Rate of Change Trajectory
advertisement

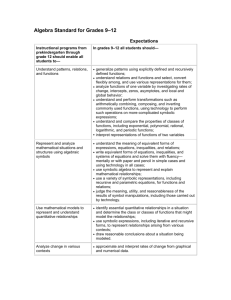
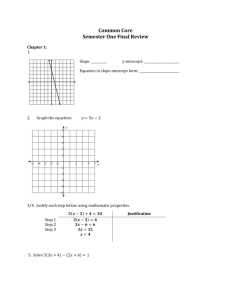
FUNCTIONS: RATE OF CHANGE Grade 7 INTERPRETING FUNCTIONS Interpret functions in applications Relationship Describe the rate of change in one variable as between variables another variable increases/decreases for linear functions including unit rate. Grade 8 Algebra Beyond Describe the rate of change in one variable as another variable increases/decreases for exponential, quadratic and inverse variation functions and relationships over an interval. Describe the rate of change in one variable as another variable increases/decreases for polynomial (cubic) and root functions and relationships over an interval. Identify and interpret the key features of a function from it’s graph or it’s equation(s). Find and interpret the average rate of change of a function over a given interval. a. Understand, estimate, calculate, and interpret rate of change for horizontal, vertical, and perpendicular lines as represented in and among tables, graphs, equations, and related contexts (mathematical and real world). Understand which transformations preserve rate of change and which do not. INTERPRETING FUNCTIONS Analyze functions with different representations Multiple a. Understand, estimate, calculate, and representations & interpret rate of change (constant) in linear Connections patterns as represented in and among tables (points), graphs, equations (recursive and/or explicit), and related mathematical and real world contexts (e.g., ratios and rates) described in words. b. Understand that when the first differences of consecutive y values are constant the function is linear. c. Make sense of first differences (linear relationship) as seen in both recursive and explicit representations and make connections between the two representations. BUILDING FUNCTIONS Building a function that models a relationship between two quantities Modeling Create and use a table, graph, words and/or equation (recursive and/or explicit) to analyze linear functions given the rate of change and/or pairs of values for various contexts (mathematical and real world) and the reverse (i.e., given the graph identify a context, rate of change, etc.) FUNCTIONS: Rate of Change w/Quadratic Version 3.0 March 7, 2011 a. Understand, estimate, calculate, and interpret rate of change for parallel, overlapping, and intersecting lines as represented in and among tables, graphs, equations (recursive and explicit), and related contexts (mathematical and real world) with respect to systems of equations described in words. b. Understand that when the second differences of consecutive y values are constant (non-zero) a function is quadratic. b. Understand that finding the point where the differences of consecutive values of f(x) are constant (non-zero) determines the degree of a polynomial. c. Make sense of a constant factor (exponential relationships) as seen in both recursive and explicit representations and make connections between the two representations. Recognize the rate of change features in linear and other basic functions (e.g., circumference and area of a circle or volume of sphere) in problem context and represent them using tables, graphs, words, and formulas. Interpret the slope of a linear regression line. BUILDING FUNCTIONS Building a function that models a relationship between two quantities Proportionality Understand and recognize directly proportional relationships as a special case of linear relationships and as it relates to rate of change and y-intercept and, how graphs, tables, equations and related contexts (mathematical and real world) described in words reflect these differences. Recognize and understand the characteristics of inversely proportional relationships as they appear in contextual, graphic, numeric, and symbolic representations. LINEAR AND EXPONENTIAL MODELS Construct and compare linear and exponential models and solve problems Relationship Compare and contrast the rate of change among Compare and contrast the rate of change in between and various linear functions and with other nonlinear functions with exponential, quadratic, among functions linear functions and relations (e.g., y=k/x or inverse variation functions and relations as change in area vs. perimeter) as represented in tables, graphs, equations (recursive and/or explicit) and related contexts (mathematical and real world) described in words. FUNCTIONS: Rate of Change w/Quadratic Version 3.0 March 7, 2011 represented in tables, graphs, equations (recursive and/or explicit) and related contexts (mathematical and real world) described in words. Compare and contrast estimated rate of change/slope over specific intervals for nonlinear functions using linear approximations.