Unit 1C Reading Guide - Ionia Public Schools
advertisement
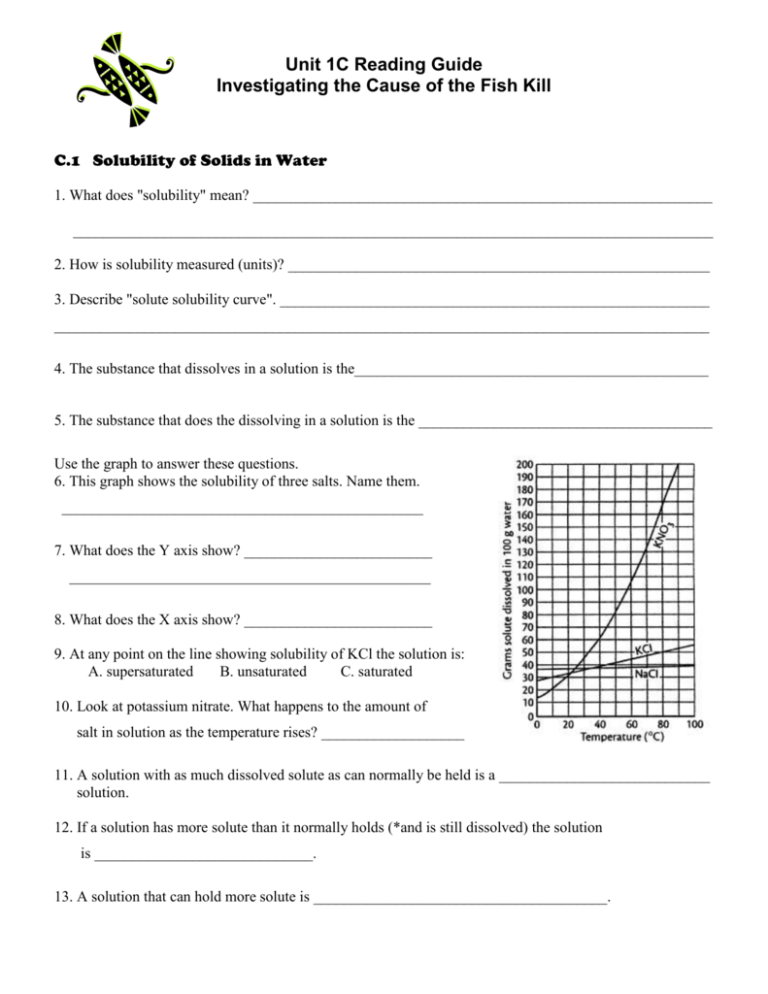
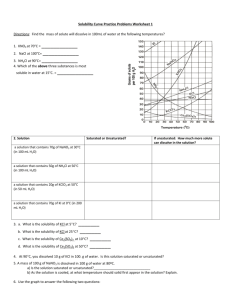
Unit 1C Reading Guide Investigating the Cause of the Fish Kill C.1 Solubility of Solids in Water 1. What does "solubility" mean? _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ 2. How is solubility measured (units)? ________________________________________________________ 3. Describe "solute solubility curve". _________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 4. The substance that dissolves in a solution is the_______________________________________________ 5. The substance that does the dissolving in a solution is the _______________________________________ Use the graph to answer these questions. 6. This graph shows the solubility of three salts. Name them. ________________________________________________ 7. What does the Y axis show? _________________________ ________________________________________________ 8. What does the X axis show? _________________________ 9. At any point on the line showing solubility of KCl the solution is: A. supersaturated B. unsaturated C. saturated 10. Look at potassium nitrate. What happens to the amount of salt in solution as the temperature rises? ___________________ 11. A solution with as much dissolved solute as can normally be held is a ____________________________ solution. 12. If a solution has more solute than it normally holds (*and is still dissolved) the solution is _____________________________. 13. A solution that can hold more solute is _______________________________________. C.2 Developing Skills: Solubility and Solubility Curves Hint: You must use the graph to answer the questions. Read carefully!! 1. (Hint: Read the graph) a. Mass KNO3 in grams = _______________ b. Mass KC1 = ______________ 2. (Hint: Where do you start? Read the graph! Show your work!) a. ________________________________________________________________________________ b. ___________ (Work space) 3. a __________________________________ (work space) b. ________________________________ (work space) C.3 Investigating Matter: Constructing a Solubility Curve 1. What is the formula for succinic acid? _________________________________ 2. What three questions should you think about before continuing with this lab? 1. __________________________________________________________________________ 2. ___________________________________________________________________________ 3. __________________________________________________________________________ 4. READ the safety precautions several times. Procedure 1. In this lab ________________________ will be the solute and _______________________ the solvent. 2. Think about this. A farmer puts a water soluble chemical on his field. What (in the natural environment will determine if it dissolves? What will determine if it becomes a saturated, unsaturated or supersaturated solution? 3. Why use a warm water bath? _____________________________________________________________ 4. Predict what will happen to the solubility of succinic acid as the temperature increases. ______________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ 5. What is the highest temperature a water bath will be heated to? ________________________________ 6. How much succinic acid will be placed into the test tube? _____________________________________ 7. How long are the liquids that have been decanted placed in the ice bath? __________________________ 8. What does "decant" mean? _______________________________________________________________ 9. What does the height of the crystals represent? _______________________________________________ C.4 Dissolving Ionic Compounds 1. Water is a polar molecule. What does this mean? _____________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 2. What is the shape of a water molecule? _____________________________________________________ 3. What is the total charge of a water molecule? _______ How is the charge distributed? Use the diagram at the right to help explain the charge distribution. ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ 4. Dissolving has been compared to a “tugging of molecules.” Explain. ____________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ Draw a sketch of polar water dissolving ionic NaCl. Explain your sketch. NaCl Na+ + Cl- _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ C.5 Modeling Matter: The Dissolving Process 1.a. What changes would you see in the beaker? ___________ __________________________________________________ b. 50C _________________________ 40C 25C __________________________ _________________________ S = saturated U = unsaturated P = supersaturated 2.a. 20 g KCl in 100 g H2O (40C) ¼ H2O evaporated ii. How much water must evaporated at 40C to create a saturated solution? 