Atoms, Bonding, and the Periodic Table Worksheet
advertisement

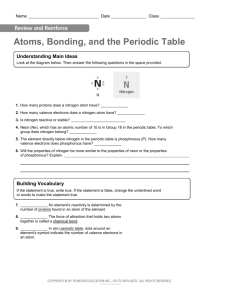
Name Date Class Atoms, Bonding, and the Periodic Table 1. What does an element’s atomic number represent? 2. In an atom, how are the number of protons and the number of electrons related? 3. APPLY CONCEPTS The atomic number for nitrogen (N) is 7. How many electrons are in a nitrogen atom? 4. APPLY CONCEPTS The element immediately below nitrogen in the periodic table is phosphorous (P). The atomic number for phosphorous is 15. How many electrons are in a phosphorous atom? 5. DEFINE What are valence electrons? b. EXPLAIN Why do the properties of elements change ina regular way across the rows(periods) of the Periodic Table. c. RELATE CAUSE AND EFFECT Explain the reactivity of the noble gases in terms of valence electrons. 129A Name Date Class Atoms, Bonding, and the Periodic Table What Determines an Element’s Chemistry? 1a. DEFINE What are valence electrons? b. EXPLAIN Why do the properties of elements change in a regular way across a period? c. RELATE CAUSE AND EFFECT Explain the reactivity of the noble gases in terms of valence electrons. I get it! Now I know that the chemical properties of an element are determined by I need extra help with 129B Name Date Class Atoms, Bonding, and the Periodic Table 129C Name Date Class Atoms, Bonding, and the Periodic Table Understanding Main Ideas Look at the diagram below. Then answer the following questions in the space provided. 1. How many protons does a nitrogen atom have? 2. How many valence electrons does a nitrogen atom have? 3. Is nitrogen reactive or stable? 4. Neon (Ne), which has an atomic number of 10 is in Group 18 in the periodic table. To which group does nitrogen belong? 5. The element directly below nitrogen in the periodic table is phosphorous (P). How many valence electrons does phosphorous have? 6. Will the properties of nitrogen be more similar to the properties of neon or the properties of phosphorous? Explain. Building Vocabulary If the statement is true, write true. If the statement is false, change the underlined word or words to make the statement true. 7. An element’s reactivity is determined by the number of protons found in an atom of the element. 8. The force of attraction that holds two atoms together is called a chemical bond. 9. In a(n) periodic table, dots around an element’s symbol indicate the number of valence electrons in an atom. 129D Name Date Class Atoms, Bonding, and the Periodic Table Read the passage, look at the diagram, and study the table. Then use a separate sheet of paper to answer the questions that follow. The Rockets’ Red Glare The basic fireworks unit is called a shell, and it is packed with chemicals that produce light, smoke, and noise when they burn. The effects depend on which chemicals are packed into the shell and how they are arranged. A simple shell is shown at the right. When the gunpowder is at the bottom of the shell is lit, it explodes and lifts the shell into the air. By the time the shell has reached the high point of its path, a second fuse ignites the other chemicals. Some shells explode all at once. Others are made of smaller shells that burst apart and explode separately. Time delays can be used to make a shell explode in stages. The table below lists some chemicals and the effects they produce. Element Effect strontium or lithium red color barium green color copper blue color sodium yellow color magnesium or aluminum white color potassium or sodium whistling sound potassium and sulfur white smoke Please answer questions on the back. To which groups of the periodic table do the majority of the elements listed in the table above belong? Why do you think elements in these groups are used in making fireworks? 2. Which group of elements could you not use in making fireworks? Explain your answer. 3. Why would you want to have two or more separate fuses in a rocket? 4. Solutions of magnesium, barium, and strontium are clear and colorless. Predict what might happen if a drop of each solution was held in the flame of a lab burner. 1. 129E Name Date Class Atoms, Bonding, and the Periodic Table If the statement is true, write true. If the statement is false, change the underlined word or words to make the statement true. An atom’s valence electrons are those electrons that have the 1. highest energy. 2. Atoms tend to be stable and nonreactive if they have six valence electrons. 3. In the periodic table, the number of valence electrons in each element decreases from left to right across each period. 4. The reactivity of a metal depends on how easily it loses its valence electrons. 5. Within each period in the periodic table, elements have similar properties because they have the same number of valence electrons. Fill in the blank to complete each statement. 6. The number of determines its chemical properties. in the atom of an element 7. The columns in the periodic table are called . 8. A(n) electrons in an atom in pictorial fashion. shows the number of valence 9. The attractive force that holds two atoms together is called a(n) . 10. Because it can either lose or share electrons when it combines with other elements, each has some of the properties of metals and some of the properties of nonmetals. 129F Atoms, Bonding, and the Periodic Table Answer Key 1. the number of protons in one atom of the 1. Groups 1 and 2; because they are very reactive element 2. the noble gases; because they do not react 2. They are the same. easily 3. 7 3. You need one fuse to ignite the gunpowder that sends the rocket into the air, and other fuses to ignite the chemical compounds that produce the light and noise once the rocket has reached its maximum height. 4. 15 4. The element in solution might burn as it does in Barium: “Ba” with 1 dot above it and 1 dot to its right Carbon: “C” with 1 dot on each of its 4 sides Cesium: “Cs” with 1 dot to the right of it Iodine: “I” with 1 dot below it and 2 dots on each of the other three sides Krypton: “Kr” with 2 dots on each of its 4 sides Phosphorous: “P” with 2 dots to its right and 1 dot on each of its other 3 sides Strontium: “Sr” with 1 dot above it and 1 dot to its right a firework rocket, giving off a color. The results could be used to tell the solutions apart. 1. true 2. eight 3. increases 4. true 5. group 6. valence electrons 7. groups 8. electron dot diagram 9. chemical bond 1. 7 2. 5 3. reactive 4. Group 15 5. 5 6. Nitrogen’s properties will be more similar to the properties of phosphorous because, unlike neon, both elements are in the same group and have the same number of valence electrons. 7. valence electrons 8. true 9. electron dot diagram 129G 10. metalloid 129H