GLOSSARY of Terms for IED
advertisement

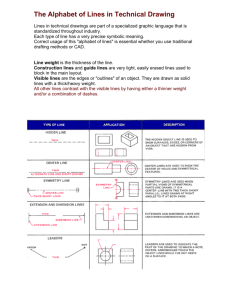
GLOSSARY of Terms for IED GLOSSARY of Terms for IED 35mm Slide: A standard slide format from 35mm film. A.A.S.: Associate in Applied Sciences degree Adaptive Part: Parts created in place and parts placed from part files can both be defined as adaptive. Adaptive parts have under constrained features that resize according to their placement in an assembly. Features designated as adaptive in the part file can change size and shape when constrained to fixed geometry in an assembly. Absolute Coordinates: A method of plotting points whereby distances are measured from the origin. Absorption: Ability of a substance to reduce the intensity of light radiation by converting the energy into another form. Acute Angle: An angle less than 90 degrees. Adaptive Design: An existing part can be defined adaptive within the assembly, thus allowing its features to resize and change shape when one constrains them to other components. Adaptive Feature: A feature that can resize when constrained to other features. Features are usually constrained to a specified size, unless they are designated as adaptive: a part that is not constrained to a specified size or shape. Additive: Creating a three-dimensional shape by adding additional shapes/mass to the model. Aesthetic: Designing products with an artistic flair and its forms and effects to influence consumers’ choice when purchasing products. Aligned Dimensioning: Dimensioning technique that requires all numerals, figures, and notes be aligned with the dimension lines so that they may be read from the bottom and from the right side of the sheet. Project Lead The Way, Inc. Copyright 2000 Clifton Park, NY Introduction to Engineering Design National Alliance for Pre-Engineering Program Page 1 of 30 GLOSSARY of Terms for IED Allowance: The difference between the maximum and minimum material conditions. Analysis: The detailed examination of something in order to understand it better or draw conclusions from it. Angle: The figure formed by the intersection of two lines at a point. Angle Constraint: The angle constraint positions, edges, or planar faces on two components at a specified angle to define a pivot point. Removes one degree of angular rotation. Angular Dimensioning Method: Dimensioning method used for angular surfaces in which one linear dimension is given to locate one of the endpoints of the angle, and an angular measurement is also given. Annotated Sketch: A detailed sketch that is labeled with critical dimensions, notes and symbols. Annotate: A note added to a text or document to clarify or explain further. Annotating: Process of adding notes and dimensions to a model or drawing. ANSI (American National Standards Institute): Establishes the standards for drafting in the United States. Arc: A part of a circle. Architecture: The science and art of planning for the building structures. Artifact: An artifact is an historical object, relic, manufactured article, or a work of art. Artistic: Work done skillfully and tastefully. Assembly Browser: The browser presents the content of an assembly in a hierarchy. Components are listed in the order in which they are placed in the assembly. Assembly Constraint: Removes the degrees of freedom between two selected components, positioning them relative to one another. Project Lead The Way, Inc. Copyright 2000 Clifton Park, NY Introduction to Engineering Design National Alliance for Pre-Engineering Program Page 2 of 30 GLOSSARY of Terms for IED Assembly Model: A model made up of two or more components that have been constrained together. Automation: An apparatus that works or moves by responding to preset controls or computerized instruction. Auxiliary View: A view that is used to show the detail of a surface when it is not parallel to one of the principle planes of projection. The auxiliary projection plane is parallel to the inclined surface of the object, and represents features on the surface in true shape and true size. AVI (Advanced Visual Interface): A standard file format for audio/visual clips. Axis: Primary direction in a coordinate system. Axonometric: A drawing only partially to scale, used to describe a method of drawing a three-dimensional object so that the vertical and horizontal axes are drawn to scale, but the curves and diagonals appear distorted. Balance: Balance is a Principle of Design. Pleasing harmony of various elements in a product, print media, or art form. Bar Graph: A graph that uses lines or bars that are horizontal or vertical to represent a quantity. Base Component: The first component placed in an assembly should be a fundamental part or sub-assembly, such as a frame or base plate, on which the rest of the assembly is built. Bisector: A plane, line, or ray that cuts an angle into two equal parts. Blister Pack: Type of package that has a thin material backing and a vacuum sealed piece of clear plastic covering the product. Brainstorming: A method of generating creative ideas spontaneously, usually for problem-solving, and especially in an intensive group discussion that does not allow time for reflection. Project Lead The Way, Inc. Copyright 2000 Clifton Park, NY Introduction to Engineering Design National Alliance for Pre-Engineering Program Page 3 of 30 GLOSSARY of Terms for IED Browser Editing: A function within Autodesk Inventor which allows one to edit the history of the design. Browser Hierarchy: In Autodesk Inventor, the browser contents correspond to the current assembly file. The hierarchy beneath the top-level assembly can expand to show the parts and sub-assemblies placed in the assembly. If additional detail is available below an entry in the assembly browser, it is indicated by a plus sign. For a sub-assembly, parts and other sub-assemblies are listed. For a part, features are listed. Just click the plus sign to expand the entry. There is no limit to the levels of nesting in the browser. One can use the scroll bars on the side and bottom of the browser window to view additional detail. B.S.: Bachelor of Science degree Career: A profession or occupation that one trains for and pursues as a life work. Career Clusters: Groups of occupational titles in related fields. Cartesian Coordinate System: A rectangular coordinate system created by three perpendicular axes labeled X, Y, and Z. Center Line: A line consisting of a long dash followed by a short dash, that is used to show and locate the centers of arcs and circles, and to describe the center axis of a cylindrical form. Center Point: The origin of a circle or arc. Centroid: A three-dimensional