Creative Writing Vocabulary Lists
advertisement

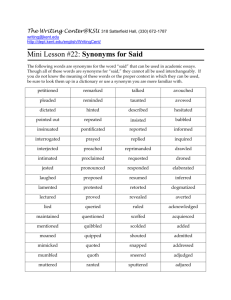
Creative Writing Vocabulary Lists Instructions: Write a story of your own creation using the vocabulary lists provided. Always use synonyms based on vocabulary words provided unless the word has no synonym. Requirements: These elements must appear and be followed strictly when submitting your story. Computerized format: Font 12 with Times New Roman 350-450 words (Maximum) Your name (left hand side of the page at the top). Date of submission (right hand side of the page at the top). Indicate below your name (skip a line), on the left hand side, the genre or genres that you are using to frame your story. You will have ten (10) vocabulary words and you must choose five (5) to tell your story. You may use all ten words but they must have impact in the story The list of vocabulary words with the synonyms you will be using to tell your story must appear at the end of the document. Find the synonyms in a thesaurus. Use the synonyms to tell your story. Do not use the dictionary meanings/definitions of the vocabulary words in your story. Do not use the examples you are given as phrases and insert them in the story. Make sure you write out the definition of the vocabulary word you are using at the end of your story. Identify the synonyms in the story with italics or bold. Finally, you must provide a word count of your story, which should appear below your story on the right hand side. You must, throughout the year, use all of the following genres at least once: Drama/Action Dear Diary Romance Dialogue/Monologue Magazine/Newspaper Article Science Fiction/Fantasy Fiction Scoring of your creative writing stories is completed in the following fashion: See attached rubric for scoring breakdown and parameters. Suggestions and Advice for writing creatively The value of a story is better served when you write a less creative piece of work with a storyline that is cleaner and more cohesive. Avoid grammar, spelling, and punctuation errors because those kinds of mistakes detract from the enjoyment of the story by the reader. Furthermore, mistakes force the reader to work harder to decode the gist or what you are trying to say with your story. As a consequence the marks for story cohesiveness tend to go down because the “sense” of the story is lost in a jumble of separate meanings. Focus on getting the story “right” first then work on the creative aspect. Write first, edit last. Do not edit while you are writing. Allow your story idea to live by writing it down right away, with as little interruptions as possible. 1 There should a clearly defined beginning, middle and end to your stories. Remember a short story can not normally have a well developed or clearly defined character (s) so you must get right into the story immediately or immediately develop your character. Major characters are also known as: main characters, protagonists, or round characters. Short stories tend to have fewer characters in them so you must introduce characters sparingly. Minor characters are also known as: secondary characters or flat characters. The Beginning of your story should contain some or all of the following elements: An introduction to a character, either through some kind of physical description or by the use of a narrator. Ex: He was an ugly guy—no one argued about that point. Introduce some kind of context or situation that involves the character. Ex: He woke up shivering, suddenly aware of the incredible wind blowing over his face, and his heart leapt into his throat as he felt hands push him out the door of the plane. “Oh, crap…,” he thought to himself. Introduce an idea, concept or musing by the character to the reader through voice. He wondered, vaguely, lying on his back staring at the sky, and floating far away from the incredible pain, How fast had that baseball bat been moving before it had hit him in the forehead? The Middle of your story is a further development of the idea, concept, character, or situation introduced in the beginning. The middle of the story is where the main action, development, or conflict takes place The middle of the story is also known as the ‘meat’ of the story. Give your reader something to bite into (my apologies to any vegetarians---this is only a well-known metaphor used for the purposes of explaining literature). The End of the story is the conclusion or resolution of the conflict, situation, concept, or idea that was introduced in the beginning, developed in the middle, and concluded at the end (the end of the story---also known as the denouement). Additional Advice on the most common problems in story telling: First, remember to break up your ideas into paragraphs. Each idea should get a separate paragraph. You have to decide what your story is about beyond the genre you’re using; what is the theme, the purpose of your story that will allow you to develop ideas that achieve that result (i.e.: the purpose behind the writing of the story) Second, use periods more often to break up run-on sentences. Periods have the effect of pacing a story. Run-on sentences are like someone who is out of breath and excited who is trying to tell you something and all their words come out in a disjointed rush. Third, don’t tell the reader what the story is about; show them through action, metaphor, imagery, dialogue (monologue), and the inner thoughts of the characters. The story should be revealed through these elements. Take your time and allow characters to come alive through their actions and expressions (both verbal and physical—on their face for example) Example: Don’t say: He was a mean person because he didn’t help the old lady up from the ground.. Say instead: Instead of helping the old lady up from the ground, he looked at her with a sneer of disgust, and walked past the injured woman. 