Chapter 18 – Anatomy of the Cardiovascular System – Test
advertisement

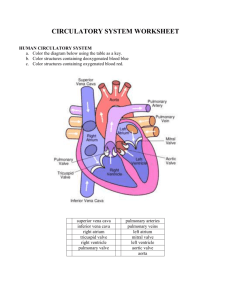
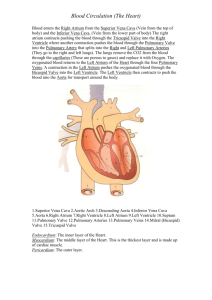
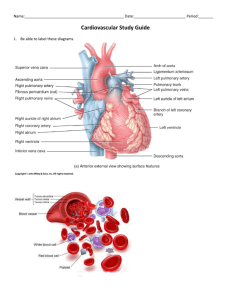
Name: ___________________________________________________________________ Test Date: _______________ Anatomy – Ms. Mullin Chapter 13 –Cardiovascular System – Study Guide Answer the following questions in preparation for the test on the chapter… 1. What is the strongest pumping chamber of the heart? Left ventricle 2. What is the function of the valves? To prevent backflow of blood 3. How many chambers does the human heart have? Four 4. What vessel would have the highest oxygen content? Pulmonary vein 5. The heart sounds are due to what? The valves closing 6. What is the correct sequence when the blood flows from the heart to the kidney? Left ventricle, aorta, renal artery 7. What is the correct sequence in the generation of the heartbeat? Sinoatrial node, atrioventricular node, Bundle of His 8. Where is blood pressure the greatest? Arteries 9. How is the heart muscle nourished? By the coronary artery 10. In a normal heart, when the right ventricle contracts, blood is forced through which valve of the heart? Tricuspid valve 11. What is another name for the visceral layer of the pericardium? Epicardium 12. The saclike structure around the heart is called the what? Pericardium 13. The muscular layer of the heart wall is the what? Myocardium 14. The internal layer of tissue in the heart is the what? Endocardium 15. The right atrioventricular valve is also called what? Tricuspid valve 16. What are the different semilunar valves of the heart? Aortic valve and pulmonary valve 17. All of the following are TRUE statements EXCEPT… a. The right coronary artery is dominant in about 50% of all hearts b. Both atria receive their blood supply from branches of the right and left coronary arteries c. The most abundant blood supply goes to the myocardium of the left ventricle, rather than the right ventricle d. Only a few connections, or anastomoses, exist between the larger branches of the coronary arteries 18. The structure referred to as the pacemaker of the heart is the what? SA node 19. What vessel does NOT have the ability to constrict and dilate? Capillaries 20. The type of vessels that serve as resistance vessels, important for the maintenance of blood pressure, is what? Arteries 21. What vessel acts as blood reservoirs? Veins 22. The structural components of the circulatory system include what structures? The heart, blood vessels 23. The atrioventricular valve on the same side of the heart as the origin of the aorta is the what? Mitral valve 24. The correct layers of the heart from deep to superficial are what? Endocardium, myocardium, epicardium 25. Atrioventricular valves prevent what from happening? Backflow of blood into the atria 26. The ventricle of the heart that ejects blood into the pulmonary trunk is what? Right ventricle 27. Chordae tendineae are associated with what structures? Tricuspid valve 28. The right atrium receives blood from where? Inferior and superior vena cava 29. During a normal cardiac cycle what percentage of blood passively moves into the ventricles? 70% 30. What happens to the pressure in the ventricles as the fill? It rises 31. What happens to the pressure in the atria as the ventricles fill? It falls 32. Valves controlling the direction of blood flow are found in what vessel? Veins 33. The order of blood flow through the vessels is what? Arteries, arterioles, capillaries, venules, veins 34. All arteries of the systemic circulation branch from the what? Aorta 35. The P wave on an ECG represents what? Atrial depolarization 36. A straight line on an ECG represents what? Lack of electrical activity 37. Ventricular repolarization is represented by what wave? T wave 38. The atria will empty during what? Atrial systole 39. The three factors that contribute to arterial blood pressure are cardiac output, blood volume, and what? Resistance 40. The three arteries that arise from the aortic arch are the left subclavian, left common carotid, and what? Brachiocephalic 41. The longest vein in the body is the what? Great saphenous vein 42. The major artery of the neck that feeds blood to the brain is the what? Common carotid artery 43. The artery that feeds the blood to the right arm and fingers is the what? Right subclavian artery 44. The blood that flows to the stomach must flow through the __________ artery. Gastric 45. Indicate the flow of blood through the heart starting with the superior vena cava and ending at the superior vena cava. Be sure to include all valves!!! Superior vena cava…Right atrium…tricuspid valve…right ventricle…pulmonary semilunar valve…pulmonary artery…lungs…pulmonary vein…left atrium…bicuspid valve…left ventricle…aortic semilunar valve…aorta…body…superior/inferior vena cava 46. Describe the similarities and differences between skeletal muscle tissue and cardiac muscle tissue. Both striated Skeletal = voluntary Cardiac = involuntary Skeletal = many nuclei; cardiac = one nucleus Cardiac has intercalated disks 47. The blood that flows from the liver back to the heart must flow through the __________ vein. Hepatic 48. What vessel receives blood from lungs? Left atrium 49. What vessel carries blood toward body tissues? Aorta 50. What vessel receives blood from the body tissues? Right atrium 51. What vessel carries blood to the heart? Pulmonary vein 52. What vessel does tissue exchange? Capillary 53. What vessel carries blood toward the heart? Veins 54. What vessel is most elastic? Arteries 55. Be able to label the following parts of the heart on a diagram… a. Inferior vena cava f. Left ventricle k. Pulmonary artery b. Right atrium g. Pulmonary semilunar valve l. Bicuspid valve c. Superior vena cava h. Right ventricle m. Myocardium d. Aorta i. Tricuspid valve n. Pulmonary vein e. Left atrium j. Chordae tendinae