Worksheet #1: Complete Dominance Problems
advertisement

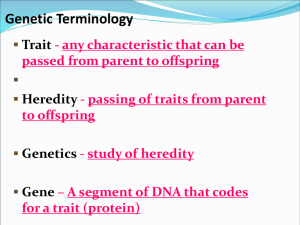
Name:________________________ Worksheet #1: Complete Dominance Problems Read the following problems and answer all missing information. At the very end, please rate what you think your level of understanding is. 1. Yellow seeds (G) are dominant to green seeds (g). Cross a pure yellow-seeded pea plant and a pure green-seeded pea plant, answer the following questions. a. Key: Yellow = ________ Green = _________ b. Which gene is Dominant? _________ Which gene is recessive? _________ c. What is the genotype of the pure yellow parent? _________ the pure green parent? ____________ d. What is the phenotype of the pure yellow parent?_________________ the pure green parent? __________________ e. Fill in the Punnett square for this cross: ________ ________ ________ ________ What are the results? f. What are the possible genotypes of this offspring? ______GG: ______Gg: ______gg g. What are the possible phenotypes of this offspring? ______Yellow: _____Green 2. Attached ear lobes (a) are recessive to free ear lobes (A). Answer the following questions if both parents are heterozygous (have one copy of each ear lobe gene – Aa) a. Key: Unattached ear lobes = ______ Attached ear lobes = ________ b. Which gene is Dominant? _________ Which gene is recessive? _________ c. What is the genotype of the male parent? __________ & the female parent?___________ d. What is the phenotype of the male parent? ______________ & the female parent? __________ e. Fill in the Punnett square for this cross: ________ ________ ________ ________ What are the results? f. What are the possible genotypes of this offspring? _______AA: ________Aa: ________aa g. What are the possible phenotypes of this offspring? _________free earlobes : _________attached earlobes 3. Rough coat (R) is dominant over smooth coat (r). Cross two guinea pigs, both being heterozygous for rough coat (Rr), answer the following questions a. Key: Rough coat = _______ Smooth coat = ______ b. Which gene is Dominant? _________ Which gene is recessive? _________ c. What are the genotypes of the parents?_______________ & _______________ d. What are the phenotypes of the parents? _____________ & ________________ e. Fill in the Punnett square for this cross: What are the results? f. What are the possible genotypes of this offspring? ________RR: _______Rr: ________rr g. What are the possible phenotypes of this offspring? __________rough: ____________smooth 4. Tall (T) is dominant to short (t). Cross a homozygous short pea plant and a heterozygous tall plant, answer the following questions. a. Key: Tall = _____ Short = _____ b. Which gene is Dominant? _________ Which gene is recessive? _________ c. What is the genotype of the tall parent?_______________ & the short parent? _______________ d. . What is the phenotype of the tall parent? ______________ & the short parent? _______________ e. Fill in the Punnett square for this cross: _______ ________ What are the results? f. What are the possible genotypes of this offspring? ______TT: _____Tt: ______tt g. What are the possible phenotypes of this offspring? _______Tall: _______short When you are finished with assignment please rate yourself. 1 2 3 4 5 I have NO clue. I don’t even know what I don’t know. I have some clue. With some help, I could figure it out. I think I understand it, but could not explain it to someone else. I’m pretty confident I could explain most of it, if not all, to a teacher. I’m so confident I understand it, that I could teach it to another student. 5. Challenge yourself! You MIGHT get extra credit Black hair (B) is dominant to brown hair (b). Cross a black rabbit and a brown rabbit. The black rabbit had a brown haired mother. a. If the black rabbit had a brown haired mother what is the genotype of the black rabbit? _________ b. What is the genotype of the brown rabbit? ________ c. What are the phenotypes of the black parent?_____________ & brown parent? _______________ f. Fill in the Punnett square for this cross: Key: Black = ______ Brown = _____