Supplement AP Chemistry –
advertisement

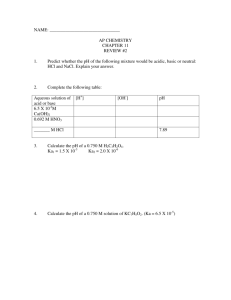
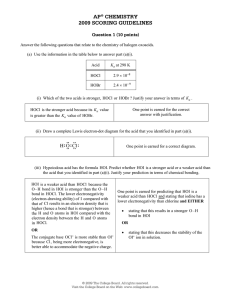
Supplement AP Chemistry – Problem Set 15.1 1) Write the net ionic equation for the reaction between solutions of a. nitric acid and lithium hydroxide b. ammonia and hydrogen iodide c. hydrogen fluoride and potassium cyanide d. calcium hydroxide and nitrous acid e. hydrochloric acid and a buffer (mixture of sodium sulfide and hydrosufuric acid) f. lithium hydroxide and a buffer (mixture of sodium sulfide and hydrosulfuric acid) 2) Write a balanced net ionic equation for the reaction of each of the following aqueous solutions with a strong acid. a. sodium formate (NaCHO2) b. calcium hydroxide c. methylamine Problem Set 15.2 1) Using the Ka values from chapter 14 in your textbook (tables 14.2, 14.3 and 14.4), calculate the K for each of the following reactions. (Hint: These equations are all related to Kw of water or Ka/Kb of various acids and bases. Use the rules you learned in ch. 13 – reciprocal rule, coefficient rule, rule of multiple equilibria.) (Ka H2S = 1.0 x 10-7; Ka oxalic acid HOOCCOOH = 6.4 x 10-5) a) CN- + H+ <==> HCN b) F- + H2O <==> HF + OHc) CN- + H2S <==> HCN + HSd) H2S + HC2O4- <==> HS- + H2C2O4 e) CH3NH3+ <==> CH3NH2+ + H+ f) C6H5NH3+ + OCl- <==> HOCl = C6H5NH2 g) OH- + HCN <==> H2O + CN2) Calculate the following a. Calculate the pH of a buffer solution prepared by adding 15.0 mL of 0.150 M NaOH to 25.0 mL of 0.200 M HCN. b. Calculate the pH of the previous buffer solution after 10.0 mL of 0.100 M HCl is added. 3) Calculate the following a. Calculate the pH of a buffer solution prepared by adding 15.0 mL of 0.125 M HBr to 35.0 mL of 0.200 M C6H5NH2. b. Calculate the pH of the previous buffer solution after 10.0 mL more of 0.125 M HBr is added. Problem Set 15.3 1) HOCl <==> OCl- + H+ Hypochlorous acid, HOCl, is a weak acid commonly used as a bleaching agent. The aciddissociation constant, Ka, for the reaction represented above is 3.2 x 10-8. (a) Calculate the [H+] of a 0.14-molar solution of HOCl. (b) Write the correctly balanced net ionic equation for the reaction that occurs when NaOCl is dissolved in water and calculate the numerical value of the equilibrium constant for the reaction. (c) Calculate the pH of a solution made by combining 40.0 milliliters of 0.14-molar HOCl and 10.0 milliliters of 0.56-molar NaOH. (d) How many millimoles of solid NaOH must be added to 50.0 milliliters of 0.20- molar HOCl to obtain a buffer solution that has a pH of 7.49? Assume that the addition of solid NaOH results in a negligible change in volume. (e) Household bleach is made by dissolving chlorine gas in water, as represented below. Cl2 (g) + H2O H+ + Cl- + HOCl Calculate the pH of such a solution if the concentration of HOCl in the solution is 0.065 molar. Supplement Ksp Problem Solve the following problem. 1. The solubility of iron (II) hydroxide, Fe(OH)2 is 1.43 x 10-3 gram per liter at 25° C. (a) Write a balanced equation for the solubility equilibrium. (b) Write the expression for the solubility product constant, Ksp, and calculate its value. (c) Calculate the pH of a saturated solution of Fe(OH)2 at 25° C. (d) A 50.0-milliliter sample of 3.00 x 10-3- molar FeSO4 solution is added to 50.0 milliliters of 4.00 x 10-6-molar NaOH solution. Does a precipitate of Fe(OH)2 form? Explain and show calculations to support your answer. Problem Set 15.5 You may complete 1,2,3,or 4 of the following assignments. You will be graded on anything you turn in. You may choose not to pass in an assignment you graded if you have a poor score (as long as you turn in at least one assignment). 1) Book questions 96,108, 114, 116; (New solubility/qualitative analysis concepts.) 2) Supplements 1-4; (Review Titration concepts/calculations) 3) Predicting Reactions a-r; 4) Predicting Reactions s-cc Supplemental Questions: 1) What indicator would you use to detect the end point for a titration (pick all that apply). a. strong acid and strong base: methyl red bromthymol blue phenolphthalein b. weak acid and strong base: methyl red bromthymol blue phenolphthalein c. weak base and strong acid: methyl red bromthymol blue phenolphthalein 2) What’s true about the pH of a solution when you’re at the half equivalence point? 3) Write equations showing how a buffer prepared by mixing acetic acid and sodium hydroxide would resist changes in pH. 4) 25.0 mL of 0.100 M C6H5NH3Cl is titrated with 0.100 M NaOH. Calculate the pH after 0.0 mL, 20.0 mL, 25.0 mL, and 28.0 mL of NaOH have been added.