3. What does “diluted” mean? ___________________________________________________________ a. 10.0 g KCl / 100g H2O at 25C H2O + 100g H2O a. b. c. Compare key features of the models above _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ C.6 Solution Concentration 1. Define solution concentration- ___________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ 2. "Percent" means ______________________________________________________________________ 3. A solution of salt and water contains 15 grams of salt and 85 g of water. The solution is ________ % salt. 4. Another way to describe the solution in #3 is __________ parts per hundred. 5. Express the example above into parts per million. (*See Sample Problem page-63) 6. Write 0.0025% as parts per billion. ____________________ ppb C.7 Describing Solution Concentration (Show all work) 1. If a sterile solution requires 4.5 g NaCl and 495 g HbO how much solution is produced? _____________ g solution 2. What is the % NaCl of this solution? C.8 Inappropriate Heavy-Metal Ion concentration in River? 1. Compare heavy-metal ions with essential metal ions. __________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ 2. This section describes bioaccumulation/ biological magnification. What happens to organisms higher up in the food chain during this process? How/why? _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ 3. Why are heavy-metal ions harmful? _______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ 4. What is the best way to prevent heavy-metal poisoning? _______________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 5. How did the heavy metal "lead" get its symbol? ______________________________________________ 6. Identify some sources of lead (Pb 2+) in our environment. ______________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 7. Why was lead added to gasoline? __________________________________________________________ 8. What is unusual about metallic mercury (Hg2+) ? ____________________________________________ 9. Identify beneficial uses of mercury. ________________________________________________________ 10. What are symptoms of mercury poisoning? _________________________________________________ 11. Identify any sources of mercury along the Snake River that could be responsible for the fish kill. ________________________________________________________________________________ C. 9 Inappropriate pH Levels in River? 1. Define pH scale- _______________________________________________________________________ 2. Solutions with pH lower than 7 are ____________ Solutions with pH higher than 7 are ____________ 3. Another name for a basic solution is ______________________________ 4. When moving up or down the pH scale a change from one number to the next indicates a ____ difference. A solution with a pH of 2 is ________ times more acidic than a pH of 4 5. A basic solution turns litmus __________ and an acid solution turns litmus ___________ 6. Are acid and base solutions conductors? ____________________________ 7. Acids and bases are corrosive. Define corrosion (hint: look in the glossary!)-_______________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ 8. Acids release ___________________ in water. Bases release _________ ions in water. 9. Substances that display neither acidic or basic properties are ________________________ 10. At _____°C a pH of ________ indicates a neutral substance. 11. How is a low pH harmful to organisms living in a stream or lake ? _______________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 12. How is a high pH harmful to organisms living in a stream or lake ?______________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 13. According to the EPA, what must the pH range for drinking water be ? ________________________ 14. Identify the pH range that most fish can survive. ____________________________________________ 15. What is the normal pH of the Snake River ? ______________________________ C.10 Inappropriate Molecular-Substance Concentrations in River? 1. When ionic substances (like NaCl) dissolve in water they release __________. 2. Substances that dissolve in water but do not release ions, rather they release molecules are called ______________________ substances. Examples are _________________________________ 3. Oxygen and carbon dioxide are examples of molecular substances that could dissolve in water. They are gases at room temperature. Why are they gases at room temperature? ___________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ 4. Molecules that may be liquids at room temperature are _______________________________________ These substances have larger between molecule attraction which causes them to be __________________ than gas molecules. 5. Some substances like succinic acid are solids at normal temperatures. Why? ________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ 6. What determines how soluble a molecular substance will be in water? _____________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 7. What causes the attractions mentioned in #6? ________________________________________________ 8. Explain electronegativity as it relates to an atoms attraction of electrons. __________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 9. There is an old saying "likes dissolve likes", in chemical terms, explain it. _________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ C. 11 Laboratory Activity. Solvents Introduction 1. What is the purpose of this lab, and how will the data you produce during the lab help you in relation to the problem being investigated in Riverwood?