Carbon Cycle Redrawn - Northwest ISD Moodle
advertisement

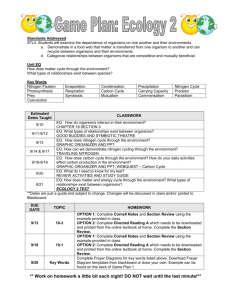
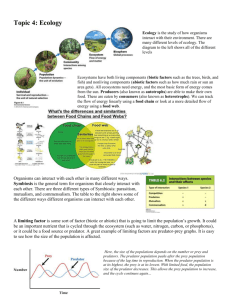
Biology I TEKS Student M EQ: Where do all the dead things go? Did dinosaurs drink my water? Ecology Cycles PPT Handout Targeted Skills models/diagrams, relationships, making generalizations, analyze, predict Enduring Understanding Energy and matter are transferred in the environment within and between organisms. Broad Brush Knowledge cycles, carbon-oxygen cycle, nitrogen cycle, water cycle Concepts Important to Know and Understand Element Cycles Core Objectives 4. Analyze the flow of elements in the carbon-oxygen, nitrogen, and water cycles. Matter Statement: _____________________________________________________________________ Define a Cycle: _______________________________________________________________________ WATER CYCLE ___ 1. evaporation a. water changing from a gas state into a liquid or solid state such as water vapor into rain, hail, sleet or snow ___ 2. condensation b. water gathering into an area such as in a pond, lake, stream or ocean ___ 3. precipitation c. ___ 4. transpiration d. water loss form plants as water vapor is lost into the air through stomates (little openings) in leaves ___ 5. runoff e. water changing from a liquid state to water vapor, a gas state ___ 6. accumulation f. water changing from a water vapor gas state to a liquid state such as water vapor into liquid drops on the cool surface of a glass water moving across a surface (water running into a stream then into the ocean) Why are water cycles said to be driven by the sun? ___________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ Use the vocabulary above to label the water cycle diagram. Ecology Cycles PPT Handout – TEKS Student M (Revised May 26, 2005) (printed 3/9/2016) p. 1 CARBON CYCLE How does carbon dioxide enter the living part of the Carbon Cycle? _________________________________________________________________________________ ___ 1. respiration a. CO2 is released back into the atmosphere as organic matter is broken down ___ 2. photosynthesis b. CO2 is released back into the atmosphere when food (glucose) is broken down ___ 3. decomposition c. CO2 is released back into the atmosphere when rock such as limestone containing CaCO3 (calcium carbonate) are broken down ___ 4. combustion d. CO2 is taken from the air and trapped into food (glucose) by plants ___ 5. erosion e. CO2 is released back into the atmosphere when organic material is burned Using the vocabulary above, label the diagram of the carbon cycle. Write a descriptive summary of the events in the animated carbon cycle diagram. ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ Ecology Cycles PPT Handout – TEKS Student M (Revised May 26, 2005) (printed 3/9/2016) p. 2 NITROGEN CYCLE How do we acquire usable nitrogen? ______________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ Why do we need nitrogen? ______________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ Can plants and animals use free nitrogen? _________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ In what form must N2 be to be used by plants? ______________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ What organisms can fix the N2 into a usable form? ___________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ Nitrogen Cycle Simplified ___ 1. free N2 “bank” a. the form of nitrogen that can be used by organisms ___ 2. nitrogen-fixation b. ___ 3. nitrates c. Dead organisms, animal waste and organic litter are decomposed by bacteria and other decomposers pure nitrogen, not in any other compound, found in the atmosphere ___ 4. organisms d. bacteria convert nitrates from decomposition back into free nitrogen. ___ 5. organic material e. ___ 6. denitrification f. Plants take in nitrates and use them in their tissues; animals eat the plants and get the nitrates from their tissues bacteria convert free nitrogen into nitrate compounds Label and write a brief description of the parts of the simplified nitrogen cycle diagram cycle. RIP Ecology Cycles PPT Handout – TEKS Student M (Revised May 26, 2005) (printed 3/9/2016) p. 3