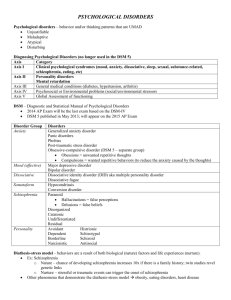
Handout-Abnormal-Mental Disorders Chart
advertisement

MENTAL DISORDERS 1.5 million hospitalized; additional 4-5 million seek help Depictions of mental disorders are often inaccurate Statistically, mental patients are less violent than those in the “normal” population What constitutes abnormal behavior? 1. Person suffers from discomfort more or less continuously. (Shows up as extreme anxiety, endless worry, or long periods of depression; feels something is wrong w/ his/her life more than the average person does) 2. Person is behaving in a bizarre fashion. (Misinterprets what is going on or what others are doing/saying; afraid to go to work or school; frequently comes completely apart over minor things or sinks into a depression about them) 3. Person is very inefficient and is therefore unable to perform their life roles properly. Characteristics of Abnormal Behavior: 1. Inflexible in their responses to almost everything (Ex: Shy, withdrawn man goes to a party and a few people are nice to him; instead, he thinks they only “feel sorry” for him) 2. Constantly see a threatening environment (Ex: See danger, rejection, and failure around every corner) Disorder Subsets -Panic Disorder Description -Frequent and overwhelming attacks of anxiety (Ex: Occur 1 while under stress) ANXIETY DISORDERS (most common) -Phobic Disorders -Disabled and overwhelmed by fear in the presence of certain objects/events (Ex: Fear of leaving familiar environment/home) -Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder -Endless preoccupation with an urge or thought combined with a symbolic, ritualized behavior that a person must keep acting out to avoid anxiety (Ex: Excessive hand washing, checking locks, compulsive gambling) -Conversion Disorders -Serious psychological trauma is unconsciously changed/converted to symbolic physical dysfunction; very SOMATOFORM DISORDERS (expressed in bodily symptoms) rare (Ex: Person who has witnessed a horrific murder may not be able to see; visual system shuts down) -Hypochondriasis -Overly concerned about health (Ex: See cough as a symptom of brain cancer and sniffles as really pneumonia) -Amnesia -Memories related to a terrible trauma “disappear” and are cut off from consciousness (Ex: Soldier selectively forgets DISSOCIATIVE DISORDERS (disconnects or disassociates certain events/behaviors from one another; very rare) the part of his identity connected with the horror of war but doesn’t forget simple things like how to tie his shoe, etc.) -Fugue -Extensive, complicated version of amnesia; starts new life somewhere else; does not remember the fugue state when 2 -Dissociative Identity they “come out of it” Disorder -Instead of forgetting specific events, they “forget” a portion of themselves; divides self into 2 or more separate personalities that can act independently; extremely rare (Ex: Individual who has experienced a history of traumatic events splits into good and evil sides to deal with guilt/desires/pain) -Dysthymic Disorder -Moderate depression that usually clears up w/ no treatment; “common cold of mental health”; serves a “function” (Ex: Occurs in someone who has just lost a friend or relative) MOOD DISORDERS (deal with one’s emotional state) -Major Depression -Very slow speech, loss of appetite and sleep, lack of energy, sense of hopelessness, extreme feelings of worthlessness, frequent thoughts of death or suicide; lasts -Mania from couple of weeks to months -Extreme agitation, restlessness, rapid speech, trouble -Bipolar Disorders concentrating; extreme up moods where one might have (Manic Depression or delusions of grandeur Manic Depressive Psychosis) -Experience swings from the downs of major depression and the ups of mania; may experience hallucinations; high levels of serotonin linked to mania and low levels linked to major depression 3 -Schizophrenia -Most serious mental disturbance; schizophrenia affects about 1% of the population; often arises in late adolescence or early adulthood; word salad (incoherence) and clang associations (rhymes); cycles of lucidity and psychosis; heredity does not seem to be the key factor PSYCHOTIC DISORDERS (Thought disorder, hallucinations, delusions, inappropriate emotional responses) (90% of patients do not have members in their immediate family who suffer from it); environment may contribute to the development for those who have a predisposition; -Catatonic linked to high levels of dopamine Schizophrenia -Disturbances of movement; does not speak or says little; appears to be in a stupor; may rigidly hold strange posture and may not move for hours -Paranoid Schizophrenia -Strong feelings of persecution or suspiciousness; delusions -Undifferentiated Schizophrenia -Lacks distinguishing symptoms -Antisocial Personality -Lack of conscience; often in conflict w/ the law and show (Psychopaths and PERSONALITY DISORDERS (Personalities Sociopaths) are “off-center”) -Borderline Personality little or no concern, guilt, or anxiety; sometimes have a family history of neglect and rough treatment -Created in 1980; characterized by intense and unstable relationships w/ others; very dependent; self-destructive behavior to manipulate others; suspicious and therefore 4 difficult to treat 5