T 7B Elastic Momentum My11esl
advertisement

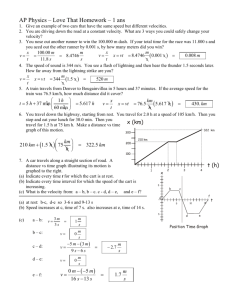
Elastics and Momentum Tuesday, May 24, 2011 Name: ______________________________ p = mv F∆t = m∆v F = – kx E=mgh E = ½ kx2 E = ½ mv2 ∆d = vit + ½ at2 ∆d = vavet vf2 = vi2 + 2ad W = F ∆d g = 9.81 m/s2 A. SHORT PROBLEMS 4 1. An arrow was shot into an apple and the apple and arrow moved together at 8.24 m/s afterward. The arrow had a mass of 65 g and the apple had a mass of 260 g. How fast was the arrow moving before it hit the apple.? [2] _____________ 2. A tennis ball of mass 0.057 kg is travelling toward you at 14 m/s. You hit the ball in the opposite direction so that it moves at 19 m/s immediately after impact. If the ball is in contact with the racquet for 8.00 10-3 s, calculate the average force of the racquet on the ball. [2] ________________ B. FILL IN THE BLANKS. 1. The name of the man who studied forces and potential energy of springs 3 _______________________________ 2. What does k represent in the equation, E = ½ k x2? ________________________________ 3. The term for the product of the average force and the time ( F ∆t ) ________________________________ C. MULTIPLE CHOICE _____ 1. _____ 2. _____ 3. _____ 4. 6 A spring that has a spring constant of 40.0 N/m is placed in a horizontal position on a frictionless surface with a 0.250-kg mass attached to the free end. If the spring is compressed 0.20 m and released, what speed will the mass have when leaves the spring? A. 0 m/s B. 2.5 m/s C. 5.6 m/s D. 8.0 m/s E. 25 m/s A 50 kg person walks at 1.2 m/s along a 150 kg boat that is floating in the water. The speed of the boat would be A. 0.3 m/s B. 0.4 m/s C. 3.6 m/s D. 4.8 m/s The impulse-momentum theorem is another way of stating A. Newton’s first law of inertia B. Newton’s second law of acceleration C. Newton’s third law of action and reaction D. Newton’s fourth law of universal gravity. A car and a truck travelling with equal speeds in opposite directions collide head-on and bounce off each other. The truck has more mass than the car. How will the momentum changes of the vehicles compare in the collision? A. The car and truck will have equal but opposite momentum changes. B. The car will have the greater change in momentum. C. The truck will have the greater change in momentum. D. The changes in momentum cannot be compared for an elastic collision such as this. For Questions 5 and 6. _____ 5. _____ 6. An astronaut in outer space is holding a hammer and drifting toward the Sun at constant velocity. The astronaut throws the hammer at the Sun. By throwing the hammer, the total momentum of the astronaut and hammer A. decreases B. increases C. stays the same By throwing the hammer, the total kinetic energy of the astronaut and hammer A. decreases B. increases C. stays the same D. SHORT EXPLANATION BEST 2 4 1. Explain, in terms of impulse and momentum, why you should bend your knees when you land after jumping. [2] 2. In a car accident, would it be safer for a passenger if the car crumpled on impact or bounced? Explain in terms of the change of momentum. [2] 3. A 600-kg car and an 1800-kg truck are both travelling at the speed limit of 90 km/h (25 m/s) in opposite directions The vehicles collide head-on and become entangled together. a. During the collision, how does the force exerted by the car on the truck compare with the force exerted by the truck on the car? Explain. [1] b. [1] In what direction will the entangled vehicles move after collision or will they be stationary? Explain. E. LAB QUESTION 3 A cart was pushed on a track toward a force sensor. The velocity toward the force sensor (vi) and the velocity after bouncing off the force sensor (vf) as well as the impulse and maximum force values are shown in the table. Complete the table (show your work below velocity in vi (m/s) velocity out vf (m/s) 0.21 – 0.18 change in velocity ∆v (m/s) impulse (N·s) maximum force Fmax (N) 0.52 28.6 calculated mass m (kg) F. PROBLEMS BEST 2 (5 POINTS EACH) 10 1. Explosion and “Elastic” Collision 5 Three carts start at rest on a dynamics track with the red and blue carts touching and the silver cart not touching the blue cart as shown below. a. Then the spring-loaded plunger of the red cart “explodes” against the blue cart, causing the BLUE cart to move at 0.20 m/s toward the silver cart. Find the speed of the RED cart after it pushes the blue cart. [2.5] _____________ b. The blue cart, still moving at 0.20 m/s, hits the silver cart and the two carts stick together. Find the speed of the SILVER and BLUE carts after the inelastic collision. [2.5] 2. Spring Energy Conservation _____________ 5 A toy dart gun uses a spring and plastic darts. Each dart has a mass of 1.5 grams. To load the dart, 15.0 N of force is required to compress the spring by 1.0 cm. a. Determine the spring constant for the dart gun [2] _____________ b. What is the maximum height of the dart if shot vertically? [3] _____________ 3. Astronauts 5 An 368-kg Canadian and a 394-kg American astronaut are floating in space when the Canadian throws a 45-kilogram object at 41.5 m/s toward the American. a. Find the velocity of the Canadian after throwing the object. [2] _____________ b. Find the velocity of the American after catching the object [3] _____________