2 Peer Editing/Writing We will be doing peer editing and writing starting in the third term. I will be pairing up students to compliment your strengths and weaknesses. Some of the activities will include: Exchange stories with your fellow students and either writing the prequel or sequel of their story. Peer editing each other’s work and then rewriting your own story. Literature circles, which will focus around groups of four of five students interpreting stories, poems, newspaper articles, etc., and then sharing those interpretations with the rest of the class. Or literature circles that will involve the entire class discussing and sharing interpretations and thoughts on a text or a video on relevant social issues. Vocabulary Lists 1-100 3 Vocabulary (1-10) Definitions 1) Infinite Without end; unbounded. 2) Gibe To speak reproachfully or sneeringly; to taunt; a jeer or a taunt. 3) Effrontery Unwarranted boldness of manner; impudence; audacity. 4) Meticulous Extremely careful of details; scrupulous. 5) Acerbate To embitter, vex, irritate. To make bad tasting. 6) Capacious Of large capacity; roomy; spacious. 7) Sordid Dirty; wretched; squalid; gross; ignoble. 8) Arduous Difficult; with great exertion or labour. 9) Hallowed Sacred, holy. 10) Acclimate To accustom or become accustomed to a new environment, situation or conditions. Vocabulary (11-20) Definitions 1) Guttural Rasping and gurgling; of the throat. 2) Deploy To send out or station more widely; to extend or spread out. 3) Peculiar Exclusive; significant of only one person or thing; odd or different. 4) Baneful Harmful, ruinous; threatening danger. 5) Foible A minor character weakness; a bland offense. 6) Opus A work, especially one of significance in music, literature, etc. 7) Lupine Wolf-like. 8) Pellucid Clear; easily understood. 9) Ancillary Of subordinate or auxiliary relationship. 10) Magnate A person of considerable rank, prestige, influence, etc. 4 Vocabulary (21-30) Definitions 1) Apposite Suitable, fit, appropriate. 2) Jubilant Full of triumphant joy; rejoicing. 3) Supplication An humble request. 4) Penchant A strong preference or liking. 5) Kiosk A small, open booth or stand. 6) Apprehensive Troubled, anxious, uneasy. 7) Ecology The science of relationships between living things and their environment. 8) Insular Severely bounded; narrow minded. 9) Misnomer An incorrect or inappropriate designation of someone or something. 10) Culinary Relating to cooking. Vocabulary (31-38) Definitions 1) Rhetorical Pertaining to the use of words artificially; said merely for effect rather than information. 2) Awry Turned aside; amiss; wrong. 3) Nonpareil Without rival or equal. 4) Impeach To discredit someone’s honour, character, etc.; to conduct a trial of a public official for wrongdoing in office. 5) Canard A deliberate untruth; a misleading report, so intended. 6) Candid Frank; open; forthright; unbiased. 7) Catharsis A purging or relieving of physical or emotional symptoms. 8) Catholic All-inclusive; universal; widespread. 9) ---------10) Obsessed Preoccupied; burdened in mind to the exclusion of other thoughts; haunted. 5 Vocabulary (41-50) Definitions 1) Quantum An elemental unit of energy. A measurable amount; a sufficiency. 2) Quatrain A verse or stanza of four lines. 3) Rabid Extremely angry; raging; fanatical. Afflicted with the disease of rabies. 4) Rankle To irritate; to cause or have deep-seated, smoldering anger, dislike, bitterness, etc. 5) Milieu A social environment or setting. 6) Militate To contend or operate against; to oppose. 7) Caucus A private meeting of members of a group or party to decide policy, select candidates, etc. 8) Mortify To injure one’s pride or dignity. To employ fasting or other selfdenial for spiritual strengthening. 9) Nadir Direct opposite of the highest point in space relative to the observer; figuratively, the lowest point of anything. 10) Naïve Simple and unaffected; artless; not sophisticated. Vocabulary (51-60) Definitions 1) Disconcerted Confused; upset; distracted; not unified. 2) Waive To relinquish; to forego; to not insist upon or claim; to temporarily defer. 3) Subsistence The means of maintaining a livelihood or existence, commonly, the barest means; the act or fact of existing. 4) Wary Cautious; watchful; suspecting and guarding against deception, danger, etc. 5) Xerography A quick reproduction process for printed matter, etc., using light and electrostatic charging. 6) Tremulous Shaking; trembling; timid; hesitant. 7) Zany Funny; crazy; silly; one with such characteristics. 6 8) Jocund Genial; cheerful; good natured. 9) Apathetic Without emotion; indifferent. 10) Surcease To be at an end; to leave off; an ending of or relief from. Vocabulary (61-70) Definitions 1) Maestro One who conducts an orchestra or other music group; one considered a master of his art. 2) Ravage To destroy with violence; to commit such destruction. The ruin resulting from violent attack. 3) Refute To oppose with proof of the opposite; to prove false or wrong. 4) Miniscule Very small; tiny. 5) Prudish Extremely or affectedly modest. 