point defining the geometric center of a solid. Certification Exam: An examination that certifies one for a certain discipline. Chain Dimensioning: Method of dimensioning from one feature to the next. Also known as point-to-point dimensioning. Project Lead The Way, Inc. Copyright 2000 Clifton Park, NY Introduction to Engineering Design National Alliance for Pre-Engineering Program Page 4 of 30 GLOSSARY of Terms for IED Chamfer: A slight surface angle used on the sharp edges of a product. Chart: A diagram that shows the relationship between two or more numerical quantities, such as the age and average height of an individual. Chord: A straight line with opposite ends that terminate on the circumference of a circle. Chronological: List of events or items in their order of occurrence. Circle: A closed curve with coplanar points at the same distance from the center point. Circumference: The distance around the outside of the circle. Circumscribed: A shape drawn around a circle. Clearance Fit: An allowable gap between two mating points. Closed Loop System: A control system that uses feedback to maintain a desired output. Coincident: Two points fixed together. Collinear: Lines or points belonging to the same line or an extension of that line. Collision Detection: The checking for interference among components. If interference is detected, an interference solid is temporarily created to illustrate where the interference occurs. One can then modify components to eliminate the interference; also, one can use the information from the interference analysis to modify components to eliminate the interference. Color: The aspect of objects and light sources that may be described in terms of hue, lightness, and saturation for objects and hue, brightness, and saturation for light sources. Complementary Angle: Two angles added together equaling 90 degrees. Project Lead The Way, Inc. Copyright 2000 Clifton Park, NY Introduction to Engineering Design National Alliance for Pre-Engineering Program Page 5 of 30 GLOSSARY of Terms for IED Component Finder: In very large assemblies, it is easy to lose track of objects. The component finder function can quickly locate parts both in the browser and the graphics window. Component: A part of a total manufactured item. Components can be an individual piece or a sub-assembly of the total product. Computer Integrated Manufacturing (CIM): This is a process in which computers are utilized in all phases of manufacturing. All departments in a manufacturing environment have control of information related to a project between itself and other departments immediately upstream or downstream in the process flow. As an example, the use of computers to design parts and produce computer numerical control code to control machine operations, and the storage of large quantities of data related to a part or product increases production and decreases cost is a small portion of this area. Computer Numerical Control (CNC): A numerical control method in which one computer is linked with a machine tool to perform a machining operation. Numerical code, controlling the X, Y, and Z axes of a machine, are generated by a computer to represent a contour of an object. A piece of raw material is inserted into a machine and the machine is activated. The numerical code guides the precise path of cutter to generate an exact copy of the original design without flaw. Concentric: Arcs and circles sharing the same centers. Concurrent Engineering: The process of involving all branches of manufacturing in the initial design pf a product. This method of design shortens the manufacturing cycle because all departmental needs have been considered and there is no need for redesign at any stage of manufacture. Constrained Move: A constrained move honors previously applied constraints. That is, the selected component and parts constrained move together in their constrained positions. A Project Lead The Way, Inc. Copyright 2000 Clifton Park, NY Introduction to Engineering Design National Alliance for Pre-Engineering Program Page 6 of 30 GLOSSARY of Terms for IED grounded component remains grounded at the new location. Components constrained to the grounded component remain in their constrained positions at the new location. Constraint: Rules that govern the position and relationships among sketch geometry or the relationships between parts in an assembly. Contour: An outline, especially of something curved or irregular. Converge: In a perspective drawing, the effect when parallel lines appear to come together in the distance. Coordinate Dimensioning Method: Dimensioning method used for angular surfaces in which two linear dimensions are given to locate the endpoints of the angle. Coordinate System: Fixed system that incorporates an origin and associated axes to define the position of objects in space. Coplanar: Belonging to the same plane. Copy: One can copy and paste features within a part file or between open part files using the Windows clipboard. One can paste only in the part modeling environment. Copying and pasting is similar to creating and placing a design element with these differences. The paste command allows dependent features to be copied as well. Newly copied features are fully independent, unlike design elements. If pattern features are copied and pasted, then the parent feature is also pasted. Core Subjects: Required courses that form the bas of one’s discipline. Cost Analysis: A process of collecting data in a manufacturing environment to determine the cost of manufacturing a product. This includes the design phase, purchasing equipment and materials, production of the product, packaging, etc. Counterbore: An enlarged drilled area used to accept the head of a bolt so that the head of the bolt is recessed below the surface of the material. Project Lead The Way, Inc. Copyright 2000 Clifton Park, NY Introduction to Engineering Design National Alliance for Pre-Engineering Program Page 7 of 30 GLOSSARY of Terms for IED Countersink: Used to recess the tapered head of a fastener below the surface of the material. Create: This function allows the creation of in-place parts in assembly. Creativity: Creativity is a Principle of Design. Being imaginative or inventive. Cutting Plane Line: A broken line that is used to indicate where an object has been sectioned. The orientation of the arrows on a cutting plane line indicates the direction in which the section is being viewed. Dark: Devoid, or partially devoid, of light. Not reflecting. Datum Dimensioning: Common dimensioning method where each feature dimension originates from a common