Ch 6 Objectives
advertisement

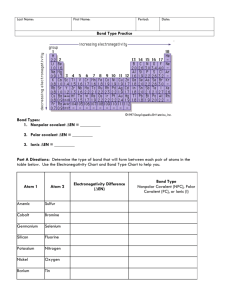
Name _________________________________ Ch 6 Objectives-Covalent Bonds and Molecular Forces- 2011 Students should review the objective list as they go through the chapter. After reading the chapter and studying notes and homework, they should be able to: Prior Knowledge: 1. Define the term electronegativity. 2. Explain the periodic trend of electronegativity (how it changes). 3. Write a noble gas electron configuration. 4. Determine the number of valence electrons in the main block. 5. Differentiate between core and valence electrons. 6. Write formulas and name ionic compounds. 7. Differentiate between metallic, ionic, and covalent bonds. Section 6-1 8. Explain how a covalent bond forms between two atoms. 9. Describe the change in energy and stability as a covalent bond forms as shown in Figure 4 on pg 192 of the text. 9. Explain how length of a covalent bond is defined. 10. Explain how the bond energy is related to bond length and bond strength. 11. Relate electronegativity difference to bond energy. 12. Describe the spring analogy for a covalent bond. 13. Create a linear line graph of Table 6-1 from text pg 193 using Excel (or use handout) and be able to describe what the graph indicates. Bring the graph the day of the test. 14. Describe the differences between polar covalent and nonpolar covalent bonds. 15. Determine whether a bond is polar, nonpolar covalent, or polar covalent using electronegativity values from a reference chart. 16. Describe a dipole and give an example labeled with its partial charges. Section 6-2 17. Draw Lewis structures to show the arrangement of valence electrons among atoms in molecules and polyatomic ions according to the VSEPR thoery. 18. Recognize when an element won’t have a full octet and still be stable. 19. Explain the differences between single, double, and triple covalent bonds. 20. Draw resonance structures for simple molecules and polyatomic ions. 21. Explain the terms: lone pair, unshared pair, and shared pair. 22. Name binary covalent compounds using prefixes, roots, and suffixes. 23. Write the formula for binary covalent compounds given the name. 24. Recognize an ionic compound from a covalent compounds in order to name them. con’t→ Section 6-3 25. State what the acronym VSEPR stands for. 26. Describe the premise behind VSEPR theory. 27. Recognize the following molecular shapes and the angles between their atoms: linear, bent, trigonal planar, trigonal pyramidal, and tetrahedral. Give examples of each. 28. Determine when a structure is polar or nonpolar. Give examples of each. 29. Explain why water molecules can be attracted by a charge and hexane, C6H14, cannot. 30. Relate the boiling point of a molecules substance to the shape and polarity of its molecules.