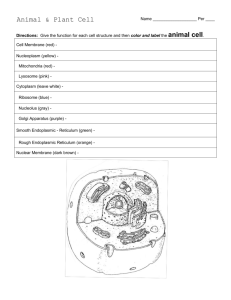
IB Biology Cells Test
1. The Golgi apparatus is found in:
A. plant and animal cells
B. only animal cells
C. animal and prokaryotic cells
D. only prokaryotic cells
2. One similarity between prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells is that they both have
A. mitochondria
B. DNA
C. A nucleus
D. Organelles
3. Which of the following processes is carried out by the chromosomes in animal cells
during prophase of mitosis?
A. Replication followed by condensation
B. Condensation (shortening) only
C. Condensation followed by crossing over
D. Condensation followed by attachment to spindle microtubules
4. What is the difference between the cell surface membrane and the nuclear
membrane?
A. The cell surface membrane is found only in plant cells
B. The cell surface membrane is found only in animal cells
C. The cell surface is a double membrane while the nuclear membrane is single
D. The cell surface is a single membrane while the nuclear membrane is double
5. What is needed for active transport of the cell?
A
B
C
D
Energy
Energy Needed
Energy Needed
Energy Not Needed
Energy Not Needed
Glucose Concentration
Higher Concentration Than Inside
Any Concentration
Higher Concentration Than Inside
Any Concentration
6. Plant and animal cells both have
A.ribosomes, cell walls and mitochondria.
A. Golgi apparatus, chromosomes and mitochondria.
B. Golgi apparatus, cell walls and ribosomes
C. Large vacuoles, cell membranes and mitochondria.
7. Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells all have
A. circular chromosomes.
B. An endoplasmic reticulum.
C. Membrane bound nuclei.
D. A cell membrane and ribosomes.
8. During mitosis
A. DNA transcription and replication occur.
B. Two genetically different nuclei are produces.
C. Replicated DNA molecules are moved to opposite ends of the cell.
D. Homologous chromosomes form pairs.
9. Which of the following cells structures does not have membranes?
A. Ribosomes
B. Mitochondria
C. Chloroplasts
D. Golgi apparatus
The following diagram represents a phospholipid molecule that is found in the lipid
bilayer of a cell membrane. It refers to questions 10 and 11.
