TRUE - FFA
advertisement

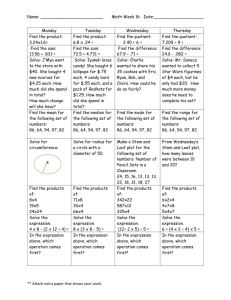
14.0 Plant Growth 14.1 Plant Parts MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Leaves are important part of plants because they: (14.1) a. site of photosynthesis b. physically support plant c. supply shade d. absorb food from the soil 2. a. b. c. d. Leaf support and transporting nutrients are the essential functions of the: (14.1) Roots Leaf Stem Vein 3. Which of the following parts of the leaf is responsible for transporting water and nutrients: (14.1) a. Petiole b. Nodes c. Veins d. Blade 4. a. b. c. d. Most of the water and minerals are absorbed by a plant through: (14.1) the root cap fibrous roots the primary root root hairs 5. a. b. c. d. What part of the leaf cell contains chlorophyll and carries out photosynthesis? (14.1) Mesophyll Epidermis Petiole Chloroplasts 6. a. b. c. d. The ____ is an example of a plant that has corms. (14.1) gladiolus tulip daffodil peony 7. a. b. c. d. The terminal bud on a plant stem is located at the (14.1) bottom of the stem. abscission layer. top of the stem. axillary bud. 8. The leaf petiole is (14.1) a. the top of the leaf. b. the bottom of the leaf. c. the stem of the leaf. d. the middle of the leaf. 9. a. b. c. d. The blade of a leaf is broken down into three parts: (14.1) the tip, margin, and base. the tip, margin, and petiole. the tip, midrib, and petiole. the margin, petiole, and midrib. 10. a. b. c. d. The ovary of a flower matures into(14.1) a seed. a fruit. a vegetable. a new plant. 11. a. b. c. d. What part of the reproductive system of the plant develops into fruit? (14.1) testes anther stem ovary 12. a. b. c. d. What part of the plant produces the pollen? (14.1) pistil anther stamen stigma 13. a. b. c. d. In which ring of the woody stem are water and nutrients transported? (14.1) pith cambium innermost ring outermost ring 14. The most important difference between a plant and an animal cell is the cell wall. What is the cell wall of a plant composed of? (14.1) a. water b. protein c. starch d. cellulose TRUE/FALSE 15. Leaves are important to the plant for water absorption. (14.1) FALSE 16. Root hairs absorb 95 % of water. (14.1) TRUE 17. Adventitious roots develop below the ground. (14.1) FALSE 18. Corms are stems that are thick, compact, and fleshy. (14.1) TRUE MATCHING Matching the following plant definitions and terms. A. food manufacturing part of plant ___B___ 19. root system B. underground, anchor, supply water and nutrients ___D___ 20. stem or trunk C. seed producing part of plant ___A___ 21. leaves D. support system for rest of above ground parts ___C___ 22. flowers Match the function to the plant part. (14.1) A. contains seed ___C___ 23. flower B. supports branches and transports food and water ___D___ 24. leaves C. attracts insects ___A___ 25. fruit D. manufactures food by photosynthesis ___F___ 26. seed E. anchors the plant and absorbs and stores food and water ___B___ 27. stem F. functions in sexual propagation of the plant ___E___ 28. roots Match the sketch to the correct names. (14.1) ___B___ ___F___ ___G___ ___A___ ___D___ ___E___ ___C___ 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. corm tubers non-tunicate bulb true bulb tuberous root rhizomes tunicate bulb Match the definition with the correct leaf structure below. (14.1) A. protects leafs and covers entire surface of leaf ___F___ 36. cuticle B. contains structures called chloroplasts ___A___ 37. epidermis 38. stoma C. divided into two sublayers, between epidermal layers ___D___ D. allows passage of air into leaf and exiting of water vapor ___C___ 39. mesophyll and oxygen ___B___ 40. palisade mesophyll E. contains xylem and phloem F. outermost layer, consists of waxy material ___E___ 41. spongy mesophyll Match the definition with the correct plant part below. (14.1) A. waxy waterproof substance keeps inner tissues from ___D___ 42. epidermis drying out B. area for food storage and the phloem ___A___ 43. cork cambium C. separates the phloem and xylem ___G___ 44. merisystematic cells D. outer section which protects plant ___B___ 45. cortex 46. sap E. at center of woody stem ___F___ F. substance through which nutrients are conducted ___C___ 47. cambium G. they divide and cause growth ___E___ 48. pith SHORT ANSWER 49. Name the two types of root systems. (14.1) taproot, fibrous roots 50. List seven parts of a flower. (14.1) filament, anther, pollen, stigma, style, ovary, petals, and sepals 51. Briefly explain the difference between vegetables and fruits. (14.1) A vegetable can be any part of a plant that is grown for its edible parts. It may be a root, stem, leaf, or ripened flower. A fruit is a ripened or mature ovary and is a specific plant part. 52. What are the two functions of leaves? (14.1) manufacture and store food for the plant 53. Name the two basic parts of the leaf. (14.1) blade and petiole 54. List four purposes the stem of the plant serves. (14.1) support for the plant, conduct water and nutrients from the roots to the branches and leaves, store food for use by the plant, and carry food 55. Name three types of specialized root systems. (14.1) adventitious roots, aerial roots, aquatic roots 56. How are rings formed in a woody stem and what do they tell about the plant? (14.1) Rings are formed around the stem by the xylem. The xylem carries water and nutrients up into the plant from the roots. Each year a new ring is added and the old ring dies. This ring is called the annual ring and is used in determining the age of the plant or tree. 57. What are three purposes of the root system of a plant? (14.1) The three purposes of the root system are: (1) to take water and nutrients from the soil for use by the plant; (2) to serve as storage space for food manufactured by the plant; and (3) to provide an anchor for the plant. 