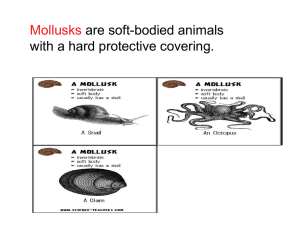
Mollusks Worksheet: Gastropoda, Bivalvia, Cephalopoda
advertisement

Name: _____________________________________________ MOLLUSKS Read the figure below, which covers topics from your textbook. Answer the questions that follow. Features of Three Classes of Mollusks Class Gastropoda Bivalvia Cephalopoda External shell one (some species) two none (most species) Head yes no yes Radula yes no yes Locomotion crawling (most) sessile (most) rapid swimming Read each question and write your answer in the space provided. SKILL: Organizing Information 1. Based on the entries in the column labeled “External shell,” how do bivalves differ from gastropods and cephalopods? ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ 2. What are two features that bivalves lack but gastropods and cephalopods possess? ________ _____________________________________________________________________________ Read the question and write your answer in the space provided. SKILL: Vocabulary Development 2. What is the meaning of the term locomotion in the table?____________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ Circle the letter of the word that best completes the analogy. 4. Bivalvia is to sessile as Cephalopoda is to a. crawling. b. swimming. c. jumping. d. Both (a) and (b) What is a coelomate? Which bivalve has eyes and can swim? Original content Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the instructor. Modern Biology Mollusca Explain the relationship between the terms in each of the following pairs of terms. 1. visceral mass, mantle _________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ 2. hemolymph, hemocoel ________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ 3. incurrent siphon, excurrent siphon _______________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ MULTIPLE CHOICE Write the correct letter in the blank. ____ 1. One advantage of a coelom over a pseudocoelom is that a coelom a. contains fluid while a pseudocoelom does not. b. is completely surrounded by endoderm. c. eliminates the need for a circulatory system. d. allows body wall muscles to contract without hindering digestion. ____ 2. One feature that is shared by many mollusks and annelids is the a. radula. b. mantle cavity. c. trochophore. d. pseudopodium. ____ 3. Mollusks in the class Gastropoda a. lack a distinct head. c. do not have a hemocoel. b. have an open circulatory system. d. are usually sessile. ____ 4. Bivalves have all of the following structures except a. a radula. b. adductor muscles.c. siphons. d. gills. ____ 5. An octopus generally moves by a. pumping a jet of water through its incurrent siphon. b. crawling along the bottom with its tentacles. c. gliding on a layer of mucus with the help of cilia. d. repeatedly opening its valves and snapping them shut. Answer the questions in the space provided. 1. Identify the two main regions of a typical mollusk’s body. _____________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ Which region contains most of the internal organs? __________________________________ Which region is directly involved with locomotion? ___________________________________ 2.What is the usual function of the mantle in a snail or clam? _____________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ 3.Contrast the feeding methods of gastropods and bivalves. _____________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ 5. A cephalopod called the paper nautilus makes a type of shell with its foot. This shell, which consists largely of protein, is formed only by the female and is used to protect the eggs. List four reasons why this shell is not a typical molluskan shell. ____________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ STRUCTURES AND FUNCTIONS Identify the structures labeled a–h in the diagram of the basic body plan of a mollusk shown below. Original content Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the instructor. Modern Biology Mollusca 1. True or False: Members of the Phylum Mollusca are among the structurally simplest multicellular organisms. 2. Mollusks are a. scavengers b. carnivores c. filter-feeders d. all of the above 3. Which of the following is NOT a characteristic trait of mollusks? a. a radula b. a shell c. a muscular foot d. tentacles with cnidocytes 4. What is the highest level of organization in mollusks? a. cellular b. tissue c. organ system d. none of the above 5. True or False? The typical molluscan body plan is greatly modified in some of the molluscan classes. 6. Mollusks have which type of symmetry? a. bilateral b. no symmetry c. radial d. pentamerous Use the Double Bubble to compare and contrast gastropods and cephalopods: