File
advertisement
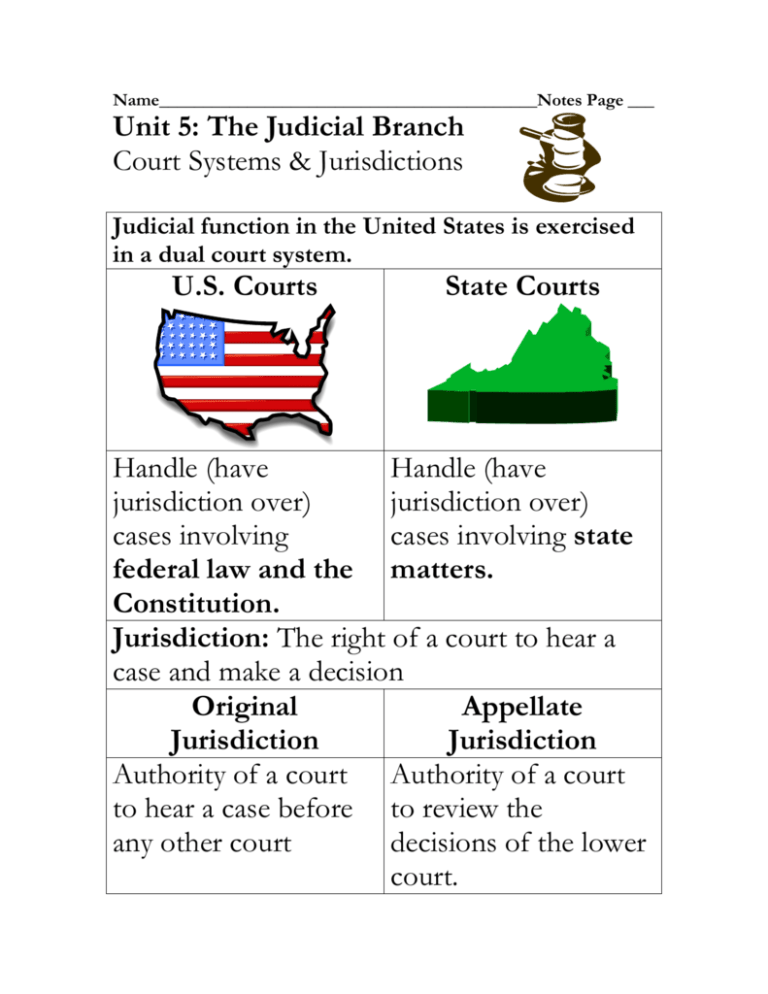
Name___________________________________________Notes Page ___ Unit 5: The Judicial Branch Court Systems & Jurisdictions Judicial function in the United States is exercised in a dual court system. U.S. Courts State Courts Handle (have Handle (have jurisdiction over) jurisdiction over) cases involving cases involving state federal law and the matters. Constitution. Jurisdiction: The right of a court to hear a case and make a decision Original Appellate Jurisdiction Jurisdiction Authority of a court Authority of a court to hear a case before to review the any other court decisions of the lower court. Name___________________________________________Notes Page ___ Unit 5: The Judicial Branch Powers Powers of the Judicial Branch Conduct Trials Interpret the Law Hear Appeals Judicial Review The power to determine the constitutionality of laws and executive acts. Name___________________________________________Notes Page ___ Unit 5: The Judicial Branch Checks and Balances Role of the Judicial Branch in the System of Checks and Balances Judicial Powers The Judicial Branch over the Legislative can declare Branch Congressional laws unconstitutional. Judicial Powers over The Judicial Branch the Executive can declare executive Branch acts unconstitutional. Legislative Powers over the Judicial Branch Executive Powers over the Judicial Branch Congress approves and can impeach federal judges The President appoints federal judges. Name___________________________________________Notes Page ___ Unit 5: The Judicial Branch The Federal Court System The federal courts try cases involving federal laws and the Constitution. U.S. Supreme Court U.S. Court of Appeals U.S. District Courts The Constitution and Laws define the jurisdictions, powers and structure of the federal courts. Types of Cases heard by Federal Courts: -Constitutional Questions -Cases arises from a law passed by Congress (federal law) -Crime committed on federal property Name___________________________________________Notes Page ___ Unit 5: The Judicial Branch Federal Court System The Federal Court System U.S. District Courts Only Trial Court Plaintiff: U.S. Government Defendant: Accused 1 Judge Jury U.S. Court of Appeals U.S. Supreme Court Original Jurisdiction If unhappy with ruling in District Court, the accused needs a legal reason to appeal to this court. 3 Justices (judges) No jury Appellate Jurisdiction Final court of appeals if unhappy with ruling in District Court of Appeals 9 Justices No Jury Appellate jurisdiction Limited Original Jurisdiction Name___________________________________________Notes Page ___ Unit 5: The Judicial Branch Judicial Review Judicial Review The power of the Supreme Court to determine if laws made by Congress and executive acts of the President are Constitutional. Marbury v. Madison 1803 *Established the principle of judicial review. *Established the Supreme Court as the interpreter of the Constitution. *1st time that the Supreme Court said an act of Congress was unconstitutional. Brown v. Board of Education 1954 Bush v. Gore 2000 *The Supreme Court declared a state law unconstitutional. *Racial segregation in public schools violated the Constitution *Violated the 14th Amendment: All citizens have equal protection under the law *The Supreme Court decided the outcome of the presidential election. *Manual recount of presidential votes in Florida would stop *Recount was unconstitutional: it could not be completed by the deadline. The Supreme Court is the guardian of the Constitution; checking the actions of the legislative and executive branches to insure that they do not violate the supreme law of the land. Name___________________________________________Notes Page ___ Unit 5: The Judicial Branch Principles Principle Due Process Rights Where is it Found? 