axis, surface, or center plane. Defects: The non-conforming parts or components produced during manufacturing, which includes the cost of raw materials, scrapped materials and parts, rework materials and labor, and labor idled by defect-caused production slowdowns. Degrees of Freedom: Each component in an assembly has six degrees of freedom. It can move along X, Y, and Z axes (translational freedom) and it can rotate around the X, Y, and Z axes (rotational freedom). When you place a constraint between two pieces of geometry, you remove one or more degrees of freedom. Movement is still possible in the unconstrained directions. Density: The mass per unit volume of an object. Design Elements: The factors, including lines, form, color, light, shadow, space, textures, etc., that define the product. These take into considerations the aesthetics and function in the development of a product. Design for Manufacture (DFM): Keeping available manufacturing methods and techniques in mind when designing a product or part. Project Lead The Way, Inc. Copyright 2000 Clifton Park, NY Introduction to Engineering Design National Alliance for Pre-Engineering Program Page 8 of 30 GLOSSARY of Terms for IED Design Principles: Ten underlying considerations that lead to an interesting design. Design View: A design view preserves an assembly display configuration which you can recall by name when you next work on the assembly. One advantage of using a design view is that you can turn off visibility of components you do not need to see and then save that view with a design view name. When you reload the design view, only the components you need are displayed. Detail: Shape or feature on a model. Detail View: A view that magnifies, or scales up, a feature on the drawing object that is small relative to the total size of the part. Dimetric: A drawing projected so that the plane of projection of a three-dimensional drawing is at an equal angle to two of the three axes of the object. Diagonal: A line that is slanting or oblique. Diameter: The straight distance from one outside curved surface through the center point to the opposite outside curved surface. The diameter is the longest chord in the circle. Dimension Line: Thin line segment capped on the ends with arrowheads that indicate the length of the dimension. Dimension: Numerical value used on a drawing to describe location, size, shape, or geometric characteristic. Dimensioning: The process of placing measurements and notes on a drawing to completely communicate its meaning. Diminution: Objects further away appear smaller. Drag and Drop Component: Drag and drop can be used to place multiple components in an assembly. The dropped components will appear at the bottom of the browser. Drive Constraint: The simulation of mechanical motion by moving a constraint through a sequence of steps. For example, Project Lead The Way, Inc. Copyright 2000 Clifton Park, NY Introduction to Engineering Design National Alliance for Pre-Engineering Program Page 9 of 30 GLOSSARY of Terms for IED you can rotate a component by driving an angular constraint from zero to 360 degrees. Durability: The ability of a product to withstand abuse and still meet the design requirements. For a package, it is the ability to protect a product from factory to market and from market to consumer. Edge: The line where two surfaces or points intersect. Editing Constraints: The following constraints can be edited in the browser: offset, angle, selected components, and direction. Ellipse: The group or set of all points in the same plane whose sum of distances from two points (foci) is constant. An ellipse looks like a squashed circle or a circle viewed at an angle. Emphasis: Emphasis is a Principle of Design. Points of attention in a design. The feature in a design that attracts one’s eye. Employment Trend: An analysis of the future demand in various careers/professions based on past/present job opportunities. Engineering: The profession that involves the complex analysis, design, and development of solutions to technical problems. Engineering Notebook: An engineering notebook contains proper documentation so that ideas are not lost and projects can be duplicated. Proper documentation in a notebook includes sketches made with notes as well as dimensions documented. Each drawing in an engineering notebook should have a sketch, design details, size requirements, a title, author’s initials, and the date. Equilateral Triangle: A triangle having all angles equal and all sides have equal lengths. Essence: The quality or nature of something that identifies it or makes it what it is. Esteem: Have a favorable opinion of, or regard highly. Project Lead The Way, Inc. Copyright 2000 Clifton Park, NY Introduction to Engineering Design National Alliance for Pre-Engineering Program Page 10 of 30 GLOSSARY of Terms for IED Ethical: Having to do with standards of right and wrong. Ethics: The study of standards of right or wrong; that part of science and philosophy dealing with moral conduct, duty, and judgment. Evolution: Changes that occur over a period of time that involve such things as the adaptation of living things to their environment or a process of improving the design of products. Extension Line: Thin lines used to establish the extent of a dimension. External Component: A part has been created as a separate part file outside of the current assembly model. Extruded Feature: A feature created by adding depth to a sketched profile. The feature’s shape, extent, and taper angle control the shape. An extruded feature can be defined by selecting a Boolean operation (join, cut, or intersect with existing feature.). Fillets: A curved surface formed at the interior intersection of two or more surfaces of an object. Feature: Any physical portion of an object, such as a hole or fillet. Fillet Feature: An arc of a specified radius placed at the corner or intersection of two lines. Its type, radius, and placement define a fillet feature. Finance: A branch of industry that determines how much a product will cost. These include, but are not limited to, direct and indirect materials, labor, processes, equipment, tooling, inventory storage, handling losses, spoilage, interest, and tax cost. This department is also responsible to determine overhead costs that must be assigned and the total manufacturing cost determined. Fit: To have the proper size or shape for a particular figure, space, etc. Project Lead The Way, Inc. Copyright 2000 Clifton Park, NY Introduction to Engineering Design National Alliance for Pre-Engineering Program Page 11 of 30 GLOSSARY of Terms for