County and City Government in Georgia
advertisement

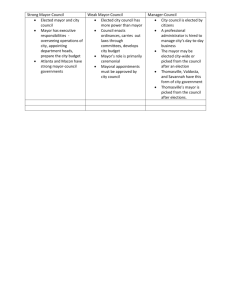
County and City Government in Georgia March 17, 2014 Local Governments Local governments are the most numerous in the U.S. Georgia’s local governments get their powers from the Georgia constitution Georgia has 159 counties and each county has a government In addition to the counties, there almost 600 cities in Georgia, each with their own government These governments are important because they are closest to the people and most likely to affect us directly County Government Counties are subdivisions of the state The state constitution sets out the powers of the county government These include the power to tax to cover the cost of police systems, road maintenance, public health, and parks and libraries The constitution requires that all county governments be organized the same way Most county governments are headed by boards of commissioners County Boards of Commissioners A board of commissioners is elected in each county to serve 4-year, staggered terms They have the authority to establish county policies, adopt county ordinances (laws), establish a budget and tax rates, and provide services to the citizens of a county A county administrator, appointed by the board, serves as chief administrative officer County Officials Each county has a different number of officials, depending on its population Each county has at least these elected officials: commissioners, superior court clerk, probate court judge, tax commissioner, sheriff, and coroner Other county officials are appointed, rather than elected. Appointed county officials include clerks, attorneys, fire chiefs, roads supervisors, and surveyors To become a city… A city with its own government is called a municipality A city becomes a political unit when it receives a charter from the state legislature A charter is a document that outlines the conditions under which a city is organized and defines its rights and privileges To be chartered, a city must meet these 3 requirements: It must have at least 200 residents It must be located at least 3 miles from the boundaries of the nearest city It must have 60% of its land divided into tracts or being used for homes, business, industry, or government purposes City Government A city government can only do what its charter authorizes it to do Most city charters allow cities to provide police protection, license businesses, maintain streets and sidewalks, control traffic, and provide water and sewage services Other services may only be provided if they are in the city charter Forms of City Government There are 3 most common forms of city government Mayor-council Form Council-manager Form Commission Form Mayor-Council Form The elected city council is responsible for making laws An elected mayor is the city’s chief executive officer The mayor also makes sure laws are carried out and city agencies do their jobs There are 2 types of mayor-council government: strong mayor and weak mayor Strong-Mayor System In this system, the mayor is a strong leader who proposes legislation, prepares the budget, appoints department heads, and has veto power The cities of Atlanta and Stockbridge are examples of strong-mayor cities Weak-Mayor System In this system, the city council has legislative and executive powers The mayor has limited powers, appoints a few city officials, and has little veto power The mayor is basically a figurehead (a person who is the head of an organization but has no powers) The mayor usually only presides over council meetings and performs ceremonial duties Council-Manager Form The voters elect a city council that establishes laws and policies There is a mayor who is either elected or appointed by the council The council hires a city manager who is responsible for the day-to-day management of the city Savannah has a council-manager form of government Commission Form The voters elect the commissioners Each commissioner is the head of a department within the city government, such as finance, streets, public safety, etc. The mayor is elected by the commissioners from among themselves Decatur has a commission form of government Special-Purpose Governments There are a number of special-purpose districts in Georgia These are created for a single job or group of tasks Most of these govern themselves An example of a special-purpose government is a school system While the state requires children to go to school, the control of each system is left up to the school board office The system establishes rules, dress codes, schedules, etc. Other Special-Purpose Districts MARTA is another special-purpose district The Public Housing Authority is another They run the system, set the cost of fares, set the routes, and schedule times They determine location of public housing, construct and maintain the buildings, rent the housing, and determine rules and regulations Community fire departments, airports, and the port authorities are other examples Consolidated Government Some counties provide services outside of cities, such as water, sewage, sanitation, and fire protection. As cities and counties grow, these can overlap To avoid duplication, a city and county government can consolidate (merge) into a single government Questions: 1) Where do Georgia’s local governments get their power? 2) How many counties does Georgia have? 3) Why are local governments important? 4) What is a county? 5) What types of powers do county governments have? 6) Who heads most county governments? 7) How long is a term of a member of a board of commissioners? 8) What authorities do county boards of commissioners have? 9) Who serves as the chief administrative officer of a board of commissioners? 10) How is the number of county officials determined in each county? 11) Which county officials are elected? 12) Which county officials are appointed? 13) What is a municipality? 14) How does a city become a political unit? 15) What is a charter? 16) What 3 requirements are necessary for a city to be chartered? 17) What powers are granted to a city by its charter? 18) What are the 3 common forms of city government? Questions… 19) Who makes laws in the mayor-council form? 20) Who is the chief executive officer in the mayor-council form? 21) What are the duties of the mayor in them mayor-council form? 22) What are the 2 types of mayor-council form? 23) What does the mayor do in the strong-mayor system? 24) Who has legislative and executive powers in the weakmayor system? 25) Describe the role of the mayor in the weak-mayor system? 26) What does the city council do in the council-manager form? 27) What does the city manager do in the council-manager form? 28) What do commissioners do in the commission form? 29) How is the mayor chosen in the commission form? 30) Why are special-purpose governments created? 31) Who governs specialpurpose governments? 32) List 3 examples of specialpurpose governments, and what they do 33) What is a consolidated government? 34) Why are consolidated governments created?