_______________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ 2. Who will prepare the laboratory procedure for this lab?_________________________________________ 3. For the purpose of this lab, how will you determine if something is insoluble?_______________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 4. What solvents will you test in this lab?______________________________________________________ 5. What solvent will you use that is polar?_____________________________________________________ 6. What solvent will you use that is nonpolar?__________________________________________________ 7. How will you rate the solubility of the solutes?________________________________________________ C.12 Inappropriate Dissolved Oxygen Levels in River? 1. What is the solubility of oxygen gas in 10°C water? __________ mg O2 / 1000 g H2O 2. What is the solubility of oxygen gas in 30°C water? __________ mg O2 / 1000 g H2O 3. Consider temperature and compare the solubility of a gas with a solid._____________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 4. How does pressure affect gas solubility? ________________ _______________________ 5. What is the metric unit for pressure? _____________ Temperature (C) C.13 Temperature Dissolved Oxygen and Life 1. Explain what cold blooded means. _________________________________________________________ 2. Fish are cold-blooded. What happens to a fish on a warm summer day?____________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ 3. Why do we have fish kills in the summer? ___________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 4. There are at least 2 common human activities that are known to raise water temperature. Give 2 examples of these activities, and name the type of pollution they are classified as (hint: think back to environmental science!) ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ 5. Look at Figure 1.51 (page 77) Which fish have the highest dissolved oxygen demand in the winter? ___________ Which have the highest dissolved oxygen demand in the summer?____________________ 6. Diagram a sample of water from a river. Label the water molecules and the dissolved oxygen molecules. (* Hint: use models ) KEY Dissolved O2= Water = 7. Can fish die from too much oxygen in the water? Explain______________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ C.14 Making Decision: Determining the Cause of the Fish Kill Data Analysis • Be sure to read the directions carefully. • Review graphing procedures if you need to • Search for patterns in the data Quiz Unit 1C Reading Guide Investigating the Cause of the Fish Kill You may use your study guide to answer these questions. No photo copies may be used. _____ 1. The substance that dissolves in a solution is the ___ A. saturated B. solute C. solvent _____ 2. What is the formula for succinic acid? (Write the formula on the answer blank) _____ 3. What is a solution that can hold more dissolved solids. A. saturated B. unsaturated C. supersaturated _____ 4. A molecule with a total charge of 0, but with an uneven distribution of charge is A. saturated B. ionic C. dilute D. polar _____ 5. In the lab "Constructing a Solubility Curve" why was a warm water bath used? A. to purify the distilled water B. to cause the solids to precipitate C. to speed up the dissolving of the solids D. to supersaturate the solvent _____ 6. In the lab, you were asked to "decant”. What did this mean? A. measure the crystals carefully with a metric ruler B. tap the sides of the test tube C. pour the liquid carefully D. heat the solution _____ 7. Express a solution having 35 grams of NaCl per 100 grams of solution in terms of pph. _____ 8. What is an unusual property of mercury? A. it is a liquid at room temperature B. it has a very high boiling point C. it has a very low boiling point D. it is quick silver _____ 9. Which is NOT a source of lead poisoning? A. paint chips in older houses B. electrical storage batteries C. certain potteries and pesticides D. gasoline _____ 10. Another name for an alkaline solution is A. caustic B. toxic C. acid D. base _____ 11. A solution with a pH of 3 is a/an A. acid B. base C. neutral _____ 12. Hydroxide ions are released by ___ in water. A. polar substances B. neutral substances C. acids D. bases _____ 13. What damage can a low water pH cause to the living organisms in a river? A. damages skin and scales by dissolving them B. damages fish eggs C. raises water temperature D. cause increase carbon dioxide levels 14. Compare polar molecules with ionic compounds. Bonus 1. A word meaning decay or deteriorate is __________________________________ 2. The EPA suggests the pH for drinking water should be _______________________________ 3. What is the pH of the Snake River? _________________________________________________ 4. A solution is composed of 30 grams of NaCl and 170 mL of H2O. What is the solution concentration? Show your work!