learning-outcomes1
advertisement

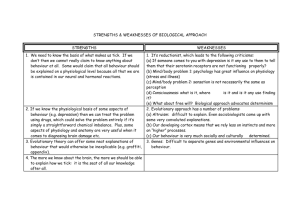
Advanced Higher – Cell and Molecular Biology Can I: Structure, function and growth of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Identify the structures in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and describe the function of each structure Explain the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic (both plant and animal) cells Describe the stages of Interphase (G1, S and G2) in the cell cycle Describe the process of mitosis (prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase) and cytokinesis Define the mitotic index Explain the control of the cell cycle with reference to the purposes and position of cell checkpoints and the role of the mitosis promoting factor (MPF) Explain how abnormal cell division occurs resulting in cancer cells Define cell differentiation and explain how it occurs Describe the techniques used to culture mammalian cells and explain some of the difficulties maintaining cell cultures Describe the requirements to culture bacterial and fungal cells and compare this to mammalian cells Describe the techniques used in plant tissue culture, comparing the totipotency of plant and animal cells and the formation of protoplasts Structure and function of cell components Describe the monomer structures of glucose Describe the structure of disaccharides and explain their formation. Describe the structure of a polysaccharide and make a comparison between starch, cellulose and glycogen Describe the functions of carbohydrates Describe the structure of glycerol, saturated and unsaturated fatty acids Describe the formation of ester linkages in fats Describe the structure of triglycerides and phospholipids, including their hydrophilic / hydrophobic nature Describe the structure of steroids Describe the functions of lipids Describe the generalised structure of amino acids and the functional group that gives the classes polar, non-polar, acidic and basic Describe the synthesis and relative strength of peptide bonds Describe the primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary structure in proteins, the types of bonds formed in each structure and the relative strength of these bonds Describe the functions of proteins Describe the structure of DNA and RNA Describe the function of polymerase and ligase Based on SQA arrangement document - 5th addition, published March 2004 Updated June 2006 Describe the fluid mosaic model of membrane structure Identify the types of membrane proteins and describe the functions they have Describe the composition of the cytoskeleton and describe its function Molecular interactions in cell events Describe the functions of different groups of enzymes including proteases, nucleases, ATPases and kinases Explain the specificity of an enzyme related to induced fit Describe the control of enzyme activity by competitive and non-competitive inhibitors, enzyme modulators and covalent modifications Explain the role of end-product inhibition in the control of metabolic pathways Explain the function and mechanism of a sodium-potassium pump Describe extracellular hydrophobic signalling as illustrated by steroid hormones Describe extracellular hydrophilic signalling as illustrated by peptide hormones and neurotransmitters Applications of DNA technology Describe the use of and techniques in genetic linkage mapping, physical mapping and DNA sequencing in sequencing the human genome Make comparisons between the human genome and genomes of other species Describe the techniques used to detect genetic disorders and the development of screening tests. Define gene therapy and describe some of the practical difficulties Describe the process of DNA profiling and identify its forensic use Describe the process of creating transgenic plants, using tomato plants as an example Explain some of the moral and ethical issues relating to the use of transgenics Describe the production of bovine somatotrophin (BST) by genetic engineering and its use in cattle Based on SQA arrangement document - 5th addition, published March 2004 Updated June 2006 Advanced Higher – Environmental Biology Can I: Circulation in ecosystems Describe energy fixation and explain how this relates to primary productivity and how primary productivity can be measured Describe the role producers, consumers/heterotrophs and decomposers have in energy flow in an ecosystem Define trophic levels and explain the transfer of energy between them and the efficiency of this transfer Explain the relationship between energy and pyramids of productivity, biomass and numbers Define decomposition and explain its importance in the ecosystem Describe some of the organisms involved in decomposition, the by products they create and the limiting factors Explain the importance of nutrient cycling in ecosystems Describe the chemical transformations in the nitrogen cycle and the organisms involved Describe the effect of water saturation and anaerobic conditions on nitrogen cycling Identify the limiting factor for productivity in aquatic ecosystems and the associated problems of enriching with this factor Interactions in ecosystems Define biotic and abiotic interactions, density-dependent and densityindependent factors and interspecific and intraspecific interactions Define predation Describe predator/prey population cycles and identify the factors that regulate them Explain the role of predators in reducing the population density of the prey species and the effect this has in the ecosystem Describe camouflage and warning colouration adopted by prey species and explain Batesian and Mullerian mimicry Describe the effects of grazing on plant communities and on diversity Define exploitation competition and interference competition Explain the concept of a fundamental niche and explain how and why it differs from a realised niche Identify, with examples, the damaging effects of exotic species Explain the importance of survival of some weak competitors Define parasitism and describe the difference between obligate parasites and facultative parasites Explain the need for stability in the parasite-host relationship Based on SQA arrangement document - 5th addition, published March 2004 Updated June 2006 Describe the methods of parasite transmission and parasite specificity as evidence of evolutionary adaptation Define commensalism and give some examples of this relationship Define mutualism and give some examples of this relationship Describe positive, negative and neutral interactions between species Describe the effects of host health and environmental factors in changing the balance in symbiotic relationships and explain how humans manage this Describe the tolerance and compensation mechanisms for coping with variation in the environmental conditions Describe patterns of growth, development and reproduction and their consequences for habitat and niche occupancy Define dormancy explaining the difference between predictive and consequential dormancy Describe some forms of dormancy and explain its importance to surviving environmental adversity Define homeostatic control in conformers and regulators, using osmoregulation and thermal control as examples Define the terms osmoconformer, osmoregulator, poikilotherm and homeotherm Explain the ability of regulators and conformers to occupy habitats Human Impact on the environment Define autogenic succession (primary and secondary succession), allogenic succession and degradative (heterotrophic) succession