58. What are the two types of root systems and what is the difference? (14.1) The two types of root systems are tap and fibrous roots. Tap roots have a strong central root that grows downward into the soil. It grows quite large and stores plant nutrients. The fibrous root system has no large central root but many branches of fine roots. This large complex network of roots helps to hold soil in place to prevent soil erosion. 59. Which plastid in the cell contains the chlorophyll to make the plants green? (14.1) chloroplasts 60. What is the name of the substance that helps give the cell wall strength in the softer plant tissues such as leaves and fruit? (14.1) pectin 61. Identify the three types of plastids within the plant cells and describe their functions. (14.1) The three types of plastids are chloroplasts, leucoplasts, and chromoplasts. The chloroplasts use energy from the sun to make carbohydrates. Leucoplasts provide storage for the cell. They may contain starches, protein, or lipids. Chromoplasts manufacture pigments that give fruit their color and leaves their brilliant color in the fall. 14.2 Classifying Plants MULTIPLE CHOICE 62. Plants which have male and female flowers on separate plants (like on pistachio trees) are called____________________.(14.2) a. monoecious b. dioecious c. separatists d. fibrous 63. a. b. c. Plants which have male and female parts on the same plants are called: (14.2) monoecious dioecious separatists d. fibrous 64. a. b. c. d. Which of the following is not a characteristic of a monocot? (14.2) has a single seed leaf leaves have parallel veins has two cotyledons flowers in groups of three 65. a. b. c. d. Which of the following is not a characteristic of a dicot? (14.2) leaves have network veins have flowers in groups of three have flowers in groups of four or five have two cotyledons 66. a. b. c. d. How many types of plants can share a scientific name? (14.2) 1 2 3 4 67. a. b. c. d. What does the scientific name not tell you? (14.2) how tall the plant will grow who discovered the plant where the plant is from features of the plant 68. In which rank, of the last five categories of botanical classification, does the order follow? (14.2) a. kingdom; species; class; phylum; variety b. order; family; genus; species; variety c. class; family; genus; order; species d. family; order; genus; class; species 69. a. b. c. d. Scales are (14.2) modified stems. modified leaves. modified roots. modified shoots. 70. a. b. c. d. A compound leaf is made up of (14.2) more than one leaf. a leaf that has divided into two halves. a leaf that has divided into a whorled arrangement. three to seven leaflets. 71. a. b. c. d. Plants that host nitrogen-fixing bacteria are known as ____. (14.2) legumes trees corn grass 72. a. b. c. d. Which of the following seeds is a dicot? (14.2) corn rice wheat alfalfa 73. a. b. c. d. Which of the following seeds is a dicot? (14.2) corn rice wheat alfalfa TRUE/FALSE 74. Mistletoe is a parasitic plant. (14.2) TRUE MATCHING Match the following sketches of leaf arrangements to the name of the arrangement. (14.2) ___B___ ___A___ ___E___ ___C___ ___D___ ___F___ 75. 76. 77. 78. 79. 80. Pinnately compound Palmately compound Whorled Bipinnately compound Alternate Opposite Match the following terms to the correct meanings. (14.2) ___C___ 81. trees with needle-like leaves A. deciduous ___A___ ___B___ ___E___ ___D___ ___G___ ___F___ 82. 83. 84. 85. 86. 87. trees that shed needles or leaves trees that do not shed needles or leaves trees, shrubs, and plants wood used for making fiber for paper woody perennial plants with single stem bushy woody plants with multiple stems B. evergreen C. conifers D. pulpwood E. forest F. shrubs G. Trees Identification Directions: Categorize the following plants as to vascular and non- vascular, place a (V) in front of the vascular plants and a (N) for non-vascular. (14.2) 88. __N__ Fungi 89. __V__ Corn Plant 90. __ V _ Ferns 91. __ V _ Shrubs 92. __ N _ Algae 93. __ V _ Beans 94. __ V _ Bermuda Grass 95. __ N _ Lichens 96. __ N _ Mosses 97. __ V _ Tomato Plant COMPLEATION 98. ___________________ is the taxonomic category between family and species. (14.2) Genus 99. ____________________ is the subgroup under genus. (14.2) Species SHORT ANSWER 100. What is the difference between a perfect and imperfect flower? (14.2) A perfect flower has all its parts, has all the parts of the stamen and pistil while the imperfect flower has one or more parts missing. 101. Define taxonomy. (14.2) Taxonomy is the science, laws, and principles of classifying organisms. 102. Name the two classifications for seeds. (14.2) dicotyledonous (dicot), monocotyledonous (monocot) 103. What are the three most common arrangements of leaves on a stem? (14.2) whorled, alternate, and opposite 104. What does gymnosperm mean? (14.2) Exposed seeds Examples include pine, spruce, ferns, and conifer trees 105. What does angiosperm mean and provide two examples? (14.2) Produce and store seeds in an ovary Examples include roses, elm trees, geraniums, and apple trees 106. Which part of the scientific name comes first? (14.2) Genus 14.3 Physiological Needs MULTIPLE CHOICE 107. What is the range of the pH scale? (14.3) a. 0-16 b. 2-18 c. 0-14 d. 4-20 108. What number is neutral on the pH scale? (14.3) a. 14 b. 2 c. 6 d. 7 109. Which one of the following items would have a low pH? (14.3) a. Vinegar b. Ammonia c. Rain Water d. Pure Water 110. Which of the following numbers represents an acid? (14.3) a. 5 b. 7 c. 14 d. 9 111. What are two synonyms for basic? (14.3) a. Alkaline and Salty b. Alkaline and Acid c. Acid and Salty d. Neutral and Base 112. What is the common pH range for Arizona Desert Soil? (14.3) a. 6.2-7.2 b. 6.5-7.5 c. 8.3-9.3 d. 7.3-8.3 113. Which is the following is NOT a common method of lower the pH soil in Arizona? (14.3) a. Adding Lime b. Adding Sulfur c. Adding Gypsum d. Adding Peat Moss 114. Changes in the air quality, pH of the soil and impurities in the water can be caused by which of the following? (14.3) a. decreased population b. increased rainfall c. pollution d. none of the above 115. Air pollution can have an effect on plant growth by:(14.3) a. reducing the amount of CO2 in the air b. increasing the amount of CO2 in the air c. increasing the amount of O2 in the air d. decreasing the amount of O2 in the air 116. pH is the measurement of the __________ concentration in a particular medium. (14.3) a. carbon b. hydrogen ion c. oxygen d. calcium 117. As the pH changes it affects the availability of __________________to the plant. (14.3) a. fire b. water c. nutrients d. light 118. The area of cell division on a root is at the (14.3) a. apical meristem. b. root hairs. c. phloem. d. xylem. 119. ____ is considered the reverse of photosynthesis. (14.3) a. Exhalation b. Expiration c. Respiration d. Perspiration 120. In order for seeds to germinate, they must take in ____.(14.3) a. oxygen b. nitrogen c. water d. light 121. Plant growth is controlled by substances called ____.(14.3) a. pollinators b. hormones c. nutrients d. tropisms 122. One of the most effective means of preventing disease in plants is through the use of disease ____ varieties. (14.3) a. proof b. absorbent c. porous d. resistant 123. Any condition which causes the systems of a plant or animal not to function properly is a ____.(14.3) a. weakness b. pathogen c. defect d. disease Match the photosynthesis or respiration with the activities listed below. (14.3) Food is produced. A. photosynthesis ___A___ 124. It occurs in dark as well as light. B. respiration ___B___ 125. Energy is released. ___B___ 126. Energy is stored. ___A___ 127. Water is produced. ___B___ 128. Water is used. ___A___ 129. Carbon dioxide is used. ___A___ 130. It occurs in cells that contain chloroplasts. ___A___ 131. Food is used for plant energy. ___B___ 132. Oxygen is used. ___B___ 133. Oxygen is released. ___A___ 134. It occurs in sunlight. ___A___ 135. It occurs in all cell walls. ___B___ 136. Carbon dioxide is produced. ___B___ 137. COMPLETION 138. The process that causes a seed to begin to grow into a new plant is ____________________.(14.3) germination 139. ____________________ is necessary to preserve a seed for the proper time when conditions are optimum for growth. (14.3) Dormancy 140. Commercially produced seeds usually have a germination rate above ____________________ percent. (14.3) 95 141. The process of plants responding to the length of daylight and darkness is called ____________________.(14.3) photoperiodism 142. If a disease attacks the ____________________ of a plant, the plant may not be able to reproduce or produce fruit. (14.3) flower 143. If a pathogen gains entry into a plant, the plant may secrete ____________________ which are toxic to pathogens. (14.3) chemicals SHORT ANSWER 144. Name the process whereby plants lose water vapor. Transpiration 145. What gas must be monitored within a greenhouse to make sure it is not too high or too low? carbon dioxide 146. Define photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is a series of processes in which light energy is converted to chemical energy in the form of a simple sugar. It is the conversion of carbon dioxide and water in the presence of light and chlorophyll into glucose, oxygen, and water. Glucose, the simple sugar, contains the building blocks for other nutrients. 147. List the three major groups of hormones that control the growth of plants. (14.3) auxins, cytokinins, gibberellins 148. Explain the effects of temperature in the germination of seeds. (14.3) The proper temperature is essential for seeds to germinate. Most seeds go through a period of cold before they will germinate. This helps prevent the seeds from sprouting as soon as they mature and are dispersed. Seeds remain dormant in the winter until the following spring when warm temperatures help start the germination process. 