Handout 1, Course Outline
advertisement

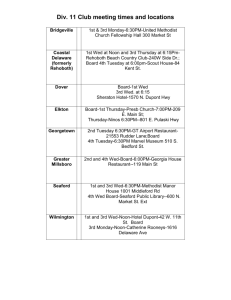
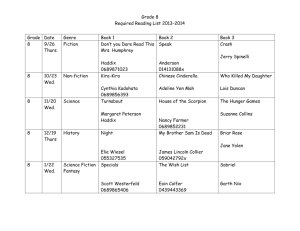
CS 200 HM COMPUTER ORGANIZATION & ASM LANGUAGE HO1 PSU WINTER 2003 Handout 1 (2/13/2003) Course Title: CRN: Time: Room: First Day: Last Day: Grading and grader: Office hours: Instructor: Class material: Book Ref: Masm reference: Computer Organization and Assembly Language, CS 200 40737, section 2 Mondays, 16:00 - 17:50 SH 212, Portland State University Monday 1/6/2003 Wednesday 3/12/2003 anshu@cs.pdx.edu , hand in HW in paper form at start of class after lectures in class, by phone, email any time, and by special appointment Dr. Herbert G. Mayer, 264-4205, herb@cs.pdx.edu http://www.cs.pdx.edu/~herb click on Class Information, and then on CS 200 http://csapp.cs.cmu.edu/public/students.html http://www.clipx.net/ng/masm Prerequisites: CS 161. Good understanding of number representation and of C++ or C. Pascal or Ada or another high-level, machine independent programming language will do, if you have good programming experience. Text Books: Required text: Computer Systems, A Programmer’s Perspective, by Randal E. Bryant and David R. O’Hallaron, PH ISBN 0-13-009757-8, © 2002 or newer. Two text books are recommended: 1.) If you are weak in C, I recommend: The C programming language, by B. W. Kernighan and D. M. Richie, Prentice Hall SW Series, ISBN 0-13-110362-8, © 1988. 2.) If you wish to learn more about x86 assembly language programming, read: Assembly Language Programming for the IBM PC Family - 3rd edition, William B. Jones, Scott/Jones Inc., El Granada, CA., 2001, ISBN 1-57676-058-8 720 pages. Class description and goals: At conclusion of this course, you understand the Software-Hardware interface and interdependence. You also acquire a beginner’s understanding of the Intel x86 architecture and assembly language. The HW aspect of computer architecture will be discussed, though not in as much detail as the Advanced Computer Architecture course CS438. HW concepts will be exemplified via low-level C programming examples and the x86 assembly language. We’ll discuss low-level system software (SSW) components, assemblers, linkers, loaders, exception handlers, and I/O. This course will enable you to select future focus areas, such as compiler optimization (SW), dynamic branch prediction (HW), caching (ARCH), or the like. Milestones: You’ll complete 5 Homework (HW) assignments, two quizzes, a Midterm, and a Final Exam. Note that the Midterm weights the same as the Final. Grading: You can acquire up to 1,000 points total (100%). HWs account for 50% of your grade. 100 points each, quizzes for 10%, 50 points each; the Midterm 20%, and the Final 20%. The first homeworks focus on low-level C constructs. Winter 2003 1 HO 1 CS 200 HM COMPUTER ORGANIZATION & ASM LANGUAGE PSU WINTER 2003 HO1 Table of Grades: A 90-100% B >= 80% C >=70% D >=60% F <60% Homework Rules: HW must be turned in on paper at the beginning of class on the due date. Late HW will be accepted up to 1 week late, but you lose 15% of the total points. Read the on-line Lecture Notes, Handouts, and Homework Assignments, and read the book as suggested in the Course Outline. The remaining chapters of the required book will be read in CS 201. Course Outline, Major Milestones (HO: means you should read the on-line HandOut) Week 1 Mo 1 Wed 2 Mo 2 Wed 3 Mo 3 Wed 4 Mo 4 Wed 5 Mo 5 Wed 6 Mo 6 Wed 7 Mo 7 Wed 8 Mo 8 Wed 9 Mo 9 Wed 10 Mo 10 Wed Winter 2003 Reading Material, Key Dates Introduction, course outline, goals read ch 1, HO: Integer Number System; number representation HW1 due: Bit Manipulation, read ch 2; low-level C programming, key computer terms HW2 due: C Number Conversion; machine organization School Closed: MLK Day read ch 3; intro to x86, C pointers, HO: Simple Asm Program, HO: Assembler Intro read HO: Simple x85 IO; simple assembler program HW3 due: Binary trees via C pointers read ch 4, HO: x86 Memory Access; computer architecture, main modules, and assembler read ch 4, HO: Multiple Assembly Units; linking, loading, executing Quiz1, read ch 6 ; memory hierarchy ; x86 instructions read HO: x86 Call Return Mechanism; Midterm, HW4 due: Char and String Output No Class, read ch 7; run time stack multiple assembly units; x86 instructions 2nd part Quiz2; recursion implementation, in C, in x86 HW5 due: PutDec, read ch 8 caching architectures System bus, van Neumann bottleneck Transforming small, slow memories into large, fast memories via caches and VMM Re-read sections from all chapters 1-8, Summary Final 2 HO 1