Molecular Genetics
advertisement

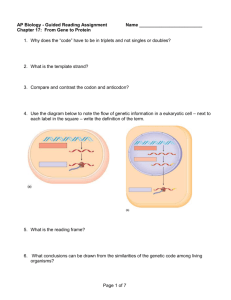
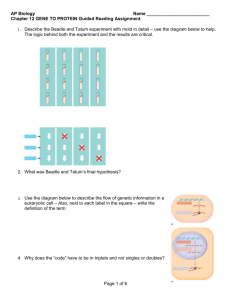
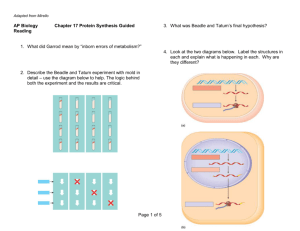
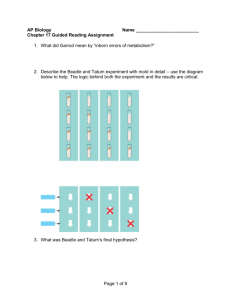
~Molecular Genetics~ Chapter 16: DNA From Gene to Protein Transcription/Translation Qs OBJECTIVES 1. Explain how RNA differs from DNA. 2. Briefly explain the central dogma of biology. 3. Distinguish between transcription and translation. 4. Describe where transcription and translation occur in prokaryotes and in eukaryotes; explain why it is significant that in eukaryotes, transcription and translation are separated in space and time. 5. Define codon, and explain what relationship exists between the linear sequence of codons on mRNA and the linear sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide. 6. List the three stop codons and the one start codon. 7. Explain in what way the genetic code is redundant and unambiguous. 8. Explain the evolutionary significance of a nearly universal genetic code. 9. Explain the process of transcription including the three major steps of initiation, elongation and termination. 10. Describe the general role of RNA polymerase in transcription. 11. Explain how RNA polymerase recognizes where transcription should begin. 12. Distinguish among mRNA, tRNA, rRNA, and siRNA. 13. Describe the structure of tRNA and explain how the structure is related to function. 14. Given a sequence of bases in DNA (GATCCTAGGAAC), predict the corresponding codons transcribed on mRNA, the corresponding anticodons of tRNA and the amino acids coded for. 15. Describe the wobble effect. 16. Explain how an aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase matches a specific amino acid to its appropriate tRNA; describe the energy source that drives this endergonic process. 17. Describe the structure of a ribosome, & explain how this structure relates to function. 18. Describe the process of translation (initiation, elongation, & termination). 19. Explain what determines the primary structure of a protein and describe how a polypeptide must be modified before it becomes fully functional. 20. Explain how proteins can be targeted for specific sites within the cell. 21. Describe the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic mRNA. 22. Explain how eukaryotic mRNA is processed before it leaves the nucleus. 23. Describe some biological functions of introns and gene splicing. 24. Explain why base-pair insertions or deletions usually have a greater effect than basepair substitutions. 25. Describe how mutagenesis can occur KEY TERMS triplet code intron anticodon point mutation one gene–one polypeptide transcription factors wobble base-pair substitution transcription initiation aminoacyl-tRNA missense mutation transcription complex synthetases nonsense mutation messenger RNA (mRNA) TATA box ribosomal RNA (rRNA) insertion deletion A site poly (A) tail primary transcript signal peptide signal-recognition particle reading frame RNA polymerase terminator translation frameshift mutation E site RNA splicing template strand codon domain transfer RNA (tRNA) P site 5' cap RNA processing mutagens polyribosome exon spliceosome mutation point mutation