149. Why is the depth seeds are planted important? (14.3) The depth that seeds are planted is important because if seeds are planted too deeply, they may not receive the proper amount of light and may not have enough oxygen. If they are planted too shallow, they may have too much light. 150. What are the three types of growth that take place when plants grow? (14.3) The three types of growth that occur when plants grow include: 1) the increase in the size of the plant cells, 2) the increase in the number of plant cells and cell differentiation, and 3) cell differentiation is the converting of cells to perform the different functions of the plant. 151. Explain the function of hormones in plant growth. (14.3) Hormones are chemical substances found in plants and animals that control or influence the activities of organs or tissues. The proper balance of the hormones produced by the plant is essential to keeping the plant growing and functioning properly. Plant hormones function together to stimulate or inhibit plant growth. 152. Explain the effects of light on plant growth. (14.3) Plants respond to light in many ways. Plants grow toward the light. If the light comes to the plant at an angle, the plant will grow in an arch toward the sun. Light also affects the time when plants bloom, shed their leaves, and go into dormancy. 153. Define geotropism. (14.3) Geotropism is the movement of the plant toward gravity. The stem grows upward and the roots grown downward. The cause of this effect is the influence of gravity on plant growth. 154. What do the xylem and phloem conduct within the plant? (14.3) Xylem brings water from the roots to the leaves. The phloem carries the products of photosynthesis to the other parts of the plant. 155. Besides providing our food, what other purposes do plants serve? (14.3) Plants convert energy from the sun into energy for animals in the form of food. Plants stabilize the soil by preventing erosion. Plants replenish the earth's oxygen supply by giving off oxygen and using carbon dioxide. Plants provide beauty for our world. 156. Define photosynthesis. (14.3) Photosynthesis is the process where the leaf makes food for the plant. In the mesophyll layer of the leaf are structures called chloroplasts. These hold chlorophyll and are the sites of photosynthesis. The chlorophyll captures light energy from the sun and allows this energy to be used for the chemical reaction of photosynthesis. The chemical reaction takes carbon dioxide and water and converts it to sugar and oxygen. 157. What problem may occur if a disease attacks a plant’s root system? (14.3) The plant may not be able to take in water and other nutrients to help it produce food and grow. 158. Explain the two types of covering a plant may have on its surface to protect itself from pathogens. (14.3) Plant hairs, called pubescence, help in collecting the pathogens before they reach the surface of the plant. Also, the cuticle, a thick waxy covering, prevents the penetration of the pathogens. 159. Name two common signs that a diseased plant may show. (14.3) look wilted; have brown spots on the leaves, fruit, or other parts 14.4 Plant Reproduction MULTIPLE CHOICE 160. Fertilization occurs in the ____________of the female plant. (14.4) a. Style b. Stigma c. Ovary d. Filament 161. A flower is called complete when it: (14.4) a. contains more than one color b. has an uneven number of petals c. has both male and female parts d. is not capable of pollination 162. When pollination occurs, pollen is released by the anther and comes in contact with the: (14.4) a. filament b. stigma c. ovary d. style 163. ____ is the union of the pollen and the stigma. (14.4) a. Flower b. Style c. Pollination d. Pagination 164. In plant breeding, what is removed from the plant to prevent natural pollination? (14.4) a. anther sac b. Petals c. Style d. Stigma 165. In terms of reproduction, plants are completely different from most animals because they can ____ an entire plant from a severed part of the parent plant. (14.4) a. preplant b. aftplant c. reincarnate d. regenerate 166. What layers should match exactly for a proper graft to take place? (14.4) a. cambium b. Pith c. callus d. anther 167. A hybrid plant is obtained by: (14.4) a. halfbreeding b. crossbreeding c. inbreeding d. Line breeding 168. The union of a small piece of bark with a bud and a rootstock is called ____ grafting. (14.4) a. spud b. Root c. Seed d. Bud 169. What is the first step in seed germination? (14.4) a. absorption of water b. light presence c. infusion of oxygen d. increased heat 170. In this unit, you have seen a picture of the tops of plants covered with paper bags. The paper bag does what? (14.4) a. Protects the top of the plant from a hard rain or hail. b. Identifies each individual plant in the scientist’s test plot. c. Stops any photosynthesis from occurring at the top of the plant. d. Prevents cross-pollination so the plant breeder can select the pollen. 171. It generally takes how many years to breed a new variety of a grass, like sorghum, to resist the changing individuals of a given pest? (14.4) a. 3 to 10 years b. 8 to 11 years c. 5 to 10 years d. 2 to 4 years 172. On a commercial level, an example of massive cloning in the field is (14.4) a. wheat. b. Corn. c. the potato. d. the gladiolus. 