IED Fixed Point: Locking a point to a position relative to the sketch coordinate system. Flexible Manufacturing System (FMS): A group or cluster of manufacturing machines connected by an automated material handling system and operated by a dedicated computer controller. Flush: The flush constraint aligns components adjacent to one another with faces flush. Positions selected faces, curves, or points so that they are aligned with surface normals pointing in the same direction. Form: The shape of a material. Formal Balance: To be symmetrical. Graphics and text are centered on the media. Formula: A set of algebraic symbols expressing a mathematical fact, rule, etc. Fragility: The degree of susceptibility or fragility a product is to damage. Freehand: Done without the use of tools or drawing equipment. Function: The way in which an object is used in a given process. Futuristic: Dealing with events that haven’t occurred yet. General Note: Note that applies to the entire part and/or drawing. General Specifications: Additional information provided in a separate document that further explains information on the working drawings. Geometric Constraints: Defined relationships between features, such as lines, arcs, and surfaces; e.g., defining two surfaces to be parallel, or defining an arc and a line to be tangent. Gesture Study: A sketch that captures the essence of shape. Project Lead The Way, Inc. Copyright 2000 Clifton Park, NY Introduction to Engineering Design National Alliance for Pre-Engineering Program Page 12 of 30 GLOSSARY of Terms for IED Graph: A visual representation that shows the relationship between certain sets of numbers. Graphic Organizer: A tool used to arrange thoughts and ideas in an orderly fashion. Graphics: Any form of visual artistic representation used to enhance printed information, logos, pictures, clip art, etc. Grid: A pattern of uniformly placed horizontal and vertical lines used to locate points. Ground Line: In a perspective drawing, the plane where objects appear to rest. Grounded Component: The first component placed in an assembly should be a fundamental part or sub-assembly, such as a frame or base plate, on which the rest of the assembly is built. Hatch Marks: A series of lines or symbols used in a section view that show where the material has been cut by the cutting plane line. Hatch mark styles can be used to indicate the type of material the object is made from. Helix: A point, which moves around and along the surface of a cylinder uniformly in a linear direction, along an axis. An example of this is a screw thread on a bolt. Hexagon: A polygon with six sides. Hole: A geometric shape defined by hole type, placement size, and dimensions. A hole requires a center point sketch for its origin and placement. Hole Note: Contains information about the diameter, depth, and type of hole being used. Horizontal: A line parallel to the horizon. Horizon Lines: In a perspective drawing, the imaginary line at eye level used as a construction line. HTML (Hypertext Markup Language): A standard language used in authoring web pages. Project Lead The Way, Inc. Copyright 2000 Clifton Park, NY Introduction to Engineering Design National Alliance for Pre-Engineering Program Page 13 of 30 GLOSSARY of Terms for IED Hue: The gradation of color. The attribute of colors that permits them to be classed as red, yellow, green, blue, or an intermediate color between any contiguous pair of these colors. Icons: Symbols used to represent an operation or function. Ideation Drawings: Sketches and drawings used in the formation of ideas. Ideation Sketching: A rapid technique of sketching to capture and develop ideas. A way to record ideas from the “mind’s eye” to a graphic form of communication. Informal Balance: Informal balance is a Principle of Design. Not symmetrical, but balanced visually. Innovation: New and unique application, concept, or product. Inscribed: A shape drawn inside a circle. Insert: This constraint selects geometry on two components to constrain together. You can specify one or more curves, planes, or points to define how pieces fit together. Integrity: A condition of being complete or whole. For a product, it would be a condition of being sound and in an unimpaired condition. For a person, integrity is the condition of being honest and sincere. Interference: In an assembly, two or more components cannot occupy the same space at the same time. To detect such errors, one can analyze assemblies for interference. Where components overlap, interference is temporarily displayed as a solid. Interference Fit: Also known as force or shrink fit. Interference fit exists when mating parts must be pressed together. For example, when a bushing must be pressed onto a housing. Internal Component: A part has been created as a separate part file inside of the current assembly model. Project Lead The Way, Inc. Copyright 2000 Clifton Park, NY Introduction to Engineering Design National Alliance for Pre-Engineering Program Page 14 of 30 GLOSSARY of Terms for IED Intonation: The manner of applying pitch to a sentence or phrase. Line: The path of an infinite series of points. A line has length, but not width or thickness. Invention: A making something new, such as the invention of a tool. Inventory: An itemized list of parts, materials, and products. ISO (International Standards Organization): The organization which sets the international standard for manufacturing. Isometric: A drawing projected so that the plane of projection of a three-dimensional drawing forms equal angles (120 degrees) to each of the three axes of the object. Isometric Axis: The axis representing height, width, and depth for an isometric drawing. Isometric View: A form of pictorial drawing that is used to show several faces of an object at once, approximately as they appear to the observer. An isometric drawing is not true shape nor true size. The sides of an isometric drawing are projected back at an angle of 30 degrees relative to the horizontal axis. Isosceles Triangle: A triangle that has two sides of equal length and two equal interior angles. Jinks Method: A form of modeling, which uses square dowels connected by gluing reinforcing gussets of index card stock. Journal: A publication appearing regularly and containing articles, findings, editorial commentaries, etc. Journals are primarily published by professional organizations. Just in Time (JIT): A process in which a company orders raw materials, pre-made parts, or sub-assemblies to be delivered to the plant as they are required. This eliminates the need for storage space and handling is kept to a