Year 11 Chemistry:~ Chapter 8 Carbon Compounds
advertisement

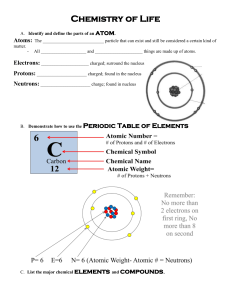
Year 11 Chemistry:~ Chapter 8 Carbon Compounds 8.1 Why is carbon important? Carbon compounds make up over ___ % of all chemical compounds and many form the basis of living systems. The study of carbon compounds being known as ‘_________ chemistry’. In organic compounds carbon is associated with _____________ and commonly oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur and chlorine. Proteins, ____________ and fats all contain ________ , hydrogen and _________ . Proteins are also a source of nitrogen and sulfur. Vitamins and minerals introduce trace elements that we need in our diets. 8.2 How does carbon form so many compounds? Carbons subshell electronic configuration is __________ . Carbon forms are wide variety of compounds because: Natural gas It is thought that natural gas and petroleum are formed by the chemical degradation of organic matter from the remains of land and aquatic plants. Under certain conditions the materials is converted into many different compounds of ________ and __________ . These are called ______________ . Natural gas is a mixture of many different compounds (see table 8.1). 8.3 Hydrocarbons Fossil fuels – coal and oil as well as natural gas – contain a wide range of hydrocarbons. Hydrocarbons can be classified into several series or families. In a _____________ series each compound differs by - and has similar properties. Alkanes – single covalent bond (saturated) Alkanes consist of only carbon and hydrogen and contain only _________ covalent bonds between carbons. Each alkane differs by -. General Molecular Formula Example: if there were 16 carbons atoms, what is the molecular formula? Crude oil contains a variety of hydrocarbons with n having values from 5 to approximately 70. *List the first 10 alkanes Molecular Formula Name Representing alkane molecules Structural formula are very similar to valence structures apart from the lone pairs being omitted. *Draw fig 8.5 (pg 137) Each of these molecules have similarities in their structure: *Draw the structural formula for butane (C4H10) Straight chain molecule branched chain molecule When there is more than one way to draw the structural formula, they are known as structural ____________ . ___________ isomers have similar chemical properties but differ in some physical properties, eg melting temperature and boiling temperature. The alkane C20H42 has _________ possible isomers. Alkanes are known as saturated because they are ‘saturated with __________ atoms. Alkenes – double covalent bond (unsaturated) Unsaturated: ____________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ A common alkene is ethene which has the molecular formula _____. It is the first member of the homologous series and contains one carbon-carbon ________ bond. General Molecular Formula *List the first 10 alkenes Molecular Formula Name Representing alkene molecules *Draw structural formula for ethene and propene Butene has three __________ isomers, two of them are straight chain isomers, differing only in the position of the ________ bond. The third isomer has a branched chain. Straight chain molecule Branched chain molecule Semistructural formula In a semistructural formula the carbon atoms and the attached hydrogen atoms are listed in order which they appear in the structural formula. Single bonds are not indicated but any ________ or ________ bonds are shown. Groups of atoms that form branches in a molecule are written in brackets after the carbon atom to which they are attached. *Write semistructural for the above alkenes Questions: 8.4 Naming carbon compounds IN the early 1960’s a common naming system was developed and endorse by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry ( ______ ). Straight chain Hydrocarbons The first part of the name refers to how many carbon atoms are in the molecule, the end depends on if it contains single, double or triple bonds. ane ene yne No. of carbon atoms Prefix 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Unsaturated compounds (contain a covalent double or triple bond) To name straight alkenes or alkynes, first number the carbon atoms in the chain, starting at the end that will give the first carbon atom involved in the double or triple bond the smallest number possible. *Copy diagrams off whiteboard for the two straight chain isomers of butene. Branched Hydrocarbons An alkyl group most often forms a branch in a branched-chain hydrocarbon. An alkyl group is an alkane molecule less one hydrogen atom and is named after the alkane from which it is derived. Remove –ane and replace with -yl -CH3 is a ______ group. C2H5 (-CH2CH3) is an _______ group. C3H7 (-CH2CH2CH3) is a ______ group. *Draw structures of alkyl groups Systematic naming requires: Identify the longest continous chain of carbon atoms. Identify the side group that forms the branch in the chain. Number the carbon atoms from one of the ends of the longest carbon chain so that the side group is attached to the carbon atom with the smallest number possible (if there is a double bond it takes precedant). *Copy diagrams from whiteboard Questions: 8.5 Properties of alkanes and alkenes Define the term volatile: ___________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ Compounds with smaller molecules are more volalite than those with larger molecules. Less energy is needed to overcome the _________ between the smaller molecules. eg petrol and oil, which one is more volatile? ______________________________ It is the vapour above the liquid that burns therefore more ___________ compounds will burn more _______ . Define the term viscosity: __________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ More volatile compounds also have a lower __________. Eg oil has a _______ viscosity and petrol would have a ________ viscosity. The boiling temperature os a hydrocarbon increases with the number of carbons in the molecule, see table 8.7. Alkenes have similar physical properties to alkanes. Boiling temperature and viscosity ___________ with molecule size and volatility __________ with molecule size. Eg. Propene has a boiling temperature of -48°C and propane is -42°C. Forces between hydrocarbon molecules (_______molecular) The bonding between atoms within a hydrocarbon molecules ( _____________ ) is covalent – one of the forms of strong bonding. The molecules of hydrocarbons are (polar / non-polar). The forces between hydrocarbon molecules are therefore ____________ forces which increase in strength as the size of the molecules ___________ . Boiling temperatures and volatility relate to the strength of intermolecular bonding. Eg the stronger the dispersion forces between the molecules the ________ the boiling temperature and _________ volatility. The higher the viscosity of the longer-chain hydrocarbons is due to the tendency of longer molecules to become ‘tangled’ together. Chemical properties of alkanes When alkanes burn in oxygen they undergo combustion. If oxygen is in excess then water and carbon dioxide are produced. *Write a structural and chemical equation for the combustion of methane. Rules for balancing chemical equations The example we will use is the complete combustion of propane (C3H8) to produce carbon dioxide and water. Step 1: identify the reactants and products (word equation) Step 2: Write down the chemical formula for reactants and products (chemical equation) Step 3: Balance the number of carbon atoms, by adding coefficients in front of the formula. Step 4: Balance the number of hydrogen atoms on each side. Step 5: Ensure the oxygen atoms are balanced. Step 6: Check equation and add states for the reactants and products. Solid: ____________ Liquid: ___________ Aqueous: _________ Gas: _____________ Chemical Properties of alkenes Alkenes like alkanes burn in oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water with the release of heat. The presence of the double carbon-carbon bond (C = C) in alkenes has a significant effect on their chemical ____________. Alkenes react more readily and with more chemicals than ____________ . Ethene and propene are starting materials (raw materials) used to manufacture many compounds, eg antifreeze, alcohols and plastics. Addition reactions of ethene 1. Reaction with bromine Ethene reacts with bromine solution (Br2 dissolved in an organic solvent). In addition reactions the double bond is converted to a single covalent bond. Red brown colour of the Bromine disappears if a _______ bond is presence. This is a general test for _____________ . 2. Reaction with hydrogen gas In the presence of a catalyst and on heating, ethene reacts with ____________ gas to produce ___________ . Converting the double bond into a _________ covalent bond. 3. Reaction with Steam Ethanol can be produced by the addition reaction of ________ and _________ in the presence of phosphoric acid catalyst. The ethanol produced in the above reaction is used for industrial purposes and as solvents in cosmetics and inks, whereas ethanol used in alcoholic beverages is fermented from sugars. 4. Formation of polyethene – addition polymerisation The ethene molecules join themselves together to form a long chain. Polymer: ____________ Monomer: ___________ QUESTIONS: