CCM3060(Published)
advertisement

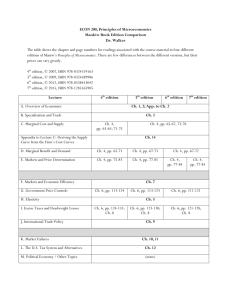
CCM3060(Published) Module Title Computer Networks Credit 20 Owning Subject Computer Communications Cross Accreditation to CMT Pre-requisites CCM2062 Aims The aim of this module is to introduce the basic concepts of computer networks. The module will provide a comprehensive overview of the principles and theories employed incomputer networks. It aims to develop develop a conceptual understanding without the aid of complex mathematical algorithms often used in computer networks. The main objectives of the module are: learn and understand the main issues of computer networks and to keep track of the continuous development in this field. Assessment Weighting Coursework: 40% Examination: 60% Learning Outcomes Knowledge On completion of this module the student will be able to: Demonstrate a knowledge and understanding of various concepts of computer networks (1) Explain various aspects of computer networks, such as, topology, OSI OSI model, access methods, signalling methods, routing strategy, concepts of circuit switching and packet switching, features of internet, , and features of network management (2) Demonstrate ways in which the above principles are applied, specially in LAN and WAN (3). Compare and contrast different characteristics of LAN, WAN, and Internet (4). Identify different types of multiplexing, switching, and and routing techniques applied in computer networks and the relationships that may exist between LAN, WAN and the Internet (5). Explain the importance of Network Management and its role in computer networks (6). Cognitive Skills On completion of this module the student will be able to: Analyse different scenarios in network environment and network problems (7). Be able to manipulate and analyse any particular set of given information (e.g., present scenario of a company, their their site/building layout, any existing network layout, cabling, topology etc.) for network design (8). Acquire skills in carrying out further study or research in network application areas (9). Be able to pick up the developments in network technology and understand the concepts of such developments and its use in data and computer communications (10). Relate the theoretical concepts to network applications (11). Develop basic management skills to manage a computer network (12). Syllabus Introduction - overview of different types of networks Network Software Protocol - Definitions, Primitives, OSI Reference Model, TCP/IP Reference Model Local Area Networks - topologies, transmission media, and access methods Types of LAN - Ethernet, frame format, transmission and reception, Token Ring, token and frame format, transmission and reception, FDDI, Other high speed LAN's Wide Area Networks - Circuit Switching, switching concepts, routing and signalling methods, Packet Switching - datagram, virtual circuit, routing ATM - ATM layer structure, services, virtual path/channel, default routing and time division switching Internetworking - autonomous system, internet protocol, internet addressing subnet masking, IPv6 Network Management - features of network management, QoS, Simple Network Management Protocol and Monitoring Devices, ASSESSMENT SCHEME The students' performance will be assessed in 3 hours unseen examination (60%) [outcomes 1-6]. Coursework 1 - each student will be expected to demonstrate their understanding of issues involved in a theoretical coursework on specially selected topics in computer networks (15%)- [outcomes 7, 9, 10, 11]. Coursework 2 - each student will be expected to demonstrate their understanding of design issues involved in a well researched individual 3000-5000 words essay on one of the given design topics (25%) - [outcomes 7, 8, 9, 10, 12]. The student will be required to keep a logbook of progress and activity report to the above mentioned exercises. Class tests (minimum two) will assess students progress throughout the term [outcomes 1-6]. Note: A minimum of 40% is required in each assessment to passthe subject. Participation in the seminar class and regular classclass attendance will also be taken into account for the overall assessment procedure. Marks will be deducted from coursework for absence from lecture or seminar class unless substantiated by genuine reasons. ExamDuration Examination, 3 hours Learning Materials Core Texts Behrouz A Forouzan Data Communications and Networking, Third Edition, McGrawHill, ISBN 0007-123241-9 Jerry Fitzgerald, Alan Dennis, Business Data Communications and Networking, 7th Ed, 2002, ISBN 0-471-39100-X And Class Notes Additional Texts James Irvine, David Harle, Data Communications and Networks, John Wiley & Sons Ltd, ISBN 0-471-80872-5 William Buchanan, Distributed Systems and Networks, McGraw Hill, ISBN 0-070709583-9 Youlu Zheng, Shakil Akhtar, Networks for Computer Scientists and Engineers, Oxford University Press, ISBN 0-19-511398-5 Andrew S. Tanenbaum, Computer Networks, 4th Ed, Prentice-Hall International, ISBN 0-13-038488-7. James Irvine, David