Cell Membrane Structure & Function Worksheet
advertisement

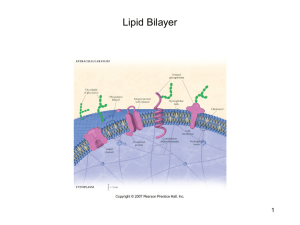
Name _________________________________ Period _____________________ Date _____________________ Objective: SWBAT describe the structure and function of the cell membrane Step 1. Draw a picture of a phospolipid. Label the hydrophilic head and the hydrophobic tail. Step 2. Now draw a picture of a phospholipids bilayer also known as the cell membrane (plasma membrane). Step 3. Read the following passage and mark up the text by underlining or circling the main terminologies or concepts. Put question marks next to the words you don’t understand. Do not use highlighters! The Cell Membrane Cell membranes are not rigid like an eggshell. Rather; they are fluid like a soap bubble. The fluidity of the cell membranes is caused by lipids, which form the foundation of membranes. The lipids form a barrier that separates the inside of the cell from the outside of the cell. This selective permeability of the cell membrane determines which substances enter and leave the cell. The selective permeability of the cell membrane is caused mainly by the way phospholipids interact with water. The phospholipid is a lipid made of a phosphate group and two fatty acids. A phospholipid has both a polar “head” and two nonpolar “tails.” The head of the phospholipid, which contains a phosphate group, is polar and is attracted to water. In contrast, the two fatty acids, or tails, are nonpolar and therefore are repelled by water. In a cell membrane, the phospholipids are arranged in a double layer called a lipid bilayer. The nonpolar tails of a phospholipids make up the interior of the lipid bilayer. Because water both inside and outside the cell repels the nonpolar tails, they are forced to the inside of the lipid bilayer. Various proteins are located in the lipid bilayer of a cell membrane. What keeps these proteins within the lipid bilayer? You may recall that proteins are made of amino acids and that some amino acids are polar, while others are nonpolar. The nonpolar part of the membrane protein is attracted to the interior of the lipid bilayer and the polar parts of the protein are attracted to the water on either side of the lipid bilayer. This attraction helps to hold the protein in the lipid bilayer. Cell membranes contain different types of proteins. Marker proteins, receptor proteins, enzymes, and transport proteins. Each protein contains a different function. (Observe the picture below to see the different functions of each protein.) Step 4. Write a summary that contains no more than 16 words to summarize your reading. Step 5. Answer the following questions. 1. True or False and why? The cell membrane is only made of phospholipids. 2. What are the functions of the marker proteins found at the cell membrane? 3. What are the functions of the receptor proteins found at the cell membrane? 4. What are the functions of the enzymes found at the cell membrane? 5. What are the functions of the transport proteins found at the cell membrane? 6. What are the functions of the cell membrane?