173. The “seed potato” farmer selects cultivars that are resistant to disease and pests by (14.4) a. identifying superior plants in the field and using them. b. leaving it up to the biotechnology industry. c. growing only three different cultivars at a time in any one season. d. observing and recording which cultivar germinates first. 174. Many plants reproduce by cloning through processes known as ____ reproduction. (14.4) a. asexual b. vegetative c. sexual d. a and b above 175. Through a process of ____ breeding, scientists have developed several varieties of seedless grapes. (14.4) a. cross b. selective c. ind. none of the above TRUE/FALSE 176. The “Scion” is the twig or bud that you graft onto the desirable rootstock. (14.4) TRUE 177. Taking plant tissue or cells from a parent plant and growing them on or in a sterile, artificial medium to produce a plantlet with its own leaves, stems, and root system is referred to as tissue culture. (14.4) TRUE 178. Stem cuttings can only be made using stems of an herbaceous plant. (14.4) FALSE 179. Corn is an example of a dioecious plant. (14.4) FALSE 180. Stem cuttings, grafting, and tissue culture are all examples of sexual reproduction. (14.4) TRUE 181. The embryo is always located in the same location, regardless of the type of seed. (14.4) FALSE 182. Seed potatoes are cut into pieces for planting. (14.4) TRUE 183. American farmers grow more than 200 varieties of wheat. (14.4) TRUE 184. There are more than 100 different varieties of cotton. (14.4) FALSE 185. There are at least 200 varieties of soybean. (14.4) TRUE 186. Hybrid seed is produced by crossbreeding two different varieties of the same species. (14.4) TRUE 187. In very general terms, it takes 12 to 18 days for common flowers and vegetables to germinate. (14.4) FALSE 188. In asexual reproduction the new plant is not identical to the parent plant. (14.4) FALSE 189. Producing plants from seed and sexual reproduction is more efficient than through vegetative means. (14.4) FALSE COMPLETION 190. ____________________ is the name of the food storing mass of cells that surround the seed? (14.4) Endosperm 191. Because of their brightly colored flowers and nectar used as food, some plants are fertilized by the action of ____________________.(14.4) insects 192. ____________________ and ____________________ are the two methods for obtaining new plants from specialized plant parts. (14.4) separation, division 193. Gladiolus and garlic are examples of plants that propagate through ____________________.(14.4) corms 194. The procedure of tissue ____________________ involves using a small amount of tissue from a plant to grow a new plant. (14.4) culture 195. Tissue culture should take place inside of a ____________________ chamber to prevent contamination. (14.4) Transfer 196. Sexual propagation is a good way to avoid passing on ____________________.(14.4) diseases 197. Plant breeders use two methods of propagation, one using both the male and female parts of the flower or plant called ____________________ reproduction and the second method that basically clones one parent plant called ____________________ reproduction. (14.4) sexual, asexual 198. Work areas should be cleaned with ____________________ bleach solution. (14.4) 10% 199. Contamination of ____________________ or bacteria could kill the plant tissue. (14.4) fungus 200. The ____________________ technique is important to use when propagating a plant using tissue culture because it will help prevent contamination. (14.4) aspectic MATCHING Match the definition with the correct plant term below. (14.4) receptacle A. colorful head of the flower ___D___ 201. 202. calyx B. colorful structure that emerges when flower opens ___F___ corolla C. receives the pollen ___B___ 203. perianth D. where the flower is attached to the stem or stalk ___A___ 204. carpels E. pollen-bearing organ of flower which consists of ___G___ 205. filament and anther stigma F. protects the developing flower bud ___C___ 206. stamen G. female organs within the flower ___E___ 207. Match the definition with the correct pollination term below. (14.4) self-pollinated A. plants that pollinate themselves ___B___ 208. cross pollinated B. pollination takes place from flowers on the same plant ___C___ 209. self fertile C. pollination is by pollen from another plant ___A___ 210. self sterile D. plants that cannot pollinate themselves ___D___ 211. Match the term stamen or pistil with the male or female part of a flower. (14.4) stigma A. stamen ___B___ 212. anther B. pistil ___A___ 213. filament ___A___ 214. ovary ___B___ 215. style ___B___ 216. ovules ___B___ 217. pollen ___A___ 218. SHORT ANSWER 219. Name four specialized parts of plants that are used for vegetative propagation. (14.4) Any four of the following: bulbs, corms, tubers, stolons, rhizomes, crowns 220. Cuttings for propagation can be taken from what part of the plant? (14.4) Any of the following: leaves, stems, roots, buds 221. What is the best season for hardwood cuttings to be taken? (14.4) dormant 222. List the four conditions for plant cuttings to grow properly. (14.4) temperature, moisture, air movement, light 223. Name the cells that a wound in the plant stimulates to grow. (14.4) callus 224. What are the upper and lower parts of a graft called? (14.4) upper is rootstock and lower is scion 225. What are two advantages of tissue culture? (14.4) Two advantages of tissue culture are: (1) only a very tiny portion of the parent plant is used, so the potential of growing a large number of genetically identical plants is greatly increased and (2) the new plants are free from disease-causing organisms. 