Types of City/Local Government
advertisement

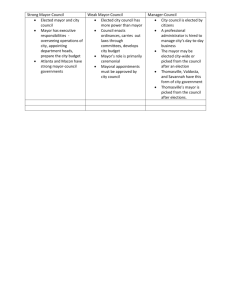
Name:______________________________ Date: ________ Government Unit #7 State & Local Government MUNICIPAL GOVERNMENT IN TEXAS There are four general forms of city government that home-rule cities may adopt: weak mayor-council, strong mayor-council, council-manager, and city commission. Most have chosen the council-manager form of government. The weak mayor-council form of government provides for the mayor to be elected at large by the voters of the city or be chosen by the city council from among its members. Council members are either elected at large or by wards (districts), or sometimes a combination of the two. The mayor’s job is largely symbolic: to preside over city council meetings, and perform ceremonial functions (ribbon-cutting ceremonies, greeting dignitaries, etc.). The mayor is equal in power to other city council members. The council as a whole hires and fires city staff and manages the city. There are also large numbers of elected officials and boards. This form of government is used in fewer than 40 Texas home-rule cities. The strong mayor-council form of government has a mayor elected citywide. The mayor is given executive authority over city government. He or she presides at city council meetings, may hire and fire department heads and other city officials, and only a few officials are elected. He also prepares the budget for the council’s consideration and may veto council actions. He is assisted by a chief administrator, who is appointed by and may be removed by the mayor, and an elected controller, who assists with the budget. Council members may be elected at large or by wards. Only the cities of Houston and Pasadena use this form of government in Texas. The most popular form of city government in use by Texas home-rule cities is the council-manager form. Over 250 home-rule cities have adopted this method of government. Council members are either elected at large, at large by place, or by wards. The selection of mayor varies: in some cities the mayor is chosen from among the council members; in others, the mayor is selected in a city-wide vote, thus giving him a bit more power and influence in council meetings. The council sets policy, but hires a professional manager to run the day-to-day city operations. Managers are paid well for performing their job, in excess of $150,000. The job is high stress and managers serve at the pleasure of the council, often bearing the brunt of criticism for failed policies set by the council. A form of city government pioneered in Texas but no longer in use in the state is the city commission form. This form originated in Galveston following a hurricane that killed 8,000 to 10,000 people and destroyed the city. The legislature allowed the city to give authority to specific commissioners, each in charge of a particular policy area, such as public health, public safety, public improvements, social services, public utilities, and economic development. The commissioners meet as a group to adopt budgets, set tax rates, and perform other community functions, but each individual member has authority over a specific function. This type of city government has fallen out of favor in Texas because of lack of coordination among officials and potential for corruption. CREATING ORGANIZATIONAL CHARTS FOR FORMS OF CITY GOVERNMENT Create an organizational chart for each of the three forms of city government currently in use by Texas home-rule cities, carefully following directions for what to include in each chart. Refer to the organizational chart for a general-law city for an example of such a chart. WEAK MAYOR-COUNCIL GOVERNMENT: Your chart should begin with the voters at the top and then indicate the offices of mayor and council. For this chart, assume that the mayor is chosen from among the members of the city council rather than being chosen by the voters. Then, indicate the relationship between the council and these appointed officials: city secretary, police chief, city attorney, fire chief, municipal judge, utility director, water/wastewater director, and economic director development director. STRONG MAYOR-COUNCIL GOVERNMENT: Your chart should begin with the voters and then indicate the offices of mayor, council, and city controller. Then, indicate the relationship of the mayor to appointed officials in charge of these areas: engineering services, transportation, economic development, fire, police, health and human services, parks and recreation, and public works and utilities. COUNCIL-MANAGER GOVERNMENT: Your chart should begin with the voters and then indicate the offices of mayor and city council, assuming that the mayor and the council are elected at large. Then, indicate the relationship between the council and the city manager, and the manager and officials in charge of these areas: public works and utilities, economic development, fire, police, health and human services, transportation, engineering services, and parks and recreation.