minimum. Inventory is scheduled to arrive to operations and assembly at the time they are needed and not before. Project Lead The Way, Inc. Copyright 2000 Clifton Park, NY Introduction to Engineering Design National Alliance for Pre-Engineering Program Page 15 of 30 GLOSSARY of Terms for IED Keyseats: Slotted openings in shafts that accept keys. Lateral Thinking (LT): Creative thinking; the ability to look at a given situation or problem in a nontraditional way. Also known as divergent thinking. Light: A quality of brightness. Line Graph: A diagram, or a visual representation, using a broken line to show the relationship between certain sets of numbers. Line Segment: A portion of a line that is defined by two points. Loft Feature: A loft feature blends two or more non-similar shapes on non-intersecting planes. Tangency condition, termination, and order of sketches are some of the sketched features that specify a loft. Mock-Up: A physical model constructed from inexpensive materials intended to represent a design and analyze a design concept, commonly called appearance models. This model is constructed proportionally correct but no normally to scale. Line Weight: The width and darkness of a line. Local Note: Information about a particular feature. Location: The relative position of one part in relationship to the entire model. Location Dimension: Dimension on a drawing that indicates the position of a feature or geometric shape in relationship to another feature, geometric shape, edge or center. Manufacturing: The total process of design, application, and production. This involves the making of goods by hand or by machinery, often on a large scale, and with a division of labor. Marketing: 1) A method of involving the consumer in the evaluation of a product to determine/evaluate the salability of a product. 2) A branch of industry that seeks out and evaluates the needs of the consumer. Marketers must determine the size of the market, what functions the product Project Lead The Way, Inc. Copyright 2000 Clifton Park, NY Introduction to Engineering Design National Alliance for Pre-Engineering Program Page 16 of 30 GLOSSARY of Terms for IED needs to accomplish, and the selling cost. They must also determine the life of the product, serviceability, reliability, and the annual production. Mass: The property of an object that is a measure of its inertia, the amount of matter it contains, and its influence in a gravitational field. M.S.: Master of Science degree Mate: This constraint position selects faces normal to one another with faces coincident. Materials: Matter that occupies space. Maximum and Minimum Conditions: The condition of a part or feature when it contains the most or least amount of material and is still considered acceptable. Mechanical: A form of energy that uses motion to do work. Model: A two- or three-dimensional representation of an object. A model represents a wireframe, hidden edge, or shaded display. Moments of Inertia: An object’s opposition to changing its motion about an axis. Move: The move component button on the assembly toolbar will allow the dragging of individual components in any linear direction in the viewing plane. Negative Space: Created by the boundaries of space within an object. Object: Something visible or tangible. Object Line: Slightly lighter than a profile line, used to add all details to a sketch. Oblique: A form of pictorial sketch in which two axes are at right angles to each other (one vertical, one horizontal) and the depth axis is at an oblique angle. Obtuse Angle: An angle greater than 90 degrees. Octagon: A polygon with eight sides. Project Lead The Way, Inc. Copyright 2000 Clifton Park, NY Introduction to Engineering Design National Alliance for Pre-Engineering Program Page 17 of 30 GLOSSARY of Terms for IED One Point Perspective: A perspective drawing using one vanishing point. Opposition: Opposition is a Principle of Design. The use of long and short, thick and thin, and black and white objects in a design. Offset Section: The cutting plane is offset through staggered interior features of an object to show those features in section as if they were in the same plane. Open Loop System: A control process which operates without knowledge of the actual output (i.e., the output is dependent only on the input). Order of Views: The relationship between the views in orthographic projection. Organizations: A group of individuals joined for some common purpose. Origin: The point at which axes intersect. Orthographic: Right angle projection. The views of an object are drawn in perpendicular planes to one another. Orthographic Projection: A multi-view drawing of an object, where each view represents two dimensions, and the observer’s viewpoint is perpendicular to the drawing plane. The standard orthographic projection consists of a front, top, and right-side view. Overhead: The continuing cost of running a business. For example, rent, utilities, maintenance, etc. Packaging: Material(s) used to protect a product during shipping and/or materials used to contain a product for display and sale. Palletized: Term used to describe the neat stacking of cartons in preparation for shipment. Cartons are stacked on platforms called pallets. Panel Bar: The panel bar contains current command icons or command names depending on how it is configured. Project Lead The Way, Inc. Copyright 2000 Clifton Park, NY Introduction to Engineering Design National Alliance for Pre-Engineering Program Page 18 of 30 GLOSSARY of Terms for IED Parallel: Two or more lines having equal distance between them. Parametric Sketch: A sketch that can be driven by its geometry. Pencil Types: Measured by the softness of the lead. Parametric: Geometric relationships used to define a sketch. Used to allow a sketch to change shape or size in relationship to other features. Part Library: A collection of pre-drawn, commonly used items, such as fasteners, springs, bearings, gears, shafts, cams, and pulleys that can be inserted into an assembly. Part Manipulation: Consists of moving, rotating, copying, and replacing components. Pattern: A regular or repeated design, form, order or arrangement. Duplicates one or more components and arranges the resulting occurrences in a circular or rectangular pattern. Pattern Feature: Multiple instances of a sketched feature arrayed in a specified pattern. Patterns are defined by type (rectangular or circular), orientation, number of features, and spacing between features. Pattern Layout: Type of drawing that is commonly used in the design of cartons and boxes. The product is drawn out and then produced on