English 9
advertisement

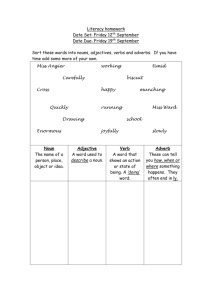
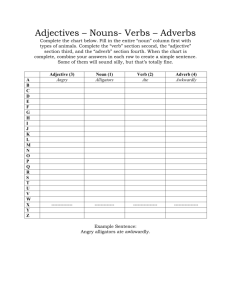
English 9 GT Final Exam Study Packet This packet is broken up into the major sections of English 9 this year: Grammar, Plot Structure, Night, Lord of the Flies, To Kill a Mockingbird, and “A Raisin in the Sun”. The packet will provide information and sample questions to test your knowledge. It may also direct you to handouts, assessments, etc. where you can find this and additional information to study from. Remember that the final will consist of but is not limited to the information in this packet. Grammar Nouns: a person, place, thing, or idea. Nouns can be concrete or abstract and serve different functions in a sentence: Subject Stacy passed John the ball under the net. Direct Object Stacy passed John the ball under the net. Indirect Object Stacy passed John the ball under the net. Object of the Preposition Stacy passed John the ball under the net. Predicate Nominative John is a classmate. Adjective: a word used to describe a noun or pronoun An adjective answers the question What kind? Which one? How many? or How much? about the nouns and pronouns they modify Examples: What kind? red house, silver jewelry, sick child, cool water Which one? third chance, any piece, this hat, those apples How many? six flowers, both answers, several reasons, few letters How much? enough space, no rain, more energy, little effort Adverb: a word that modifies a verb, an adjective, or another adverb An adverb modifying a verb answers the questions Where? When? In what manner? or To what extent? Examples: Where? fell below, move aside, went there, climbs down When? arrived today, left early, should have spoken before, begins then In what manner? happily ran, will end completely, danced awkwardly To what extent? partly understands, have not completed, wash completely An adverb modifying an adjective answers only one question: To what extent? Examples: very glad, almost ready, absolutely wrong, entirely grateful An adverb modifying another adverb answers just one question: To what extent? Examples: moved very quickly, not completely wrong, climbed almost over Phrase: a group of words, without a subject and verb, that works as a part of speech Prepositional Phrase: a phrase composed of a preposition1 and an object of the preposition (either a noun or pronoun) that works like an adjective or adverb Examples: by the lake, out of gas, with brown eyes Adjective Phrase: a prepositional phrase that modifies a noun or pronoun by telling what kind or which one Example: The man with a mask frightened the children. Adverb Phrase: a prepositional phrase that modifies a verb, adjective, or adverb by pointing out where, when, in what manner, or to what extent. Example: The team played with great skill Appositive Phrase: a noun or pronoun with modifiers, placed next to a noun or pronoun to add information and details. Examples: Shelly’s sister, a track star at UCLA, runs three miles daily. Two boys, friends of ours, gave us a ride. Participial Phrase: a participle (the –ing or –ed form of a verb that acts like an adjective) modified by an adverb or adverb phrase that acts as an adjective in the sentence. Examples: The boy wearing the blue sweater is my brother. Frightened by the cat, the bird flew away. Gerund Phrase: a gerund ( the –ing form of a verb that acts like a noun) with modifiers or a complement, all acting together as a noun in the sentence. Examples: The loud, irregular snoring annoyed him. Their parents forbade shouting in the house. Infinitive Phrase: an infinitive ( the “to” form of the verb that acts as a noun, adjective, or adverb) with modifiers, complements, or a subject, all acting together as a noun, adjective, or adverb in the sentence. Examples: Professional dancers need to practice daily. To stroll along the boardwalk at sunset is relaxing. Clause: a group of words with its own subject and verb Independent Clause: a clause that can stand by itself as a complete sentence Subordinate Clause: a clause that cannot stand by itself as a complete sentence; it can only be part of a sentence Adjective Clause2: a subordinate clause that begins with a relative pronoun or relative adverb that modifies a noun or pronoun by telling what kind or which one Example: We selected those who were best qualified for the job. Dave, who is six feet tall, is Elaine’s boyfriend San Diego is the city where we grew up. 1 : Refer to the Prepositions Handout for a list of commonly used prepositions : Refer to the Adjective Phrase vs. Adjective Clause handout for more examples and to test your knowledge 2 Adverb Clause3: a subordinate clause that begins with a subordinating conjunction that modifies verbs, adjectives, adverbs, or verbals by telling where, when, in what manner, to what extent, under what condition, or why. Example: He ran as if he had a twisted ankle Because the school bus broke down, Jess missed first period. I am three year older than she is. Noun Clause4: a subordinate clause that acts as a noun in the sentence. It may acts as a subject, direct object, indirect object, predicate nominative, or object of the preposition. Example: Whomever you bring will be welcome. The big questions is whether she will finish the marathon. Please give whoever calls this message. Grammar Check Identify the italicized item on the line to the right and draw an arrow to the word being modified Adverb vs. Adjective 1. I spoke too hastily. 