226. Identify the two ways in which plants reproduce and describe the difference. (14.4) Two ways in which plants reproduce are sexually and asexually. With sexual reproduction there must be two gametes the sperm and the egg. With asexual reproduction, the plant can be created without the joining of the egg and sperm but reproduce by using a part of the parent plant to start a new plant. 227. What is the difference between a complete flower and a pistilate flower? (14.4) A complete flower has sepals, petals, a stamen, and a pistil. The pistilate flower has no stamen. 228. How is pollen carried from flower to flower by insects? (14.4) Pollen is caught on legs or body parts of insects as they go from flower to flower collecting nectar. As they travel around, some pollen is dropped into the next flower while more is picked up, moving the pollen from flower to flower. 229. Identify two reasons why plants are reproduced vegetatively. (14.4) One reason for vegetatively reproducing plants is the time factor. Plants propagated from seed must undergo the entire cycle of life. If the new plant is grown from a part of the parent plant, it can be produced without going through all the cycles. Another reason is that seedless plants can be grown. This is especially helpful for the food producer. 230. What is plant propagation by layering? (14.4) Plant propagation by layering is where the plant is covered with soil or other material and the growth of roots is stimulated while still attached to the parent plant. 231. Identify four disadvantages of tissue culture. (14.4) 1. Initial cost of the lab is high. 2. Requires greater skill. 3. Tissue culture produces clones that do not have genetic variation. 4. It is possible that one disease could wipe out all the plants. 5. Not all plants can be tissue cultured. 232. What are the two types of plant propagation? (14.4) sexual, asexual 233. List the four primary methods of asexual propagation. (14.4) cuttings, layering, grafting, tissue culture 234. What is rooting hormone? (14.4) Rooting hormone is a chemical that reacts with the newly formed cells and encourages the plant to make roots faster. 235. What conditions are necessary for successful grafting? (14.4) For successful grafting the scion and rootstock must be compatible, each must be at the right stage of growth, the cambium layer of each section must meet, and the graft union must be protected from drying out until the wound has healed. 236. What is cloning? (14.4) Cloning generates multiple, genetically identical offspring from the nonsexual tissues of a parent plant. 14.5 Plant Tissue Culture Techniques MULTIPLE CHOICE 237. When transferring materials into tissue culture tubes, one of the most important objectives is to(14.5) a. transfer quickly and in a clean environment. b. keep the culture tubes from falling over. c. wash the plant material longer than the protocol advises to keep the plant clean. d. transfer slowly and deliberately so that the plant material has time to adjust to the new environment. 238. ____ is a grass that is propagated by rhizomes. (14.5) a. Fescue b. Bluegrass c. Bermuda d. Wheat 239. What is the name of the tissue that is removed for tissue culture? (14.5) a. foreplant b. explant c. preplant d. aftplant 240. Hardwood cuttings grow best if taken during the ____ season. (14.5) a. summer b. spring c. dormant d. rainy 241. A humidity range from ____ to ____ percent is generally considered ideal for rooting most cuttings. (14.5) a. 20; 40 b. 40; 50 c. 50; 60 d. 60; 80 242. ____ is used to propagate large house plants such as the rubber plant. (14.5) a. Tip layering b. Mound layering c. Air layering d. Root cutting 243. Tissue culture began in ____ during the mid-1960s. (14.5) a. England b. France c. China d. South America 244. Callus sales are those sales that are ____. (14.5) a. stems b. unfertilized c. undifferentiated d. none of the above TRUE/FALSE 245. Plant cloning is one of the oldest examples of biotechnology. (14.5) TRUE 246. Plants can be cloned to produce desired characteristics and uniform quality. (14.5) TRUE 247. The differences in plant and animal cells make cloning animals easier than cloning plants. (14.5) FALSE 248. When a plant cutting is being rooted, a high rate of photosynthesis is highly desirable. (14.5) FALSE 249. A high relative humidity is needed when rooting cuttings. (14.5) TRUE 250. To properly root, plant cuttings need intense light. (14.5) FALSE 251. Layering is not a labor-intensive method of propagation. (14.5) FALSE 252. Tissue culture helps solve problems caused by diseases contracted during shipping of seeds and plants. (14.5) TRUE 253. An advantage of tissue culture is that it requires great skill. (14.5) FALSE 254. A disadvantage of tissue culture is that it creates an infinite number of plants from one original specimen. (14.5) FALSE 255. 