Lesson - The Hereford Academy
advertisement
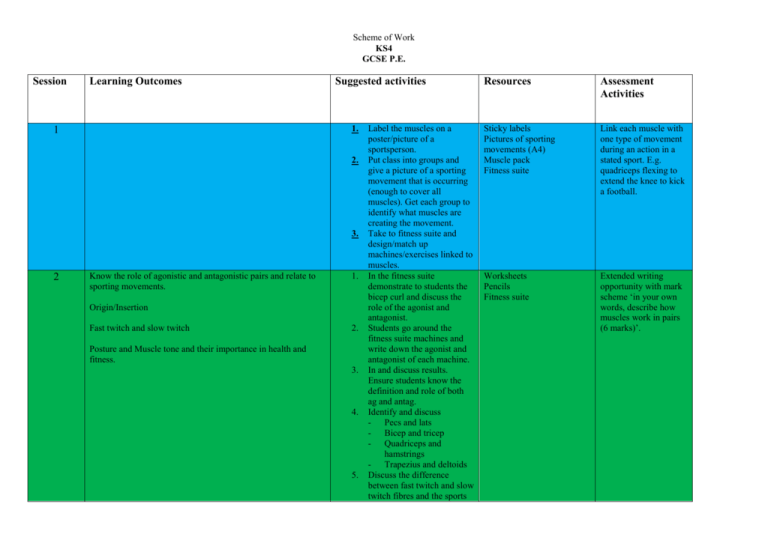
Scheme of Work KS4 GCSE P.E. Session Learning Outcomes Suggested activities 1. 1 2. 3. 2 Know the role of agonistic and antagonistic pairs and relate to sporting movements. 1. Origin/Insertion Fast twitch and slow twitch 2. Posture and Muscle tone and their importance in health and fitness. 3. 4. 5. Label the muscles on a poster/picture of a sportsperson. Put class into groups and give a picture of a sporting movement that is occurring (enough to cover all muscles). Get each group to identify what muscles are creating the movement. Take to fitness suite and design/match up machines/exercises linked to muscles. In the fitness suite demonstrate to students the bicep curl and discuss the role of the agonist and antagonist. Students go around the fitness suite machines and write down the agonist and antagonist of each machine. In and discuss results. Ensure students know the definition and role of both ag and antag. Identify and discuss - Pecs and lats - Bicep and tricep - Quadriceps and hamstrings - Trapezius and deltoids Discuss the difference between fast twitch and slow twitch fibres and the sports Resources Assessment Activities Sticky labels Pictures of sporting movements (A4) Muscle pack Fitness suite Link each muscle with one type of movement during an action in a stated sport. E.g. quadriceps flexing to extend the knee to kick a football. Worksheets Pencils Fitness suite Extended writing opportunity with mark scheme ‘in your own words, describe how muscles work in pairs (6 marks)’. Scheme of Work KS4 GCSE P.E. 6. 3 Isometric and isotonic contractions and sport example 1. 2. 3. 4. 4 Short term effects of exercise on the muscles Increased fuel/energy demands/lactic acid/muscle fatigue. 1. Long term effects of exercise 1. Increased strength and size/hypertrophy 2. 3. 5 Muscular Injuries Strains and atrophy – how caused, symptoms and treatments. 1. they are best suited to and why. Discuss the importance of muscle tone and posture in health and fitness. Students compete in a number of sporting movements and after identify the types of contractions that have occurred. Ensure know definition of contractions. Students take part in a vigorous activity session (interval sprints/circuit session) and write down how their body/muscles are feeling. Discussion of effects of exercise and why they happen (could be a card matching activity) Students given a picture of before and after photo of somebody who has increased muscle mass through training. Theory work on how muscular hypertrophy occurs and type of training that increases strength and muscle mass and why. Students could take part in a strength circuit and discuss feeling of their muscles as a starter point. Picture game/brainstorm ideas to identify types of muscular injuries. Worksheets Cones Tape measure Pencils Sports equipment Choose four sporting examples of each type of contraction, stating which muscle is contracting in each. Create exercise sessions for a training programme for improving strength and endurance Describe and explain the cause and treatment of the 3 types of injury Scheme of Work KS4 GCSE P.E. 2. 6 Training and performance 1. Rest - rest required for adaptation to take place, time for recovery before next exercise session 2. Diet - effects of protein in building and repairing muscles 3. performance enhancing drugs - use of steroids to aid muscle building and recovery. 1. 2. 3. 4. 7 1.2.5 Role of Skeletal System in Physical Activity Functions – movement/support/protection during physical activity 1. 2. 8 9 Joint movements - flexion, extension, rotation, abduction, adduction at :Hinge – knee and elbow Ball and Socket – shoulder Linked to sporting activities. 1. Long term effects of exercise 1. Increased bone density 2. Increased strength of tendons and ligaments 3. Importance of weight bearing exercise (walking/running/tennis/aerobics) to prevent osteoporosis. 1. 2. 2. 3. Students in groups given injury scenarios and experience treatment of injuries. Students design a strength training programme for an individual and justify their thoughts on reps/sets/times. Theory behind rest periods and overtraining. Importance of protein in diet. Students design an ideal days meal for a body builder. Intro to steroids – pros and cons. Students watch a number of video clips of a range of sporting activities and have to name the functions of the skeleton. Individually students give their own sport example of how these functions help improve performance. Introduction of the types of joints and types of movements. Students design and deliver a yoga/aerobic/warm up routine that incorporates all of them. Brainstorm what students think happens to bones and joints after prolonged exercise. Theory and advantages of the effects. Intro and experience of weight bearing exercise and highlight the advantages. associated with the muscular system. Discuss the different factors associated with maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and potential performance enhancing drugs athletes may come across. Scheme of Work KS4 GCSE P.E. 4. 10 Injuries and causes 1. Fractures (compound, greenstick, simple, stress) 2. Joint (tennis elbow, golfer’s elbow, dislocation, sprain, torn cartilage) 11 Treatment of injuries 1. Fractures (compound, greenstick, simple, stress) 2. Joint (tennis elbow, golfer’s elbow, dislocation, sprain, torn cartilage) 12 diet (effect of calcium and vitamin D on bones). Intro and visual of the dangers that osteoporosis will cause. 1. Students match injuries to pics on the board. 2. Video clip highlighting some of the injuries in action. 3. Brainstorm/group activity on highlighting the symptoms of different types of injuries. 4. Students to create scenarios where the different injuries occur. 1. Students take part in scenario based activity whereby they have attended an accident and have to treat them. Introduction of calcium and vitamin D. Students create individual poster highlighting the importance of them and what foods are high in those compounds.