2. Alice took the late bus back to Minneapolis. 3. Many of the guests stayed very late. Adjective Clause vs. Adjective Phrase 4. This is another book by the same author. 5. Have you thought of a place where we can meet? 6. Rob bought a car with power brakes. Adverb Clause vs. Adverb Phrase 7. Wherever he travels, he collects souvenirs. 8. The Cardinals played at Spartan Stadium. 9. He ran as if he had a twisted ankle. Phrase Identification: identify the following phrases by the examples to the right: 3 10. Appositive Phrase a. We admire their ability to succeed at difficult tasks. 11. Participial Phrase b. Running out of gas is a horrible experience. 12. Gerund Phrase c. The house on the corner of the street needs paint. 13. Infinitive Phrase d. Our house, shaded by trees, stays cool in the summer. 14. Prepositional Phrase e. Two boys, friends of ours, gave us a ride. : Refer to the Adverb Clauses handout for more examples, a list of subordinating conjunctions, and examples of modifying different parts of speech 4 : Refer to the Noun Clause definition sheet and exercises for introductory words and to discern between noun clauses and adj/adv clauses. Verb, Gerund, or Participle? In the section below, identify whether the underlined word in each sentence is a verb, gerund, or participle. 15. Someone has stolen a valuable painting from the museum. 16. My little brother loves frozen yogurt. 17. Carol, walking to school, saw an owl. 18. Dancing helps a person to lose weight. 19. Soaring high above the clouds, the jet is flying to Paris. Sentence Revision Follow the directions below to correctly combine or revise the following sentences. Rewrite the following sentences beginning with the given words: Boo Radley saved Jem and Scout when Bob Ewell attacked them. When Bob Ewell Jem learned an important lesson about courage from his experiences with Mrs. Dubose. From his Combine the following sentences to make one, solid complex statement Scout is a tomboy. She dresses in overalls. Scout is very aggressive. Boo Radley is thought to be a monster. There are many rumors about Boo Radley. Boo Radley is a timid, shy man. Identifying Clauses: Identify the clauses in the following sentences as either adjective, adverb, or noun clause. She remembered that she had no choice. The card that she received made her laugh. His sisters were happy that he was there. When it is sunny outside, I like to play soccer. I had a surprise party on my birthday when I turned thirteen. Our teachers loves to talk about when she was in high school. The Lord of the Flies The chapter review sheets on Lord of the Flies are a great resource for examples, terms, and sample constructed response questions. Refer to those sheets to review and re-test your knowledge on this novel by William Golding. Main Characters: Be sure you know who the following characters are and why they are important to the novel. Also make sure you can identify the relationships between all the characters and their story lines. Ralph Roger Samneric Piggy Maurice Henry Simon Percival Jack Johnny Symbols: Be sure you know what each symbol means in the novel and also how the symbol is introduced to the story: Conch Smoke Rocks Scar Specs The Dance Island Fire Masks The ‘Beast’ The “Lord of the Flies” Lord of the Flies Check True/False 1. Piggy is given his name by Jack because he doesn’t like Piggy and thinks that he is a “fatty”. 2. Piggy can’t help build shelters because his uncle always told him to be aware of physical labor on account of his “ass-mar”. 3. In the novel, Percival introduces the idea of a beast from the water that comes on land in the night. 4. The “beast from the air” floats away after the storm and never eats the children. 