a flat piece of stock then creased and folded to create the carton or box. Patterning Component: This function duplicates one or more components and arranges the resulting occurrences in a circular or rectangular pattern. Pentagon: A polygon with five sides. Perpendicular: Two lines forming a 90 degree angle. Perspective: A view of an object created with one or more points vanishing to the horizon. Ph.D.: Doctor of Philosophy degree Project Lead The Way, Inc. Copyright 2000 Clifton Park, NY Introduction to Engineering Design National Alliance for Pre-Engineering Program Page 19 of 30 GLOSSARY of Terms for IED PHANTOM LINES Phantom lines are used most frequently to indicate an alternate position of a moving part, as shown in the left-hand view of figure 3-36 Physical Plant: A building that provides space for all functions a company needs to conduct business. Company requirements may dictate that existing buildings are not practical for their use and require that a new building be built to house a process or product line. Pictograph: A graph that uses small pictures or symbols to represent a certain quantity following the format of a bar graph. Picture Plane: In a perspective drawing, it is the plane of projection. Pie Graph: A chart or diagram that is useful for representing percentages; a pie represents the entire percentage (100), so a particular slice can represent a portion of the whole. Plagiarize: To take or use ideas, writings, etc., without giving credit. Point: An exact location in space. The exact point in space is where the two lines of the grid intersect. Polar: A method of plotting points whereby distances are measured using angles. Polar Dimensioning: Angular dimensions used to locate features from centerlines or planes. Polygon: A closed plane figure with three or more straight sides. Portfolio: A record of history and important events, samples of best work, and evidence of original work. Posture: The position of the body. Poster Board: A visual aid used in presentations commonly constructed by placing images and text on heavy construction paper or foam board. Primary Color: Any one of the three basic colors of the spectrum, red, yellow, or blue, from which all other colors can Project Lead The Way, Inc. Copyright 2000 Clifton Park, NY Introduction to Engineering Design National Alliance for Pre-Engineering Program Page 20 of 30 GLOSSARY of Terms for IED be blended. Any one of the three basic colors cyan, magenta, or yellow, which when subtracted from white can produce all other colors. Principal Moments: Moments of inertia related to the principal axes of the part. Process: A series of changes, or a number of steps, which transform an object. This can be as drastic as raw materials being developed into a part, or as minor as a part receiving a protective coating. Process Route: A fixed order of procedures that a component takes in order to be completed. The order is sequential in nature and is usually designed by an industrial engineer to be the most efficient and cost effective method of producing that component. Products of Inertia: An object’s opposition to changing its motion about two axes. Professional Societies: Organizations or groups of specially educated, trained, and/or licensed occupational fields. Profile Line: In sketching, a dark heavy line that outlines the object drawn. Prototype: A full size, functional, working model of a design that is completed before a part is manufactured, which allows the object to be tested and analyzed before production begins. Project Geometry Tool: Projected geometry is fixed in position relative to the sketch where it originates, but one can constrain, or dimension, sketch geometry to projected geometry. Projected geometry can be in profiles or paths. Projection Plane: An imaginary plane in the line of sight on which an image appears. Proportion: Proportion is a Principle of Design. Comparative relationships between things with respect to size. Project Lead The Way, Inc. Copyright 2000 Clifton Park, NY Introduction to Engineering Design National Alliance for Pre-Engineering Program Page 21 of 30 GLOSSARY of Terms for IED Proprietary Specifications: Additional information provided in a separate document that details mandatory parts, processes, and materials to be used to manufacture the part(s) on the working drawings. Purchasing: A branch of industry that will provide information and suggestions relevant to a product as to whether to buy or make components of the design. The availability of raw materials and the quantity of a material may change the desired output and is also determined by the purchasing department. Parts may be manufactured out-of-house at a lower cost and a higher quality than could be made in-house. Some components may be purchased by quantity discounts or just in time delivery methods to lower costs. Quadrilateral: A polygon with four sides. Quality Control: 1) The process of maintaining pre-determined standards throughout the design-to-manufacturing process. 2) This branch of industry is concerned with providing assurance that the product specifications are met. During all phases of manufacturing, this department inspects and tests parts to ensure that the components conform to design requirements. They also must participate in consumer complaints, rework and scrap costs, and process control, including statistical process control (SPC). Radii of Gyration: The distance from the axis of interest where all the mass can be concentrated and still produce the same moment of inertia. Radius: The distance from the center point to the outside curved surface. The radius is half the diameter Range of Motion: The path a component or linkage travels when a drive constraint is applied. Real Time Inspection (RTI): Observation taking place during a process whereby at any time the process can be stopped, altered, or changed to get the proper results. Project Lead The Way, Inc. Copyright 2000 Clifton Park, NY Introduction to Engineering Design National Alliance for Pre-Engineering Program Page 22 of 30 GLOSSARY of Terms for IED Receiving: A department in a company where all materials and supplies necessary for that company to function are “received.” Having a central location to inventory everything that enters a company to ensure that materials are allocated and charged to the correct departments within that company. Rectangle: A four-sided polygon with four right angles. Rectangular Dimensioning: Linear dimensions used to locate features from centerlines or planes. Recycle: To submit or return for reuse. Reference Dimensioning: A dimension usually without