Harle, Data Communications and Networks, John Wiley, ISBN 0471-80872-5 Douglas E Comer, Computer Networks and Internets, Prentice Hall, ISBN 0-13091449-5 Total Notional Hours 180 BIS2000(Published) Module Title Business Information Systems Credit 20 Owning Subject Business Information Sys Cross Accreditation to BUS Pre-requisites ( BIS1000 ) or ( MBS1111 ) or ( CMT1111 ) Aims The aim is to give an overall understanding of Business Information Systems: the different types, their functionality, development, management, use and the social impact; the value and the use of information systems in business, managerial decision making and strategic advantage from the perspective of both a user and that of a manager. Assessment Weighting Coursework: 40% Examination: 60% Learning Outcomes Knowledge: On completion of this module, the successful student will be able to: Define basic concepts, terminology, and principles of Information Systems.(1) Explain the functionality of different types of Information systems in use, their impact and use to the organisation.(2) Recognise the importance of information system technology to the success of an organisation.(3) Identify the information needs of organisational business processes.(4) Identify the type of Information System which best support the business needs of an organisation.(5) Identify advantages and disadvantages of different methods of system development.(6) Identify the successful factors for a systems development project.(7) Identify advantages and disadvantages of different methods of system implementation.(8) Demonstrate knowledge of how to use the Information system securely.(9) Skills: This module will call for the successful student to demonstrate the ability to: Model the business process of an organisation.(10) Analyse the business procedures of the organisation.(11) Analyse the different roles involved and the interactions among them.(12) Analyse the required activities and their logical relationship.(13) Select the type of Information System that will support the business needs and will bring value to the organisation.(14) Explain issues involved in successful development and implementation of Information Systems.(15) Select the method of system development suitable for a particular Information System.(16) Analyse the security needs of an organisational business information system.(17) Discuss the security measures that could be implemented to safeguard a business information system.(18) Construct business process models using graphical notations of Role Activity Diagrams.(19) Participate in Information Systems development projects contributing to successful development and implementation.(20) Use Business Information Systems to bring value to the organisation.(21)Participate in group discussions.(22) Make oral presentations in class demonstrating the ability to impart ideas clearly and precisely on a given subject.(23) Think analytically: critically analysing business processes, their information needs, and their security requirements.(24) Syllabus Fundamentals of Information Systems: Overview of organisations - a system view and a process view, system concepts and management concepts. Different types of Information Systems used in business: Transaction Processing Systems, Management Information Systems, Decision Support Systems, Group Decision Support Systems, Executive Information Systems, Expert Systems and Hybrid AI Systems. Enterprise Resource Planning, Enterprise Collaboration Systems. Business Process Modelling. Information Systems Development and Project Management. Information System Security. ASSESSMENT SCHEME: COURSEWORK: Group assignment (maximum of 3 students) Task: Produce analyse and design specifications based on a case study Submission Week: 7/8 % of the module overall grade: 40% EXAMINATION: 2 hour unseen exam 3 questions from 5 % of the module overall grade: 60% For Distance Learning Students: The distance learning material will be used to impart theoretical content. Face-to-face sessions at the LSCs will be used to extend the theoretical material through discussion and practical exercises. Students must pass both assessed components of a module individually, coursework and examination, in order to pass the module overall. Failure in one of the components will result in failure of the module. ExamDuration Examination, 2 hours Learning Materials Core Texts: Ralph M Stair and George W Reynolds - Principles of Information Systems, A Managerial Approach, 4th Edition, 1999, International Thompson Publishing Europe, ISBN 0-760-01079-X. James O'Brien - Management Information Systems, Managing Information Technology in the Internet worked Enterprise, 1999, 4th Ed Irwin McGraw-Hill, ISBN 0-072-90611-1. Additional Texts: Steven Alter, Information Systems - A Management Perspective, 1999, 3rd Edition, Addison-Wesley, ISBN 0-201-35109-9. Robert Schulthesis and Mary Sumner - Management Information Systems, The Manager's View, 1997, 4th Edition, Irwin McGraw-Hill, ISBN 0-256-25195-9. Paul Bocij, Dave