Scientific Method Reading Samples Activity
advertisement

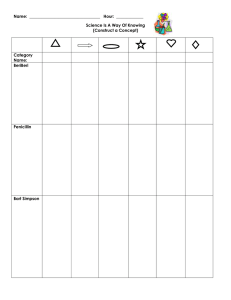
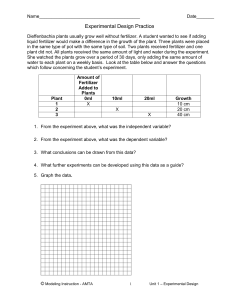
LESSON STUDY COVER PAGE LESSON TITLE: Steps of Scientific Method Construct a Concept LEAD TEACHER (S): Who will be teaching the new lesson? OBSERVING TEACHER(S): Who will be observing and collecting data? RESEARCHING STUDENT NEED AND INTERVENTION STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT NEED: what student need has the lead teacher identified? Could be qualitative/observation quantitative/data. May be life skills or content specific. STUDENT LEARNING GOALS : You might have one for all three or focus on social (life skills), content, and/or language. This is from the explicit instruction model. CONTENT/LANGUAGE: I will be able to describe 7 science concepts in my own words and match them to a book definition. I will do this by reading and thinking critically. SOCIAL: I will collaborate with the class, team/partner, and then on my own by reading and recording examples in the correct place in a courteous and respectful manner. LESSON DESCRIPTION: (if on the document just refer to that) Brief description of what will be happening. What will the teacher andstudent be doing? What teaching will be method used: Teacher begins with allowing students to read the first example. Then simply give the students the first reading samples entries on the graphic organizer. This establishes a pattern. Then have them read the second reading sample and the as a class enter the examples for each shape. Finally, have them read the next sample and fill in the shapes with their team. Scaffold down until you are at the individual level. This example (individual) can be used as a formative assessment. Then students need to write their own description of each category. Wrap up with giving them the book definitions. These can also be used as a formative assessment. Part of the core (content, standard, objective, indicator): ILO: How Science is Done ASSESSMENT: Formative quiz-like, mini-experiment that the students will take and teachers use to assess student achievement. OBSERVING AND COLLECTING DATA OBSERVER TEACHER(S): Who will be observing: What data does the lead teacher want the observer to collect to assess student achievement: PROJECTED DATE TO TEACH AND OBSERVE LESSON: Approximate date REFLECTION AND REVISION PROJECTED REVISION DATE: Approximate date ASSESSMENT: What did the collected data and formative assessment show us? WHAT DID THE LEAD TEACHER SEE THAT TELLS THEM THE LESSON WENT WELL? Engaged kids. Felt confident that the students HAD to be thinking in order to get the answers and identify patterns. Same for writing the group (shapes ) descriptions. WHAT WOULD THE LEAD TEACHER DO DIFFERENTLY NEXT TIME? Provide highlighted or shorter reading samples for ESL or SpEd students. Another thing that was tried was to put lower reading level students in groups and give them the rule (for each box/cell) so that they have something specific to look for. This seemed to chunk it down to a single achievable goal. These students did not get lost as much as when they were having to think about and construct the ideas AND be reading. Too much too fast for these students. INCLUDE: COMPLETED COVER PAGE COPY OF LESSON COPY OF FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT Name: __________________________________ Hour: _____________ Steps of Scientific Method Construct a Concept Science Is A Way Of Knowing (Construct a Concept) BeriBeri Penicillin Bart Simpson Why are people dying Disease caused loss of appetite, read medical books. Thought the new disease was caused by bacteria in blood Injected one group of chickens with blood from patients and another group of chickens did not get injected. Injected chickens got sick, but so did those that were not injected Maybe the disease is not caused by bacteria in blood. Compare Chickens that eat polished rice to those that eat whole grain and see which get sick SpongeBob & Patrick MythBusters Your Team’s Definition of each column Book Term and Definition of each column Science Is A Way of Knowing Stories: The Strange Case of BeriBeri In 1887 a strange nerve disease attacked the people in the Dutch East Indies. The disease was beriberi. Symptoms of the disease included weakness and loss of appetite, victims often died of heart failure. The scientists read medical books and found several