23 questions
advertisement

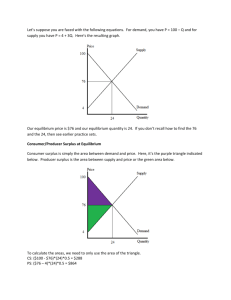
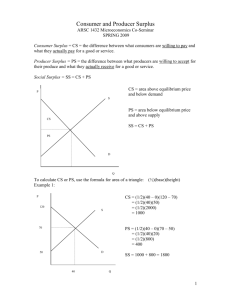
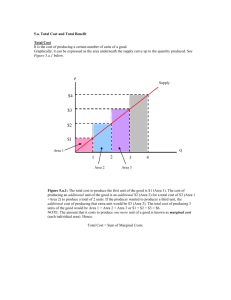
ECON 201: Introduction to Macroeconomics Midterm Exam 1: Answer Packet October 18, 2010 NAME: _________________________________ Circle your TA’s name: Brian Circle your section time: Meysam 9 a.m. Travis Yaron 4 p.m. Directions: This test is in two parts, a multiple choice question part and a short-answer part. Use this answer packet to complete the exam. Calculators are permitted. Books, notes, reference materials, etc. are prohibited. Good luck! Part 1: Referring to the questions in the Multiple Choice Questions Packet, choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Each question is worth one point. There is no penalty to guessing, so be sure to answer all of them. Write your answers in the following table using capital letters. 1 6 11 16 21 26 2 7 12 17 22 27 3 8 13 18 23 28 4 9 14 19 24 29 5 10 15 20 25 30 Part 2: Solve the following four problems in the spaces provided. Show all your work! PROBLEM 1: 10 points: 1 point per blank Use the following graphs to fill in the blanks for the following questions. 1. Assume the USA produces 200 bushels of corn. Of all the quantities of cars it could produce, which quantity is efficient? __________. 160 2. For the USA, what is the opportunity cost of corn in terms of cars? __________. For Japan, what is the opportunity cost of corn in terms of cars? __________. Who has the comparative advantage in the production of cars? _______________ 0.4, 2/3, Japan 3. Assume the USA is producing 100 bushels of corn and 200 cars, and Japan is producing 120 bushels of corn and 220 cars. If the USA gives 50 bushels to Japan in exchange for 25 cars, how many bushels of corn will it have? __________. How many cars? __________. Would both countries agree to this trade? __________. 50, 225, Yes 4. Now assume the USA is producing 475 bushels of corn and 50 cars, and Japan is producing 300 bushels of corn and 100 cars. If the USA gives 30 bushels to Japan in exchange for 10 cars, how many bushels of corn will it have? __________. How many cars? __________. Would both countries agree to this trade? __________. 445, 60, No PROBLEM 2: 2 points: 1 points per blank Assume that demand and supply are linear. Use the following table to determine the demand and supply equations. Price 10 50 Quantity Demanded 150 145 Quantity Supplied 0 100 1. The demand equation is P = ______________________________. P = 1210 - 8Qd 2. The supply equation is P = ______________________________. P = 0.4Qs + 10 PROBLEM 3: 4 points: 1 point per blank. Assume that demand is given by P = 43 – 4Qd Assume that supply is given by P = 0.5Qs + 7 Complete the following statement. 1. The free-market competitive equilibrium is at a quantity of __________, and a price of __________. In this situation, consumer surplus is __________ and producer surplus is __________. 8, 11, 128, 16 PROBLEM 4: 14 points: 1 point per blank Assume that demand is given by P = 100 – 2Qd Assume that supply is given by P = 10 + 4Qs Given these equations, the free-market competitive equilibrium is at P = 70 and Q = 15. Consumer surplus is 225, producer surplus is 450, and total economic surplus is 675. Complete the following statements. 1. Suppose that the government wants to limit quantity bought and sold to 10 using a price floor. To do so, the government should set the price floor at a price of __________. In this situation, consumer surplus is __________, producer surplus is __________, and deadweight loss is __________. 80, 100, 500, 75 2. Suppose now that the government wants to impose a per-unit tax of 48. Then the quantity bought and sold will be __________. Total tax revenues will be _________ and producer surplus will be __________. Deadweight loss will be __________. Producers will pay __________ of the tax out of $48. Hint: Compare your Ps with the original equilibrium price provided to you at the beginning of this problem. 7, 336, 98, 192, 32 3. Suppose now that the government wants to provide a per-unit subsidy such that quantity bought and sold will be 20. To achieve this, the per-unit subsidy amount must be __________. Under this subsidy, consumer surplus increases by _________, producer surplus increases by __________, and total government cost for providing subsidy is __________. Therefore, the deadweight loss is _________. Hint: You are being asked to calculate the change in consumer surplus and producer surplus, from the starting case of a free-market competitive equilibrium, where CS = 225 and PS = 450. 30, 175, 350, 600, 75 ECON 201: Introduction to Macroeconomics Midterm 1: Multiple Choice Questions Packet October 18, 2010 NAME: _________________________________ Circle your TA’s name: Circle your section time: Brian Meysam 9 a.m. Travis Yaron 4 p.m. 1) Elvira decreased her consumption of bananas when the price of peanut butter increased. For Elvira, peanut butter and bananas are A) substitutes in consumption. B) both inferior goods. C) complements in consumption. D) both luxury goods. 