5. The officer is disgusted by the un-British behavior of the boys and only takes Ralph back with him. Character ID 6. Percival 7. Henry 8. Maurice 9. Roger 10. SamnEric 11. Johnny Symbols Fire Smoke Conch Scar Beast Island 12. represents hope, rescue 13. represents the evil in all humans 14. represents paradise, eden 15. represents intelligence, creativity, intuition 16. represents safety, protection 17. represents society, teamwork, social order 18. represents social taboos 19. represents freedom, anonyminity 20. represents imperfection 21. represents rituals, religion, deism a. enjoys “irresponsible authority” b. betrays Ralph at the end c. a bigun who raids the camp with Jack and Roger d. boy eaten by the beast e. enjoys controlling small life forms in the water f. cannot remember his phone # Masks Rocks Specs Dance To Kill a Mockingbird The chapter sheets for To Kill a Mockingbird are a great resource for examples, terms, and sample constructed response questions. Refer to those sheets and your chps 1-6 and 7-11 quizzes to review and re-test your knowledge on this novel by Harper Lee. Below are some terms, concepts, and themes that we discussed while reading this book.5 Main Characters: Make sure that you know who the main characters of this novel are and be able to describe them. We focused on character development while reading this novel, so it is very important to be able to map out each of these characters according to: Internal Character Characters: Scout Bob Ewell Boo Radley External Character Jem Mayella Ewell Miss Maudie Actions Atticus Heck Tate Calpurnia Background Tom Robinson Dill Mrs. Dubose Themes: You will be expected to be able to discuss the main themes from the novel. While there were many themes, there are two that we focused on the most: 5 : Refer to the chapter sheets, written and scantron exams, chapter quizzes, and any other material on TKM for additional study material Coming of Age: tracking the life lessons that were learned by Jem and Scout and how those lessons were tested during their troubling times in the second part of the novel. Be able to discuss the dynamics of these characters and how their immature ideas/understandings/actions were changed by the end from their experiences and life lessons. Mockingbird: With Scout’s final realization that making Boo a local hero would be like shooting a mockingbird, the theme of innocence and other mockingbird characters are brought to light. Be able to explain Scout’s realization and to present other potential “mockingbirds” who were preserved or sinned against. Characterization: Be prepared to provide explanations and descriptions of characterization, the creation process, and the different elements of a character in a writing prompt. To Kill a Mockingbird Check Character identification: Identify the following characters according to their descriptions Atticus Scout Jem Dill Bob Ewell Mayella Tom Mrs. Dubose Boo Radley Heck Tate 1. Character who is a 9 year old summer friend 2. Character who won a spelling bee 3. Character who decides Bob Ewell committed suicide 4. Character who saved “seb’m” nickels 5. Character who reads to the elderly 6. Character who doesn’t mind helping people for free 7. Character who dies completely free of burden 8. Character who is abusive when intoxicated 9. Character who tries anything to get out of school 10. Character who has poor eyesight Multiple Choice: Choose the correct answer to the questions below 11. The name of the prosecuting attorney is: 1. Gomer 2. Gilligan 3. Gilmer 4. Gopher 15. Bob Ewell is killed by: 1. a giant ham 2. a kitchen knife 3. a dead squirrel 4. strangulation 12. Heck Tate is: 1. the county sheriff 2. a state deputy 3. a welfare worker 4. an FBI agent 16. Scout’s full name is: 1. John - Louis Finch 2. Jeremy Finch 3. Charles Baker Harris 4. Jean - Louise Finch 13. The children receive 1. a dog named Tim Johnson 2. a squirrel for Boo 3. new clothes for school 4. none of the above for Christmas: 17. Who does not live on Scout’s street? 1. Ms. Stephanie 2. Ms. Rachel 3. Ms. Maudie 4. Ms. Mayella 14. Dill’s says his father is: 1. a famous bank robber 2. a conductor on a train 3. a senator from Mississippi 4. a lawyer like Atticus 18. Tom Robinson dies because: 1. Bob Ewell stabbed him 2. he was found guilty 3. a guard shot him 4. he starved in prison 19. The Ewells live: 1. down by the corner 2. down the street towards town 3. down by the junkyard 4. down by the river 20. What is the name of the rabid dog? 1. Tom Johson 2. Tom Robinson 3. Tim Robinson 4. Tim Johnson *As extra review try to identify when the incorrect options above occurred and provide as much information about them as you can. Written Section In addition to the brief scantron portion, you will be asked to write a two-page response during your final exam. This response will be asking you to connect the ideas presented in a poem to two of our works from the 2nd semester. Two poems for consideration are: “Sympathy” by Paul Lawrence Dunbar “Dream Deferred” by Langston Hughes Consider connecting the ideas of these two poems to Lord of the Flies, To Kill a Mockingbird, and A Raisin in the Sun