever a cell divides to make two cells, that process is called cell division. Cell division, also called mitosis, is responsible for creating offspring and for growth and repair of the parent cell. Asexual reproduction requires cell division to take place in the cell. There are three types of asexual reproduction: 1) binary fission 2) budding 3) vegetative 1. Binary fission- This is a simple type of cell division in which 1 cell splits into 2 cells. Binary fission is common in bacteria. 2. Budding- When a small part of the parent’s body begins to grow and form a new organism. This “bud” breaks off to form an offspring that is genetically identical to the parent. Budding is common in unicellular plants and animals. 3. Vegetative- This type of asexual reproduction is also called fragmentation. In vegetative asexual reproduction, a piece, or fragment, of the parent may be used to create a new whole organism. Sometimes the fragment is broken off by accident, but often the piece is broken off on purpose to start a new organism. For example, certain types of plant are made by taking cuttings from a parent plant and placing them in water to grow their own roots. The offspring is genetically identical to the parent. Interesting Scientific Fact: Star fish eat oysters. In early ties, watermen would try to kill star fish by breaking off the arms of the star fish and throwing them back into the water. Unfortunately for the watermen, each arm would grow into a new organism by vegetative asexual reproduction. So rather than getting rid of the star fish, the watermen actually helped to create new ones! Question 1. What is the purpose of reproduction? Question 2. What are the 2 types of reproduction? Question 3. How would you explain asexual reproduction to someone who has no idea what it means? Question 4. List and explain the 3 types of asexual reproduction. Mitosis: Role in growth and Repair Mitosis is the process of cell division. Cells divide for 2 reasons: 1) To make new cells (asexual reproduction) 2) For growth and repair of existing cells. 1. Growth and repair: Whenever an organism is growing from a child to an adult, it requires new cells. Mitosis is the process where existing cells divide to create more cells. These new cells are genetically identical to the parent cell. In other words, the offspring have the same DNA and chromosomes as the parent. Whenever an organism is repairing or replacing a cell that may have been injured, mitosis is the process that creates new cells to replace the damaged cells. The DNA and chromosomes are the same in the new cells as they were in the parent cells. REMEMBER THIS!!! Mitosis is the process of cell division. Cells divide for 2 reasons: 1) reproduction 2) growth and repair. Question 5. What are the 2 reasons for mitosis? Question 6. What happens during mitosis? SEXUAL REPRODUCTION Sexual reproduction produces offspring by combining the genetic material, (DNA), of 2 parents. The offspring receives its DNA from both parents. ½ of the DNA comes from the male and ½ of the DNA comes from the female. So the offspring is similar to both parents but is not genetically identical to either parent. Both parents contribute DNA to the offspring. The offspring receives equal amounts of DNA from each parent. Sexual reproduction is different from asexual reproduction in 2 ways: 1) In sexual reproduction the offspring receives DNA from 2 parents. In asexual reproduction there is only 1 parent. 2) In sexual reproduction, the offspring are genetically different from the parents. In asexual reproduction, the offspring are genetically the same as the parents. The picture above is of cell that has undergone meiosis to create egg and sperm cells for sexual reproduction. REMEMBER THIS!!! In sexual reproduction, the DNA from 2 parents combines to create a new individual; in asexual reproduction, the DNA of 1 parent is passed on to the new individual. In sexual reproduction, the offspring are genetically different from the parent; in asexual reproduction, the offspring are genetically the same as the parent. Sexual reproduction creates genetic variations. How It Works In sexual reproduction, sperm is created by the male to carry the chromosomes that contain the DNA from the male organism. The female creates an egg to carry chromosomes that contain the DNA from the female organism. The sperm and egg unite to form a new kind of cell called a zygote. This is called fertilization. When a zygote is formed by the union of sperm and egg the process is called fertilization. Fertilization is sexual reproduction. Plants: Angiosperms Angiosperms are flowering plants that produce flowers and fruits. They are the most common type of vascular plant. Angiosperms include houseplants, flower bed ornamentals and garden crops. They reproduce sexually. After fertilization, angiosperms produce seeds within fruits. Apples, oranges, tomatoes and most garden and fruit crops are good examples of fruits that are easy to see. Grasses and most trees are also examples of angiosperms that produce fruits but the fruits are often very small and hard to see. Animals: Mammals Mammals are a type of animal that includes dogs, cats, deer, and