95% ethanol solution is used to sterilize equipment. (14.5) TRUE 256. A plant created through tissue culture is genetically identical to the original. (14.5) TRUE MATCHING Match the following descriptions with the correct types of cuttings. (14.5) stem tip cuttings A. leaf cut without petiole ___C___ 257. heal cuttings B. stem cut 1/2 inch above and below same node, plant ___F___ 258. ___H___ 259. ___A___ 260. cane cuttings leaf cuttings ___I___ 261. leaf petiole cuttings ___E___ ___B___ ___D___ 262. 263. 264. stem section cuttings single eye cuttings double eye cuttings ___J___ 265. ___G___ 266. split vein cuttings leaf section cuttings has alternate leaves C. end of stem or branch, includes terminal bud D. stem cut 1/2 inch above and below same node, plant has opposite leaves E. section of stem used in middle or behind tip cutting, cut above nodes on both ends F. used with woody stem plants, shield shape cut G. leaves cut into sedges each containing one vein H. stems cut into sections with one or two eyes or nodes, nodes face upward in medium I. cut leaf used with petiole J. veins are slit on lower surface of leaf Match the following layering definitions: (14.5) simple layering A. Stem is girdled with two cuts 1 inch apart, bark is ___B___ 267. removed, wound dusted with rooting hormone and damp sphagnum moss put around, then plastic around moss and tied at both ends tip layering B. Stem is bent to the ground and covered with medium, ___C___ 268. last 6-10 inches of stem is left exposed air layering C. tip of shoot is placed in hole in medium which grows ___A___ 269. downward then turns upward, roots form at bend COMPLETION 270. Another word for micropropagation is ____________________. (14.5) Tissue culture 271. Plant ____________________ by tissue culture is one of the most widely used biotechnologies. (14.5) cloning 272. ____________________ is material that the plant is placed into to root. (14.5) Media 273. The reproduction of cells is controlled in a large part by plant hormones called ____________________.(14.5) auxins 274. ____________________ involves the use of a small amount of tissue from a plant to grow a new plant. (14.5) Tissue culture 275. In ____________________ tissue, the cells are still undifferentiated. (14.5) meristem 276. Tissue culture is the process of ____________________ plants from a single cell. (14.5) regenerating SHORT ANSWER 277. Why is cloning so advantageous to producers? (14.5) Because the cloned plant is genetically identical to the parent and retains all of its superior qualities 278. List four important environmental conditions that are important for rooting cuttings. (14.5) Proper temperature, moisture control, air movement, and light 279. Why must the container used for in vitro culture be sterile? (14.5) Because the solution is an ideal environment for the growth of microorganisms and the new plant must be disease free. 280. What is the first requirement for tissue culture? (14.5) a very clean environment 281. How long from beginning to a successfully growing plant, is the process for tissue culture? (14.5) from three to six weeks 282. Scientists have successfully spliced firefly genes into what organism? (14.5) Tobacco plant 14.6 Careers with Biotech MULTIPLE CHOICE 283. One of the four areas of biotechnology is research, which of the following jobs would fall into that category? (14.6) a. Veterinarian b. plant technician c. cancer research scientist d. materials manager 284. A quality control analyst is responsible for testing samples at the end of production, which area of biotechnology would this be under? (14.6) a. research b. development c. production d. management and marketing 285. The three basic technologies that make up the biotechnology industry are; genetic engineering, diagnostic technologies, and: (14.6) a. plant research b. materials management c. cell and tissue techniques d. animal research 286. Diagnostic technologies are essential in the: (14.6) a. equine industry b. livestock industry c. human medicine d. all of the above 287. In today’s society the primary source used when conducting a career search is the: (14.6) a. school counselor b. internet c. newspaper d. yellow pages 288. Biotechnology is a part of most areas of ____ science. (14.6) a. physical b. mechanical c. biological d. medical 289. The only limits to advancements in biotechnology are ____.