5th Amendment prohibits the national government from acting in an unfair manner. 14th Amendment prohibits the states and local governments from acting in an unfair manner. What does it mean? The Constitutional protection against unfair government action and laws. Trial by Jury Rights of the Accused 6th Amendment right to a speedy and public trial, by an impartial jury 6th Amendment Equal Protection under the law 14th Amendment to be informed of the charges to cross examine witnesses to have witness on their behalf assistance of counsel States can not deny any person equal protection. Further defined that all men are created equal The judicial branch interprets the law in order to protect individuals from the power of the government. Name___________________________________________Notes Page ___ Unit 5: The Judicial Branch Criminal Cases The court determines whether a person accused of breaking the law is guilty or not guilty of a misdemeanor, a less serious crime with a punishment of less than a year in jail or felony, a more serious crime punishable by more than a year in prison. Procedures for a criminal case Arrest Jail or Bail Arraignment Preliminary Hearing Trial Sentencing Name___________________________________________Notes Page ___ Unit 5: The Judicial Branch Criminal Cases Arrest Arraignment Preliminary Hearing Trial (District Court) Sentencing Police can place someone under arrest if: - There is probable cause- reason to believe someone is guilty of a crime. - The police officer witnesses a crime. - An arrest warrant is issued. Miranda rights must be read: right to remain silent, to have an attorney Meeting in front of the judge Charges are read. Attorney is appointed by the court if requested Judge sets bail Preliminary hearing date is set Guilty or not guilty plea is entered Judge reviews probable cause (is there enough evidence to proceed to trial?) Trial date is set Prosecution- Government Attorney Defense- Accused and Attorney Jury is chosen Opening Statements Witness Testimony and Cross-Examination Closing Arguments Jury Instruction Jury Deliberation- must find the accused guilty beyond a reasonable doubt. Verdict Defendant may appeal a guilty verdict. If a defendant is found guilty of a misdemeanor or felony, the judge will sentence them to probation, prison or to pay a fine. Name___________________________________________Notes Page ___ Unit 5: The Judicial Branch Civil Cases Civil Cases The court settles a disagreement between two parties; often over money or harm to someone’s reputation. Plaintiff Defendant Person who feels that Served a copy of the they have been wronged complaint Initiates (begins) lawsuit Defends themselves against the complaint Files complain to recover damages or to Has to be proven guilty receive money by a preponderance (majority) of the evidence Describes plaintiff’s injury, asks court to order relief Disagreement Settled by: Jury Judge Judge explains law that Bench Trial is relevant in the case Determines if defendant Determine if defendant is responsible is responsible Determines amount of Determine damages or damages or compensation compensation The court decides which side is right or wrong; the decision can be appealed to Court of Appeals or to the Supreme Court. Name___________________________________________Notes Page ___ Unit 5: The Judicial Branch Judicial Review Name___________________________________________Notes Page ___ Unit 5: The Judicial Branch Judicial Review