tolerance used for information purposes only. Relative: A method of plotting points whereby distances are measured from the previous point. Reliability: A quality which displays how trustworthy and dependable a person or product is. Re-manufacturing: Term used to describe products that are designed in such a way that the product can be returned to the manufacturer, and parts of the product can be utilized for newer products. Render: To create an artistic representation of an object. Repetition: Repetition is a Principle of Design. The use of repeated lines, spaces and textures. Replace Component: In the design process, one often needs to replace one or more components in an assembly. One can select a part to replace an existing assembly component regardless of its location in the directory structure. The new component is placed in the same location as the original component, but all assembly constraints are deleted. The origin of the replacement component is coincident with the origin of the replaced component. One reapplies constraints, as needed, to correctly position the component. Research: 1) The process of scientific investigation. 2) A department within a company that develops new products or Project Lead The Way, Inc. Copyright 2000 Clifton Park, NY Introduction to Engineering Design National Alliance for Pre-Engineering Program Page 23 of 30 GLOSSARY of Terms for IED redesigns existing products to improve company profits. This department is sometimes referred to as a “Research and Development (R & D)” department. Responsible: An expectation of a person to be obliged to account for something or someone. Résumé: Summary of your education, degree(s) earned, work history, accomplishments, etc. Revolved Feature: A profile revolved around an axis to create a solid feature. Rhombus: A quadrilateral with four equal sides and opposite angles equal. Right Angle: An angle measuring 90 degrees. Rotate: The rotate component button on the assembly toolbar will rotate an individual component. Round: Two or more exterior surfaces rounded at the intersection. Rhythm: Rhythm is a Principle of Design. Repeated lines, planes, or surface treatments. Right Triangle: A triangle having a 90 degrees angle, or right angle, in it. Rounds: Fillets created on convex edges. Saturation: Chromatic purity. Freedom from dilution with white. Scale: The ability to change the proportions or size of one part of the image in relationship to the other. Scalene Triangle: A triangle with no sides and no angles equal. Section View: A section view is used in an orthographic drawing to show the internal detail of an object. Typically the section view is used when the drawing detail is complex enough to obscure the hidden detail. Self-Motivation: A personal trait of displaying some inner drive that causes one to act in a certain way. A person that has Project Lead The Way, Inc. Copyright 2000 Clifton Park, NY Introduction to Engineering Design National Alliance for Pre-Engineering Program Page 24 of 30 GLOSSARY of Terms for IED an inner force that drives that person to set goals and incentives and to accomplish them. Serendipity: The faculty of finding valuable or agreeable things. Shade: A color mixed with black to absorb more light. Shaded View: A life-like view that has been modified to appear photo realistic. Shading: An area of relatively dark tone or close lines, dots, or hatch marks that produces darkness or shadow in a drawing or picture. Shape: The physical geometry of a model. Shell: A feature in which material is removed from a specified face, leaving a cavity with walls of a specified thickness. Shell walls are usually uniform thickness, but may have specific wall thickness assigned to them. A shell is used most frequently for cast or molded parts. Shrink-Wrap: A thin piece of film or plastic that when heated forms tightly to the product or container. Common technique used to place safety seals on medicine bottles for consumer protection. Size Dimension: Dimension on a drawing that indicates the size of a part. Size: Numerical value placed on a model and its features. Sketch: A freehand drawing of an idea, or solution to a problem without concern for detail, which could be done either on paper or on a computer. Sketching: A freehand type of drawing; without the use of drawing tools. Skilled: A person who has obtained a level of competence through education and/or experience in an occupational field. Slide Show: A number of visual aids used for presentations. Slots: A recessed area that commonly has fully rounded ends and tangent to its sides. Project Lead The Way, Inc. Copyright 2000 Clifton Park, NY Introduction to Engineering Design National Alliance for Pre-Engineering Program Page 25 of 30 GLOSSARY of Terms for IED Snap: The cursor will travel to a predetermined distance. Spatial (Spacial) Relations: The relative position and size of objects in a three-dimensional environment. Specification Sheet: Describes materials, manufacturers, qualities, cost, and other information needed to produce a part. Spectrum: A continuum of color formed when a beam of white light is dispersed (as by passage through a prism) so that its component wavelengths are arranged in order. Spotface: An enlarged drilled area that is used to provide a flat bearing area for a washer or bolt head. Square: A polygon with four equal sides and four right angles. Station Point: The point where the viewer stands to observe the image on the picture plane. Statistical Process Control (SPC): Statistical process control is a system of collecting data on a process to predict the desired outcome. This process can control the process so items being produced will conform more consistently to the design criteria. This process produces more usable items and reduces rework or scrapped parts. Statistical Tolerancing: The assigning of tolerances to related dimensions in an assembly based on the requirements of statistical process control. Sub-Assembly: A group of components that are constrained to act as one in a larger assembly. Style: the current, fashionable way of dressing, acting, etc. Subordination: Subordination is a Principle of Design. Less important aspects of a design, less eye-catching, but are essential to the overall effectiveness of the design. Subtractive: Creating a three-dimensional shape by subtracting, or removing, shapes/mass from the model. Supplemental Angle: Two angles added together equaling 180 degrees. Project Lead The Way, Inc. Copyright 2000 Clifton Park, NY Introduction to Engineering Design National Alliance for Pre-Engineering Program Page 26 of 30 GLOSSARY of