Syllabus
advertisement

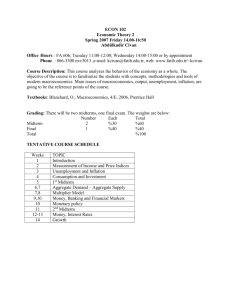
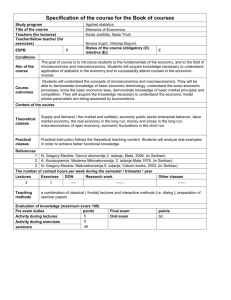
Course Outline (please complete as appropriate) Introduction to economy COURSE TITLE NAME OF LECTURER Urszula Mrzygłód COURSE DESCRIPTION This course is designed to introduce students to the principles of economics. The aim of the course is to familiarize students with the economical way of thinking which will allow students to understand main economic concepts, data and news that are published on daily basis. By completion of this course, students should have accomplished the following major objectives: 1) by attending the course should acquire the understanding of the major theories and concepts and relationships in the field of economics; 2) by doing in-class exercises students should gain understanding of economical ratios/ measures/ data and be able to recognize its meanings as well as be able to search for necessary data on their own from open sources; 3) by investigating data and exploring given examples should be able to assess whether the economy is in “good or bad shape”; 4) by discussing economical problems and solving given exercises and homework should achieve deeper understanding of current economical problems; Course concentrates on the problems of macroeconomics, the practical problems and issues that affect governments, central banks etc. and have impact on the markets (labour market, money market etc.). During classes the PPT presentations will be prepared and students will be encouraged to participate in discussion and share their point of view. During classes problems will be explained from the theoretical point of view, as well empirical data and research will be presented and discussed with students in order to achieve better understanding of the selected problems. RECOMMENDED READINGS Students will be given the prepared for each class PPT handouts. Students will be given several articles (open source) that will be discussed during course as well practical exercises with empirical data. TEACHING METHODS Lectures using PPT, group discussions, in-class exercises and cases, student presentations. ASSESSMENT METHODS Mid term exam (25%) - multiple choice test; Final exam (30%) - multiple choice test and several open questions Homework Assignments (25%): 1st assignment – individual exercise/ topic (written homework) (10%); 2nd assignment – small group assignment which will be presented during the course (15%); Class participation (20%). CLASS TOPICS (each class is 3 hrs) Class 1: Introduction to economics – basic concepts (macroeconomics scope and coverage; micro and macroeconomics relations; economic policy; main problems of macroeconomics; types of economic systems). Class 2: Circular flows in the economy and markets (circular flows; aggregate demand and supply; equilibrium; short history of macroeconomics thought; individuals, firms and government in an economy; types of markets). Class 3: Measures to assess the economy (data and information from different sources; national income fluctuations and its determinants; cyclical behavior of economic variables; structure of the economy). Class 4: Money and banking (history of money and banking; functions and types of money; credit creation; role of central banks in the economy; demand for money and money stock) *1st homework assignment. Class 5: Inflation and monetary policy (price measures; causes and effects of inflation; deflation, monetary policy types; Philips curve; yield curves) Class 6: Exchange rates and balance of payments (types of exchange rates; revaluation/devaluation; deficits and surpluses in balance of payments; determinants of the exchange rate). Class 7: Mid-term Exam Class 8: The government role in the economy, macroeconomic equilibrium again (government budget; taxes; public goods and externalities; deficits, debt consequences and future generations; Laffer curve; budget surpluses; macroeconomics equilibrium – short and long term; adverse economic shocks). Class 9: Labour market (employment and unemployment, Philips curve again; types of unemployment, supply and demand; causes of unemployment, theoretical perspectives, unions, labour market trends). Class 10: Financial markets (types; role in the economy and welfare; basic financial instruments, speculation). Class 11: Compare economies (“good or bad shape”) 2nd homework assignment. Class 12: Economic growth and development (income levels; income disparities; economic growth, cost of living; measures of economic development). Class 13: The global economy (processes of integration and globalization, trade, foreign direct investments and its the role in the economy). Class 14: Contemporary economic problems - economic crisis. Economic thought at the crossroads. Recapitulation. Class 15: Final Exam SPECIAL COMMENTS