other similar diseases that were caused by bacteria. Scientists thought the disease might be caused by bacteria. They injected chickens with bacteria from the blood of patients with beriberi. The injected chickens became sick. However, so did a group of chickens that were not injected with bacteria. One of the scientists, Dr. Eijkman, noticed something. Before the experiment, all the chickens had eaten whole-grain rice, but during the experiment, the chickens were fed polished rice. Dr. Eijkman researched this interesting case. He found that polished rice lacked thiamine, a vitamin necessary for good health. How Penicillin Was Discovered In 1928, Sir Alexander Fleming was studying Staphylococcus bacteria growing in culture dishes. He noticed that a mold called Penicillium was also growing in some of the dishes. A clear area existed around the mold because all the bacteria that had grown in this area had died. He thought this was strange so he looked in the culture dishes without the mold and no clear areas were present. The bacteria had not died in these. Fleming thought that the mold must be producing a chemical that killed the bacteria. He decided to isolate this substance and test it to see if it would kill bacteria. Fleming transferred the mold to a nutrient broth solution. This solution contained all the materials the mold needed to grow. After the mold grew, he removed it from the nutrient broth. Fleming then added the nutrient broth in which the mold had grown to a culture of bacteria. He observed that the bacteria died in the cultures he added the mold nutrient broth to. Bart Simpson Grows Vegetables Bart Simpson loves to grow broccoli for his dad, Homer, who loves big, colorful broccoli. He found a new brand of seeds coated with a special “booster” fertilizer that said it would produce huge vegetables. He went and talked to Apu, who is a great gardener, and asked him if he thought fertilizer could caused vegetables to grow bigger. Apu said he thinks so. So Bart planted 5 of the new seeds in one container and 5 of the old brand of seeds in another container. He placed both containers on a sunny windowsill and watered them every day. He measured the diameter of each plant, which is shown in the chart. Old Seeds 10 cm 12 cm 14 cm 6 cm 8 cm New Seeds 8 cm 14 cm 10 cm 12 cm 16 cm Ave= 10cm Ave= 12cm SpongeBob and Patrick Go Deep Sea Diving SpongeBob and Patrick love to go deep sea diving. They wondered if a new brand of diving suit would help them dive deeper. They wondered why and checked online. They found that they new suit has a new type of material that is supposed to help with going deeper faster and it has more weight. They definitely thought this new suit would be better. To test their idea, they bought one new suit and used one old suit for their next 3 trips to their top-secret diving spot. SpongeBob dived with the old suit, while Patrick used the new suit. Both of them kept track of how deep they were able to dive in 30 minutes, which is shown in the chart. Patrick SpongeBob 30 31 18 28 26 25 Ave=24.7 Ave=28 Mythbusters Get Green Thumbs The Mythbusters team uncovers the myth of if you talk to your plants they will grow better. They start by talking to a botanist (a person who studies plants) and the botanist says that they don’t really know, but they doubt it. Jamie and Adam put the myth to the test thinking that the extra talking will not help the plants grow more. They buy two ivies. Both plants will get the same amount of water and sunlight but they will each talk to only one plant for 5 minutes each day. They measure the height of each plant at the end of each week for one month. At the end of one month, the plant that did not get the extra talking was 2cm taller. Category Book Definitions: Book Definition Category Name An educated guess based on some information. Usually beginnings with how, when, why, where. State the Question Conducting an experiment Test /Observe To create a follow up or second test to help learn more about the question. Repeat Graphs, tables, data and charts that describe the findings in an experiment Results Getting some information about a problem. Information may be from experts, online, or other resources. Gather Information An educated guess. Usually based on some information. Form a Hypothesis Based on analyzing the results you should be able to describe whether to accept or reject the hypothesis. Conclusion