Terms for IED Surface: A two-dimensional area on a plane. Surface Area: The squared dimensions of the exterior surface. Sweep Feature: A profile that is created by moving along a planar path. Two sketches are required to create a sweep, a profile, and a path on intersecting planes. Symbol Library: A collection of pre-drawn, commonly used images representing such things as electronics, hydraulic, and pneumatic devices. Tolerancing: Communicating the total allowable range of size and fit of parts. Tools: Anything used to modify another material or object, from a stone ax to a CNC lathe. Total Quality Control (TQC): A theory, which is based on the concept that it is possible to produce a perfect part each and every time. The responsibility for quality is placed on the individual operator to perform their task correctly all the time. Total Quality Management (TQM): A method that uses inputs from all levels of personnel to ensure continuous quality improvement. Tangent: A line that intersects a circle or an arc at one and only one point. Tangent Constraint: The tangent constraint causes curves or lines to be tangent to other curves. One curve can be tangent to another even if they do not physically share a point. Technical Drawing: A drawing used to express technical ideas. Technician: A person skilled in the technique of some art or science. Technological Change: Modifications brought about by improving processes or products. Technology: The science of creating objects. Project Lead The Way, Inc. Copyright 2000 Clifton Park, NY Introduction to Engineering Design National Alliance for Pre-Engineering Program Page 27 of 30 GLOSSARY of Terms for IED Three-Dimensional Solid Modeling: Three-dimensional representation possessing material characteristics, such as mass, volume, and density. Thumbnail Sketches: Small developmental sketches to communicate design ideas. Timeline: An order or sequence. Tint: A color mixed with white to give low saturation and high lightness. Tool Bar: The portion of the Inventor user interface that appears under the title bar in the graphics window. Contains icon buttons for tools that are used in all types of Inventor files. Trade-Off: A compromise to get one from the best solution to the optimum solution. Transition: Transition is a Principle of Design. The changing from one aspect of a design to another. Trapezoid: A quadrilateral with two parallel sides. Unconstrained Move: One can move a component to get a better view of its features. An unconstrained move is simply a temporary "get out of the way" move. The part remains in the moved location, but snaps back to its constrained position when one applies a new constraint, updates or refreshes the assembly. Trimetric: A drawing projected so that the plane of projection of a three-dimensional drawing is at a different angle to all three axes of the object. Two Point Perspective: Drawing using vertical lines and two vanishing points. Types of Fit: Classes of fits are arranged in three general groups known as running and sliding fits, locational fits, and force fits. They are based on equipment design and limits of size between mating parts. Project Lead The Way, Inc. Copyright 2000 Clifton Park, NY Introduction to Engineering Design National Alliance for Pre-Engineering Program Page 28 of 30 GLOSSARY of Terms for IED Unidirectional Dimensioning: Dimensioning technique commonly used in mechanical drafting that requires all numerals, figures, and notes be placed horizontally and read from the bottom of the sheet. Unity: Unity is a Principle of Design. Unity is applying consistent use of lines, color, and texture. To be harmonious. Unskilled: A person who lacks a level of competence through education and/or experience in an occupational field. Utilities: A company that provides something useful to the public such as electricity, gas, and water. Value: The lightness or darkness of a color. Vanishing Point: The point on the horizon where parallel objects appear to intersect due to convergence. Ventilation: The circulation of fresh air through a duct system into a room or building, or the removal of gas or foul air through the said system. Vertex: The point where the two sides of an angle intersect. Vertical Thinking (VT): Also called high-probability thinking or convergent thinking. Vertical: Perpendicular to the horizon. Views: The different viewing perspectives found in mechanical drawing. Visibility Control: In a large assembly, one may need some components only for context, or the components one needs may be obscured by other components. One can change components to not enabled or turn the visibility of components on and off as needed. Assembly files open and update faster when nonessential components are turned off. Visualization: To form a mental image of something. Volume: The space occupied by a three-dimensional object measured in cubic units. Warehousing: Storage of products waiting for distribution and/or use. Project Lead The Way, Inc. Copyright 2000 Clifton Park, NY Introduction to Engineering Design National Alliance for Pre-Engineering Program Page 29 of 30 GLOSSARY of Terms for IED Waste: Any activity that involves the use of time and materials which is not required for the task of production. Wavelength: The distance from the start of one wave to the start of the next. Work Axis: A work axis is a construction line of infinite length that is parametrically attached to a part. Working Drawings: A drawing for manufacturing or building purposes; term synonymous with detail drawings. Wireframe View: A transparent view that shows all surface edges of an object. Work Features: A parametric plane, axis, or point that you use to control the position and orientation of geometric features on a part. Work Plane: An infinite construction plane that is parametrically attached to a part. Work planes can be placed at any orientation in space, offset from existing part faces, or rotated around an axis or edge in a part face. A work plane can be designated as a sketch plane and can be dimensioned or constrained to other features. It is useful when no planar face exists to use as a sketch plane. Work Point: A construction feature that defines a point in three-dimensional space. A work point can be placed onto a sketch and incorporated into dimension and constraint schemes. Project Lead The Way, Inc. Copyright 2000 Clifton Park, NY Introduction to Engineering Design National Alliance for Pre-Engineering Program Project Lead The Way, Inc. Copyright 2000 Clifton Park, NY Introduction to Engineering Design National Alliance for Pre-Engineering Program Page 30 of 30