Applied Science University
Faculty of Engineering
Civil Engineering Dept.
Course Syllabus
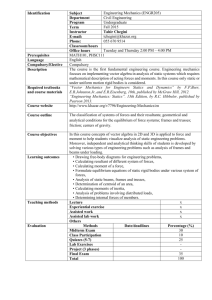
Course Title: Statics
Section: 1 and 3
Credit Hours: 3
Course No.: 805221
Prerequisite: Physics I (202101)
Year (semester): 2010-2011 (1)
Lec./Lab. Credit: Lecture: 3 Lab.: 0
Lecturer: Dr. Ahmed Ashteyat
Room No.: 111
E-mail: aashteyat@asu.edu.jo
Office Hours:
12 – 1:00 , Tue and Thur
11:00 – 12:30 Mon and Wed
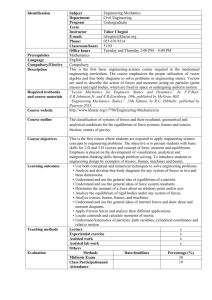
Course Objectives: Statics is an
introductory course that introduces the
student to the engineering mechanics
concepts; force systems;
static
equilibrium; centroid and center of
gravity calculations; shear and moment
concepts; and moments of inertia.
Course Description: The subject of
Statics deals with forces acting on rigid
bodies at rest covering coplanar and
non-coplanar forces, concurrent and
non-concurrent forces, friction forces,
centroid and moments of inertia.
Much time will be spent finding
resultant forces for a variety of force
systems, as well as analyzing forces
acting on bodies to find the reacting
forces supporting those bodies.
Students will develop critical thinking
skills
necessary
to
formulate
appropriate approaches to problem
solutions.
Intended Learning Outcomes:
Successful completion of this course
should lead to the following learning
outcomes:
A- Knowledge and Understanding:
1) Understand the basic concepts of
static analysis. 2) Demonstrate the
ability
to
calculate
force
resultants/components in 2D or 3D
space. 3) Understand and apply the
knowledge of Cartesian vector
manipulations in solving problems. 4)
Demonstrate an understanding of the
principle of moments caused by a force
acting on a rigid body. 5) Understand
the principle of transmissibility and
demonstrate the use of the principle of
transmissibility to solve for reaction or
for forces causing stress in members of
a truss. 6) Understand the Varignon's
Theorem and demonstrate the use of
the theorem to solve for the location of
the resultant forces and to locate the
centriod of an area. 7) Calculate the
reaction forces at the support of a rigid
body at rest. 8) Display ability to
determine the force in members of a
truss using the method of joints and the
method of sections. 9) Understand how
to locate the centriod and the center of
gravity of a rigid body at rest. 10)
Demonstrate
proficiency
in
determination of moment of inertia or
radius of gyration of a composite
area.11) understand how to calculate
internal forces in a structure and
acquire basic knowledge of shear force
and bending moment diagrams.
B- Intellectual Skills:
1) Distinguish between finding the
resultant of a system of forces and
decomposing a force into a system of
components.
2)
Compare
the
difference between a moment of a
single force and a couple. 3)
Distinguish between bodies at rest and
bodies in equilibrium. 4) Compare
reactions and resultant forces. 5)
Compare the applicability of the
method of joints and the method of
section to a certain required solution.
6) Distinguish between pin joint
frames (trusses) and other kinds of
frames/machines.
C- Subject Specific Skills:
1) Implement the basic knowledge of
vector mechanics into solving linear
static problems. 2) Implement the
principle of equilibrium to solve for
internal forces in a structure.
D- Transferable skills:
1) Homeworks. 2) Quizzes and class
drills. 3) Assignments.
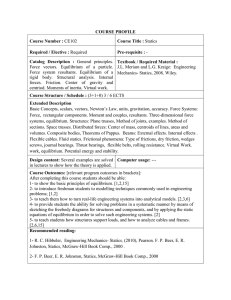
Course Content
Week
Topics
Hws
1
Introduction
Basic Concepts of
Mechanics
Units
2
HW1
Statics of Particles
Basic Vector
Manipulations
Resultants/Components
2D
Cartesian Coordinates
2D
3
Cartersian Vectors 3D
Position Vectors
4
Dot (Inner) Product
HW2
Equilibrium of a
Particle
Free Body Diagram
Coplanar Force System
5
3D Force System
HW3
Moment of a Force 2D
1st
6
Cross Product
Moment of a Force 3D Exam
7
Moment of a Force
HW4
about a Specified Axis
Moment of a Couple
Equivalent Systems
8
Equivalent Systems
HW5
cont.
Distributed Loads
9
Equilibrium of Rigid
Bodies
10
Equilibrium of Rigid HW6
Bodies cont.
Structural Analysis
Trusses/ Method of
Joints
Trusses/ Method of
Sections
11
Trusses/ Method of
HW7
Sections cont.
Zero Force Members
Frames and Machines
2nd
12
Internal Forces
13
14
15
16
Shear Force and
Bending Moment
Diagrams
Bending Moment
Diagrams cont.
Centriod Calculations
Moment of Inertia
Moment of Inertia
cont.
Final Exams
Exam
HW8
HW9
Final
Exam
Course Quality Improvement
1) Introduce the students to basic
software packages.
2) Account for student feedback
(evaluation).
Grading Distribution
First Exam
20%
Second Exam
20%
Assignments, Quizzes, and
10%
Attendance
Final Exam
50%
* Make-up Exams will be offered for
valid reasons only. It may be different
from regular exams in content and
format.
Reading List
Textbook (required)
Engineering Mechanics-Statics by R.
C. Hibbeler, Pearson Prentice Hall,
11th edition, 2006.
References
Vector Mechanics for Engineers:
Statics by F. Beer, E. Johnston, E.
Eisenberg, and D. Mazurek, McGrawHill, 8th Edition, 2006.
Engineering Mechanics - Statics by J.
L. Meriam and L. Kraige, Wiley, 6th
Edition, 2006.
Exam Schedule:
First Exam: 25/11/2010
Second Exam 30/12/2010
Final Exam:
2-3:30
2-3:30