humans. Mammals reproduce sexually. After the union of sperm and egg, the DNA from the mother and father are joined to create a zygote. When this happens, the process of fertilization has occurred. Since both parents each contribute ½ of the DNA for the offspring, the offspring is similar to both parents. However, the offspring is not genetically identical to either parent. Therefore genetic variation occurs. Summary Asexual and Sexual Reproduction 3.2.1.5 Reproduction occurs when living things make more of their own kind. Many organisms reproduce sexually, which means by uniting a sperm with an egg to form a zygote. Other organisms reproduce asexually, without uniting a sperm with an egg. Asexual reproduction can occur because of the process called cell division. Cell division is more than just splitting one cell into two cells. It first requires the cell’s nucleus to copy its DNA, and then to divide the DNA equally. This is called mitosis. Genetically, the two new cells are identical to each other and to the first cell from which they formed. They are also called clones. There are three types of asexual reproduction: 1. Binary fission - a process in which one cell pinches into two cells 2. Budding - a process in which a small cell pinches off from a large cell 3. Vegetative reproduction - a process in which new plants grow from the roots, stems, or leaves of other plants Most larger organisms reproduce sexually, using sperm and egg. Sexual reproduction produces offspring that are genetically different. This variation is an advantage for survival of the species. Organisms that reproduce asexually tend to be more primitive. They can produce many offspring quickly, but the offspring are all clones. Bacteria reproduce asexually by binary fission. Sponges, hydra, and yeast reproduce by budding. Plants can reproduce both sexually and by vegetative reproduction. Test Yourself Matching _____ 1. sexual reproduction a. uses budding to reproduce _____ 2. asexual reproduction b. uses binary fission to reproduce _____ 3. binary fission c. uses vegetative reproduction to reproduce _____ 4. budding d. one cell pinches into two cells _____ 5. vegetative reproduction e. a small cell pinches off from a large cell _____ 6. yeast f. new plants grow from parts of old plants _____ 7. bacteria g. reproduction uniting a sperm and an egg _____ 8. plants h. reproduction without using sperm and egg True or False _____ 1. Sexual reproduction occurs when living things make offspring using sperm and egg. _____ 2. Asexual reproduction occurs when living things make offspring using sperm and egg. _____ 3. Binary fission is a form of sexual reproduction. _____ 4. Binary fission is a form of asexual reproduction. _____ 5. Budding is a form of sexual reproduction. _____ 6. Budding is a form of asexual reproduction. _____ 7. Vegetative reproduction is a form of sexual reproduction. _____ 8. Vegetative reproduction is a form of asexual reproduction. _____ 9. Clones are genetically identical to their parent. _____ 10. Sexual reproduction produces clones. _____ 11. Asexual reproduction produces clones. _____ 12. Most higher level organisms reproduce sexually. _____ 13. Most higher level organisms reproduce asexually. _____ 14. Yeast reproduce by binary fission. _____ 15. Bacteria reproduce by binary fission. _____ 16. Plants reproduce by binary fission. _____ 17. Yeast reproduce by budding. _____ 18. Bacteria reproduce by budding. _____ 19. Plants reproduce by budding. _____ 20. Yeast reproduces by vegetative reproduction. _____ 21. Bacteria reproduces by vegetative reproduction. _____ 22. Plants reproduce by vegetative reproduction. Fill in the Blank budding sperm binary fission egg vegetative reproduction sexual asexual clones bacteria yeast plants hydra 1. Most organism produce offspring using _____________ reproduction. 2. Sexual reproduction occurs when a ______________ is united with an __________. 3. _______________ reproduction occurs when offspring are produced without uniting a sperm and egg. 4. __________________ is form of asexual reproduction that occurs when a small cell pinches off from a large cell. 5. ___________________ is a form a asexual reproduction that occurs when new plants grow from the roots, stem, or leaves of other plants. 6. ______________________ is a form of asexual reproduction that occurs when one cell pinches into two cells. 7. __________________ and __________________ both use budding for reproduction. 8. __________________ can reproduce by vegetative reproduction. 9. ____________________ can reproduce by binary fission. 10. Asexual reproduction results in offspring that are _____________, genetically identical to each other. Answer the Following 1. List and explain the similarities and differences between sexual and asexual reproduction . 2. What are clones? 3. What is binary fission? Give an example of an organism that reproduces using this. 4. What is budding? Give an example of an organism that reproduces using this. 5. What is vegetative reproduction? Give an example of an organism that reproduces using this. 6. Explain how a zygote is formed. 7. Explain the difference between a zygote and a clone.