6) Puissant Mighty; forcible. 7) Annihilate To utterly destroy; to completely wipe out or crush, as an enemy, opponent, fortress, etc 8) Foist To cause acceptance of something false by slyly representing it as valid; to “palm off.” 9) Halyard A rope or tackle used for hoisting sails, flags, etc. 10) Harangue Blustering talk; long disconnected or boring speech; talk in such a manner. Vocabulary (71-80) Definitions 1) Hegemony Dominion, rulership---especially of one country or one ruler over another. 2) Larcenous Intending to commit theft; thieving. 3) Predatory Hunting to kill and devour; living by vandalism. 4) Ultimatum A final demand or proposal. 5) Tandem Positioned one behind the other. A team of horses so harnessed or a carriage drawn by such a team. 7 6) Vegetate To become inactive and useless. 7) Axiomatic Having obvious truth; self-evident. 8) Misconstrue To interpret incorrectly. 9) Compatible Agreeable; suitable; combining well; getting along well together. 10) Aggregate A total or whole made up of distinct things. To gather into a mass or body. Vocabulary (81-90) Definitions 1) Waggish Frolicsome; comical; mischievously, humourous, slyly joking. 2) Benevolent Disposed to do good; kind; charitable. 3) Bibliophile One who loves books; an appreciative collector of books. 4) Bereft Deprived of; stripped away; made destitute---especially with great emotional significance. 5) Unconscionable Unthinkably excessive; completely unreasonable; unguided or unrestrained by conscience. 6) Quandary Puzzlement; uncertainty; dilemma. 7) Narcissism Love of oneself; obvious, pronounced self-esteem. 8) Impetuous Acting hastily without due consideration. 9) Implacable Not to be appeased, thwarted, dissuaded; relentless. 10) Abdicate To formally give up a right or position. Vocabulary (91-100) Definitions 1) Quandom Formerly; former. 2) Blasé Bored with pleasure; over full and tired by excess of enjoyment. 3) Boisterous Violent, turbulent; loudly exuberant. 4) Bombastic Pompous; high sounding. 5) Cant The specialized vocabulary of a certain occupation; argot; pretended piousness in speech; to speak in such a manner. 8 6) Ursine Like a bear; of great bulk and strength. 7) Knack Ability to do something with ease; dexterity. 8) Dissertation An elaborate speech; a formal presentation, spoken or written. 9) Bowdlerize To delete personally offensive words or passages; expurgate. 10) Nascent At the inception; beginning to emerge or grow. Term 4 Vocabulary Lists Vocabulary (101-110) 1) Qualm A misgiving; a doubt; a pang of conscience 2) Unscathed Unharmed; not injured. 3) Brusque Abrupt, curt, rough --- in speech or manner. 4) Knell An evil omen; to sound or portend ominously. 5) Bucolic Of the countryside; pastoral; rustic. 6) Factious That which produces division, dissension. 7) Cabal A group of people engaged in intrigue; a faction or junta 8) Cache A secret place for hiding supplies, food, etc… 9) Cairn A heap of stones marking some special site. 10) Surfeit Too much of something; overindulgence. Vocabulary (111-120) 1) Objurgate To reprove or rebuke. 2) Ecumenical Universal; general; fostering unity. 3) Apiary A place where bees are kept and tended. 4) Zealous Very devoted and purposeful; fervent. 5) Apocalyptic Relating to a revelation; containing forsight. 9 6) Apostasy Abandonment of a faith or a dedication to basic beliefs. 7) Auspices Patronage; sponsorship; influence. 8) Pantheism The doctrine that all phenomena, forces, etc. of the whole universe are God. 9) Codicil A supplementary statement, especially as in a will. 10) Eclectic Chosen or selected from various sources; selective. Vocabulary (121-130) 1) Horology The science of time measurement. 2) Dissimulate To mask or confuse by false appearance; feign; pretend. 3) Hortatory That which exhorts or consists of advice. 4) Unkempt Slovenly; not tidy. 5) Annular Ring-shaped; forming a ring. 6) Pre-empt To take the place of something else; to replace unexpectedly. 7) Obscure Unclear; vague; not well known; hidden; dark. 8) Subtlety A keen, crafty or skilful and delicate action or statement. 9) Huckster A peddler; one who is loud, persistent, overbearing in selling. 10) Hysteria Emotional excess. Vocabulary (131-140) 1) Hustings The process of campaigning. 2) Edify To enlighten; to instruct; to increase awareness. 3) Quagmire Treacherously soft, miry, boggy ground. 4) Hymeneal Pertaining to marriage or weddings. 5) Icon A venerated stature or picture 10 6) Idiom Regional or class dialect; an individual style of expression which characterizes a person. 7) Append To attach; add to. 8) Idyllic Simple and pleasing, especially in connection with rural and domestic life. 9) Jeremiad A doleful speech or story; a woeful tale. 10) Rote A fixed or inflexible way of doing something; memorization. Vocabulary (141-150) 1) Saccharine Sugary; overly sweet; affectedly sweet in manner or expression. 2) Impromptu Without deliberation, preparation or forethought; unrehearsed. 3) Quaff To drink deeply with enjoyment; such a drinking. 4) Scrutiny A very intense examination; a lengthy of penetrating look. 5) Saga A long story of heroes and heroism. 6) Scourge To whip or otherwise punish severely. A whip or punishing device or action. 7) Kine Cattle; cows. 8) Timbre The quality of sound that characterizes different voices or instruments. 9) Dissipate To disperse, scatter, make to disappear; to squander or waste. 10) Natal Pertaining to one’s birth. 11