Layers of the Epidermis: Stratum Basale
advertisement

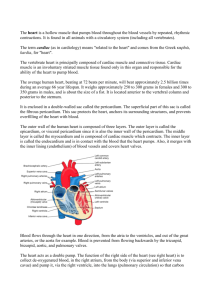
SKIN AND BODY MEMBRANES Epithelial Membranes • The cutaneous membrane is the: • Mucous membranes • Mucosae • • Serous Membranes • Paired membranes that line: • Parietal layer • Visceral layer – • Serous Membranes are named based on their location: •Parietal and visceral pleura surround: •Parietal and visceral pericardium surround: •Parietal and visceral peritoneum surround: (e.g., digestive and respiratory tracts) Skin (Integument) • Consists of three major regions 1. 2. 3. Epidermis— Dermis— Hypodermis (superficial fascia)— • Epidermis • • Cells of epidermis • Keratinocytes— • Melanocytes • Layers of the Epidermis: Stratum Basale • • Also called stratum germinativum: • Cells travel from basal layer to surface • Takes 25–45 days Layers of the Epidermis: Stratum Spinosum • • Layers of the Epidermis: Stratum Granulosum • • 1 Layers of the Epidermis: Stratum Lucidum • • • Layers of the Epidermis: Stratum Corneum • • • Functions • • Dermis • Made up of Two layers: • Papillary layer • Reticular layer Layers of the Dermis: Papillary Layer • Papillary layer • Composed of: • Contains dermal papillae which may have: • • • Layers of the Dermis: Reticular Layer • Reticular layer •Composed of: • Skin Color • Three pigments contribute to skin color: 1. Melanin • • 2. Carotene • 3. Hemoglobin • 2 Appendages of the Skin • Derived from the epidermis • • • • Sweat Glands • Two main types of sweat (sudoriferous) glands 1. Eccrine sweat glands— abundant on palms, soles, and forehead • Sweat: • • 2. Apocrine sweat glands—confined to: • Sebum: • • Sebaceous (Oil) Glands • • • • Sebum • • • Hair • Functions • • • Consists of: Hair Follicle • Two-layered wall consisting of: • Hair bulb: • Hair follicle receptor (root hair plexus): 3 • • Arrector pili • • Structure of a Nail • •Structures of the nail: Functions of the Integumentary System 1.Protection— • Chemical • • Physical/mechanical barriers • • • Biological barriers • 2.Body temperature regulation • • 3.Cutaneous sensations • 4.Metabolic functions • • 5.Blood reservoir— 6.Excretion— Skin Cancer • Three major types: • Basal cell carcinoma • Squamous cell carcinoma • Melanoma Basal Cell Carcinoma • •Appearance: 4 • • Squamous Cell Carcinoma • • Appearance: • Melanoma • • Appearance: • • Melanoma • Characteristics (ABCDE rule) A: AsymmetryB: BorderC: ColorD: DiameterE: EvolutionPartial-Thickness Burns • First degree • • • Second degree • • Full-Thickness Burns • Third degree • • • • 5 THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Heart Anatomy • Approximately the size of a fist • Location • • • • Enclosed in pericardium, a double-walled sac Pericardium • Superficial fibrous pericardium • • Deep two-layered serous pericardium • • • Parietal layer lines: Visceral layer (epicardium) is on : Separated by fluid-filled pericardial cavity (decreases friction) Layers of the Heart Wall 1.Epicardium = 2.Myocardium • 3.Endocardium Chambers • Four chambers • Two atria • • Separated internally by: • Two ventricles • • Separated internally by: Major Blood Vessels of the Heart • Vessels entering right atrium • • • • Vessels entering left atrium • • Vessel leaving the right ventricle • • Vessel leaving the left ventricle • 6 Pathway of Blood Through the Heart • The heart is two side-by-side pumps • Right side is the pump for the pulmonary circuit • Left side is the pump for the systemic circuit • • • Right atrium tricuspid valve right ventricle Right ventricle pulmonary semilunar valve pulmonary trunk pulmonary arteries lungs Lungs pulmonary veins left atrium Left atrium bicuspid valve left ventricle Left ventricle aortic semilunar valve aorta Aorta systemic circulation • Anatomy of the ventricles reflects differences in pulmonary and systemic circuits Coronary Circulation • • Arteries • • • Veins • Homeostatic Imbalances • Angina pectoris • • Myocardial infarction (heart attack) • • Heart Valves • Ensure unidirectional blood flow through the heart • Atrioventricular (AV) valves • • • • Chordae tendineae anchor AV valve cusps to papillary muscles • Semilunar (SL) valves • • • 7 Microscopic Anatomy of Cardiac Muscle • • • • • Intercalated discs: junctions between cells anchor cardiac cells • • Desmosomes prevent : Gap junctions allow : • Heart muscle behaves as a functional syncytium Heart Physiology: Electrical Events • Intrinsic cardiac conduction system • Defined: Autorhythmic Cells • • Heart Physiology: Sequence of Excitation 1.Sinoatrial (SA) node (pacemaker) • • 2.Atrioventricular (AV) node • • • 3.Atrioventricular (AV) bundle (bundle of His) • 4.Right and left bundle branches • 5.Purkinje fibers • • Homeostatic Imbalances • Defects in the intrinsic conduction system may result in 1. Arrhythmias: 2. Fibrillation: rapid, irregular contractions; useless for pumping blood • Defective AV node may result in • • Extrinsic Innervation of the Heart • • Cardiac centers are located in the medulla oblongata 8 • Cardioacceleratory center innervates: • Cardioinhibitory center inhibits: Electrocardiography • Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG): a composite of all the action potentials generated by nodal and contractile cells at a given time • Three waves 1. P wave: 2. QRS complex: 3. T wave: Mechanical Events: The Cardiac Cycle • Cardiac cycle: all events associated with blood flow through the heart during one complete heartbeat • • Systole— Diastole— Cardiac Output (CO) • • CO = heart rate (HR) x stroke volume (SV) • • HR = SV = Cardiac Output (CO) • At rest • CO (ml/min) = HR (75 beats/min) SV (70 ml/beat) = 5.25 L/min • Maximal CO is 4–5 times resting CO in nonathletic people • Maximal CO may reach 35 L/min in trained athletes Homeostatic Imbalances • Tachycardia: abnormally fast heart rate (>100 bpm) • • Bradycardia: heart rate slower than 60 bpm • Developmental Aspects of the Heart • Fetal heart structures that bypass pulmonary circulation • • 9 BLOOD VESSEL PHISIOLOGY Blood Vessels Arteries: Capillaries: Veins: Structure of Blood Vessel Walls Arteries and veins o Tunica intima – o Tunica media o Tunica externa - Lumen Capillaries o o o Functions: Capillary Exchange of Respiratory Gases and Nutrients Diffusion of o o Hydrostatic Pressures Capillary hydrostatic pressure (HPc) (capillary blood pressure) o o Osmotic Pressures Capillary oncotic pressure (OP c) o Created by: o Arteries to Know: Aorta Coronary arteries Subclavian arteries (what is the difference btwn. Left and right subclavian arteries in terms of how they branch) Brachiocephalic trunk Axillary artery Brachial artery Radial and ulnar artery Palmar arch and digital arteries Celiac trunk (foregut) o Common hepatic o Left gastric o splenic Superior mesenteric artery (midgut) Inferior mesenteric artery (hindgut) Hepatic portal system o Splenic vein and superior mesenteric vein are final tributaries to the hepatic portal vein o Blood is drained from liver via hepatic veins into inferior vena cava to right atrium of heart 10