Describe the increase of complexity of ecosystems through succession and explain how this increase is shown Describe how complexity can be lost from an ecosystem using monoculture, eutrophocation, toxic pollution and oxygen depletion as examples Describe the effects of intensive food production Explain the finite nature of some of the worlds sources of energy and the need for conservation and the use of alternative sources Describe global warming and the greenhouse effect and its effects on the abundance and distribution of species e.g. zooxanthellae and coral bleaching Describe the effects of changes in the biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) and explain how this might occur Describe biological magnification in food chains using DDT and heavy metals as examples Based on SQA arrangement document - 5th addition, published March 2004 Updated June 2006 Advanced Higher – Biotechnology (optional module) Can I: Biotechnological Techniques Explain the requirements for growing culture, including obtaining pure cultures and growth conditions in laboratory culture and fermenters Describe the conditions needed to scale up from petri dish to full scale production Describe the stages of growth of microbes in culture and the calculation of growth rate constants Describe the measurement of growth using cell counts, dilution plating and turbidometric methods Describe diauxic growth and explain how it arises using the lac operon as an example Describe, with examples, the use of microbes in the production of enzymes Describe the procedure, conditions and limitations of culturing animal cells Describe the growth of explants and plant cell lines in a fermenter Describe protoplast isolation using cellulases and pectinases Describe the use of hybridisation to form new varieties of plants and the use of tissue culture in plant propagation Applications of biotechnological processes Describe the use of micro-organisms and enzymes in silage production Describe methods to enhance nitrogen fixing Describe the role of nutraceuticals in competing with pathogens, anti cancer activity, reducing blood cholesterol and improving lactose intolerance Describe the types of yeast extracts and their uses and explain the autolysis of yeast to produce a number of flavours Describe the use of cellulases, pectinases and amylases in the production of fruit drinks Describe the use of microbial fermentation and product recovery in the production of antibodies Explain the difference between bacteriastatic and bacteriacidal modes of antibiotic action Describe the preparation of polyclonal sera and its disadvantages. Describe monoclonal antibody production Describe the uses of monoclonal antibodies in the detection and treatment of disease and the diagnosis of pregnancy Based on SQA arrangement document - 5th addition, published March 2004 Updated June 2006 Advanced Higher – Animal Behaviour (optional) Can I: Measuring behaviour Describe some methods of observing animal behaviour Define the terms latency, frequency, duration and intensity Describe the need to be factual and objective when recording animal behaviour Define anthropomorphism and explain the problems associated with it Explain the difference between proximate and ultimate causes of behaviour using nest building by birds in spring as an example Development of Behaviour Describe the difference between innate and learned behaviour and the role each plays in the behaviour of vertebrates and invertebrates Explain the comparison between life span of an adult invertebrate with that of a primate and relate to time to learn behaviour Define imprinting and give examples Define sign stimuli and fixed action patterns and give examples using Stickleback behaviour and feeding of young by parent birds Describe the variation and consequent natural selection of behaviour patterns as illustrated by nest building in birds, shoaling in fish and herding in mammals Describe the single gene effect on behaviour Describe some behavioural adaptation to human influences Behavioural Interactions Describe predation strategies in solitary and co-operative hunting Describe the modification of behaviour to optimise gain and minimise energy expenditure in foraging behaviour Describe some defence strategies including mimicry, camouflage, crypsis, masquerading and disruptive camouflage/colouration, vigilance and escape responses Explain male versus female investment in terms of sperm and egg production, external and internal fertilisation and parental investment Describe courtship and display behaviours, including male-male rivalry and female choice Describe how inbreeding is avoided in social groups Define agonistic and appeasement behaviour and explain the advantages of this behaviour in the establishment of a social hierarchy Explain the concept of the selfish gene Define kin selection and reciprocal altruism Explain the social organisation in primates Based on SQA arrangement document - 5th addition, published March 2004 Updated June 2006 Advanced Higher – Physiology, Heath and Exercise (optional module) Can I: Exercise and the cardiovascular system Describe the components of the cardiovascular system and their functions Describe normal values for blood pressure, heart rate, stroke volume and cardiac output Describe the following cardiovascular diseases: atherosclerosis, thrombosis, angina pectoris, myocardial infarction, hypertension and stroke Describe the incidence of heart disease in the UK and compare this to the incidence in other countries Describe the risk factors in cardiovascular disease and explain which ones are able to be modified and which are non-modifiable Describe the effects of exercise on heart rate, systolic and diastolic blood pressure, cardiac output, recovery time and the distribution of blood to the tissues during exercise Define cardiac hypertrophy and explain how it is achieved and the advantages Describe protective effects of exercise Describe some tests of exercise levels and indicate their application to stress testing and cardiac patients rehabilitation Exercise and metabolism Identify the sources of food energy, describe what the energy is used for and the units it is measured in Describe energy balance and state how it can be calculated Explain the link between diet, coronary heart disease and obesity Define basal metabolic rate (BMR), describe the basic body processes associated with BMR and describe how it is measured Identify the factors affecting total energy expenditure Describe how energy expenditure is measured Describe methods for measuring body composition Explain the difference between being overweight related to large muscle or bone mass and that due to excess fat Explain the problem of rising incidence of obesity in the UK and possible causes and treatments for obesity Describe the role of exercise in weight control programmes Describe the effect of frequency, intensity, duration and the type of exercise on body composition and weight control Define osteoporosis and describe the effects on the bones and the groups of people it effects Describe the effects of exercise on bone mass and the advantages of this Describe the role of insulin and glucagons in the control of blood sugar levels Describe Non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) and describe the health condition it is normally associated with Describe the effect of exercise on NIDDM Based on SQA arrangement document - 5th addition, published March 2004 Updated June 2006