Practice final
advertisement

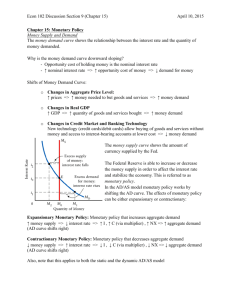
1. The narrowest official definition of the money supply is A) Ml B) M2 C) M3 D) L 2. If the bank of Wachovia receives a $10,000 deposit, and the reserve requirement is .1 how much can the bank loan out? (Assume that before the deposit this bank is just meeting its legal reserve requirement.) A) $10,000 B) $1,000 C) $9,000 D) $11,000 3. A commercial bank like Wachovia creates money by A) printing paper money. B) earning profits. C) selling corporate bonds. D) making loans. 4. Which of the following is (are) responsible for managing the money supply in the United States? A) The Federal Reserve Bank of New York B) The twelve Federal Reserve Banks. C) The Federal Open Market Committee D) The Board of Governors. 5. Open market operations refer to the buying and selling of ________ by the _______ to control the money supply. A) Treasury securities; Treasury Department B) Treasury securities; Federal Reserve C) Stocks and bonds; Treasury Department D) Stocks and bonds; Federal reserve 6. If the Fed buys U.S. Treasury securities, then this A) increases reserves, encourages banks to make more loans, and increases the money supply. B) decreases reserves, causes banks to reduce their loans, and decreases the money supply. C) decreases reserves, causes banks to reduce their loans, and increases the money supply. D) increases reserves, causes banks to reduce their loans, and increases the money supply. 7. Which of the following is an appropriate policy for the Fed to pursue if it wants to increase the money supply? A) raise the reserve requirement B) raise the discount rate C) buy U.S. treasury bills D) lower taxes 8. Which of the following describes the degree of control that the Fed has over the money supply? A) The Fed has absolute control over the money supply. B) The Fed has no control of the money supply. C) The Fed has substantial control over the money supply. D) The Fed is not concerned about the level of the money supply, and does not attempt to control it. 9. Monetary policy refers to the actions the Federal Reserve takes to manage A) the money supply and income tax rates to pursue its economic objectives. B) The money supply and interest rates to pursue its economic objectives. C) income tax rates and interest rates to pursue its economic objectives. D) government spending and income tax rates to pursue its economic objectives. 10. Federal Reserve Board Chairmen Paul Volker, Alan Greenspan, and Ben Bernanke all have focused on which of the following as their main goal of monetary policy? A) high employment B) price stability C) economic growth D) stability of financial markets 11. The Fed seeks to promote stability of financial markets because A) they want to lift the self esteem of workers. B) Congress directed them to do so by the Employment Act of 1946. C) resources are lost when there is not an efficient matching of savers and borrowers. D) unstable markets result in increased efficiency. 12. The Fed's two main monetary policy targets are A) the money supply and the inflation rate. B) the money supply and the interest rate. C) the interest rate and real GDP. D) the inflation rate and real GDP 13. The money demand curve, against possible levels of interest rates, has a A) positive slope. B) negative slope. C) zero slope. D) positive slope for low levels of money demand, a negative slope for high levels of money demand. 14. Refer to this figure: In the figure above, the money demand curve would move from MD1 to MD2 if A) real GDP decreased. B) the price level increased. C) the interest rate increased. D) the Federal Reserve sold Treasury securities. 15. Refer to this figure: In the figure above, the movement from point A to point B in the money market would be caused by A) an increase in the price level. B) a decrease in real GDP. C) an open market sale of Treasury securities by the Federal Reserve. D) an increase in the required reserve ratio by the Federal Reserve. 16. Refer to this figure: In the figure above, the movement from point A to point B in the money market would be caused by A) an increase in the price level. B) a decrease in real GDP. C) an open market sale of Treasury securities by the Federal Reserve. D) an increase in the required reserve ratio by the Federal Reserve. 17. The federal funds rate is A) the interest rate the Fed charges commercial banks. A) the interest rate a bank charges its best customers. B) the interest rate banks charge each other for overnight loans. C) the interest rate on a Treasury Bill. 18. If money demand is extremely sensitive to changes in the interest rate, the money demand curve becomes almost horizontal. If the Fed expands the money supply under these circumstances, then the interest rate will A) fall substantially and investment and consumer spending will fall substantially. B) rise substantially and investment and consumer spending will rise substantially. C) fall substantially and investment and consumer spending will change very little. D) change very little and investment and consumer spending will change very little. 