2) A subsidy has a DWL because A) prices are controlled B) government spending is insufficient to cover the loss of CS and PS C) government spending is greater than the gain of CS and PS D) a price ceiling is imposed as a part of the subsidy E) B) and D) 3) It is necessary for all economic systems to provide people with goods and services and also restrict them from getting as much of these goods and services as they wish, because failure to do this could ________ the efficiency of the system by producing some goods and services that are ________. A) reduce; not as highly valued as others B) increase; not as highly valued as others C) reduce; valued more than others D) increase; valued more than others 4) If, in a competitive market, marginal benefit is less than marginal cost, A) the net benefit to consumers from participating in the market is less than the net benefit to producers. B) the government must force producers to raise prices in order to achieve economic efficiency. C) the quantity sold is greater than the equilibrium quantity. D) the quantity sold is less than the equilibrium quantity. 5) The government proposes a tax on halogen light bulbs. Sellers will bear the entire burden of the tax if the A) supply curve of halogen bulbs is horizontal. B) demand curve for halogen bulbs is vertical. C) demand curve for halogen bulbs is horizontal. D) demand curve is downward sloping and the supply curve is upward sloping. 6) The type of market failure which is not caused by government is A) externalities B) price ceilings C) quotas D) subsidies E) C) and D) 7) Assume that both the demand curve and the supply curve for MP3 players shift to the right but the demand curve shifts more than the supply curve. As a result A) both the equilibrium price and quantity of MP3 players will increase. B) the equilibrium price of MP3 players will increase; the equilibrium quantity may increase or decrease. C) the equilibrium price of MP3 players may increase or decrease; the equilibrium quantity will increase. D) the equilibrium price of MP3 players will decrease; the equilibrium quantity may increase or decrease. 8) Voluntary exchange between buyers and sellers generates ________ in a market economy. A) scarcity B) allocative efficiency C) productive efficiency D) equity E) liberty 9) When a recession strikes, which of the following does not increase? A) applicants to business school B) employment of lawyers C) unemployment rate D) applicants to law school E) A) and D) Lawns Mowed Gardens Cultivated George 10 Jack 6 5 4 10) Refer to the table above. Which of the following statements is true? A) Jack has a comparative advantage in both tasks. B) George has a comparative advantage in both tasks. C) Jack has a comparative advantage in lawn mowing and George in garden cultivating. D) Jack has a comparative advantage in garden cultivating and George in lawn mowing. 11) The ________ effect of a price change refers to the impact of a change in the price of a good on a consumer's purchasing power. A) income B) substitution C) demographics D) ceteris paribus 12) Economists reason that the optimal decision is to continue any activity up to the point where the A) marginal benefit is zero. B) marginal benefit is greater than the marginal cost. C) marginal cost is zero. D) marginal benefit equals the marginal cost. 13) The lecture chalkboard diagram showing the loss of consumer surplus and the deadweight loss for a monopoly industry is most similar to the textbook diagram for A) price ceilings B) price floors C) taxes D) quotas E) subsidies 14) ________ is defined as a market outcome in which the marginal benefit to consumers of the last unit produced is equal to the marginal cost of production, and in which the sum of consumer surplus and producer surplus is at a maximum. A) Economic efficiency B) Consumer efficiency C) Producer efficiency D) Deadweight efficiency 15) A student comments to his roommate that the only way he will be able to pass his final exams is to not sleep for the next three days. This statement suggests that A) students are more concerned about good grades than good health. B) society should value sleep more highly than good grades. C) there is a trade-off between studying and sleep. D) society should value good grades more highly than sleep because students can catch up on their sleep once final exams are over. 16) When the PPF is ___________, the OC line drawn on the classroom chalkboard is ______________. A) a straight line; downward sloping B) a curved line; horizontal C) a curved line; upward sloping D) a curved line; downward sloping E) A) and C) 17) Which of the following is motivated by an equity concern? A) Some U.S. colleges have cut back on merit scholarships since these programs siphon money from need-based programs, thus harming lower-income students with greater financial need. B) Following the removal of subsidies in urban water use, household demand for water decreased quite significantly in Bogor, Indonesia. C) In November 2003, the Federal Communications Commission implemented the "local number portability" rule which gives cell phone customers the option of keeping their number when they switch carriers within the same geographic region. D) The United States protects intellectual property rights, allowing inventors to prevent others from using their inventions without payment. 