Chaffey, Andrew Greasley, and Simon Hickie Business Information Systems, Technology, Development, and Management, 1999, Financial Times - Pitman Publishing, ISBN: 0-27363849-1. Graham Curtis - Business Information Systems, Analysis and Design, 1998, 3rd Edition, Addison-Wesley, ISBN 0-201-33136-5. Kenneth C Laudon and Jane Price Laudon - Management Information Systems, 2000, 6th edition, Prentice Hall, ISBN 0-130-15682-5. Martyn A Ould - Business Processes, Modelling and Analysis for Reengineering and Improvement, 1995, John Wiley & Sons, ISBN 0-47195352-0. Every attempt has been made to ensure this information is correct at the time of publishing. However additional information may be provided in the module handbook. Total Notional Hours 180 BIS3051(Published) Module Title Commercial Web Design Credit 20 Owning Subject Business Information Sys Pre-requisites BIS2021 Aims Enables students to generate dynamic websites using ASP, ASP.NET, XML, XSL/T and HTML. Students will be required to set up an online database on a server and render this database correctly for display to the client. The module also compares the relationship with XML and databases and how this technology can be used to display queries. Assessment Weighting Coursework: 100% Learning Outcomes Knowledge: On completion of this module, the successful student will be able to: Explore programmable aspects of ASP and ASP.NET.(1) Explain how a server responds to client requests.(2) Produce server-side applications to access and respond to information from client-side.(3) Differentiate between the need for server and client side scripts.(4) Explain the concept via demonstration of XML and XSL and their relationship.(5) Produce valid and well-formed mark-up languages.(6) Explain to a third party the benefits of dynamic webpages.(7) Skills: This module will call for the successful student to demonstrate the ability to: Discriminate when to use GET or POST methods.(8) Create a structured program using ASP and object oriented program using ASP.NET .(9) Given a DTD produce a well-formed XML document and vice-versa.(10) Identify the necessity of cookies for the success of e-commerce.(11) Criticise the unnecessary use of server side script.(12) Validate non well-formed mark-up languages.(13) Explore the relationship between XML/XSL.(14) Programme server side applications.(15) Analyse XML schemas.(16) Analyse XSL to produce rendered data.(17) Render XML documents using XSL/XPath.(18) Experiment with mark-up languages, associated stylesheet languages and scripting languages to produce dynamic webpages.(19) Demonstrate these skills via the development of a professional validated Website.(20) Realise how to explain and document a problem.(21) Analyse Website security and performance issues.(22) Explain solutions to other members of a team with clarity, conviction and comprehension.(23) Rely on experiential knowledge to solve unexpected solutions.(24) Communicate with other members of a team and assist in finding a solution to unexpected problems.(25) Principles of mark-up languages and therefore be able to use any that may occur in the future.(26) Syllabus This module is divided into seven major parts which are as follows: Review of HTML, how to develop a webpage using HTML Validation of mark-up languages and the importance of browser independent applications Advantages and disadvantages of server-side applications Advantages and disadvantages of client-side applications CSS document maintenance Structured programming - Iteration and Selection - using ASP Object Oriented programming - Iteration and Selection - using ASP.NET Using HTML and XML to provide interactive and structured Webpages ASP, learning key objects in ASP eg response, request and server By means of demonstrations implement server-side applications How to query and update an on-line database using ADO and ADO.NET HTML to manage data and layout of Website XSL to format data and manage display of XML data Designing your own mark-up language Differentiate between GET and POST methods of obtaining data How to verify the security of a Website ASSESSMENT SCHEME: COURSEWORK - 100% Task - Design and prototype a database application. Submission Week: 12 For Distance Learning Students: The distance learning material will be used to impart theoretical content. Face-to-face sessions at the LSCs will be used to extend the theoretical material through discussion and practical exercises. Learning Materials Core Text: Harold, ER and Means, WS - XML in a Nutshell. O'Reilly 2001.ISBN:0596-00058-8 Weissinger, A. Keyton - ASP in a Nutshell. O'Reilly 2001.ISBN:156592-843-1 Additional Text: Deitel, HM, Deitel, PJ, Nieto, TR, LIN TM and Sadhu, P - XML: How to Program. Prentice-Hall ISBN:013-028417-3 Knuckles, CD - Introduction to Interactive Programming on the Internet using HTML and Javascript. Wiley 2000. ISBN:0-471-38366-X Martin, D et al Professional XML WROX, 2000. ISBN:186-1003-11-0 * Niederst, J - Web Design in a Nutshell. O'Reilly ISBN:1-56592-515-7 Total Notional Hours 180