Rule of 70
advertisement

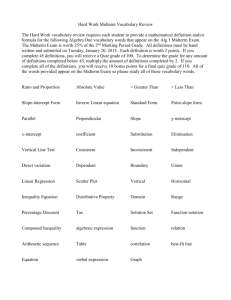
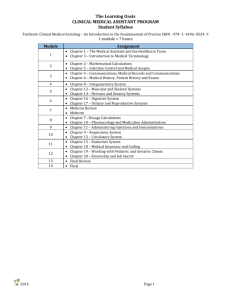
1 APES midterm review 2015 MIDTERM 2014-2015 AP ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE Topics that will be covered on exam - Summer assignment (environmental history, invasive species, famous people) Chemistry / Physics / Thermodynamics Geology Soil Atmosphere / climate / weather / El Nino Human Population / Population Ecology Community Ecology / Ecosystems Diversity Aquatic Life Zones / Biomes Biogeochemical cycles Math Historical Tribal Era: Conservationist Era Preservationist movement Green Revolution The Environmental Era Sagebrush Rebellion People John Muir Teddy Roosevelt Franklin Roosevelt Ronald Reagan Jimmy Carter Rachel Carson Gifford Pinchot Thomas Malthus Ideas The tragedy of the commons The law of tolerance 2 APES midterm review 2015 Limiting factor principle Exclusionary Principle Ecological (carbon) Footprint Feedback loops Ecosystem Services Environmental Issues Climate Change Ozone Depletion Ocean Acidification Coral Bleaching Invasive species Reasons for species extinctions: HIPPO Trophic levels NPP and GPP Energy flow (and law of conservation of energy Rule of 10%) Producers Primary consumers Secondary consumers Scavengers Decomposers 1st Law of thermodynamics 2nd Law of thermodynamics Geology Convergent Faults Divergent Faults 3 APES midterm review 2015 Transform Faults Earthquakes o Epicenter o Richter Scale Tsunamis Volcanoes o The Ring of Fire Soil Layers of soil horizons How to use a soil triangle Component of soil Texture/consistence Permeability vs Porosity Cycles: Nitrogen Nitrogen Fixation Nitrification Assimilation Ammonification Denitrification Carbon/oxygen o Photosynthesis o Respiration o Fossil fuel formation o Combustion 4 APES midterm review 2015 Phosphorous Water Characteristics of a system Weather/climate o Atmospheric levels o Prevailing winds o Coriolis effect o Altitude o Latitude o Winds / Convection cells Hadley Ferrel Polar o Warm fronts/ Cold Fronts o Relative Humidity Ecosystems Range of tolerance: Indicator species Keystone Species Theory of Island Biogeography Evolution - adaptive radiation - convergent vs divergent - geographic isolation Coevolution Speciation 5 APES midterm review 2015 Natural Selection Adaptations Species Interactions Commensalisms Predation Mutualism Competition Parasitism Habitat Niche Density dependent / Density independent limiting factors Interspecific vs intraspecific competition Analyze food web or food chain Succession Primary Secondary o Population o Population changes Irruptive Stable Cycle Irregular o Distribution Uniform Clumped Random r-strategists vs K-strategists o Community o Ecosystem 6 APES midterm review 2015 o Organism o Edge Effect/ Ecotones Biomes: not only descriptions, but what climatograms would look like, and locations on world map Deciduous forests Taiga Tropical rain forests Deserts Savannas Temperate rainforest Tundra Chaparral Aquatic Ecosystems Limiting factors of aquatic ecosystems: Phytoplankton Zooplankton Benthos Decomposers Nekton Open ocean Coral Reef Estuary Intertidal zone Abyssal plain Marine Fresh Water (break down of each) Lotic: Rivers 7 APES midterm review 2015 Lentic o Seasonal characteristics o Swamps o Marshes o Lakes Populations Age structure diagrams Demographic transition Calculating natural rate of increase or population growth Rule of 70 Complete the following on the below images of the Earth: 8 APES midterm review 2015 Draw the various convection currents that exist in the atmosphere. Identify latitudes that are associated with dry and wet climates. The direction of prevailing winds and how Coriolis effect would occur. identify location of El Nino Identify areas where Volcanic Island Chains have formed (what process of the earth is associated with these islands? Identify the layers of the cross section below. o Give a characteristic of each layer (composition or physical property) 9 APES midterm review 2015 Draw the convection currents that occur within the earth. Explain what these convection currents result in. Math Dimensional analysis Practice 10 APES midterm review 2015 Conversions Factors 1 hr = 60 min 1 min = 60 sec 1 ton = 2000 lbs 7 days = 1 week 24 hrs = 1 day 1 kg = 2.2 lbs 1 gal = 3.79 L 264.2 gal = 1 cubic meter 1 mi = 5,280 ft 1 kg = 1000 g 1 lb = 16 oz 20 drops = 1 mL 365 days = 1 yr 52 weeks = 1 yr 2.54 cm = 1 in 1 L = 1000 mL 1 cc is 1 cm3 1 mL = 1 cm3 0.621 mi = 1.00 km 1 yd = 36 inches 1.) How many miles will a person run during a 10 kilometer race? 2.) The moon is 250,000 miles away. How many feet is it from earth? 3.) A family pool holds 10,000 gallons of water. How many cubic meters is this? 4) Lake Michigan holds 1.3 x 1015 gallons of water. How many liters is this? 5) Chicago uses 1.2 x 109 gallons of water /day. How many gallons per second must be pumped from the lake every second to supply the city? Recognizing the prefix of different units Complete the chart below Symbol Prefix Multiplication Factor G Giga 109 M Mega k Kilo m milli μ micro n nano 10-3 10-9 Use the chart from the previous page to answer the questions below 1) Convert 10 GW (gigawatt) to MW (Megawatts). 11 APES midterm review 2015 2) Convert 4 kilograms to micrograms. Natural Increase Rate Practice 1) A population has a crude birth rate of 42 and a crude death rate of 25, what is the natural rate of increase for that population? 2) If the crude death rate of a country is 13 and the population is growing at a rate of 3%, what is the crude birth rate for that nation? Rule of 70 Practice 1) In 1900, the US was growing at a rate of 2%. In what year did that population double. 2) A population doubled in 10 years. What is the growth rate of this population?