18) Refer to the above graph. Suppose the market is initially in equilibrium at price P0 and now the government imposes a tax on every unit sold. Which of the following statements best describes the impact of the tax? For demand curve D0 A) the producer bears a greater share of the tax burden if the supply curve is S1. B) the producer bears a greater share of the tax burden if the supply curve is S0. C) the producer's share of the tax burden is the same whether the supply curve is S0 or S1. D) the producer bears the entire burden of the tax if the supply curve is S0 and the consumer bears the entire burden of the tax if the supply curve is S1. 19) If an increase in income leads to a decrease in the demand for popcorn, then popcorn is A) a Veblen good B) a neutral good. C) a necessity. D) a normal good. E) an inferior good. 20) An example of a factor of production is A) a car produced by an auto manufacturer. B) a worker hired by an auto manufacturer. C) a loan granted to an auto manufacturer. D) the automobiles exported by an auto manufacturer. 21) The course packet reading on the NYC taxicab industry illustrates which of the following? A) price ceilings B) price floors C) quotas D) taxes E) A) and C) 22) The traditional objection to raising the minimum wage is that A. It causes inflation B. It causes unemployment of high-skilled workers C. It causes unemployment of low-skilled workers D. It is ineffective 23) If the price of pork rinds falls, the substitution effect due to the price change will cause A) an increase in the demand for pork rinds. B) an increase in the demand for corn chips, a substitute for pork rinds. C) an increase in the quantity of pork rinds demanded. D) a decrease in the quantity of pork rinds demanded. 24) Deadweight loss refers to A) the opportunity cost to firms from producing the equilibrium quantity in a competitive market. B) the total sunk costs incurred by market participants. C) the loss of economic surplus when the marginal benefit equals the marginal cost of the last unit produced. D) the reduction in economic surplus resulting from not being in competitive equilibrium. 25) Individuals who have never been the best at doing anything A) cannot have a comparative advantage in producing any product. B) can still have a comparative advantage in producing some product. C) perform all tasks at a higher opportunity cost than others. D) must have an absolute advantage in at least ones task. 26) Cassie's Quilts alters, reconstructs and restores heirloom quilts. Cassie has just spent $800 purchasing, cleaning and reconstructing an antique quilt which she expects to sell for $1,500 once she is finished. After having spent $800, Cassie discovers that she would need some special period fabric that would cost her $200 in material and time in order to complete the task. Alternatively, she can sell the quilt "as is" now for $900. What should she do? A) She should cut her losses and sell the quilt now. B) It does not matter what she does; she is going to take a loss on her project. C) She should purchase the period fabric, complete the task and then sell the quilt. D) She should not do anymore work on the quilt because she has already spent too much time on it and has not been paid for that time. 27) According to the course packet reading “Dead End”, which was not one of the components of the Communist system? A) command economy B) control of information C) efficiency D) authoritarian bureaucrats E) hunger for vengeance 28) Each point on a demand curve shows A) the willingness of consumers to purchase a product at different prices. B) the consumer surplus received from purchasing a given quantity of a product. C) the economic surplus received from purchasing a given quantity of a product. D) the legally determined maximum price that sellers may charge for a given quantity of a product. 29) Adam Smith's ________ refers to the process by which individuals acting in their own self-interest bring about a market outcome that benefits society as a whole. A) Utopian society B) comparative advantage model C) invisible hand D) survival of the fittest theory E) pin factory 30) Which of the following would cause a decrease in the supply of milk? A) an increase in the price of cookies (assuming that milk and cookies are complements) B) a decrease in the price of milk C) an increase the price of a product that producers sell instead of milk, such as cheese D) an increase in the number of firms that produce milk