10. Structure I is likely to be
A. hydrophilic.
B. An amino acid.
C. An unsaturated fatty acid.
D. A saturated fatty acid.
11. Structure II is
A. likely to be hydrophilic.
B. More charged than structureI.
C. Also a common component of RNA.
D. A hydrocarbon component.
12. Who first described cells?
A. Darwin
B. Golgi
C. Linnaeus
D. Hooke
E. Leeuwenhoek
13. Who first looked at tiny living cells and called them as “animalecules”?
A. Darwin
B. Golgi
C. Leeuwenhoek
D. Hooke
E. Linnaeus
14. Schleiden and Schwann stated the “cell theory,” which includes all the follwing
statements except
A. all organisms are composed of one or more cells.
B. All cells need oxygen
C. Cells are the smallest living things
D. Cells arise only by division of a previously existing cell
E. Cells vary in size and shape
15. Prokaryotic cell movement is attributed to the
A. capsule
B. ribosomes
C. pili
D. nucleoid area
E. flagella and cilia
16. Plant cells often have a large membrane-bound sac that is used for storing water and
other substances. This organelle is called
A. nucleus
B. chloroplast
C. Golgi body
D. centriole
E. central vacuole
17. Which of the following is not present in all eukaryotic cells?
A. endoplasmic reticulum
B. ribosome
C. plasma membrane
D. cell wall
E. Golgi bodies
18. Some ribosomes are embedded into
A. chromosomes
B. smooth endoplasmic reticulum
C. rough endoplasmic reticulum
D. histones
E. vacuoles
19. The eukaryotic organelle that is directly involved in the transport of proteins
synthesized on the surface of the rough ER is called
A. mitochondria
B. vacuole
C. cytoskeleton
D. golgi comples
E. nucleus
20. Lipid synthesis occurs in which eukaryotic organelle?
A. rough ER
B. smooth ER
C. lysosomes
D. mitochondria
E. nucleolus
21. Nucleolus of the nucleus is the site of
A. protein synthesis
B. ribosome assembly
C. chromosome replication
D. lipid synthesis
E. uncoiling and unraveling of chromosomes
22. Lysosomes are vesicles bounded by membranes that contain oxidative enzymes.
Their funtions include all of the following expect they
A. catalyze the rapid breakdown of macromolecules
B. break down old organelles
C. eliminate substances taken into the cell by phagocytosis
D. participate in the phenomenon of selective cell death
E. allow bacteria to pass through unaffected
23. Mitochondria and chloroplasts are the other organelles besides the nucleus that
contain
A. genes
B. pores
C. channels
D. plasms membranes
E. pigments
24. The endosymbiotic theory is supported by the finding of non-nuclear DNA in which
of the following organelles?
A. lysosomes
B. ER
C. Mitochondria
D. Chloroplasts
E. Both in C and D
25. Which of the following is not found in the cytoskeleton?
A. actin filaments
B. intermediate filaments
C. spindle fibers
D. microfilaments
E. none of the above
26. Bacteria are generally
A. 1 to 2 centimeters thick
B. 1 to 2 millimeters thick
C. 1 to 2 micrometers thick
D. 1 to 2 nanometers thick
E. 1 to 2 meters thick
27. On the outer surface of the plasma membrane there are marker molecules that identify
the cell-type. Often these molecules are
A. ATP
B. amino acids
C. nucleotides
D. carbohydrate chains
E. inorganic ions
28. The movement of substances to regions of lower concentration is called
A. active transport
B.
C.
D.
E.
diffusion
osmosis
pumping
exocytosis
29. If two solutions have unequal concentrations of a solute, the solution with the lower
concentration is called
A isotonic
B. hypertonic
C. hypotonic
D.hypnotic
E. osmosis
30. The process often thought of as “cell eating” is
A. osmosis
B. pinocytosis
C. phagocytosis
D. diffusion
E. active transport
31. Carrier-mediated transport is also called
A. facilitated diffusion
B. active transport
C. exocytosis
D. endocytosis
E. phagocytosis
32. Osmosis can only occur if water travels through the
A. cell wall
B. semi-permeable membrane
C. vacuole
D. ER
E. Cytoskeleton
33. In a single sodium-potassium pump cycle, ATP is used up with the result that
A. 3 sodium ions leave and 2 potassium ions enter
B. 1 sodium ions enters and 1 potassium ions leaves
C. 1 sodium ion leaves and 1 potassium ions enters
D. 3 sodium ions enter and 2 potassium ions leave
E. sodium and potassium ions enter and water leaves
34. Cholesterol functions in the plasma membrane to
A. transport ions
B. serve as an energy molecule
C. maintain fluidity
D. mediate steroid action
E. maintain hypertension
35. Communication between cells can occur by all of the following basic mechanisms
except
A. direct contact
B.
C.
D.
E.
signaling to digest plasma membrane
paracrine signaling
endocrine signaling
synaptic signaling
36. Which of the following sequence of cell-cycle phases is characteristic of eukaryotes?
A. G to S to M
B. G1 to S to G2 to M to C
C. S to M to C
D. G1 to G2 to S to C
E. G1 to G2 to G3 to S to C
37. The first stage of mitosis, when the chromosomes become shorter and thicker is
A. anaphase
B. interphase
C. metaphase
D. prophase
E. telophase
38. The chromosomes line up at the equator of the spindle during
A. anaphase
B. interphase
C. metaphase
D. prophase
E. telophase
39. The framework of microtubules that appears in cell division which eventually moves
the chromatids apart is called the
A. aster
B. cell plate
C. centriole
D. spindle apparatus
E. centromere
40. Microtubules become shorter, pulling chromatids to the ends of the spindle, during
A. anaphase
B. interphase
C. metaphase
D. prophase
E. telophase
41. Animals cells typically achieve cytokinesis by
A. binary fission
B. forming a cell plate across the middle of the cell
C. forming a cleavage furrow that pinches the cell into two
D. chromosome condensation
E. chromosome elongation
The diagram below represents the nucleus of a cell 2n=4 in late Prophase of mitosis. It
refers to question 6.
42. Which diagram represents a cell of the same species in Metaphase II of meiosis?
 0
0