(14.6) a. level of education b. interests c. determination d. all of the above 290. Most scientists have earned a(n) ____ degree in a specialized area such as genetics, nutrition, or microbiology. (14.6) a. Ph.D. b. M.S. c. B.S. d. associate’s 291. In practically all scientific research, the data almost always has to be analyzed using ____ tools. (14.6) a. mechanical b. electronic c. expensive d. statistical 292. A lab assistant position in biotechnology requires at least a(n) ____ degree in science. (14.6) a. associate’s b. B.S. c. M.S. d. Ph.D. 293. A ____ is responsible for implementing plans for mating various lines and strains of plant genetics. (14.6) a. lab assistant b. plant breeder c. research analyst d. production assistant 294. Who is responsible for growing and caring for plants in a greenhouse? (14.6) a. HVAC technician b. Plant breeder c. Greenhouse assistant d. Lab technician TRUE/FALSE 295. As research in biotechnology increases, the need for well-trained individuals will also increase. (14.6) TRUE 296. To become a research scientist, you will need several years of education beyond a basic four-year college degree. (14.6) TRUE 297. Today, plant breeders work only indoors. (14.6) FALSE 298. Technical writers write reports to be distributed among scientists. (14.6) FALSE 299. To become a biostatistician usually requires at least a master’s degree in statistics. (14.6) TRUE 300. A field of lessening importance is that of social science in biotechnology. (14.6) FALSE 301. A customer sales representative sometimes has to answer questions about new technology, thus a Bachelor of Science degree in a technical or scientific field is required. (14.6) TRUE 302. Careers in biotechnology are limited to scientists and researchers. (14.6) FALSE 303. If you are good at math and enjoy solving complex problems, you might enjoy a career as a biostatistician. (14.6) TRUE 304. Jobs in manufacturing and production of biotechnology products require a wide range of experiences from business to electronics. (14.6) TRUE COMPLETION 305. A ____________________ can compute statistical tests and tell a scientist the probability that the difference in the results of a scientific experiment happened by chance. (14.6) biostatistician 306. Once the research has been conducted and product approval received, it is up to the _________________________ to make the product commercially available. (14.6) manufacturing industry SHORT ANSWER 307. What is the outlook for jobs in biotechnology? (14.6) The field is steadily growing. 308. What is the mission of agriculture education? (14.6) To teach people about agriculture, which includes biotechnology 14.7 Plant Biotech & Sustainability MULTIPLE CHOICE 309. Using living organisms to “eat” or degrade pollutants found in soil is called? a. phytoremediation b. bioremediation c. bacteriamediation d. plantmediation 310. The use of plants to clean up environmental pollutants is called: (14.7) a. phytoremediation b. bioremediation c. bacteriamediation d. plantmediation 311. What is being used to micropropagate many of the trees grown by lumber paper companies. (14.7) a. selected reproduction b. tissue culture c. genetic engineering d. both b & c 312. (14.7) Biotechnology aids in the economic profitability by: (14.7) a. growing replacement trees more efficiently b. protect plants from insect damage c. reducing need for pesticides d. all of the above and 313. Sustainable agriculture systems have three goals; environmental health, economic profitability, and: (14.7) a. Lower cost b. economic loss c. social and economic equity d. higher cost of products 314. An example of social and economic equity may include: (14.7) a. making our environment safer due to less pesticides at the same time saving cost of pesticides b. bioremediation c. phytoremediation d. none of the above 315. Bacillus thuringiensis, or B.t. B.t. is a: (14.7) a. naturally occurring microorganism b. protein that is indigestible to target insects c. harmless to other living things d. all of the above 316. It is estimated that ____ percent of the world’s supply of food is lost to pests, diseases, and spoilage. (14.7) a. 20 b. 30 c. 40 d. 50 317. Since the mid ____, the yearly yield rates for rice and wheat have been decreasing. (14.7) a. 1960s b. 1970s c. 1980s d. 1990s 318. Today, there are over ____ people in the world. (14.7) a. 6 billion b. 7 billion c. 8 billion d. 9 billion 319. The Green Revolution began during the ____.(14.7) a. 1960s b. 1970s c. 1980s d. 1990s 320. During the Green Revolution, the greatest increase came about in what two crops? (14.7) a. Rice and wheat b. Rice and beans c. Wheat and potatoes d. Rice and corn 321. Most scientists today say that the future of agriculture is in ____.(14.7) a. biology b. physics c. biotechnology d. new machines 322. In 2001, U.S. farmers grew ____ million acres of genetically engineered crops. (14.7) a. 58 b. 68 c. 78 d. 88 TRUE/FALSE 323. Biotechnology can offer genetically altered crops that can be resistant to insect damage. (14.7) TRUE 324. Weeds compete with plants for nutrients and space. (14.7) TRUE 325. Currently, there are very few acres of genetically altered crops produced in the world. (14.7) FALSE 326. There is still hunger in the world today. (14.7) TRUE COMPLEATION 327. Projections are that by the year ____________________ the world’s population will approach 10 billion people. (14.7) 2050 328. The greatest impact of biotechnology has come in the area of _________________________.(14.7) plant agriculture 329. A failed tomato that was more costly than consumers were willing to pay because of the research investment was the ____________________ tomato. (14.7) flavr-savr SHORT ANSWER 330. BT, bacillus thuringiensis, a soil bacteria is spliced into plants for what purpose? (14.7) to help control insects 331. What are the two main advantages of breeding insect-resistant and herbicide-tolerant plants? (14.7) Producing biodegradable industrial raw material, cleaning up the environment