Pedigree Charts
advertisement

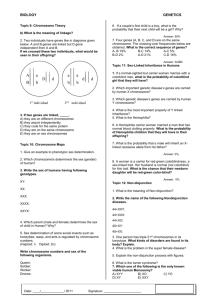
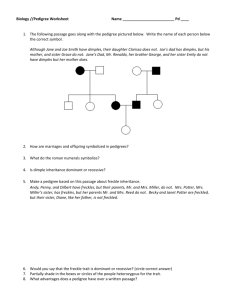
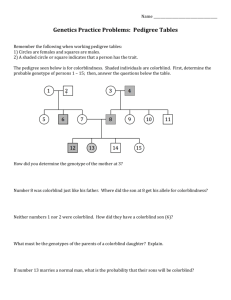
How is colorblindness transmitted? LAB HANDOUT # _____ Background: Three human genes associated with color vision are located on the X chromosome. In males a defective version of any one of these gene produces colorblindness. Colorblindness is found in about 1 in 10 males in the United States. Among females however, colorblindness is only found in about 1 in 100 females. In this lab you will simulate how colorblindness is transmitted by using beans and cups. The white beans in the lab represent X chromosomes and the red bean represents the Y chromosome. The black circle on a bean represents the gene for colorblindness. What you need: 1 cup labeled mother with 2 beans (1 white bean with black circle and 1 plain white bean) 1 cup labeled father with 2 beans (1 white bean with black circle and 1 red bean) Procedure: 1. Without looking draw one bean out from the mother cup and one bean out from the father cup. 2. Record bean colors on the data table. 3. Based on the colors of the beans indicate the sex and vision of the offspring. 4. Put the beans back and repeat steps 1-3 for a total of 10 trials. Key: 1 plain white bean + 1 red bean = Male, normal vision 1 white bean with black circle + 1 red bean = Male, colorblind 1 plain white bean+ 1 white bean with black circle= Female, normal vision 2 white beans with black circles = Female, colorblind RED Name___________________________________________________________Date______________Period_____ Lab: How is colorblindness transmitted? Background: Colorblindness is is the decreased ability to perceive differences between some of the colors that others can distinguish. There are many forms of colorblindness but one of the major types is individuals who have difficultly distinguishing between red and green. Look at the colorblind test at your table and write the number or word you see in the picture below. Picture 1. _______________________ Picture 2. _______________________ Picture 3. _______________________ Picture 4. _________________________ Picture 5. _________________________ Picture 6. _________________________ Look at the pedigree chart below for colorblindness. Use the key and the pedigree to answer the questions that follow. 1. What does the square represent? ____________________ 2. What does the circle represent? ______________________ 3. What does the color white represent? ______________________________ 4. What does the color black represent? ______________________________ 5. In order to be male, which chromosome must you receive? ________ 6. Who can give you a Y chromosome? ________________ 7. If colorblindness were linked to the Y chromosome then all (MALE OR FEMALE) offspring would be colorblind. 8. Look at the pedigree chart. The first male is colorblind. Are his sons colorblind as well? YES OR NO 9. Because none of the sons of a colorblind father are colorblind, we now know that colorblindness is linked to which chromosome? X OR Y 10. If N stands for normal vision. What would be the genotype of the carrier female? ___________ 11. Why are all the daughters of a colorblind male either colorblind or carriers? ___________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________ Carefully read the lab handout to fill in the chart below. How is colorblindness transmitted? Trial Bean colors Male or female? Example Red White with black circle Male Normal vision or colorblind? colorblind 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Use your chart and the lab handout to answer the following questions. 12. What did the white bean represent? _________________ red bean?____________________ 13. What did the black circle represent? __________________________________________________ 14. How many males where there? __________________ females? _______________ 15. How many were colorblind? _____________________ normal vision? ______________ 16. How many females were colorblind? ____________ males? _________________ 17. Which sex had more trials of being colorblind? MALE OR FEMALE 18. After completing this activity, which sex do you think is more likely to inherit a recessive x-linked trait for colorblindness? MALE OR FEMALE Polygenetic Traits – Some traits, like height or skin color, are controlled by two or more genes. These traits often work like light switches- The more genes are “on,” the taller or darker you are, the more genes are “off,” the shorter or lighter you are. Flip a coin for each gene- Heads is “on” and tails if “off.” Gene On or Off 1 2 8 on/ 0 off 7 on/ 1 off 6 on/ 2 off 7 ft. tall 6 ft. 9 in. 6 ft. 6 in. 3 4 5 6 7 8 5 on/ 3 off 4 on/ 4 off 3 on/ 5 off 2 on/ 6 off 1 on/ 7 off 0 on/ 8 off 6 ft. 5 ft. 9 in. 5 ft. 6 in. 5 ft. 3 in. 5 ft. How tall were you? __________________ 4 ft. 9 in.