At the Clinic Answers: Integumentary System
advertisement

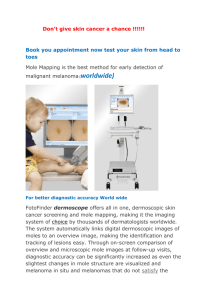
At the Clinic Answers: Integumentary System 1. Do you think this is an example of a growing mole, or could it be a different condition? If it is a different condition, what do you think it is? This is almost certainly a malignant melanoma. 2. What were the features of the mole that led to your answer in #1? Today a clinical diagnosis of whether a mole (nevus) is benign or malignant can be made with approximately 90% accuracy by using the ABCD rule: A stands for asymmetry. Benign moles tend to be symmetric in shape, whereas melanomas are asymmetric. B stands for border irregularity: the borders of melanomas are irregular and often show indentations and protrusions. Nevi have regular, well-circumscribed borders. C stands for color: melanomas often have multiple colors, including black, brown, tan, pink, blue, gray, and white tones; nevi usually only exhibit shades of brown and black. D stands for diameter: moles over 6 millimeters in diameter have a higher likelihood of being a melanoma than moles under 6 millimeters. 3. Can you name some risk factors for the condition? a. Age: his middle age is a risk factor; melanoma occurs most frequently in individuals between 40 and 60 years of age. It is uncommon in children. b. Red hair: individuals with red or blond hair have a higher incidence of melanoma. c. Caucasian race with fair skin: dark-skinned populations have rates one-seventh to one-tenth that noted for lighter-skinned Caucasians d. History of being a surfer in Hawaii: although the connection between sun and melanoma is not as clear-cut as it is for squamous cell carcinoma and basal cell carcinoma, most melanoma studies have linked increased melanoma risk to a history of sunburn or chronic sun exposure. 4. List and explain at least three tests that should be performed on this patient to obtain the information detailed above. a. A procedure called a full-thickness excisional biopsy should be performed. This would cure the lesion if it were benign. If it is melanoma, the full thickness biopsy allows for accurate measurement of the thickness of the lesion. Thicker lesions have a worse prognosis and a higher chance of metastases. b. The combination of elevated alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, and alkaline phosphatase suggests liver damage. Although a variety of inflammatory disorders may cause this, one should be suspicious of liver metastases. Melanoma commonly metastasizes to the liver. An imaging study of his liver such as a contrast-enhanced CT or MRI scan should be performed. c. Depending on the depth of invasion, surgeons may wish to examine regional lymph nodes (those that drain lymph from the involved area), because these may very well contain metastases.