19. Refer to this figure: In the figure above, if the economy is at point A, the appropriate countercyclical monetary policy by the Federal Reserve would be to A) lower interest rates. B) raise interest rates. C) lower income taxes. D) raise income taxes. 20. Refer to this figure: In the figure above suppose the economy is initially at point A. The movement of the economy to point B as shown in the graph illustrates the effect of which of the following policy actions by the Federal Reserve? A) A decrease in income taxes B) An increase in the required reserve ratio C) An open market purchase of Treasury bills D) An open market sell of Treasury bills 21. If the Fed pursues expansionary monetary policy, A) aggregate demand will rise, and the price level will rise. B) aggregate demand will fall, and the price level will fall. C) aggregate demand will rise, and the price level will fall. D) aggregate demand will fall, and the price level will rise. 22. Refer to this figure: In the figure above, suppose the economy in Year 1 is at point A and expected in Year 2 to be at point B. Which of the following policies could the Federal Reserve use to move the economy to point C? A) decrease income taxes. B) increase the required-reserve ratio C) buy Treasury bills D) sell Treasury bills 23. Refer to this figure: In the figure above, suppose the economy in Year 1 is at point A and expected in Year 2 to be at point B. Which of the following policies could the Federal Reserve use to move the economy to point C? A) decrease income taxes. B) increase the required-reserve ratio C) buy Treasury bills D) sell Treasury bills 24. Refer to this table: Year 2011 2012 Potential Real GDP $14 trillion $14.5 trillion Real GDP $14 trillion $14.8 trillion Price Level 150 154 Consider the hypothetical information in the table above for potential real GDP, real GDP and the price level in 2011 and in 2012 if the Federal Reserve does not use monetary policy. If the Fed wants to keep real GDP at its potential level in 2012, it should A) buy Treasury securities. B) sell Treasury securities. C) decrease the required-reserve ratio. D) decrease income taxes. 25. Refer to this table: Year 2011 Potential Real GDP $14 trillion Real GDP $14 trillion Price Level 150 2012 $14.5 trillion $14.8 trillion 154 Consider the hypothetical information in the table above for potential real GDP, real GDP and the price level in 2011 and in 2012 if the Federal Reserve does not use monetary policy. If the Fed uses monetary policy successfully to keep real GDP at its potential level in 2012, which of the following will be lower than if the Fed had taken no action? A) real GDP and the unemployment rate. B) real GDP and the inflation rate. C) real GDP and potential GDP. D) potential GDP and the inflation rate. 26. Which of the following summarizes the president's and Congress' role in conducting monetary policy? A) The president submits input to the chairman and the FOMC votes on it. B) Congress directs the FOMC on what its interest rate targets should be. C) Congress and the president do not playa role in conducting monetary policy. D) Both the president and Congress determine the level of funds that the Fed needs to operate, and thereby influence policy. 27. Fiscal policy is defined as changes in federal _______ and _______ to achieve macroeconomic objectives such as price stability, high rates of economic growth, and high employment. A) taxes; interest rates B) taxes; the money supply C) interest rates; money supply D) taxes; expenditures 28. Which of the following is an appropriate discretionary fiscal policy if equilibrium real GDP falls below potential real GDP? A) An increase in government purchases. B) An increase in the supply of money. C) An increase in individual income taxes. D) A decrease in transfer payments. 29. To combat a recession with discretionary fiscal policy, Congress and the president will A) decrease government spending to balance the budget. B) decrease taxes to increase consumer disposable income. C) lower interest rates and increase investment by increasing the money supply. D) raise taxes on interest and dividends, but not on personal income. 30. Expansionary fiscal policy __________ the price level and _________ equilibrium real GDP. A) decreases; increases B) increases; decreases C) increases; increases D) decreases; decreases Answer: 1. A 2. C 3. D 4. C 5. B 6. A 7. C 8. C 9. B 10. B 11. C 12. B 13. B 14. B 15. C 16. A 17. C 18. D 19. A 20. C 21. A 22. C 23. D 24. B 25. B 26. C 27. D 28. A 29. B 30. C