Kapi'olani Community College Associate Degree Nursing Program
advertisement
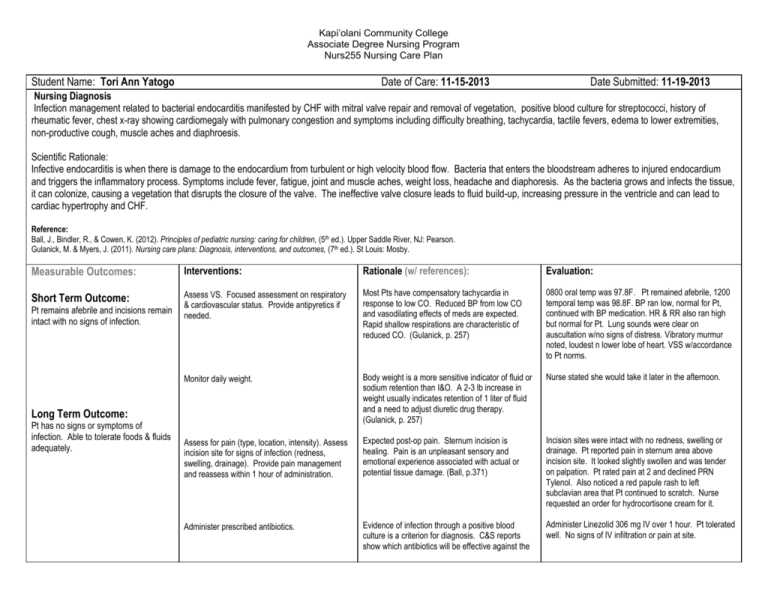
Kapi’olani Community College Associate Degree Nursing Program Nurs255 Nursing Care Plan Student Name: Tori Ann Yatogo Date of Care: 11-15-2013 Date Submitted: 11-19-2013 Nursing Diagnosis Infection management related to bacterial endocarditis manifested by CHF with mitral valve repair and removal of vegetation, positive blood culture for streptococci, history of rheumatic fever, chest x-ray showing cardiomegaly with pulmonary congestion and symptoms including difficulty breathing, tachycardia, tactile fevers, edema to lower extremities, non-productive cough, muscle aches and diaphroesis. Scientific Rationale: Infective endocarditis is when there is damage to the endocardium from turbulent or high velocity blood flow. Bacteria that enters the bloodstream adheres to injured endocardium and triggers the inflammatory process. Symptoms include fever, fatigue, joint and muscle aches, weight loss, headache and diaphoresis. As the bacteria grows and infects the tissue, it can colonize, causing a vegetation that disrupts the closure of the valve. The ineffective valve closure leads to fluid build-up, increasing pressure in the ventricle and can lead to cardiac hypertrophy and CHF. Reference: Ball, J., Bindler, R., & Cowen, K. (2012). Principles of pediatric nursing: caring for children, (5th ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson. Gulanick, M. & Myers, J. (2011). Nursing care plans: Diagnosis, interventions, and outcomes, (7th ed.). St Louis: Mosby. Measurable Outcomes: Interventions: Rationale (w/ references): Evaluation: Short Term Outcome: Assess VS. Focused assessment on respiratory & cardiovascular status. Provide antipyretics if needed. Most Pts have compensatory tachycardia in response to low CO. Reduced BP from low CO and vasodilating effects of meds are expected. Rapid shallow respirations are characteristic of reduced CO. (Gulanick, p. 257) 0800 oral temp was 97.8F. Pt remained afebrile, 1200 temporal temp was 98.8F. BP ran low, normal for Pt, continued with BP medication. HR & RR also ran high but normal for Pt. Lung sounds were clear on auscultation w/no signs of distress. Vibratory murmur noted, loudest n lower lobe of heart. VSS w/accordance to Pt norms. Monitor daily weight. Body weight is a more sensitive indicator of fluid or sodium retention than I&O. A 2-3 lb increase in weight usually indicates retention of 1 liter of fluid and a need to adjust diuretic drug therapy. (Gulanick, p. 257) Nurse stated she would take it later in the afternoon. Assess for pain (type, location, intensity). Assess incision site for signs of infection (redness, swelling, drainage). Provide pain management and reassess within 1 hour of administration. Expected post-op pain. Sternum incision is healing. Pain is an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage. (Ball, p.371) Incision sites were intact with no redness, swelling or drainage. Pt reported pain in sternum area above incision site. It looked slightly swollen and was tender on palpation. Pt rated pain at 2 and declined PRN Tylenol. Also noticed a red papule rash to left subclavian area that Pt continued to scratch. Nurse requested an order for hydrocortisone cream for it. Administer prescribed antibiotics. Evidence of infection through a positive blood culture is a criterion for diagnosis. C&S reports show which antibiotics will be effective against the Administer Linezolid 306 mg IV over 1 hour. Pt tolerated well. No signs of IV infiltration or pain at site. Pt remains afebrile and incisions remain intact with no signs of infection. Long Term Outcome: Pt has no signs or symptoms of infection. Able to tolerate foods & fluids adequately. invading organism. (Gulanick, p.344) Administer furosemide & captopril. Monitor I&Os and for fluid and electrolyte imbalances. Diuretics mobilize fluids & facilitate excretion. Adequate output is a good indicator of renal perfusion. Electrolyte imbalance is common when diruetics are given. (Ball, p.626) ACE-inhibitors decrease peripheral vascular resistance & venous tone and suppress aldosertone output thus reducing BP and demands on the heart. (Gulanick, p.258) Pt tolerated medications well. 0800 BP was 94/66 but that was normal for Pt. Urine output during 7 hour shift was 3.5 ml/kg/hr. Assess GI function. Adhere to low tyramine diet. Encourage food and fluids. Children who have insufficient dietary intake experience a higher rate of infectious disease due to lowered immune response. (Ball, p.348) Low tyramine diet because of reaction with Linezolid drug including HA, chest pains, tachycardia, N&V. Mother received handout on low tyramine diet teaching and stated understanding. Pt ate egg whites, 3 large spoon fulls of rice and 1/3 of sausage.